- Table of Contents
-
- H3C S5500-EI Series Switches Operation Manual-Release 2102(V1.01)
- 00-Preface
- 01-CLI configuration
- 02-RBAC configuration
- 03-Login management configuration
- 04-FTP and TFTP configuration
- 05-File system management configuration
- 06-Configuration file management configuration
- 07-Software upgrade configuration
- 08-Emergency shell configuration
- 09-Automatic configuration
- 10-Device management configuration
- 11-Tcl configuration
- 12-Python configuration
- 13-License management
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 09-DLDP Configuration | 96 KB |
Table of Contents
1.2 DLDP Configuration Task List
1.2.3 Setting the Interval for Sending Advertisement Packets
1.2.4 Setting the DelayDown Timer
1.2.5 Setting the Port Shutdown Mode
1.2.6 Configuring DLDP Authentication
1.3 Displaying and Maintaining DLDP
1.4 DLDP Configuration Example
1.4.1 DLDP Configuration Example
Chapter 1 DLDP Configuration
When performing DLDP configuration, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l Overview
l DLDP Configuration Task List
l Setting the Interval for Sending Advertisement Packets
l Setting the Port Shutdown Mode
l Configuring DLDP Authentication
l Displaying and Maintaining DLDP
1.1 Overview
A special kind of links, namely, unidirectional links, may occur in a network. When a unidirectional link appears, the local device can receive packets from the peer device through the link layer, but the peer device cannot receive packets from the local device. Unidirectional link can cause problems such as loops in a Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) enabled network.
As for fiber links, two kinds of unidirectional links exist. One occurs when fibers are cross-connected, as shown in Figure 1-1. The other occurs when one end of a fiber is not connected or one fiber of a fiber pair gets disconnected, as illustrated by the hollow arrows in Figure 1-2.
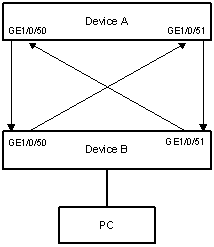
Figure 1-1 Unidirectional fiber link: cross-connected fiber
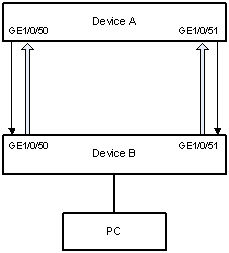
Figure 1-2 Unidirectional fiber link: fiber not connected or disconnected
1.1.1 DLDP Introduction
Device Link Detection Protocol (DLDP) can detect the link status of a fiber cable or twisted pair. On detecting a unidirectional link, DLDP can shut down the related port automatically or prompt users to take measures as configured to avoid network problems.
As a data link layer protocol, DLDP cooperates with physical layer protocols to monitor the link status of a device. The auto-negotiation mechanism provided by physical layer protocols detects physical signals and faults. DLDP, however, performs operations such as identifying peer devices, detecting unidirectional links, and shutting down unreachable ports. The cooperation of physical layer protocols and DLDP ensures that physical/logical unidirectional links be detected and shut down. For a link with the devices on the both sides of it operating properly, DLDP checks to see if the cable is connected correctly and if packets can be exchanged between the two devices. Note that DLDP is not implemented through auto-negotiation.
1.1.2 DLDP Fundamentals
I. DLDP link states
A device is in one of these DLDP link states: Initial, Inactive, Active, Advertisement, Probe, Disable, and DelayDown, as described in Table 1-1.
