- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-Text | 979.06 KB |
Chapter 1 Product Introduction
1.2 Introduction to S3100 Series Ethernet Switches
1.3 Introduction to Front Panel LEDs
1.3.2 Auto-Sensing 10/100BASE-TX Ethernet Port Status LED
1.3.3 1000 Mbps Uplink Port Status LED
1.5 SFP Modules Supported by S3100 Series Ethernet Switches
Chapter 2 Installation Preparation
2.2 Requirements on Environment
2.2.1 Temperature/Humidity Requirements
2.2.3 Anti-interference Requirements
3.2 Connection of Power Cable and Grounding Cable
3.2.1 Connecting AC Power Cable
3.2.2 Connecting DC Power Cable
3.2.3 Connecting Grounding Cable
3.4 Connection of Console Cable
3.4.2 Connecting Console Cable
4.1 Establishing Configuration Environment
4.2 Connecting the Console Cable
4.3 Setting Terminal Parameters
4.4.1 Checking Before Powering on the Switch
4.4.3 Changing the Startup Mode
Chapter 5 Boot ROM and Host Software Loading
5.1 Introduction to Loading Approaches
5.2.2 Loading Software Using XModem Through Console Port
5.2.3 Loading Software Using TFTP Through Ethernet Port
5.2.4 Loading Software Using FTP Through Ethernet Port
5.3.1 Remote Loading Using FTP
5.3.2 Remote Loading Using TFTP
Chapter 6 Maintenance and Troubleshooting
6.2.2 Missing Boot ROM Password
6.4 Configuration System Failure
Chapter 1 Product Introduction
1.1 Overview
H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches are high-performance, high-density, easy-to-install, NMS-manageable intelligent Ethernet switches which support wire-speed Layer 2 switching.
l Table 1-1 lists the models of H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches.
Table 1-1 Models of H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches
|
Model |
Power supply |
Number of 10/100 Mbps electrical ports |
1000 Mbps uplink ports |
Number of console ports |
|
S3100-26TP-EI-W |
AC and +12V RPS DC |
24 |
2 Combo ports |
1 |
|
S3100-16TP-EI-W |
AC |
16 |
2 Combo ports |
1 |
|
S3100-8TP-EI-W |
8 |
1 Combo port |
1 |
1.2 Introduction to S3100 Series Ethernet Switches
1.2.1 S3100-26TP-EI-W
I. Front panel
S3100-26TP-EI-W Ethernet switches each provide twenty-four auto-sensing 10/100/1000Base-TX Ethernet ports, two 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet ports, two 100/1000Base-X SFP ports, and one console port. Each SFP port and the corresponding 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet port form a Combo port. For each Combo port, either the SFP port or the corresponding 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet port can be used at a time.
Figure 1-1 shows the front panel of an S3100-26TP-EI-W Ethernet switch.

|
(1) Auto-sensing 10/100Base-TX Ethernet port status LED |
|
|
(2) Link LED for Combo port |
(3) Console port |
|
(4) Power LED (PWR) |
(5) RPS DC power LED |
|
(6) A/L LED |
(7) D/S LED |
|
(8) Mode button |
(9) Active LED for Combo port |
Figure 1-1 Front panel of an S3100-26TP-EI-W Ethernet switch
& Note:
For details about LEDs on the front panel, refer to section 1.3 “Introduction to Front Panel LEDs”.
II. Rear panel
Figure 1-2 shows the rear panel of an S3100-26TP-EI-W Ethernet switch.

|
(1) AC power socket |
(2) RPS DC power socket |
|
(3) Grounding screw |
|
Figure 1-2 Rear panel of an S3100-26TP-EI-W Ethernet switch
III. Power system
S3100-26TP-EI-W Ethernet switches can adopt AC input, or RPS 12 VDC input, or both to provide backup. Only the recommended RPS can be used.
AC input:
l Rated voltage range: 100 VAC to 240 VAC, 50 Hz/60 Hz
l Input voltage range: 90 VAC to 264 VAC, 47 Hz to 63 Hz
RPS DC input:
l Rate voltage range: 10.8 VDC to 13.2 VDC
IV. Cooling system
S3100-26TP-EI-W Ethernet switches cool off naturally.
1.2.2 S3100-16TP-EI-W
I. Front panel
S3100-16TP-EI-W Ethernet switches each provide sixteen auto-sensing 10/100Base-TX Ethernet ports, two 10/100/1000Base-T Ethernet ports, two 100/1000Base-X SFP ports, and one console port. Each SFP port and the corresponding 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet port form a Combo port. For each Combo port, either the SFP port or the corresponding 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet port can be used at a time.
Figure 1-3 shows the front panel of an S3100-16TP-EI-W Ethernet switch.

|
(1) Auto-sensing 10/100Base-TX Ethernet port status LED |
|
|
(2) Link LED for Combo port |
(3) Console port |
|
(4) Power LED (PWR) |
(5) A/L LED |
|
(6) D/S LED |
(7) Mode button |
|
(8) Active LED for Combo port |
|
Figure 1-3 Front panel of an S3100-16TP-EI-W Ethernet switch
& Note:
For details about LEDs on the front panel, refer to section 1.3 “Introduction to Front Panel LEDs”.
II. Rear panel
Figure 1-4 shows the rear panel of an S3100-16TP-EI-W Ethernet switch.

|
(1) AC power socket |
(2) Grounding screw |
Figure 1-4 Rear panel of an S3100-16TP-EI-W Ethernet switch
III. Side panel
Each S3100-16TP-EI-W Ethernet switch provides a security slot, through which you can lock the device together with an irremovable object to prevent theft.
The security slot is located at the rear end of the left side panel, as shown in Figure 1-5.

|
(1) Security slot |
Figure 1-5 Security slot on left side panel of an S3100-16TP-EI-W Ethernet switch
& Note:
If the left screw hole above the security slot is used, the security slot cannot be used.
IV. Power system
S3100-16TP-EI-W Ethernet switches:
l Rated voltage range: 100 VAC to 240 VAC, 50/60Hz
l Input voltage range: 90 VAC to 264 VAC, 47Hz to 63Hz
V. Cooling system
S3100-16TP-EI-W Ethernet switches cool off naturally.
1.2.3 S3100-8TP-EI-W
I. Front panel
S3100-8TP-EI-W Ethernet switches each provide eight auto-sensing 10/100Base-TX Ethernet ports, one 10/100/1000Base-T Ethernet port, one 100/1000Base-X SFP port, and one console port. The SFP port and the 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet port form a Combo port. Either the SFP port or the 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet port can be used at a time.
Figure 1-6 shows the front panel of an S3100-8TP-EI-W Ethernet switch.

|
(1) Auto-sensing 10/100Base-TX Ethernet port status LED |
|
|
(2) Link LED for Combo port |
(3) Console port |
|
(4) Power LED (PWR) |
(5) A/L LED |
|
(6) D/S LED |
(7) Mode button |
|
(8) Active LED for Combo port |
|
Figure 1-6 Front panel of an S3100-8TP-EI-W Ethernet switch
& Note:
For details about LEDs on the front panel, refer to section 1.3 “Introduction to Front Panel LEDs”.
II. Rear panel
Figure 1-7 shows the rear panel of an S3100-8TP-EI-W Ethernet switch.

