- Table of Contents
-
- 17-Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-System maintenance and debugging configuration
- 02-NQA configuration
- 03-NTP configuration
- 04-PoE configuration
- 05-SNMP configuration
- 06-RMON configuration
- 07-Event MIB configuration
- 08-NETCONF configuration
- 09-CWMP configuration
- 10-EAA configuration
- 11-Process monitoring and maintenance configuration
- 12-Sampler configuration
- 13-Mirroring configuration
- 14-NetStream configuration
- 15-IPv6 NetStream configuration
- 16-sFlow configuration
- 17-Information center configuration
- 18-Flow log configuration
- 19-SmartMC configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 19-SmartMC configuration | 134.21 KB |
Setting the FTP server information
Modifying the password for the default user on TCs
Performing bulk configuration deployment
Backing up configuration files·
Upgrading the startup software and configuration file on TCs
About upgrading the startup software and configuration file on TCs
Restrictions and guidelines for startup software and configuration file upgrade
Upgrading the startup software and configuration file on TCs
Upgrading the startup software and configuration file on all TCs in SmartMC groups
Refreshing the network topology
Display and maintenance commands for SmartMC
SmartMC configuration examples
Configuring SmartMC
About SmartMC
Smart Management Center (SmartMC) centrally manages and maintains dispersed network devices at network edges. In a SmartMC network, only one device acts as the TM and the remaining devices all act as TCs. SmartMC provides the following features for you to manage the TCs from the TM:
· Configuration file backup and download.
· Software upgrade.
· Configuration deployment.
· Faulty member replacement.
SmartMC network framework
Figure 1 shows the basic framework of a SmartMC network.
Figure 1 SmartMC network framework
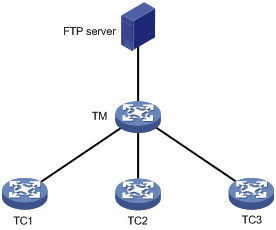
The SmartMC network contains the following elements:
· TM—Topology master, which manages all TCs in the SmartMC network.
· TC—Topology client, which is managed by the TM.
· FTP server—Stores startup software images and configuration files for the TM and TCs.
SmartMC network establishment
Automatic SmartMC network establishment
The TM and TCs use the following procedure to establish a SmartMC network:
1. After SmartMC is enabled, the TM broadcasts a SmartMC packet at 15-second intervals to detect TCs in the network. The SmartMC packet contains information of the TM, such as its bridge MAC address and the IP address of VLAN-interface 1.
2. When a TC receives the packet, it records the TM information, and returns a response packet to the TM. The response packet contains information of the TC, such as its bridge MAC address and the IP address of VLAN-interface 1.
3. When the TM receives the response packet, it initiates a NETCONF session to the TC with the default username admin and the default password admin. The TM then obtains detailed information about the TC through the session, including port information, LLDP neighbor information, STP information, device type, and software version.
4. The TM establishes a connection to the TC for tracking the liveliness of the TC, and adds the TC to the SmartMC network.
5. Based on the LLDP neighbor information obtained from all TCs, the TM forms a SmartMC topology.
After the SmartMC network is established, the TM and TCs check for the existence of each other by exchanging SmartMC packets.
· When a TC receives a SmartMC broadcast packet from the TM, it compares the bridge MAC address in the packet with the recorded bridge MAC address. If the two bridge MAC addresses are the same, the TC returns a response packet to the TM. If the TC does not receive a broadcast packet from the TM within 45 seconds, the TC determines that the TM does not exist in the network anymore. Then, the TC clears the TM information.
· When the TM receives a response packet from a TC, it compares the bridge MAC address in the packet with the recorded bridge MAC address. If the two bridge MAC addresses are the same, the TM determines that the TC still exists in the network. If the TM does not receive a response packet from a TC within 150 seconds, the TM determines that the TC is offline. Then, the TM sets the status of the TC to offline.
Manual SmartMC network establishment
You can log in to the Web interface of the TM, and enter the IP address, username, and password of the TCs to manually add them to the network. The TCs can join the network without exchanging SmartMC packets with the TM.
After the TCs join the SmartMC network, the TM obtains the following information from the TCs to form a SmartMC topology:
· LLDP neighbor information (through NETCONF).
· Hardware information (through SNMP).