Table 1-1 DLDP link states
|
State |
Description |
|
Initial |
This state indicates that DLDP is not enabled. |
|
Inactive |
This state indicates that DLDP is enabled but the link is down. |
|
Active |
This state indicates that: l DLDP is enabled and the link is up. l The neighbor entries are cleared. |
|
Advertisement |
This state indicates that a device can communicate normally with all its neighbors in both directions or DLDP remains in active state for more than five seconds. It is the normal state where no unidirectional link is detected. |
|
Probe |
A device enters this state if it receives a packet from an unknown neighbor. In this state, DLDP sends packets to check whether the link is a unidirectional link. After a device enters this state, the probe sending timer is triggered, and an echo waiting timer is triggered for each neighbor to be detected. |
|
Disable |
A device enters this state when: l A unidirectional link is detected. l The contact with a neighbor in enhanced mode gets lost. In this state, no DLDP packet is sent or accepted. |
|
DelayDown |
A device in the Active, Advertisement, or Probe DLDP link state transits to this state rather than remove the corresponding neighbor entry and transits to the Inactive state when it detects a port-down event. When a device transits to this state, the DelayDown timer is triggered. |
II. DLDP timers
Table 1-2 DLDP timers
|
DLDP timer |
Description |
|
Active timer |
Determines the Interval to send Advertisement packets with RSY tag, which defaults to 1 second. When a device transits to the active DLDP link state, it sends Advertisement packets with RSY tag according to this timer. The maximum number of this type of packets that can be sent successively is 5. |
|
Advertisement timer |
Determines the interval to send advertisement packets, which defaults to 5 seconds. |
|
Probe timer |
Determines the interval to send Probe packets, which defaults to 0.5 seconds. The maximum number of this type of packets that can be sent successively is 10. |
|
Echo timer |
This timer is set to 10 seconds and is triggered when a device transits to the Probe state or an enhanced detect is launched. When the Echo waiting timer expires and no Echo packet is received from a neighbor device, the link is set as a unidirectional link and the device transits to the Disable state. In this case, the device sends Disable packets, prompts the user to shut down the port or shuts down the port automatically (depending on the DLDP down mode configured), and removes the corresponding neighbor entries. |
|
Entry timer |
When a new neighbor joins, a neighbor entry is created and the corresponding entry timer is triggered. And when a DLDP packet is received, the device updates the corresponding neighbor entry and the entry aging timer. In the normal mode, if no packet is received from a neighbor when the corresponding entry aging timer expires, DLDP sends advertisement packets with RSY tags and removes the neighbor entry. In the enhanced mode, if no packet is received from a neighbor when the Entry timer expires, DLDP triggers the enhanced timer. The setting of an Entry timer is three times that of the Advertisement timer. |
|
Enhanced timer |
In the enhanced mode, this timer is triggered if no packet is received from a neighbor when the entry aging timer expires. Enhanced timer is set to 10 seconds. After the Enhanced timer is triggered, the device sends up to eight probe packets to the neighbor at a frequency of one packet per second. If no Echo packet is received from the neighbor when the Echo timer expires, the link is set as a unidirectional link and the device transits to the Disable state. In this case, the device sends Disable packets, prompts the user to shut down the port or shuts down the port automatically (depending on the DLDP down mode configured), and removes the corresponding neighbor entries. |
|
DelayDown timer |
A device in the Active, Advertisement, or Probe DLDP link state transits to DelayDown state rather than removes the corresponding neighbor entry and transits to the Inactive state when it detects a port-down event. When a device transits to this state, the DelayDown timer is triggered. The setting of the timer ranges from 1 to 5 (in seconds). A device in DelayDown state only responds to port-up events. A device in the DelayDown state resumes its original DLDP state if it detects a port-up event before the DelayDown timer expires. Otherwise, it removes the corresponding DLDP neighbor information and transits to the Inactive state. |
|
RecoverProbe timer |
Determines the interval to RecoverProbe packets, which are used to detect whether a unidirectional link is restored. This timer is set to 2 seconds. |
III. DLDP mode
DLDP can operate in two modes: normal mode and enhanced mode, as described below.
l In normal DLDP mode, when an entry timer expires, the device removes the corresponding neighbor entry and sends an Advertisement packet with RSY tag.
l In enhanced DLDP mode, when an entry timer expires, the Enhanced timer is triggered and the device sends up to eight Probe packets at a frequency of one packet per second to test the neighbor. If no Echo packet is received from the neighbor when the Echo timer expires, the device transits to the Disable state.