|
(1) AC power socket |
(2) Grounding screw |
Figure 1-7 Rear panel of an S3100-8TP-EI-W Ethernet switch
III. Side panel
Each S3100-8TP-EI-W Ethernet switch provides a security slot, through which you can lock the device together with an irremovable object to prevent theft.
The security slot is located at the rear end of the left side panel, as shown in Figure 1-5.
& Note:
If the left screw hole above the security slot is used, the security slot cannot be used.
IV. Power system
S3100-8TP-EI-W Ethernet switches:
l Rated voltage range: 100 VAC to 240 VAC, 50/60Hz
l Input voltage range: 90 VAC to 264 VAC, 47Hz to 63Hz
V. Cooling system
S3100-8TP-EI-W Ethernet switches cool off naturally.
1.3 Introduction to Front Panel LEDs
1.3.1 Power LED
Table 1-2 Description of the power LED on S3100 series
|
LED |
Mark on the panel |
Status |
Description |
|
Power LED |
PWR |
ON |
The switch is powered on. |
|
OFF |
The switch is powered off. |
||
|
RPS DC power LED |
RPS |
ON |
DC input is normal. |
|
OFF |
There is no DC input. |
& Note:
Only S3100-26TP-EI-W Ethernet switches have an RPS DC power LED.
1.3.2 Auto-Sensing 10/100BASE-TX Ethernet Port Status LED
There are two port status LEDs on both sides (yellow LED on the left and green LED on the right) of each 10/100BASE-TX Ethernet port of S3100 series. They indicate the active, link, duplex, and speed statuses of the port.
In addition, there are an A/L LED and a D/S LED on each model of S3100 series. These two LEDs indicate the mode of the port status LEDs. When the A/L LED is on, the port status LEDs respectively indicate the active status and link status of ports. When the D/S LED is on, the port status LEDs respectively indicate the duplex status and speed status of ports. Either the A/L LED or the D/S LED is on at a specific time. For details, see Table 1-3.
Table 1-3 Description of port status LEDs on S3100 series
|
Port status mode LED |
Port status LED |
Description |
|
|
The A/L LED is on |
Yellow LED (left) |
BLINKING |
The port is in the active state and there is traffic on the port. |
|
OFF |
The port is in the active state but there is no traffic on the port. |
||
|
Green LED (right) |
ON |
The port is connected properly. |
|
|
OFF |
The port is not connected or is incorrectly connected. |
||
|
The D/S LED is on |
Yellow LED (left) |
ON |
The port operates in the full duplex mode. |
|
OFF |
The port operates in the half duplex mode. |
||
|
Green LED (right) |
ON |
The port rate is 100 Mbps. |
|
|
OFF |
The port rate is 10 Mbps. |
||
You can switch the mode of the port status LEDs by pressing the Mode button. After a switch is powered on, the A/L LED is on initially. If you press the Mode button, the D/S LED will be on. After that, if you press the Mode button again within 45 seconds, the A/L LED will be on again. Otherwise, the A/L LED will automatically be on 45 seconds later.
1.3.3 1000 Mbps Uplink Port Status LED
Table 1-4 Description of 1000 Mbps uplink port status LED on S3100 series
|
LED |
Mark on the panel |
Status |
Description |
|
1000 Mbps uplink port link LED |
LINK |
ON |
The port is connected properly. |
|
OFF |
The port is not connected or is incorrectly connected. |
||
|
1000 Mbps uplink port active LED |
ACT |
BLINKING |
The port is in the active state and there is traffic on the port. |
|
OFF |
The port is in the active state but there is no traffic on the port. |
1.4 Technical Specifications
Table 1-5 Technical specifications for S3100 Series Ethernet switches
|
Model |
S3100-26TP-EI-W |
S3100-16TP-EI-W |
S3100-8TP-EI-W |
|
|
Physical dimensions (H x W x D) |
43.6 x 440 x 260 mm (1.7 x 17.2 x 10.2 in) |
43.6 x 300 x 220 mm (1.7 x 11.8 x 8.7 in) |
43.6 x 230 x 200 mm (1.7 x 9.1 x 7.9 in) |
|
|
Weight |
<3.5 kg (7.7 lb) |
<2.5 kg (5.5 lb) |
<1.8 kg (4 lb) |
|
|
Number of fixed ports |
24 x auto-sensing 10/100BASE-TX Ethernet port 2 x 1000 Mbps Combo port |
16 x auto-sensing 10/100BASE-TX Ethernet port 2 x 1000 Mbps Combo port |
8 x auto-sensing 10/100BASE-TX Ethernet port 1 x 1000 Mbps Combo port |
|
|
Number of management port |
1 x console port |
|||
|
Power system |
S3100-16TP-EI-W/S3100-8TP-EI-W Ethernet switches support only AC input. S3100-26TP-EI-W AC-powered switches support AC input and RPS DC input. AC input: l Rated voltage range: 100 VAC to 240 VAC, 50/60 Hz l Maximum voltage range: 90 VAC to 264 VAC, 47 Hz to 63Hz RPS DC input: l Rated voltage range: 10.8 VDC to 13.2 VDC |
|||
|
PoE (as powered device) |
Not supported |
Not supported |
Not supported |
|
|
System power consumption (full load) |
22 W |
17 W |
14 W |
|
|
Fan |
None |
None |
None |
|
|
Operating temperature |
0°C to 45°C (30°F to 113°F) |
|||
|
Relative humidity (non- condensing) |
10% to 90% |
|||
1.5 SFP Modules Supported by S3100 Series Ethernet Switches
The front panel of S3100 Ethernet switches provides one or two 1000 Mbps SFP ports in which you can select the required small form-factor pluggable (SFP) modules to insert. For the models of SFP modules, see Table 1-6.
Table 1-6 SFP modules supported by S3100 Series Ethernet switches
|
Type |
Model |
|
|
SFP module |
100 Mbps SFP module |
l SFP-FE-SX-MM1310-A l SFP-FE-LX-SM1310-A |
|
1000 Mbps SFP module |
l SFP-GE-SX-MM850-A l SFP-GE-LX-SM1310-A |
|
|
SFP stack module |
SFP-STACK-Kit |
|
|
100 Mbps bidirectional (BIDI) module |
l SFP-FE-LX-SM1310-BIDI l SFP-FE-LX-SM1550-BIDI |
|
|
1000 Mbps BIDI module |
l SFP-GE-LX-SM1310-BIDI l SFP-GE-LX-SM1490-BIDI |
|
& Note:
l The types of SFP modules may vary over time. Consult H3C marketing personnel or technical support personnel to obtain the latest information about SFP modules.
l For specifications of SFP modules, refer to H3C Low End Series Ethernet Switches Pluggable Module Manual.
Chapter 2 Installation Preparation
2.1 Precautions
To avoid any device impairment and body injury resulting from improper use, please take the following precautions:
l Before cleaning the switch, disconnect the power. Do not clean the switch with wet cloth or liquid.
l Keep the switch away from water or dampness. Prevent water or moisture from entering the switch chassis.
l Do not place the switch on an unstable case or desk, because the switch might be damaged severely in case of a fall.
l Keep the switch room drafty and the switch ventilation hole free of obstruction.
l The switch can operate normally only under correct voltage input. Make sure that the operating voltage is consistent with that labeled on the switch.
l To prevent electric shock, do not open the chassis while the switch is operating, and do not open the chassis arbitrarily even when the switch is powered off.
l Before changing interface cards, wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap to prevent the cards from being damaged by electrostatic discharge.
2.2 Requirements on Environment
S3100 Series Ethernet Switches must be used indoors. When you install your switch in a cabinet or on a desk, you must ensure:
l Enough space is reserved near the air-intake hole and the ventilation hole of the switch for heat dissipation of the switch chassis.
l The cabinet or the workbench takes good ventilation and heat dissipation system.
l The cabinet or the desk is solid enough to bear the weight of the switch and the accessories.
l The cabinet or the desk is well grounded.
To ensure normal operation and to prolong the life span of the switch, the following requirements on the installation site must also be satisfied.
2.2.1 Temperature/Humidity Requirements
You should keep your equipment room within the proper temperature and humidity ranges to ensure the normal operation and working life of your switch. If the humidity in the equipment room is too high for a long time, it may decrease the insulation attribute of insulating material or even cause electric leakage of insulating material, and, sometimes, may change the mechanical performance of material and cause the rustiness and corrosion of metal parts. If the relative humidity is too low, the captive screws may become loose due to the shrinking of insulation washers; in addition, electrostatic is more likely to be produced in a dry environment, which may damage the circuit of the switch. High temperature may cause even greater damage to the switch. High temperature for a long time will speed up the aging of insulation material, greatly lower the reliability of the switch and greatly reduce the life span of the switch.
For the temperature and humidity requirements of different models, refer to section 1.4 “Technical Specifications”.
2.2.2 Cleanness Requirements
Dust is a potential hazard to the safe operation of the switch. Falling on the equipment, it may cause electrostatic adsorption, and hence result in poor contact of the metal connectors or connection points. This is more likely to happen when the indoor relative humidity is low; in this case, it may not only shorten the device’s working life, but also incur communication failure. The requirements on dust content and particle diameter in the equipment room are shown in the following table:
Table 2-1 Requirements on dust content in the equipment room
|
Physical active substance |
Unit |
Content |
|
Dust particle |
particle/m³ |
≤ 3 x 104 (No visible dust on desk in three days) |
|
Note: Dust particle diameter ≥ 5µm |
||
Besides the requirements on dust, rigorous requirements are also set on the content of chloride, acid, and sulfide in the air of the equipment room. These kinds of harmful gas will accelerate metal corrosion and aging of certain parts. The equipment room should be protected from the intrusion of harmful gases such as SO2, H2S, NH3 and Cl2. The limits of these kinds of harmful gas are shown in the following table.
Table 2-2 Limits on harmful gas in the equipment room
|
Gas |
Max content (mg/m³) |
|
SO2 |
0.2 |
|
H2S |
0.006 |
|
NH3 |
0.05 |
|
Cl2 |
0.01 |
2.2.3 Anti-interference Requirements
A switch in use may be affected by the interference from outside the system by way of capacitance coupling, inductance coupling, electromagnetic radiation, public impedance (including the grounding system) coupling or conducting line (power line, signaling line, and transmission line). Therefore, you should pay attention to the following:
l If AC supply system is TN system, AC power socket should be a single-phase three-line power socket with Protection Earth (PE) so that the filter circuit on the equipment can effectively filter out the interference coming from the power supply system.
l Keep the switch far away from high-power radio transmitters, radars, and high-frequency heavy-current devices.
l Adopt electromagnetic shielding measure if necessary. For example, you can adopt shielded interface cable.
l Wire interface cables indoors. Do not wire cables outdoors in case that over-voltage and over-current damage the device.
2.2.4 Laser Usage Security
S3100 Series Ethernet Switches are category-1 laser equipment.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
When an optional interface card of the S3100 Series Ethernet Switches is operating, avoid staring into the optical interface because the high-energy laser beam emitted from the optical fiber may hurt your eyes.
2.3 Installation Tools
l Phillips screwdriver
l Flat-blade screwdriver
l ESD-preventive wrist strap
![]() Caution:
Caution:
These installation tools are not shipped with S3100 Series Ethernet Switches. You will have to prepare them beforehand.
Chapter 3 Installation
![]() Caution:
Caution:
On a mounting screw of the chassis of H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches, there is a seal labeled with H3C. You must keep it intact before asking the agent to maintain the switch. You must get the permission of the local agent before you can open the chassis. Otherwise, you will be responsible for irreversible damages caused by your operations.
3.1 Installing a Switch
3.1.1 Cabinet Mounting
You can install a switch into a 19-inch standard cabinet in one of the following ways:
l Use front mounting ears
l Use front mounting ears and a tray
l Use front mounting ears and guide rails
The installation methods of a switch depend on the depth and width of the switch. For the specific installation methods, see Table 3-1.
Table 3-1 Installation methods for S3100 switches
|
Model |
Use front mounting ears |
Use front mounting ears and a tray |
Use front mounting ears and guide rails |
|
S3100-26TP-EI-W |
√ |
√ |
√ |
|
S3100-16TP-EI-W |
√ |
√ |
— |
|
S3100-8TP-EI-W |
√ |
√ |
— |
& Note:
When the depth of a switch is greater than 300 mm (11.8 in), the front mounting ears only secure the switch rather than bear its weight.
I. Introduction to mounting ear
Figure 3-1 shows the appearance of a front mounting ear.