SmartMC features
Bulk configuration deployment
The procedure for bulk configuration deployment is as follows:
1. The TM acts as a Telnet client and establishes Telnet connections to the TCs.
2. The TM deploys a batch file to the TCs through Telnet connections. The batch file is created on the TM and contains command lines to be deployed.
3. The TCs run the command lines in the file.
Configuration file backup
You can use the following methods to back up the next-startup configuration file on the TM and TCs:
· Automatic backup—Enable this feature for the TM and all TCs in the network to immediately perform a backup. After that, the TM and TCs back up the configuration file at a user-specified interval.
· Manual backup—Manually trigger a backup on specified TCs or SmartMC groups.
The TM instructs the TCs to back up the next-startup configuration file by unicasting a SmartMC packet to them. When a TC receives the packet, it saves the running configuration to the next-startup configuration file and uploads the file to the FTP server.
Startup software and configuration file upgrade
Before upgrade, you must upload the upgrade files from the TM to the FTP server and specify the upgrade files on the FTP server for the TCs to download.
The procedure for startup software and configuration file upgrade is as follows:
1. The TM instructs the TCs (or SmartMC group) to download the upgrade files from the FTP server.
2. The TCs download the upgrade files from the FTP server.
3. The TCs upgrade the startup software and configuration file as follows:
? Startup software upgrade—Uses the boot loader method to upgrade startup software files. The members might be restarted during the upgrade process.
? Configuration file upgrade—Replaces the current configuration file with the upgrade configuration file. The TCs will not be restarted during the upgrade process.
Faulty TC replacement
You can use the following methods to replace a faulty TC:
· Automatic replacement—Enables the TM to record the positions of all TCs in the topology for replacement. When the TM discovers that a new TC has physically replaced the faulty TC, it compares the new TC with the faulty one. The TM performs a replacement if the following requirements are met:
? The new TC is deployed at the same topological position as the faulty one.
? The models of the new TC and faulty TC are the same.
The TM then instructs the new TC to download the configuration file of the faulty TC from the FTP server. After downloading the configuration file, the new TC runs the configuration file to complete the replacement.
· Manual replacement—After the faulty TC is physically replaced, you manually trigger a configuration replacement. The new TC will download the configuration file of the faulty TC from the FTP server and run the file to complete the replacement.
SmartMC tasks at a glance
To configure SmartMC, perform the following tasks:
Enable SmartMC on both the TM and TCs and perform all subsequent tasks only on the TM.
2. Setting the FTP server information
This task is required for configuring automatic configuration file backup, replacing faulty TCs, and upgrading the configuration file on TCs.
3. Modifying the password for the default user on TC
This task is required for upgrading the startup software and configuration file for SmartMC groups and performing bulk configuration deployment to SmartMC groups.
5. Managing TCs through SmartMC
? Performing bulk configuration deployment
? Backing up configuration files
? Upgrading the startup software and configuration file on TCs
? Managing the network topology
Prerequisites for SmartMC
Before you configure SmartMC, perform the following tasks on the TM and TCs:
· Enable the Telnet service, and configure scheme authentication for VTY user lines. For information about Telnet service and VTY user lines, see CLI login configuration in Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
· Configure a local user.
? Specify the username and password.
? Specify the Telnet, HTTP, and HTTPS services for the user.
? Set the RBAC role of the local user to network-admin.
For information about local users, see AAA configuration in Security Configuration Guide. For information about user roles, see RBAC configuration in Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
· Enable NETCONF over SOAP over HTTP. For information about NETCONF over SOAP, see NETCONF configuration in Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
· Enable LLDP globally. For information about LLDP, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
· To manage the TM and TCs through a Web interface, you must enable the HTTP and HTTPS services, and set the service type to HTTP and HTTPS for the local user. For information about Web login, HTTP, and HTTPS, see login management configuration in Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
· To manually establish a SmartMC network, you must configure the snmp-agent community read public and snmp-agent sys-info version all commands on the TCs. For information about SNMP, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Enabling SmartMC
Restrictions and guidelines
A SmartMC network must have one and only one TM.
Perform this task on both the TM and TCs and perform all subsequent tasks only on the TM.
If you change the role of the TM to TC or disable SmartMC on the TM, all SmartMC settings in its running configuration will be cleared.
For manual SmartMC network establishment, the TM preferentially uses the user-specified username and password. If no username and password are specified, the TM uses the default username admin and password admin.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable SmartMC and set the device role.
smartmc { tm [ username username password { cipher | simple } string ] | tc } enable
By default, SmartMC is disabled.
