- Released At: 02-04-2024
- Page Views:
- Downloads:
- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
Contents
Examining the installation site
Installing the switch in a 19-inch rack
Rack-mounting procedures at a glance
Attaching the mounting brackets, chassis rails, and grounding cable to the chassis
Attaching the slide rails to the rack
Mounting the switch in the rack
Grounding the switch by using a grounding strip
Installing and removing a fan tray
Installing and removing a power module
Connecting the power cord for an LSVM1DC300/LSVM1DC650 power module
Connecting the power cord for a PSR450-12AHD power module
Connecting the power cord for a PSR450-12D power module
Installing and removing an expansion module
Installing an expansion module
3 Accessing the switch for the first time
Setting up the configuration environment
Planning IRF fabric size and the installation site
Identifying the master switch and planning IRF member IDs
Planning IRF topology and connections
Identifying physical IRF ports on the member switches
Configuring basic IRF settings
Connecting the physical IRF ports
Accessing the IRF fabric to verify the configuration
Planning for setting up an M-LAG system
Determining device installation locations
Reserving physical ports for M-LAG connection
Planning the cable connection scheme
Configuring the M-LAG system settings
Connecting the M-LAG member switches
6 Maintenance and troubleshooting
No display on the configuration terminal
Garbled display on the configuration terminal
1 Preparing for installation
Table1-1 lists the S6800 switch series models and their product codes.
Table1-1 S6800 Series switch models
|
Model |
Product code |
|
S6800-32Q |
· LS-6800-32Q · LS-6800-32Q-H1 |
|
S6800-54QF |
· LS-6800-54QF · LS-6800-54QF-H1 · LS-6800-54QF-H3 · LS-6800-54QF-H5 |
|
S6800-54QT |
· LS-6800-54QT · LS-6800-54QT-H1 · LS-6800-54QT-H3 |
|
S6800-54HF |
LS-6800-54HF |
|
S6800-54HT |
LS-6800-54HT |
|
S6800-2C |
· LS-6800-2C · LS-6800-2C-H1 |
|
S6800-2C-FC |
LS-6800-2C-H1-FC |
|
S6800-4C |
· LS-6800-4C · LS-6800-4C-H1 |
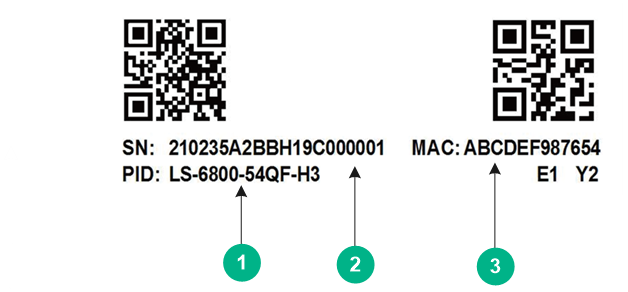
You can view the product code of a switch from the barcode product label (Figure1-1) or QR code product label (Figure1-2) on the rear panel or the top panel.
|
(1) Product serial number |
(2) Product code |
|
(1) Product code |
(2) Product serial number |
|
(3) MAC address |
|
Safety recommendations
To avoid any equipment damage or bodily injury caused by incorrect use, read the following safety recommendations before installation. Note that the recommendations do not cover every possible hazardous condition.
· Before cleaning the switch, remove all power cords from the switch. Do not clean the switch with wet cloth or liquid.
· Do not place the switch near water or in a damp environment. Prevent water or moisture from entering the switch chassis.
· Do not place the switch on an unstable case or desk. The switch might be severely damaged in case of a fall.
· Ensure good ventilation of the equipment room and keep the air inlet and outlet vents of the switch free of obstruction.
· Connect the yellow-green protection grounding cable before power-on.
· Make sure the operating voltage is in the required range.
· To avoid electrical shocks, do not open the chassis while the switch is operating or when the switch is just powered off.
· When replacing FRUs, including power modules, fan trays, and expansion modules, wear an ESD wrist strap to avoid damaging the units.