|
(1) Screw hole used to fix the mounting ear to the cabinet (Use one M6 screw) |
|
(2) Screw hole used to fix the switch to the mounting ear |
Figure 3-1 Appearance of a standard front mounting ear
When you install S3100 Series Ethernet Switches into 19-inch standard cabinets, you should select front mounting ears with a proper length (L1 as shown in Figure 3-1) according to the physical dimensions of switches. For the selection of front mounting ears, see Table 3-2.
Table 3-2 Selection of mounting ear for S3100 Series Ethernet Switches
|
Model |
Physical dimensions (H x W x D) |
Configuration type of front mounting ear |
|
S3100-26TP-EI-W |
43.6 x 440 x 260 mm (1.7 x 17.3 x 10.2 in) |
Standard |
|
S3100-16TP-EI-W |
43.6 x 300 x 220 mm (1.7 x 11.8 x 8.7 in) |
Optional |
|
S3100-8TP-EI-W |
43.6 x 230 x 200 mm (1.7 x 9.1 x 7.9 in) |
Optional |
II. Use front mounting ears to install a switch
Follow these steps to mount a switch into a 19-inch standard cabinet:
1) Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap to check the grounding and stability of the cabinet.
2) Take out the screws which are packed together with the front mounting ears, and fix one end of mounting ears to the switch, as shown in Figure 3-2.

Figure 3-2 Fix front mounting ears (1)
3) Place the switch horizontally in a proper position, and fix the other end of mounting ears to the front brackets with screws and captive nuts, as shown in Figure 3-3.