Setting the FTP server information
About files stored on the FTP server
In a SmartMC network, an FTP server is used to store the following files:
· Upgrade startup software files and upgrade configuration file for TCs.
· Backup configuration files of the TM and TCs.
Restrictions and guidelines
You can use the following methods to specify an FTP server:
· Specify the IP address of an FTP server.
· Specify the IP address of the TM. The TM will act as an FTP server.
To configure the TM to act as an FTP server, make sure the TM has enough storage space for storing the files required by TCs. For information about FTP, see Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the FTP server information.
smartmc ftp-server server-address username username password { cipher | simple } string
By default, no FTP server information is set.
Modifying the password for the default user on TCs
About modifying the password for the default user on a TC
During SmartMC network establishment, the TM establishes NETCONF sessions to TCs and adds them to the network. The default username and password on the TCs for NETCONF session establishment are admin and admin. To enhance security, you can perform this task to change the password for the default user admin of the TCs after the TM adds the TCs to the network.
Restrictions and guidelines
Do not modify the password for TCs that are manually added to the SmartMC network. If you modify the password for a manually added TC, you will not be able to manage that TC from the TM.
You can use the display smartmc tc verbose command to identify the method that is used to add the TCs.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Modify the password for the default user on TCs.
smartmc tc password string
Creating a SmartMC group
About SmartMC groups
This feature allows you to create a SmartMC group on the TM and add TCs to the group. When you perform the following operations, you can specify a SmartMC group to apply the operations to all TCs in the group:
· Startup software upgrade.
· Configuration file upgrade.
· Configuration deployment.
Restrictions and guidelines
If the device type of the TCs is not predefined on the TM, you must manually add the device type to the TM. This enables TCs of an undefined type to join a SmartMC group created on the TM. The device types added to the TM cannot be the same as the predefined types on the TM. To view the predefined device types on the TM, use the match device-type ? command.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. (Optional.) Add a device type to the TM.
smartmc tc sysoid sysoid device-type device-type
To obtain the SYSOID of a TC, execute the display smartmc tc verbose command.
3. Create a SmartMC group and enter its view.
smartmc group group-name
4. Set a match criterion.
match { device-type device-type | ip-address ip-address { ip-mask-length | ip-mask } | mac-address mac-address mac-mask-length }
By default, no match criterion is set.
Performing bulk configuration deployment
1. Create a batch file and edit the command lines to be deployed to TCs.
create batch-file cmd-filename
Execute this command in user view.
Each command occupies a line in the batch file. When you finish editing, enter a percent sign (%) to return to user view.
Make sure the command lines that you enter are correct because the system does not verify whether the command lines are correct.
2. Enter system view.
system-view
3. Deploy the batch file to a list of TCs or SmartMC groups.
smartmc batch-file cmd-filename deploy { group group-name-list | tc tc-id-list }
Backing up configuration files
Restrictions and guidelines
Configuration files automatically backed up to the FTP server are named in the format of device bridge MAC address_backup.cfg.
When you change the TM in the SmartMC network, make sure the backup configuration file of the original TM on the FTP server is deleted. If the file still exists, the new TM might download the file and run the settings. This will cause a TM conflict in the network.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the maximum number of TCs that can perform configuration file backup at the same time.
smartmc backup configuration max-number max-number
3. Back up configuration files.
Choose one option as needed:
? Enable automatic configuration file backup and set the backup interval.
smartmc backup startup-configuration interval interval-time
By default, automatic configuration file backup is disabled.
? Manually back up the configuration file on TCs.
smartmc backup configuration { group group-name-list | tc [ tc-id-list ] }
Upgrading the startup software and configuration file on TCs
About upgrading the startup software and configuration file on TCs
You can use the following methods to upgrade the startup software and configuration file on TCs:
· Schedule an upgrade by specifying an upgrade time or upgrade delay.
· Upgrade immediately by not specifying an upgrade time or upgrade delay.
Restrictions and guidelines for startup software and configuration file upgrade
A TC can perform only one upgrade task at a time.