Examining the installation site
The S6800 switches must be used indoors.
Mount your switch in a rack and verify the following items:
· Adequate clearance is reserved at the air inlet and outlet vents for ventilation.
· The rack has a good ventilation system.
· Identify the hot aisle and cold aisle at the installation site, and make sure ambient air flows into the switch from the cold aisle and exhausts to the hot aisle.
· Identify the airflow designs of neighboring devices, and prevent hot air flowing out of the bottom device from entering the top device.
· The rack is sturdy enough to support the switch and its accessories.
· The rack is reliably grounded.
To ensure correct operation and long service life of your switch, install it in an environment that meets the requirements. For more information about installation site requirements, see indoor installation requirements of H3C device operation.
Temperature/humidity
Maintain appropriate temperature and humidity in the equipment room.
· Lasting high relative humidity can cause poor insulation, electricity leakage, mechanical property change of materials, and metal corrosion.
· Lasting low relative humidity can cause washer contraction and ESD and cause problems including loose screws and circuit failure.
· High temperature can accelerate the aging of insulation materials and significantly lower the reliability and lifespan of the switch.
For the temperature and humidity requirements of different switch models, see H3C S6800 Switch Series Hardware Information and Specifications.
Cleanliness
Dust buildup on the chassis might cause electrostatic adsorption and dust corrosion, resulting in poor contact of metal connectors and contact points. This might shorten the device's lifetime and even cause device failure in the worst case. Table1-2 describes the switch requirement for cleanliness.
Table1-2 Switch requirement for cleanliness
|
Substance |
Particle diameter |
Concentration limit |
|
Dust particles |
≥ 0.5 µm |
≤ 1.8 × 107 particles/m3 |
To maintain cleanliness in the equipment room, follow these guidelines:
· Keep the equipment room away from pollution sources. Do not smoke, eat, or drink in the equipment room.
· Use double-layer glass in windows and seal doors and windows with dust-proof rubber strips. Use screen doors and window screens for doors and windows open to the outside and make sure the external windows are air tight.
· Use dustproof materials for floors, walls, and ceilings and use wallpaper or matt paint that does not produce powders.
· Clean the equipment room regularly and clean the air filters of the rack each month.
· Wear ESD clothing and shoe covers before entering the equipment room, keep the ESD clothing and shoe covers clean, and change them frequently.
Corrosive gas limit
Corrosive gases can accelerate corrosion and aging of metal components. Make sure the corrosive gases do not exceed the concentration limits as shown in Table1-3.
Table1-3 Corrosive gas concentration limits
|
Gas |
Average concentration (mg/m3) |
Maximum concentration (mg/m3) |
|
SO2 |
0.3 |
1.0 |
|
H2S |
0.1 |
0.5 |
|
Cl2 |
0.1 |
0.3 |
|
HCI |
0.1 |
0.5 |
|
HF |
0.01 |
0.03 |
|
NH3 |
1.0 |
3.0 |
|
O3 |
0.05 |
0.1 |
|
NOX |
0.5 |
1.0 |
|
CAUTION: As a best practice, control the corrosive gas concentrations in the equipment room at their average values. Make sure the corrosive gas concentrations do not exceed 30 minutes per day at their maximum values. |
To control corrosive gases, use the following guidelines:
· As a best practice, do not build the equipment room in a place with a high concentration of corrosive gases.
· Make sure the equipment room is not connected to sewer, vertical shaft, or septic tank pipelines and keep it far away from these pipelines. The air inlet of the equipment room must be away from such pollution sources.
· Use environmentally friendly materials to decorate the equipment room. Avoid using organic materials that contains harmful gases, such as sulfur or chlorine-containing insulation cottons, rubber mats, sound-proof cottons, and avoid using plasterboards with high sulfur concentration.
· Place fuel (diesel or gasoline) engines separately. Do not place them in the same equipment room with the device. Make sure the exhausted air of the engines will not flow into the equipment room or towards the air inlet of the air conditioners.