Figure 3-3 Fix front mounting ears (2)
III. Use front mounting ears and a tray
Follow these steps to install a switch into a 19-inch standard cabinet:
1) Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap to check the grounding and stability of the cabinet.
2) Fix the delivered tray horizontally in a proper position.
3) Take out the screws which are packed together with the front mounting ears, and fix one end of mounting ears to the switch, as shown in Figure 3-2.
4) Place the switch on the tray horizontally, slide the tray into the cabinet, and fix the other end of mounting ears to the front brackets with crews and captive nuts, as shown in Figure 3-3.
IV. Use front mounting ears and guide rails
l Introduction to guide rail
Figure 3-4 shows the appearance of a guide rail.

|
Slotted hole 1: Used to fix the guide rail to the rear bracket. You can adjust the screw hole position according to the position of the switch. |
|
Cooling hole: Used for heat dissipation between switch and cabinet |
|
Slotted hole 2: Used to fix the guide rail to the front bracket |
Figure 3-4 Appearance of a guide rail
& Note:
Guide rails purchased from H3C apply only to standard cabinets 1,000 mm (39.4 in) deep. Use other supports to substitute for guide rails in the case of other cabinet depths.
l Installation procedure
Follow these steps to install a switch into a 19-inch standard cabinet:
l Wear an ESD-preventive wrist strap to check the grounding and stability of the cabinet.
1) Take out the screws packed together with the front mounting ears and fix one end of the front mounting ears to the switch, as shown in Figure 3-2.
2) Install guide rails on the brackets on both sides of the cabinet with M5 self-tapping screws. Figure 3-5 is for reference only.

Figure 3-5 Install guide rails
3) Hold the two sides of the switch and slide it gently along the guide rails into the cabinet until it is located in a proper position, as shown in Figure 3-6. Ensure that the bottom side of the guide rails and the switch are in close contact.

Figure 3-6 Install front mounting ears and guide rails
4) Fix the other end of front mounting ears to the front brackets of the cabinet with M6 screws and captive nuts and ensure that the front mounting ears and guide rails have fixed the switch in the cabinet securely, as shown in Figure 3-7.

Figure 3-7 Effect diagram of front mounting ear and guide rail installation
& Note:
l No guide rails are delivered with the device.
l Ensure a clearance of 1U (44.45 mm, namely, 1.75 inches) between devices for the purpose of heat dissipation.
3.1.2 Desk Mounting
When a 19-inch standard cabinet is not available, you can simply place the switch on a clean desk. When doing so, you should ensure that:
l The desk is stable and well grounded.
l A clearance about 10 cm (3.9 in) is reserved around the switch for heat dissipation.
l No heavy object is placed on the switch.
l S3100 Series Ethernet Switches are designed with no fan. Therefore, you should install them in a drafty environment, and keep at least a vertical distance of 1.5 cm (0.6 in) between devices if you need to stack switches one upon another.
3.1.3 Wall Mounting
You can mount some models of S3100 Series Ethernet Switches on concrete walls or wood walls. Table 3-3 lists the models that support wall mounting.
Table 3-3 Models supporting wall mounting
|
Subseries |
Models supporting wall mounting |
Hole distance (mm) |
|
S3100 Ethernet switches |
S3100-8TP-EI-W |
170 mm (6.69 in.) |
|
S3100-16TP-EI-W |
I. Introduction to screw and anchor kit
Figure 3-8 and Figure 3-9 show the recommended sizes (in mm) of screws and anchor kits used for mounting:

|
(1) Outside edge of anchor kit |
II. Installation procedure
The wall-mounting procedure is as follows:
l As shown in Figure 3-10, drill two holes 5 mm across in the wall on the same horizontal line, with a distance of X=170 mm (6.69 in.).
& Note:
Drill two holes according to the sizes of anchor kits and screws so that anchor kits could go into the holes, only the edges could remain outside the wall, and the screws could be fixed on the wall tightly.
1) Insert anchor kits into the holes and keep only the edges outside the wall.
2) Drive screws into the anchor kits, keeping the inside of screw head at least 1.5 mm (0.06 in) away from the edge of the anchor kit so that the switch could hang on the screws securely.

3) Align the two installation holes at the bottom of the switch with these two screws to hang the switch.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
When mounting the switch, keep the Ethernet ports of the switch facing downwards and the two sides with ventilation holes vertical to the ground.
3.1.4 Magnet Mounting
The following four models support magnet mounting:
l S3100-8TP-EI-W
l S3100-16TP-EI-W
I. Introduction to magnetic accessories
A set of magnetic mounting accessories consists of one permanent magnets and one M3*6 countersunk head screws, as shown in Figure 3-11. Four sets of magnetic mounting accessories are needed for each S3100 switch.

|
(1) Permanent magnet |
(2) M3*6 countersunk head screw |
Figure 3-11 Magnets and countersunk head screws
II. Installation procedure
Follow these steps to complete magnet mounting:
1) As shown in Figure 3-12, use a Phillips screwdriver to pass the countersunk head screw through the round hole at the center of the permanent magnet, fasten it to a blind nut in the dent of the switch bottom, and ensure that the permanent magnet and the switch are fastened reliably.
& Note:
l Remove the cushion, if any, from the dent before installation.
l To ensure the firmness of installation, be sure to use four permanent magnets to secure each S3100 switch.
2) Attach the magnet-mounted device to the specified location. Take care not to get your fingers stuck between because the magnetism is very huge.

|
(1) Blind nut in the dent of the switch bottom |
(2) Permanent magnet |
|
(3) M3*6 countersunk head screw |
|
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l Apply magnet mounting to only the above four models. Otherwise, a falloff or mis-operation may occur.
l Select the installation location carefully. In the case of poor surface, magnet mounting may not be reliable.
l Put the device at a stable place free from vibrations or shocks. Otherwise, personal injuries or equipment damage may occur.
l Avoid installing the device at a high place because personal injuries or equipment damage may occur in case of a falloff.
l Avoid frequently moving the desk-mounted device because such movements may damage the surface coating.
l Keep the front panel of the device facing downwards and the two sides with ventilation holes vertical to the ground, if you want to install the device vertically.
l Pay attention that the weight of external cables should not bring about a falloff, which may result in personal injuries or equipment damage.
l Keep floppy disks and magnetic cards away from magnets to avoid erasure of any information.
l Keep computers and monitors that are easily influenced by magnetic fields away from magnets. Otherwise, faults may occur to these electronic devices.
3.2 Connection of Power Cable and Grounding Cable
3.2.1 Connecting AC Power Cable
I. AC power socket (recommended)
You are recommended to use a mono-phase three-core power socket with a neutral point or a multi-function power socket for computers. The neutral point of the power in your building must be well grounded. Normally, the neutral point of the power supply system in your building has already been grounded during the construction and wiring; but you should make sure this is the fact.

