- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-EVPN overview | 102.64 KB |
EVPN overview
Ethernet Virtual Private Network (EVPN) is a Layer 2 VPN technology that provides both Layer 2 and Layer 3 connectivity between distant network sites across an IP or MPLS network. EVPN uses MP-BGP in the control plane and MPLS in the data plane. EVPN is typically used in data centers for multitenant services.
EVPN solutions
EVPN provides the EVPN Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) and EVPN Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) solutions.
EVPN VPWS
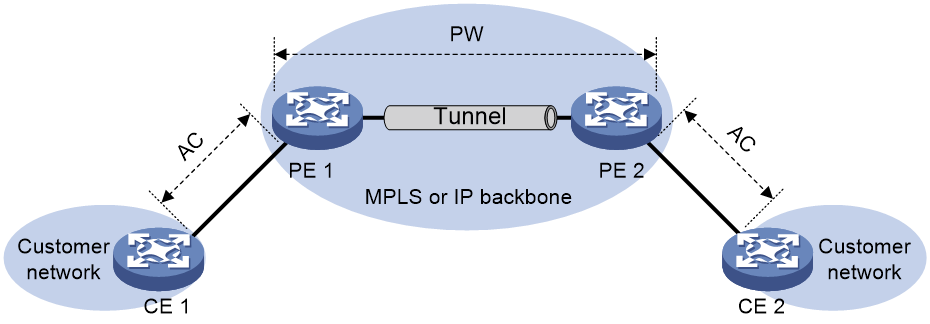
As shown in Figure 1, EVPN VPWS is a Layer 2 VPN technology that uses EVPN for PW establishment in the control plane and MPLS for forwarding in the data plane. EVPN VPWS provides point-to-point forwarding services for users by using ACs and PWs associated with cross-connects without MAC address table lookup.
For more information about EVPN VPWS, see "Configuring EVPN VPWS."
Figure 1 EVPN VPWS network model
EVPN VPLS
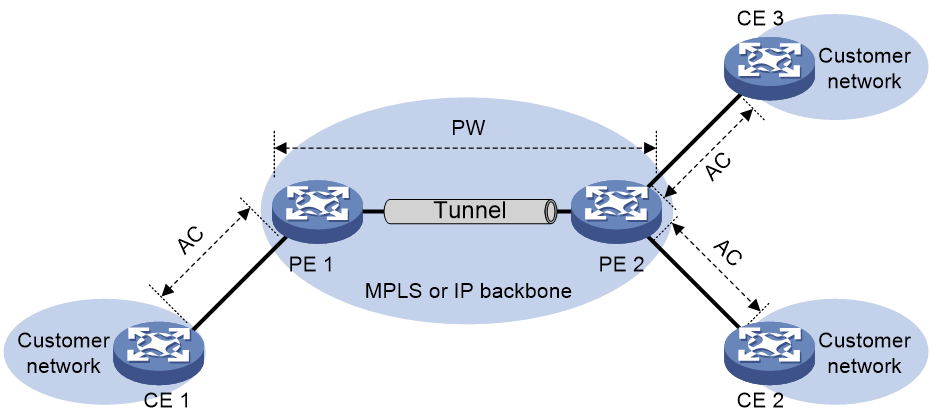
As shown in Figure 2, EVPN VPLS is a Layer 2 VPN technology that uses EVPN for PW establishment in the control plane and MPLS for forwarding in the data plane. EVPN VPLS provides point-to-multipoint forwarding services for users by using the MAC address table.
For more information about EVPN VPLS, see "Configuring EVPN VPLS."
Figure 2 EVPN VPLS network model
EVPN benefits
EVPN provides the following benefits:
· Configuration automation—MP-BGP automates PE discovery and PW establishment to ease deployment.
· Separation of the control plane and the data plane—EVPN uses MP-BGP to advertise host reachability information in the control plane and uses MPLS to forward traffic in the data plane.
· Point-to-point and point-to-multipoint connection—Layer 2 frames are transmitted transparently across the IP or MPLS transport network between sites after they are encapsulated into MPLS packets.
Layered transport network
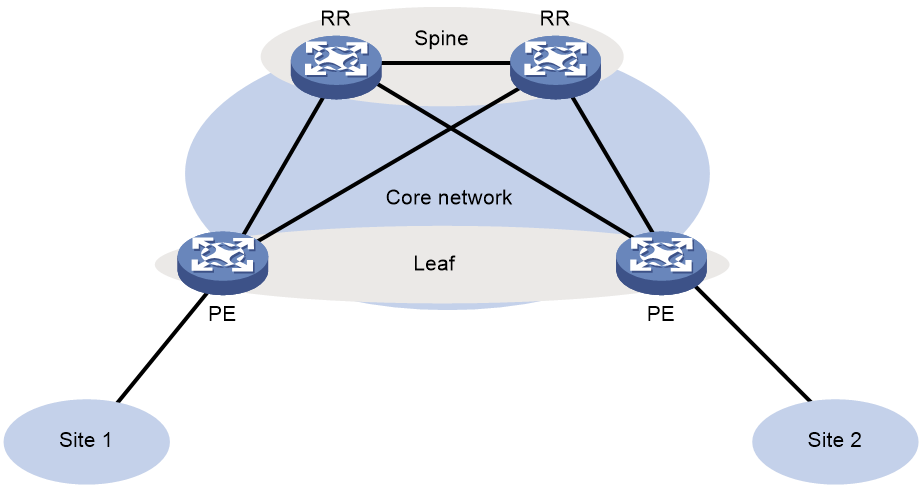
As shown in Figure 3, typically the EVPN transport network uses a layered structure. On the transport network, leaf nodes act as PEs to provide MPLS services, and spine nodes perform forwarding for MPLS traffic based on the outer IP header or MPLS labels. If all PEs and transport network devices of an EVPN network belong to the same AS, the spine nodes can act as route reflectors (RRs) to reflect routes between the PEs. In this scenario, the spine nodes advertise and receive BGP EVPN routes, but do not perform MPLS encapsulation and de-encapsulation.