· Place batteries separately. Do not place them in the same room with the device.
· Employ a professional company to monitor and control corrosive gases in the equipment room regularly.
EMI
All electromagnetic interference (EMI) sources, from outside or inside of the switch and application system, adversely affect the switch in the following ways:
· A conduction pattern of capacitance coupling.
· Inductance coupling.
· Electromagnetic wave radiation.
· Common impedance (including the grounding system) coupling.
To prevent EMI, use the following guidelines:
· If AC power is used, use a single-phase three-wire power receptacle with protection earth (PE) to filter interference from the power grid.
· Keep the switch far away from radio transmitting stations, radar stations, and high-frequency devices.
· Use electromagnetic shielding, for example, shielded interface cables, when necessary.
· To prevent signal ports from getting damaged by overvoltage or overcurrent caused by lightning strikes, route interface cables only indoors.
Laser safety
|
WARNING! Disconnected optical fibers or transceiver modules might emit invisible laser light. Do not stare into beams or view directly with optical instruments when the switch is operating. |
The S6800 switches are Class 1 laser devices.
Installation tools
No installation tools are provided with the switch. Prepare the following tools yourself:
· Phillips screwdriver.
· ESD wrist strap.
· Marker.
2 Installing the switch
|
CAUTION: Keep the tamper-proof seal on a mounting screw on the chassis cover intact, and if you want to open the chassis, contact H3C for permission. Otherwise, H3C shall not be liable for any consequence caused thereby. |
Figure2-1 Hardware installation flow
Installing the switch in a 19-inch rack
Installation accessories
Only the S6800-4C provides cable management brackets, which are attached to the mounting brackets when shipped, as shown in Table2-2.
Table2-2 Installation accessories
|
Switch model |
Mounting brackets |
Rack mounting rail kit |
|
S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3 and LS-6800-54QF-H5) |
1U high, one pair (provided). See Figure2-3. |
· 1U high, including one pair of chassis rails and one pair of long slide rails (provided). See Figure2-8. · 1U high, including one pair of chassis rails and one pair of super-short slide rails (optional). See Figure2-6. |