Figure 3-13 Recommended AC power socket
II. Connecting AC power cable
1) Connect one end of the grounding cable (delivered with the switch) to the grounding screw on the rear of the chassis and the other end to the ground nearby.
2) Connect one end of the power cable to the power socket on the rear panel of the chassis and the other end to an outside AC power socket.
3) Check whether the PWR LED on the front panel of the switch is ON. If yes, the power is properly connected.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
Before powering on the switch, you should properly connect the grounding cable.
3.2.2 Connecting DC Power Cable
I. 12V-RPS DC power cable connection for S3100-26TP-EI-W Ethernet switch

|
Pin Number |
Designation |
Pin Number |
Designation |
|
1 |
GND |
8 |
GND |
|
2 |
— |
9 |
— |
|
3 |
12V |
10 |
RPS_pres |
|
4 |
12V |
11 |
— |
|
5 |
12V |
12 |
— |
|
6 |
12V |
13 |
Control Pin |
|
7 |
GND |
14 |
GND |
Figure 3-14 12V-RPS DC power socket
l Connect one end of the grounding cable (delivered with the switch) to the grounding screw and the other end to the ground nearby.
1) Connect the 12V-RPS DC power supply as follows:
l As shown in Figure 3-15, loosen the fastening screws and remove the air filter from the 12V-RPS DC power socket. (In the case of no 12V-RPS DC power supply, re-install the air filter.)

|
(1) Air filter |
(2) Fastening screw |
Figure 3-15 12V-RPS power socket for an S3100-26TP-EI-W Ethernet switch
l Connect one connector (in A direction) of the 12V-RPS DC power cable (Figure 3-16 shows a recommended 12V-RPS DC power cable) to the RPS DC power socket of the switch, and the other connector (in B direction) to the corresponding 12 V power output socket of the RPS power module.

Figure 3-16 12V-RPS DC power cable
l Connect one end of the delivered AC power cable to the power socket of the RPS power module and the other end to the socket of an external AC power supply.
2) Check whether the PWR LED on the front panel of the switch is ON. If yes, the power is properly connected.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l Before powering on the switch, you should properly connect the grounding cable.
l The DC power cable should be less than 3 meters long.
l Only the recommended 12V-RPS DC power supply and power cables can be used.
3.2.3 Connecting Grounding Cable
![]() Caution:
Caution:
You should properly connect the switch grounding cable since it is crucial to the lightning protection and electromagnetic shield (EMS) of your switch.
Ground the switch as follows:
l When a grounding strip is available at the installation site, attach one end of the yellow-green grounding cable of the switch to the grounding screw on the grounding strip and fasten the captive nut. (Note that the fire main and lightning rod of your building are not suitable for grounding the switch. The grounding cable of the switch should be connected to the construction engineering ground of the equipment room.)

|
(2) Grounding screw |
|
|
(3) Protection grounding cable |
(4) Grounding strip |
Figure 3-17 Ground the switch through a grounding strip
l When there is no grounding strip but there is cement floor nearby where a grounding body is allowed to be buried, hammer an angle steel/steel pipe no shorter than 0.5 m (19.7 in.) into the earth, with the yellow-green grounding cable of the switch welded onto the angle steel/steel pipe and the jointing point being processed against erosion.

|
(2) Grounding screw |
|
|
(3) Protection grounding cable |
(4) Earth |
|
(5) Angle steel |
|
Figure 3-18 Ground the switch by burying the grounding body into the earth
l For an AC-powered switch, if none of the above two conditions is available, ground it through the PE cable of the AC power supply. In this case, make sure this PE cable is well connected to the ground at the power distribution room or AC transformer.

|
(1) AC power socket |
(2) Grounding screw |
|
(3) Power transformer |
(4) PE cable |
|
(5) 3-core cable for AC power input |
(6) Ethernet switch |
Figure 3-19 Ground the switch through AC PE cable
l For a DC-powered switch (–48 VDC), if none of the first two conditions is available, ground it through the return cable (RTN) of the DC power supply. In this case, make sure this RTN cable is well connected to the ground at the DC output of the DC power cabinet.

|
(2) –48V strip |
(3) –48V |
|
|
(4) RTN strip |
(5) RTN |
(6) PGND strip |
|
(7) Grounding to the earth |
(8) Grounding cable |
(9) Screw |
|
(10) Ethernet switch |
(11) DC power input |
|
Figure 3-20 Ground the switch through the PGND of the power cabinet
3.3 Connecting Optical Fiber
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l After a switch starts, the optical port may emit invisible radial when there is no optical connector connected to it and the protective cap is removed from it. Therefore, do not stare into the optical interface.
l Be sure to cover the protective cap within 10 seconds if an optical connector is not in use to keep the optical connector clean.
l Be sure to cover the protective cap if an optical port has no optical connector attached.
l Place the protective caps in a safe place when an optical port has fiber connected to prepare for the cases the fiber is pulled out.
3.4 Connection of Console Cable
3.4.1 Console Cable
The console cable is an 8-core shielded cable. At one end of the cable is a crimped RJ-45 connector to be connected to the console port of the switch; at the other end of the cable is a DB-9 (female) connector to be connected to the 9-core (pin) serial port on the console terminal. See the following figure.

Table 3-4 Console cable connector pinouts and mapping relation
|
RJ-45 |
Signal |
Direction |
DB-9 |
|
1 |
RTS |
← |
7 |
|
2 |
DTR |
← |
4 |
|
3 |
TXD |
← |
3 |
|
4 |
CD |
→ |
1 |
|
5 |
GND |
— |
5 |
|
6 |
RXD |
→ |
2 |
|
7 |
DSR |
→ |
6 |
|
8 |
CTS |
→ |
8 |
3.4.2 Connecting Console Cable
Follow these steps to connect a terminal device, a PC for example, to the switch:
Step 1: Connect the DB-9 female connector of the console cable to the serial port of the PC or the terminal device used to configure the switch.
Step 2: Connect the RJ-45 connector of the console cable to the console port of the switch.
Identify the label of the port before connecting a connector.
& Note:
When connecting a PC to a powered-on switch, you are recommended to connect the DB-9 connector of the console cable to the PC before connecting the RJ-45 connector to the switch. When disconnecting a PC from a powered-on switch, you are recommended to disconnect the DB-9 connector of the console cable from the PC after disconnecting the RJ-45 connector from the switch.
3.5 Installation Verification
After completing the installation, check that:
l The correct power is used.
l The grounding cable is connected.
l Both console cable and power cable are properly connected.
l All the interface cables are wired indoors. If there is any cable wired outdoors, verify that socket strip with lightning protection and lightning arresters for network ports have been properly connected.
Chapter 4 First Power-on
4.1 Establishing Configuration Environment
The following figure shows the configuration environment you will establish:
l In this environment, a terminal (a PC in this example) is connected to the console port of the switch through the console cable.

Figure 4-1 Network diagram for the configuration of the switch when it is first powered on
4.2 Connecting the Console Cable
Step 1: Connect the DB-9 female connector of the console cable to the serial port of the PC used to configure the switch.
Step 2: Connect the RJ-45 connector of console cable to the console port of the switch.
4.3 Setting Terminal Parameters
Step 1: Start the PC and run the terminal emulation program such as the Terminal of Windows3.1 or the HyperTerminal of Windows95/98/NT/2000/XP.
Step 2: Set terminal parameters (take the HyperTerminal of Windows2000 as an example).
Parameter requirements: Set bits per second to 9600, data bits to 8, parity check to none, stop bits to 1 and flow control to none. Select VT100 as terminal emulation. The following is the specific procedure:
1)
Select
[Start/Program/Accessories/Communications/HyperTerminal] to enter the
HyperTerminal window, where click the  icon to establish a new connection. The
system displays the Connection Description interface, as shown in the following
figure.
icon to establish a new connection. The
system displays the Connection Description interface, as shown in the following
figure.