Figure 3 Layered transport network
MP-BGP extension for EVPN
To support EVPN, MP-BGP introduces the EVPN subsequent address family under the L2VPN address family and the following network layer reachability information (BGP EVPN routes):
· Ethernet auto-discovery route—Advertises ES and service ID information in multihomed sites and advertises service ID information in an EVPN VPWS network.
· MAC/IP advertisement route—Advertises MAC reachability information and host route information (host ARP or ND information).
· Inclusive multicast Ethernet tag (IMET) route—Advertises PE information for automating PE discovery and PW establishment in an EVPN VPLS network.
· Ethernet segment (ES) route—Advertises ES and PE mappings.
· IP prefix advertisement route—Advertises BGP IPv4 or IPv6 unicast routes as IP prefixes.
· Selective multicast Ethernet tag (SMET) route—Advertises IGMP multicast group information among edge devices in an EVPN network.
· IGMP join synch route—Advertises IGMP membership reports among redundant edge devices for an ES.
· IGMP leave synch route—Advertises IGMP leave group messages for withdrawal of IGMP join synch routes among redundant edge devices for an ES.
MP-BGP uses the route distinguisher (RD) field to differentiate BGP EVPN routes of different VSIs or cross-connect groups and uses route targets to control the advertisement and acceptance of BGP EVPN routes.
MP-BGP supports the following types of route targets:
· Export targets—A PE sets the export targets for BGP EVPN routes learned from the local site before advertising them to remote PEs.
· Import targets—A PE checks the export targets of BGP EVPN routes received from remote PEs. The PE imports the BGP EVPN routes only when their export targets match the local import targets.
RD and route target selection of BGP EVPN routes
As shown in Table 1, you can configure RDs and route targets for BGP EVPN routes in multiple views.
Table 1 Supported views for RD and route target configuration
|
Item |
Views |
|
RD |
· VSI EVPN instance view · VPN instance view · Public instance view · Cross-connect group EVPN instance view |
|
Route targets |
· VSI EVPN instance view · VPN instance view · VPN instance IPv4 address family view · VPN instance IPv6 address family view · VPN instance EVPN view · Public instance view · Public instance IPv4 address family view · Public instance IPv6 address family view · Public instance EVPN view · Cross-connect group EVPN instance view NOTE: Route targets configured in VPN instance view apply to IPv4 VPN, IPv6 VPN, and EVPN. Route targets configured in IPv4 address family view apply only to IPv4 VPN. Route targets configured in IPv6 address family view apply only to IPv6 VPN. Route targets configured in VPN instance EVPN view apply only to EVPN. Route targets configured in IPv4 address family view, IPv6 address family view, or VPN instance EVPN view take precedence over those in VPN instance view. The precedence order for different views of a VPN instance also applies to the views of the public instance. |
The device selects RDs and route targets for BGP EVPN routes by using the following rules:
· Ethernet auto-discovery routes—The device uses the RD and route targets configured in EVPN instance view of a VSI or cross-connect group when advertising the routes. The device uses the route targets configured in EVPN instance view of a VSI or cross-connect group when accepting the routes.
· IMET routes and MAC/IP advertisement routes that contain only MAC addresses—The device uses the RD and route targets configured in VSI EVPN instance view when advertising and accepting the routes.
· MAC/IP advertisement routes that contain ARP or ND information—The device uses the following settings when advertising the routes:
¡ RD and export route targets configured in VSI EVPN instance view.
¡ Export route targets configured for EVPN on a VPN instance or the public instance (VPN instance view, EVPN view of a VPN instance or the public instance, and public instance view).
The device uses the import route targets configured for the EVPN instance on a VSI and EVPN on a VPN instance or the public instance when accepting the routes.
· ES routes—The device uses the RD and export route targets configured for an EVPN instance on a VSI or cross-connect group when advertising the routes. The device uses the import route targets configured for an EVPN instance on a VSI or cross-connect group when accepting the routes.
· IP prefix advertisement routes—The device uses the route targets configured for IPv4 or IPv6 VPN on a VPN instance or the public instance when advertising and accepting the routes.