Table 1-3 DLDP mode and neighbor entry aging
|
DLDP mode |
Detecting a neighbor after the corresponding neighbor entry ages out |
Removing the neighbor entry immediately after the Entry timer expires |
Triggering the Enhanced timer after an Entry timer expires |
|
Normal DLDP mode |
No |
Yes |
No |
|
Enhanced DLDP mode |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
The enhanced DLDP mode is designed for addressing black holes. It prevents the cases where one end of a link is up and the other is down. If you configure the speed and the duplex mode by force on a device, the situation shown in Figure 1-3 may occur, where Port B is actually down but the state of Port B cannot be detected by common data link protocols, so Port A is still up. In enhanced DLDP mode, however, Port A tests Port B after the Entry timer concerning Port B expires. Port A then transits to the Disable state if it receives no Echo packet from Port A when the Echo timer expires. As Port B is physically down, it is in the Inactive DLDP state.
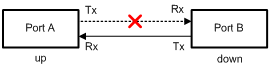
Figure 1-3 A case for Enhanced DLDP mode
& Note:
l In normal DLDP mode, only fiber cross-connected unidirectional links (as shown in Figure 1-1 ) can be detected.
l In enhanced DLDP mode, two types of unidirectional links can be detected. One is fiber cross-connected links (as shown in Figure 1-1). The other refers to fiber pairs with one fiber not connected or disconnected (as shown in Figure 1-2). To detect unidirectional links that are of the latter type, you need to configure the ports to operate at specific speed and in full duplex mode. Otherwise, DLDP cannot take effect. When a fiber of a fiber pair is not connected or gets disconnected, the port that can receive optical signals is in Disable state; the other port is in Inactive state.
IV. DLDP authentication mode
You can prevent network attacks and illegal detect through DLDP authentication. Three DLDP authentication modes exist, as described below.
l Non-authentication. In this mode, the sending side sets the Authentication field and the Authentication type field of DLDP packets to 0. The receiving side checks the values of the two fields of received DLDP packets and drops the packets with the two fields conflicting with the corresponding local configuration.
l Plain text authentication. In this mode, before sending a DLDP packet, the sending side sets the Authentication field to the password configured in plain text and sets the Authentication type field to 1. The receiving side checks the values of the two fields of received DLDP packets and drops the packets with the two fields conflicting with the corresponding local configuration.
l MD5 authentication. In this mode, before sending a packet, the sending side encrypts the user configured password using MD5 algorithm, assigns the digest to the Authentication field, and sets the Authentication type field to 2. The receiving side checks the values of the two fields of received DLDP packets and drops the packets with the two fields conflicting with the corresponding local configuration.
V. DLDP implementation
1) On a DLDP-enabled link that is in up state, DLDP sends DLDP packets to the peer device and processes the DLDP packets received from the peer device. DLDP packets sent vary with DLDP states. Table 1-4 lists DLDP states and the corresponding packets.
Table 1-4 DLDP packet types and DLDP states
|
DLDP state |
Type of DLDP packets sent |
|
Active |
Advertisement packet with RSY tag |
|
Advertisement |
Normal Advertisement packet |
|
Probe |
Probe packet |
|
Disable |
Disable packet and RecoverProbe packet |
& Note:
When a device transits from a DLDP state other than Inactive state or Disable state to Initial state, it sends Flush packets.
2) A received DLDP packet is processed as follows.
l In any of the three authentication modes, the packet is dropped if it fails to pass the authentication.
l The packet is dropped if the setting of the interval for sending Advertisement packets it carries conflicts with the corresponding local setting.
l Other processes.