Figure 4-2 Connection description interface of HyperTerminal
2) Type in the name of the new connection in the connection description interface and click <OK>. The system pops up the following interface. Select the serial port to be used from [Connect using].

Figure 4-3 Setting the serial port used by the HyperTerminal connection
3) Click <OK> after selecting a serial port and the system pops up the following interface. In the interface, set the bits per second to 9600, data bits to 8, parity check to none, stop bits to 1, and flow control to none.
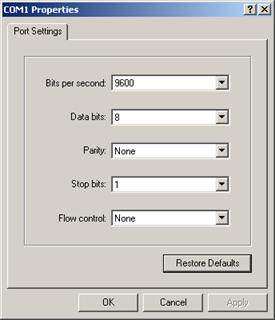
Figure 4-4 Setting serial port parameters
4) Click <OK> after setting the serial port parameters, and the system enters the following interface.

Choose [Properties] in the HyperTerminal dialog box to enter the properties window. Click [Settings] to enter the following properties setting window, and select VT100 as the terminal emulation. Click <OK> when the selection is done.
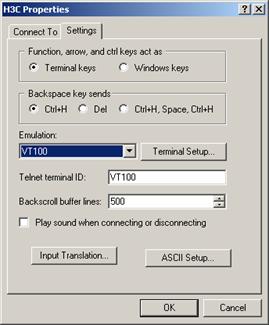
Figure 4-6 Set terminal emulation in H3C Properties window
4.4 Booting Switch
4.4.1 Checking Before Powering on the Switch
Before powering on the switch, verify that:
l The power cable and grounding wire are properly connected.
l The supply voltage is consistent with that required by the switch.
l The console cable is properly connected; the terminal (which can be a PC) used for configuration has been started; and the configuration parameters have been set.
4.4.2 Powering on the Switch
All the S3100 series Ethernet switches have the same BOOTROM display style. This document takes the BOOTROM display of the S3100-26TP-EI-W switch as example:
Starting......
***********************************************************
* *
* H3C S3100-26TP-EI-W BOOTROM, Version 517 *
* *
***********************************************************
Copyright(c) 2004-2007 Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Creation date : Dec 8 2007, 13:47:55
CPU Clock Speed : 200MHz
BUS Clock Speed : 33MHz
Memory Size : 64MB
Mac Address : 00e0fc003100
Press Ctrl-B to enter Boot Menu... 2
The last line prompts you to enter the Boot Menu and waits two seconds for your response.
& Note:
l The system has two startup modes: normal and fast. The normal startup mode spends a little more time than the fast startup mode because the former takes more self-test operations.
l By default, the system starts up in fast mode and the waiting time here is two seconds. While, if you set the startup mode to normal, this waiting time is five seconds. For the setting of the startup mode, refer to the next section.
l If you press <Ctrl+B> within 2 seconds, the Boot Menu is displayed:
BOOT MENU
1. Download application file to flash
2. Select application file to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Modify bootrom password
6. Enter bootrom upgrade menu
7. Skip current configuration file
8. Set bootrom password recovery
9. Set switch startup mode
0. Reboot
Enter your choice(0-9):
l If you perform no operation or press a key other than <Ctrl+B> within two seconds, once the waiting time becomes zero, the system begins to automatically start up and the following information is displayed:
Auto-booting...
Decompress Image...................................................
...................................................................
...................................................................
...................................................................
...................................................................
...............................................OK!
Starting at 0x80100000...
User interface aux0 is available.
Press ENTER to get started.
4.4.3 Changing the Startup Mode
By default, the system starts up in fast mode. If you want to change the startup mode to normal, press <Ctrl+B> within two seconds to enter the Boot Menu showed below:
BOOT MENU
1. Download application file to flash
2. Select application file to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Modify bootrom password
6. Enter bootrom upgrade menu
7. Skip current configuration file
8. Set bootrom password recovery
9. Set switch startup mode
0. Reboot
Enter your choice(0-9):
Enter 9, and the system prompts you to change the startup mode:
The current mode is fast startup mode!
Are you sure to change it to full startup mode? Yes or No(Y/N)
Enter Y, and the system gives the following prompts:
Setting startup mode...done!
BOOT MENU
1. Download application file to flash
2. Select application file to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Modify bootrom password
6. Enter bootrom upgrade menu
7. Skip current configuration file
8. Set bootrom password recovery
9. Set switch startup mode
0. Reboot
Enter your choice(0-9):
Enter 0, the system reboots in normal mode and displays the following information:
Starting......
***********************************************************
* *
* H3C S3100-26TP-EI-W BOOTROM, Version 517 *
* *
***********************************************************
Copyright(c) 2004-2007 Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Creation date : Dec 8 2007, 13:47:55
CPU Clock Speed : 200MHz
BUS Clock Speed : 33MHz
Memory Size : 64MB
Mac Address : 00e0fc003100
Press Ctrl-B to enter Boot Menu... 5
In normal startup mode, the waiting time here is five seconds. If you press <Ctrl+B> within five seconds, the Boot Menu is displayed. If you perform no operation or press a key other than <Ctrl+B> within five seconds, the system begins to automatically starts up and the following information is displayed:
Auto-booting...
Decompress Image...................................................
...................................................................
...................................................................
...................................................................
...................................................................
...............................................OK!
Starting at 0x80100000...
Board checking...................... LSN1LTSG0
SDRAM fast selftest........................OK!
Flash fast selftest........................OK!
Switch chip selftest.......................OK!
Slot 1/1/1 has FIX_COMBO_PORT module
Slot 1/2/1 has FIX_COMBO_PORT module
PHY selftest...............................OK!
Please check port leds...............FINISHED!
User interface aux0 is available.
Press ENTER to get started.
The appearance of "Press ENTER to get started" indicates that the switch finishes the auto-startup.
Press <Enter>, and the following prompt is displayed:
<H3C>
You can configure the switch now.
& Note:
The H3C S3100 Series Switches provides abundant command views. For detailed descriptions about the configuration commands and CLI, refer to H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Operation Manual (For Soliton) and H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Command Manual (For Soliton).
Chapter 5 Boot ROM and Host Software Loading
Traditionally, the loading of switch software is accomplished through the serial port. This approach is slow, inconvenient, and cannot be used for remote real-time loading. To resolve these problems, the TFTP and FTP modules are introduced into the switch. With these modules, the software and files can be loaded through Ethernet port conveniently.
This chapter introduces how to load Boot ROM and host software into a switch locally and how to do this remotely.
5.1 Introduction to Loading Approaches
You can load the software locally by using:
l XModem via console port
l TFTP via Ethernet port
l FTP via Ethernet port
You can load the software remotely by using:
l FTP
l TFTP
& Note:
Boot ROM software version should be compatible with the host software version when you load the Boot ROM and host software.
5.2 Local Software Loading
If your terminal is directly connected to the switch, you can load Boot ROM and host software locally.
Before loading the software, make sure that your terminal is correctly connected to the switch to ensure the successful loading.
& Note:
The loading process of the Boot ROM software is the same as that of the host software, except that during the Boot ROM loading process, you should press <Ctrl+U> and <Enter> after entering the Boot Menu and the system gives somewhat different prompts. The following text mainly describes the Boot ROM loading process.
5.2.1 Boot Menu
Take S3100-26TP-EI-W switch as example. After the switch is powered on, the system displays:
Starting......
***********************************************************
* *
* H3C S3100-26TP-EI-W BOOTROM, Version 517 *
* *
***********************************************************
Copyright(c) 2004-2007 Hangzhou H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Creation date : Dec 8 2007, 13:47:55
CPU Clock Speed : 200MHz
BUS Clock Speed : 33MHz
Memory Size : 64MB
Mac Address : 00e0fc003100
Press Ctrl-B to enter Boot Menu... 5
Press <Ctrl+B>. The system displays:
Password :
& Note:
To enter the Boot Menu, you should press <Ctrl+B> within five seconds after the information “Press Ctrl-B to enter Boot Menu...” appears. Otherwise, the system starts to decompress the program; and if you want to enter the Boot Menu at this time, you will have to restart the switch.
Input the correct Boot ROM password (by default, no password is set on the switch). The system enters the Boot Menu:
BOOT MENU
1. Download application file to flash
2. Select application file to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Modify bootrom password
6. Enter bootrom upgrade menu
7. Skip current configuration file
8. Set bootrom password recovery
9. Set switch startup mode
0. Reboot
Enter your choice(0-9):
5.2.2 Loading Software Using XModem Through Console Port
I. Introduction to XModem
XModem is a file transfer protocol that is widely used due to its simplicity and good performance. XModem transfers files via console port. It supports two types of data packets (128 bytes and 1 KB), two check methods (checksum and CRC), and error packet retransmission mechanism (generally the maximum number of retransmission attempts is ten).
The XModem transmission procedure is completed by the cooperation of a receiving program and a sending program: The receiving program sends a negotiation packet to negotiate a packet check method. After the negotiation, the sending program starts to transmit data packets. When receiving a complete packet, the receiving program checks the packet using the agreed method. If the check succeeds, the receiving program sends an acknowledgement packet and the sending program proceeds to send another packet; otherwise, the receiving program sends a negative acknowledgement packet and the sending program retransmits the packet.
II. Loading Boot ROM software
Follow these steps to load the Boot ROM software:
Step 1: At the prompt "Enter your choice (0-9):" in the Boot Menu, press <6> or <Ctrl+U>, and then press <Enter> to enter the Boot ROM update menu shown below:
Bootrom update menu:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameter
2. Set FTP protocol parameter
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameter
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
Step 2: Enter 3 in the above menu to load the Boot ROM software using XModem. The system displays the following download bits per second setting menu:
Please select your download baudrate:
1.* 9600
2. 19200
3. 38400
4. 57600
5. 115200
0. Return
Enter your choice (0-5):
Step 3: Choose an appropriate download bits per second. For example, if you enter 5, the 115200 bps rate is chosen, and the system displays the following information:
Download baudrate is 115200 bps
Please change the terminal's baudrate to 115200 bps and select XMODEM protocol
Press enter key when ready
Now, press <Enter>.
& Note:
If you have chosen 9600 bps, you do not need to modify the HyperTerminal’s bits per second, and therefore you can skip Step 4 and 5 below and proceed to Step 6 directly. In this case, the system will not display the above information.
Step 4: Select [File/Properties] in HyperTerminal, click <Configuration> in the popup dialog box, and select the bits per second of 115200bps in the appeared console port configuration dialog box.