Upgrading the startup software and configuration file on TCs
Upgrading the startup software and configuration file in one step
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Upgrade the startup software on TCs in one step.
smartmc upgrade boot-loader tc { tc-id-list { boot boot-filename system system-filename | file ipe-filename } }&<1-40> [ delay delay-time | time in-time ]
3. Upgrade the configuration file on TCs in one step.
smartmc upgrade startup-configuration tc { tc-id-list cfg-filename }&<1-40> [ delay delay-time | time in-time ]
Configuring startup software and configuration file upgrade step by step
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure startup software upgrade for TCs step by step:
a. Specify the upgrade startup software files.
smartmc tc tc-id boot-loader { ipe-filename | boot boot-filename system system-filename }
b. Upgrade the startup software on TCs.
smartmc upgrade boot-loader tc tc-id-list
3. Configure configuration file upgrade for TCs step by step:
a. Specify the upgrade configuration file.
smartmc tc tc-id startup-configuration cfg-filename
b. Upgrade the configuration file on TCs.
smartmc upgrade startup-configuration tc tc-id-list
Upgrading the startup software and configuration file on all TCs in SmartMC groups
Upgrading the startup software and configuration file in one step
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Upgrade the startup software on all TCs in SmartMC groups in one step.
smartmc upgrade boot-loader group { group-name-list [ boot boot-filename system system-filename | file ipe-filename ] }&<1-40> [ delay minutes | time in-time ]
3. Upgrade the configuration file on all TCs in SmartMC groups in one step.
smartmc upgrade startup-configuration group { group-name-list cfg-filename }&<1-40> [ delay minutes | time in-time ]
Configuring startup software and configuration file upgrade step by step
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter SmartMC group view.
smartmc group group-name
3. Specify the upgrade startup software files for the SmartMC group.
boot-loader file { ipe-filename | boot boot-filename system system-filename }
By default, no upgrade startup software files are specified for a SmartMC group.
4. Specify the upgrade configuration file for the SmartMC group.
startup-configuration cfgfile
By default, no upgrade configuration file is specified for a SmartMC group.
5. Return to system view.
quit
6. Upgrade the startup software and configuration file on all TCs in the SmartMC group.
Choose one option as needed:
? Upgrade the startup software.
smartmc upgrade boot-loader group group-name-list [ delay minutes | time in-time ]
? Upgrade the configuration file.
smartmc upgrade startup-configuration group group-name-list [ delay minutes | time in-time ]
Managing the network topology
Refreshing the network topology
About refreshing the network topology
You can use the following methods to refresh the network topology:
· Automatic topology refresh—Specify the refresh interval to allow the TM to refresh the network topology periodically.
· Manual topology refresh—Execute the smartmc topology-refresh command to manually refresh the network topology.
Restrictions and guidelines
The topology refresh time depends on the number of TCs in the network.
Procedure
Choose one option as needed:
· Manually refresh the network topology in any view.
smartmc topology-refresh
· Configure automatic network topology refresh.
a. Enter system view.
system-view
b. Set the automatic topology refresh interval.
smartmc topology-refresh interval interval
By default, the automatic topology refresh interval is 60 seconds.
Saving the network topology
About saving the network topology
This task allows you to save the current network topology to the topology.dba file in the flash memory. After the TM reboots, it uses the topology.dba file to restore the network topology.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Save the network topology.
smartmc topology-save
Replacing faulty TCs
Restrictions and guidelines
Make sure the new TC for replacement and the faulty TC have the same neighbor relationship, device model, and IRF member ID.
Prerequisites
Before you replace a faulty TC, perform the following tasks:
1. Install the new TC at the location where the faulty TC was installed.
2. Connect all cables to the new TC.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Replace faulty TCs.
Choose one option as needed:
? Enable automatic faulty TC replacement.
smartmc auto-replace enable
By default, automatic faulty TC replacement is disabled.
? Manually replace a faulty TC.
smartmc replace tc tc-id1 faulty-tc tc-id2
Display and maintenance commands for SmartMC
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the backup status on TCs. |
display smartmc backup configuration status |
|
Display the batch file execution results. |
display smartmc batch-file status [ last number ] |
|
Display SmartMC configuration. |
display smartmc configuration |
|
Display connections between the devices in the SmartMC network. |
display smartmc device-link |
|
Display SmartMC group information. |
display smartmc group [ group-name ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display the faulty TC replacement status. |
display smartmc replace status |
|
Display TC information. |
display smartmc tc [ tc-id ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display TC upgrade status. |
display smartmc upgrade status |
SmartMC configuration examples
Example: Configuring SmartMC
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, TC 1, TC 2, and TC 3 belong to the same device type: S5560-EI series. The IP address of the FTP server is 192.168.2.1. The FTP username is admin and the FTP password is admin.