Table 1-5 Procedures for processing different types of DLDP packets
|
Packet type |
Processing procedure |
||
|
Advertisement packet with RSY tag |
Retrieving the neighbor information. |
If the corresponding neighbor entry does not exist, creates the neighbor entry, triggers the Entry timer, and transits to Probe state. |
|
|
If the corresponding neighbor entry already exists, resets the Entry timer and transits to Probe state. |
|||
|
Normal Advertisement packet |
Retrieves the neighbor information. |
If the corresponding neighbor entry does not exist, creates the neighbor entry, triggers the Entry timer, and transits to Probe state. |
|
|
If the corresponding neighbor entry already exists, resets the Entry timer. |
|||
|
Flush packet |
Determines whether or not the local port is in Disable state. |
If yes, no process is performed. |
|
|
If not, removes the corresponding neighbor entry (if any). |
|||
|
Probe packet |
Retrieves the neighbor information. |
If the corresponding neighbor entry does not exist, creates the neighbor entry, transits to Probe state, and returns Echo packets. |
|
|
If the corresponding neighbor entry already exists, resets the Entry timer and returns Echo packets. |
|||
|
Echo packet |
Retrieves the neighbor information. |
If the corresponding neighbor entry does not exist, creates the neighbor entry, triggers the Entry timer, and transits to Probe state. |
|
|
The corresponding neighbor entry already exists |
If the neighbor information it carries conflicts with the corresponding locally maintained neighbor entry, drops the packet. |
||
|
Otherwise, sets the flag of the neighbor as two-way connected. In addition, if the flags of all the neighbors are two-way connected, the device transits from Probe state to Advertisement state and disables the Echo timer. |
|||
|
Disable packet |
Check to see if the local port is in Disable state. |
If yes, no process is performed. |
|
|
If not, the local port transits to Disable state. |
|||
|
RecoverProbe packet |
Check to see if the local port is in Disable or Advertisement state. |
If not, no process is performed. |
|
|
If yes, returns RecoverEcho packets. |
|||
|
RecoverEcho packet |
Check to see if the local port is in Disable state. |
If not, no process is performed. |
|
|
If yes, the local port transits to Active state if the neighbor information the packet carries is consistent with the local port information. |
|||
|
LinkDown packet |
Check to see if the local port operates in Enhanced mode. |
If not, no process is performed. |
|
|
If yes and the local port is not in Disable state, the local transits to Disable state. |
|||
3) If no echo packet is received from the neighbor, DLDP performs the following processing.
Table 1-6 Processing procedure when no echo packet is received from the neighbor
|
No echo packet received from the neighbor |
Processing procedure |
|
In normal mode, no echo packet is received when the Echo timer expires. |
DLDP transits to the Disable state, outputs log and tracking information, and sends Disable packets. In addition, depending on the user-defined DLDP down mode, DLDP shuts down the local port or prompts users to shut down the port, and removes the corresponding neighbor entry. |
|
In enhanced mode, no echo packet is received when the enhanced timer expires. |
VI. DLDP neighbor state
A DLDP neighbor can be in one of the three states described in Table 1-7. You can check the state of a DLDP neighbor by using the display dldp command.
Table 1-7 Description on DLDP neighbor states
|
DLDP neighbor state |
Description |
|
Unknown |
A neighbor is in this state when it is just detected and is being probed. No information indicating the state of the neighbor is received. A neighbor is in this state only when it is being probed. It transits to Two way state or Unidirectional state after the probe operation finishes. |
|
Two way |
A neighbor is in this state after it receives response from its peer. This state indicates the link is a two-way link. |
|
Unidirectional |
A neighbor is in this state when the link connecting it is detected to be a unidirectional link. After a device transits to this state, the corresponding neighbor entries maintained on other devices are removed. |
1.2 DLDP Configuration Task List
Complete the following tasks to configure DLDP:
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
Required |
|
|
Optional |
|
|
Optional |
|
|
Optional |
|
|
Optional |
|
|
Optional |
|
|
Optional |
Note that:
l DLDP works only when the link is up.
l To ensure unidirectional links can be detected, make sure these settings are the same on the both sides: DLDP state (enabled/disabled), the interval for sending Advertisement packets, authentication mode, and password.
l Keep the interval for sending Advertisement packets adequate to enable unidirectional links to be detected in time. If the interval is too long, unidirectional links cannot be terminated in time; if the interval is too short, network traffic may increase in vain.
l LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) events have no effect on DLDP. Links in an aggregation group are treated individually in DLDP.
l 802.1X has no effect on DLDP.
l When connecting two DLDP-enabled devices, make sure the DLDP version ID fields of the DLDP packets exchanged between the two devices are the same. Otherwise, DLDP may operate improperly.