Figure 5-1 Properties dialog box

Figure 5-2 Console port configuration dialog box
Step 5: Click the <Disconnect> button to disconnect the HyperTerminal from the switch and then click the <Call> button to reconnect the HyperTerminal to the switch.

Figure 5-3 Call and disconnect buttons
& Note:
The new bits per second takes effect only after you disconnect and reconnect the terminal emulation program.
Step 6: Press <Enter> to start downloading the program. The system displays the following information:
Now please start transfer file with XMODEM protocol.
If you want to exit, Press <Ctrl+X>.
Loading ...CCCCCCCCCC
Step 7: Choose [Transfer/Send File] in the HyperTerminal’s window, and in the following popup dialog box click <Browse>, select the software you need to download, and set the protocol to XModem.

Figure 5-4 Send file dialog box
Step 8: Click <Send>. The system displays the following page.

After the download completes, the system displays the following information:
Loading ...CCCCCCCCCC done!
& Note:
You do not need to reset the HyperTerminal’s bits per second and can skip the last step if you have chosen 9600 bps. In this case, the system displays the prompt “Bootrom is updating now.....................................done!” instead of the prompt "Your baudrate should be set to 9600 bps again! Press enter key when ready".
Step 9: Reset HyperTerminal’s bits per second to 9600 bps (refer to Step 4 and 5). Then, press any key as prompted. The system will display the following information when it completes the loading.
Bootrom is updating now.....................................done!
III. Loading host software
Follow these steps to load the host software:
Step 1: Select <1> in Boot Menu. The system displays the following information:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameter
2. Set FTP protocol parameter
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameter
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):3
The subsequent steps are the same as those for loading the Boot ROM software, except that the system gives the prompt for host software loading instead of Boot ROM loading.
5.2.3 Loading Software Using TFTP Through Ethernet Port
I. Introduction to TFTP
TFTP, one protocol in TCP/IP protocol suite, is used for trivial file transfer between client and server. It uses UDP to provide unreliable data stream transfer service.
II. Loading Boot ROM software

Figure 5-6 Local loading using TFTP
Step 1: As shown in Figure 5-6, connect the switch through an Ethernet port to the TFTP server, and connect the switch through the console port to the configuration PC.
& Note:
You can use one PC as both configuration device and TFTP server.
Step 2: Run the TFTP server program on the TFTP server, and specify the path of the program to be loaded.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
TFTP server program is not provided with the H3C Series Switches.
Step 3: Run the terminal emulation program on the configuration PC. Start the switch. Then enter the Boot Menu.
At the prompt "Enter your choice (0-9):" in the Boot Menu, press <6> or <Ctrl+U>, and then press <Enter> to enter the Boot ROM update menu shown below:
Bootrom update menu:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameter
2. Set FTP protocol parameter
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameter
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
Step 4: Enter 1 to download the Boot ROM software using TFTP. Then set the following TFTP-related parameters as required:
Load File name :S3100-EI.btm
Switch IP address :1.1.1.2
Server IP address :1.1.1.1
Step 5: Press <Enter>. The system displays the following information:
Are you sure to update your bootrom?Yes or No(Y/N)
Step 6: Enter Y to start file downloading or N to return to the Boot ROM update menu. If you enter Y, the system begins to download and update the Boot ROM software. Upon completion, the system displays the following information:
Loading........................................done
Bootrom updating..........done!
III. Loading host software
Follow these steps to load the host software of the switch.
Step 1: Select <1> in Boot Menu. The system displays the following information:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameter
2. Set FTP protocol parameter
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameter
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):1
The subsequent steps are the same as those for loading the Boot ROM software, except that the system gives the prompt for host software loading instead of Boot ROM loading.
5.2.4 Loading Software Using FTP Through Ethernet Port
I. Introduction to FTP
FTP is an application-layer protocol in the TCP/IP protocol suite. It is used for transferring files between server and client. FTP runs over UDP to provide unreliable data transmission.
You can use FTP to load software to the switch through an Ethernet port. In this case, the switch can act as an FTP server or an FTP client. In the following example, the switch acts as an FTP client.
II. Loading Boot ROM software