Perform the following tasks to establish a SmartMC network and upgrade the configuration file on the TCs:
1. Configure the TM and TCs to automatically establish a SmartMC network.
2. Create a SmartMC group and add the TCs to the group.
3. Upgrade the configuration file on all TCs in the SmartMC group.
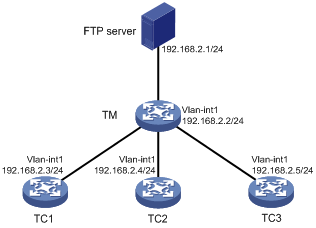
Procedure
1. Configure TC 1:
# Configure VLAN-interface 1.
<TC1> system-view
[TC1] interface vlan-interface 1
[TC1-Vlan-interface1] ip address 192.168.2.3 24
# Enable the Telnet service on TC 1.
[TC1] telnet server enable
# Enable NETCONF over SOAP over HTTP.
[TC1] netconf soap http enable
# Enable LLDP globally.
[TC1] lldp global enable
# Create a user. Set the username and password to admin, add the telnet, http, and https service types, and authorize the user to use the network-admin user role.
[TC1] local-user admin
[TC1-luser-manage-admin] password simple admin
[TC1-luser-manage-admin] service-type telnet http https
[TC1-luser-manage-admin] authorization-attribute user-role network-admin
[TC1-luser-manage-admin] quit
# Set scheme authentication for VTY user lines 0 to 63.
[TC1] line vty 0 63
[TC1-line-vty0-63] authentication-mode scheme
[TC1-line-vty0-63] quit
# Enable SmartMC and set the device role to TC.
[TC1] smartmc tc enable
2. Configure TC 2 and TC 3 in the same way TC 1 is configured. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure the TM:
# Configure VLAN-interface 1.
<TM> system-view
[TM] interface vlan-interface 1
[TM-Vlan-interface1] ip address 192.168.2.2 24
[TM-Vlan-interface1] quit
# Enable the Telnet service.
[TM] telnet server enable
# Enable NETCONF over SOAP over HTTP.
[TM] netconf soap http enable
# Enable LLDP globally.
[TM] lldp global enable
# Create a local user, and specify the username, password, service types, and RBAC role as admin, admin, Telnet, HTTP, and HTTPS, and network-admin, respectively.
[TM] local-user admin
[TM-luser-manage-admin] password simple admin
[TM-luser-manage-admin] service-type telnet http https
[TM-luser-manage-admin] authorization-attribute user-role network-admin
[TM-luser-manage-admin] quit
# Set scheme authentication for VTY user lines 0 to 63.
[TM] line vty 0 63
[TM-line-vty0-63] authentication-mode scheme
[TM-line-vty0-63] quit
# Enable SmartMC and set the device role to TM.
[TM] smartmc tm enable
# Set the FTP server IP address, username, and plaintext password to 192.168.2.1, admin, and admin, respectively.
[TM] smartmc ftp-server 192.168.2.1 username admin password simple admin
# Create SmartMC group S1 and enter its view.
[TM] smartmc group S1
# Create a device type match criterion to add all TCs to SmartMC group S1.
[TM-smartmc-group-S1] match device-type s5560-ei
# Specify the upgrade configuration file startup.cfg for SmartMC group S1.
[TM-smartmc-group-S1] startup-configuration startup.cfg
[TM-smartmc-group-S1] quit
# Upgrade the configuration file on all TCs in SmartMC group S1.
[TM] smartmc upgrade startup-configuration group s1 startup.cfg
Verifying the configuration
# Display brief information about all TCs after the SmartMC network is established.
[TM] display smartmc tc
TCID DeviceType IpAddress MacAddress Status Version Sysname
1 S5560-EI 192.168.2.3 201c-e7c3-0300 Normal R1308 S1
2 S5560-EI 192.168.2.4 201c-e7c3-0301 Normal R1308 S2
3 S5560-EI 192.168.2.5 201c-e7c3-0302 Normal R1308 S3
# Display the configuration file upgrade status on the TCs.
<TM> display smartmc upgrade status
ID IpAddress MacAddress Status UpdateTime UpdateFile
1 192.168.2.3 201c-e7c3-0300 Finished Immediately startup.cfg
2 192.168.2.4 201c-e7c3-0301 Finished Immediately startup.cfg
3 192.168.2.5 201c-e7c3-0302 Finished Immediately startup.cfg