1.2.1 Enabling DLDP
Follow these steps to enable DLDP:
|
Use the command… |
Remarks |
||
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enable DLDP globally |
dldp enable |
Required Globally disabled by default |
|
|
Enter Ethernet port view or port group view |
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Either of the two is required. The configuration performed in Ethernet port view applies to the current port only. The configuration performed in port group view applies to all the ports in the port group. |
|
Enter port group view |
port-group { aggregation agg-id | manual port-group-name } |
||
|
Enable DLDP |
dldp enable |
Required Disabled on a port by default You can perform this operation on an optical port or an electrical port. |
|
& Note:
DLDP takes effect only when it is enabled both globally and on a port.
1.2.2 Setting DLDP Mode
Follow these steps to set DLDP mode:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Set DLDP mode |
dldp work-mode { enhance | normal } |
Optional Normal by default |
1.2.3 Setting the Interval for Sending Advertisement Packets
You can set the interval for sending Advertisement packets to enable unidirectional links to be detected in time.
Follow these steps to set the interval for sending Advertisement packets:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Set the interval for sending Advertisement packets |
dldp interval time |
Optional 5 seconds by default The interval for sending Advertisement packets applies to all the DLDP-enabled ports. |
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l Set the interval for sending Advertisement packets to a value not longer than one-third of the STP convergence time. If the interval is too long, STP loops may occur before unidirectional links are torn down; if the interval is too short, network traffic may increase in vain due to excessive Advertisement packets.
l To enable DLDP to operate properly, make sure the intervals for sending Advertisement packets on both sides of a link are the same.
1.2.4 Setting the DelayDown Timer
On some ports, when the Tx line fails, the port goes down and then comes up again, causing optical signal jitters on the Rx line. When a port goes down due to a Tx failure, the device transits to the DelayDown state instead of the Inactive state to prevent the corresponding neighbor entries from being removed. In the same time, the device triggers the DelayDown timer. If the port goes up before the timer expires, the device restores the original state; if the port remains down when the timer expires, the devices transits to the Inactive state.
Follow these steps to set the DelayDown timer
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Set the DelayDown timer |
dldp delaydown-timer time |
Optional 1 second by default DelayDown timer setting applies to all the DLDP-enabled ports. |
1.2.5 Setting the Port Shutdown Mode
On detecting a unidirectional link, the ports can be shut down in one of the following two modes.
l Manual mode. This mode applies to networks with low performance, where normal links may be treated as unidirectional links. It protects service packet transmission against false unidirectional links. In this mode, DLDP only detects unidirectional links and generates log and traps. The operations to shut down unidirectional link ports are accomplished by the administrator.
l Auto mode. In this mode, when a unidirectional link is detected, DLDP transits to Disable state, generates log and traps, and set the port as DLDP Down.
Follow these steps to set port shutdown mode
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Set port shutdown mode |
dldp unidirectional-shutdown { auto | manual } |
Optional auto by default |
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l On a port with both remote OAM loopback and DLDP enabled, if the port shutdown mode is auto mode, the port will be shut down by DLDP when it receives a packet sent by itself, causing remote OAM loopback to operate improperly. To prevent this, you need to set the port shutdown mode to auto mode.
l If the device is busy, or the CPU utilization is high, normal links may be treated as unidirectional links. In this case, you can set the port shutdown mode to manual mode to eliminate the effects caused by false unidirectional link report.
1.2.6 Configuring DLDP Authentication
Follow these steps to configure DLDP authentication:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure DLDP authentication |
dldp authentication-mode { md5 md5-password | none | simple simple-password } |
Required none by default |
![]() Caution:
Caution:
To enable DLDP to operate properly, make sure the DLDP authentication modes and the passwords of the both sides of a link are the same.