Figure 5-7 Local loading using FTP
Step 1: As shown in Figure 5-7, connect the switch through an Ethernet port to the FTP server, and connect the switch through the console port to the configuration PC.
& Note:
You can use one computer as both configuration device and FTP server.
Step 2: Run the FTP server program on the FTP server, configure an FTP user name and password, and specify the path of the program to be downloaded.
Step 3: Run the terminal emulation program on the configuration PC. Start the switch. Then enter the Boot Menu.
At the prompt "Enter your choice (0-9):" in the Boot Menu, press <6> or <Ctrl+U>, and then press <Enter> to enter the Boot ROM update menu shown below:
Bootrom update menu:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameter
2. Set FTP protocol parameter
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameter
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):
Step 4: Enter 2 in the above menu to download the Boot ROM software using FTP. Then set the following FTP-related parameters as required:
Load File name :S3100-EI.btm
Switch IP address :10.1.1.2
Server IP address : 10.1.1.1
FTP User Name :3100-SI
FTP User Password :abc
Step 5: Press <Enter>. The system displays the following information:
Are you sure to update your bootrom?Yes or No(Y/N)
Step 6: Enter Y to start file downloading or N to return to the Boot ROM update menu. If you enter Y, the system begins to download and update the program. Upon completion, the system displays the following information:
Loading........................................done
Bootrom updating..........done!
III. Loading host software
Follow these steps to load the host software:
Step 1: Select <1> in Boot Menu. The system displays the following information:
1. Set TFTP protocol parameter
2. Set FTP protocol parameter
3. Set XMODEM protocol parameter
0. Return to boot menu
Enter your choice(0-3):2
The subsequent steps are the same as those for loading the Boot ROM software, except for that the system gives the prompt for host software loading instead of Boot ROM loading.
5.3 Remote Software Loading
If your terminal is indirectly connected to the switch through Internet, you can telnet to the switch, and use FTP or TFTP to load Boot ROM and host software remotely.
5.3.1 Remote Loading Using FTP
As shown in Figure 5-8, a PC is used as both configuration device and FTP server. You can telnet to the switch, and then execute the FTP commands to download the host program s3100-EI.bin and the Boot ROM program s3100-EI.btm from the remote FTP server (with IP address 202.10.10.53) to the switch.

Figure 5-8 Remote loading using FTP
Step 1: Download the software to the switch using FTP commands.
<H3C> ftp 202.10.10.53
Trying ...
Press CTRL+K to abort
Connected.
220 WFTPD 2.0 service (by Texas Imperial Software) ready for new user
User(none):abc
331 Give me your password, please
Password:
230 Logged in successfully
[ftp] get s3100-EI.bin
[ftp] get s3100-EI.btm
[ftp] bye
Step 2: Update the Boot ROM program on the switch.
<H3C> boot bootrom s3100-EI.btm
please wait ...
Bootrom is updated!
Step 3: Update the host program on the switch.
<H3C> boot boot-loader s3100-EI.bin
<H3C> display boot-loader
Unit 1:
The current boot app is: s3100-EI.bin
The main boot app is: s3100-EI.bin
The backup boot app is:
Step 4: Restart the switch.
<H3C> reboot
& Note:
Before restarting the switch, make sure other configurations are all saved to avoid the loss of configuration information.
After the above operations, the Boot ROM and host software loading is completed.
Pay attention to the following:
l Host software loading takes effect only after you restart the switch with the reboot command.
l If the space of the flash memory is not enough, you can delete the useless files in the flash memory before software downloading.
l No power-breaking is permitted during software loading.
5.3.2 Remote Loading Using TFTP
The remote loading by using TFTP is similar to the remote loading by using FTP. The only difference is that it is TFTP that you use when loading software to the switch. In this case, the switch can only be used as a TFTP client.
Chapter 6 Maintenance and Troubleshooting
6.1 Software Loading Failure
If software loading fails, the system keeps running in original version.
In this case, check if the physical ports are properly connected:
l If not, reconnect them correctly and restart the loading procedure.
l If so, check the loading procedure information displayed on the HyperTerminal for input errors. If there is any input error, restart the loading procedure with correct input. For example:
1) When using XModem, verify that you have reset the bits per second of the HyperTerminal to 9600 bps after loading the software with a bits per second other than 9600 bps;
2) When using TFTP, verify that you have provided:
l Correct server and switch IP addresses,
l Correct name of the software to be loaded,
l Correct working path of TFTP server;
3) When using FTP, verify that you have provided:
l Correct server and switch IP addresses,
l Correct name of the software to be loaded,
l Correct username and password.
If software loading fails but there are neither physical connection problems nor input errors, please contact your agent for help.
6.2 Missing Password
6.2.1 Missing user password
If you forget your user password, you can:
Access the Boot Menu:
BOOT MENU
1. Download application file to flash
2. Select application file to boot
3. Display all files in flash
4. Delete file from flash
5. Modify bootrom password
6. Enter bootrom upgrade menu
7. Skip current configuration file
8. Set bootrom password recovery
9. Set switch startup mode
0. Reboot
Enter your choice(0-9):
Select <7> and restart the switch. After that, the system will skip the configuration file.
6.2.2 Missing Boot ROM Password
Please contact your agent.
6.3 Power System Failure
You can check whether the power system of the switch fails by viewing the POWER indicator on the front panel. If it is in normal operation, the POWER indicator should stay on. Otherwise, please check that:
l The switch power cable is correctly connected.
l The power input to the switch matches the requirement as labeled on the switch.
6.4 Configuration System Failure
After the switch is powered on and the system is normal, the booting information will be displayed on the configuration terminal. If the configuration system has any faults, there will not be any screen display at the configuration terminal or the displayed characters will be totally illegible.
I. Troubleshooting when there is no terminal display
If there is no output information after the configuration is powered on, please check that:
l The power supply is normal
l The console cable is properly connected
If no problems are found after the above-mentioned items have been checked, the cause may lie in the console cable or the settings of the terminal (such as HyperTerminal) parameters. Please perform the corresponding check.
II. Troubleshooting when the terminal display is illegible
If there is illegible display at the configuration terminal, the cause might lie in the parameter setting error at the terminal (such as HyperTerminal). Please confirm the following terminal parameter (such as HyperTerminal) settings:
l Bits per second: 9600
l Data bits: 8
l Parity check: None
l Stop bits: 1
l Flow control: None