1.2.7 Resetting DLDP State
After a unidirectional link is detected, DLDP shuts down the corresponding port. To enable the port to perform DLDP detect again, you can reset DLDP state for it. A port can be in different state after you reset DLDP state for it. That is, it can be in Inactive state (if the port is physically down) or in Active state (if the port is physically up) after you reset DLDP state for it.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l The configuration of resetting DLDP state performed in system view applies to all the ports shut down by DLDP.
l The configuration of resetting DLDP state performed in port view or port group view applies to the current port or all the ports in the port group shut down by DLDP.
I. Resetting DLDP State in System view
Follow these steps to reset DLDP in system view:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Reset DLDP state |
dldp reset |
Required |
II. Resetting DLDP State in Port view/Port Group View
Follow these steps to reset DLDP state in port view/port group view:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enter Ethernet port view/port group view |
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Either is required. The configuration performed in Ethernet port view applies to the current port only; the configuration performed in port group view applies to all the ports in the port group. |
|
Enter port group view |
port-group { aggregation agg-id | manual port-group-name } |
||
|
Reset DLDP state |
dldp reset |
Required |
|
1.3 Displaying and Maintaining DLDP
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display the DLDP configuration of a port |
display dldp [ interface-type interface-number ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display the statistics on DLDP packets passing through a port |
display dldp statistics [ interface-type interface-number ] |
Available in any view |
|
Clear the statistics on DLDP packets passing through a port |
reset dldp statistics [ interface-type interface-number ] |
Available in user view |
1.4 DLDP Configuration Example
1.4.1 DLDP Configuration Example
I. Network requirements
l Device A and Device B are connected through two fiber pairs, in which two fibers are cross-connected, as shown in Figure 1-4.
l It is desired that the unidirectional links can be disconnected on being detected; and the ports shut down by DLDP can be restored after the fiber connections are corrected.
II. Network diagram
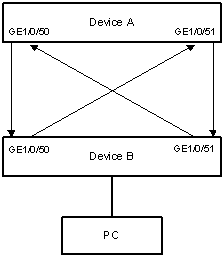
Figure 1-4 Network diagram for DLDP configuration
III. Configuration procedure
1) Configuration on Device A
# Enable DLDP on GigabitEthernet1/0/50 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/51.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/50
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/50] dldp enable
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/50] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/51
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/51] dldp enable
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/51] quit
# Set the interval for sending Advertisement packets to 6 seconds.
[DeviceA] dldp interval 6
# Set the DelayDown timer to 2 seconds.
[DeviceA] dldp delaydown-timer 2
# Set the DLDP mode as enhanced mode.
[DeviceA] dldp work-mode enhance
# Set the port shutdown mode as auto mode.
[DeviceA] dldp unidirectional-shutdown auto
# Enable DLDP globally.
[DeviceA] dldp enable
# Check the information about DLDP.
[DeviceA] display dldp
DLDP global status : enable
DLDP interval : 6s
DLDP work-mode : enhance
DLDP authentication-mode : none
DLDP unidirectional-shutdown : auto
DLDP delaydown-timer : 2s
The number of enabled ports is 2.
Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/50
DLDP port state : disable
DLDP link state : down
The neighbor number of the port is 0.
Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/51
DLDP port state : disable
DLDP link state : down
The neighbor number of the port is 0.
The output information indicates that both GigabitEthernet1/0/50 and GigabitEthernet1/0/51 are in Disable state and the links are down, which means unidirectional links are detected and the two ports are thus shut down.
# Reset DLDP state for the ports shut down by DLDP.
[DeviceA] dldp reset
2) Configuration on Device B
The configuration on Device B is the same as that on Device A and is thus omitted.
& Note:
If two fibers are cross-connected, all the four ports involved will be shut down by DLDP.
1.5 Troubleshooting
Symptom:
Two DLDP-enabled devices, Device A and Device B, are connected through two fiber pairs, in which two fibers are cross-connected. The unidirectional links cannot be detected; all the four ports involved are in Advertisement state.
Analysis:
The problem can be caused by the following.
l The intervals for sending Advertisement packets on Device A and Device B are not the same.
l DLDP authentication modes/passwords on Device A and Device B are not the same.
Solution:
Make sure the interval for sending Advertisement packets, the authentication mode, and the password on Device A and Device B are the same.