|
S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT–H3) |
1U high, one pair (provided). See Figure2-3. |
· 1U high, including one pair of chassis rails and one pair of long slide rails (provided). See Figure2-8. · 1U high, including one pair of chassis rails and one pair of slide rails (optional). See Figure2-7. |
|
S6800-32Q |
1U high, one pair (provided). See Figure2-2. |
1U high, including one pair of chassis rails and one pair of slide rails (provided). See Figure2-7. |
|
S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT and LS-6800-54QT-H1) |
||
|
S6800-54HT |
||
|
S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF and LS-6800-54QF-H1) |
1U high, one pair (provided). See Figure2-2. |
· 1U high, including one pair of chassis rails and one pair of long slide rails (provided). See Figure2-8. · 1U high, including one pair of chassis rails and one pair of slide rails (optional). See Figure2-7. |
|
S6800-54HF |
||
|
S6800-2C |
1U high, one pair (provided). See Figure2-4. |
1U high, including one pair of chassis rails and one pair of slide rails (provided). See Figure2-6. |
|
S6800-2C-FC |
||
|
S6800-4C |
2U high, one pair (provided). See Figure2-5. |
2U high, including one pair of chassis rails and one pair of slide rails (provided). See Figure2-9. |
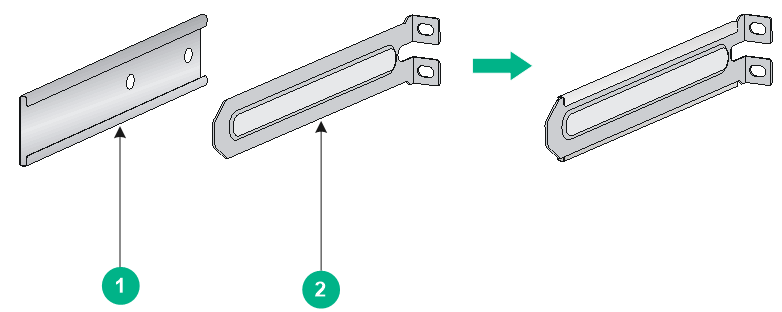
Figure2-2 Mounting brackets for the S6800-32Q, S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT and LS-6800-54QT-H1), S6800-54HF, S6800-54HT, and S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF and LS-6800-54QF-H1) switches
Figure2-3 Mounting brackets for the S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3), S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H5) and S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT-H3) switches
Figure2-4 Mounting brackets for the S6800-2C and S6800-2C-FC switches
Figure2-5 Mounting brackets for the S6800-4C switch
|
(1) Cable management bracket |
(2) Mounting bracket |
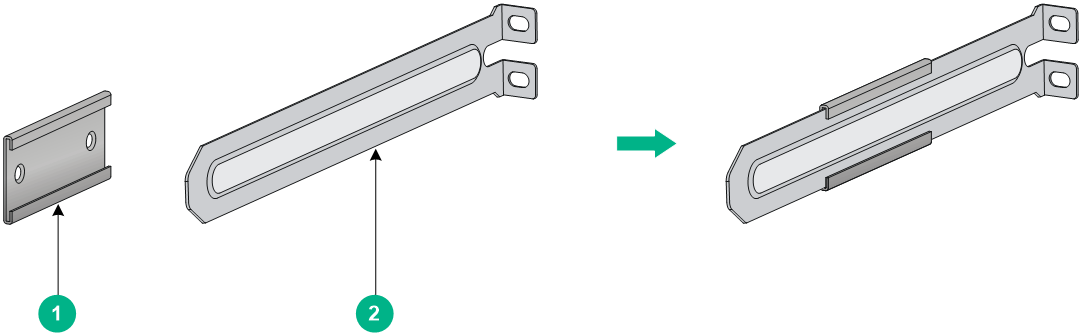
Figure2-6 1U chassis rail and super-short slide rail
|
(1) Chassis rail |
(2) Super-short slide rail |
Figure2-7 1U chassis rail and slide rail
|
(1) Chassis rail |
(2) Slide rail |
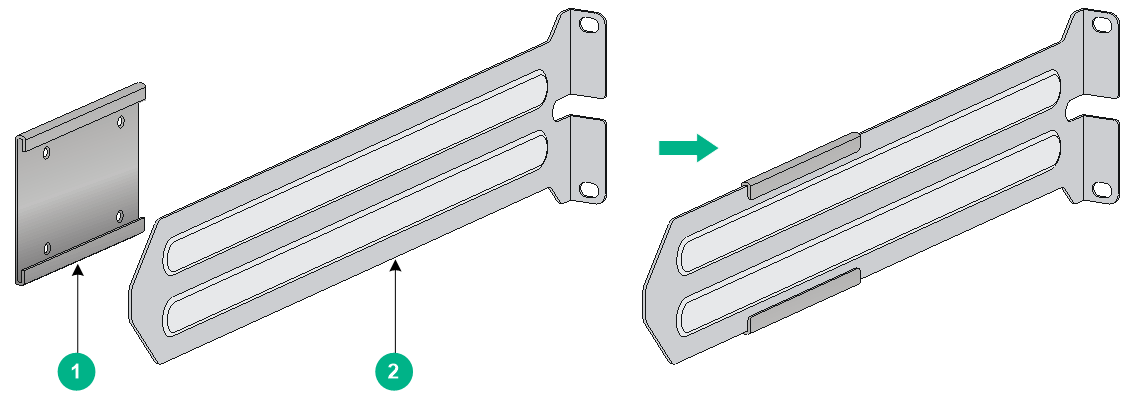
Figure2-8 1U chassis rail and long slide rail
|
(2) Long slide rail |
Figure2-9 2U chassis rail and slide rail
|
(1) Chassis rail |
(2) Slide rail |
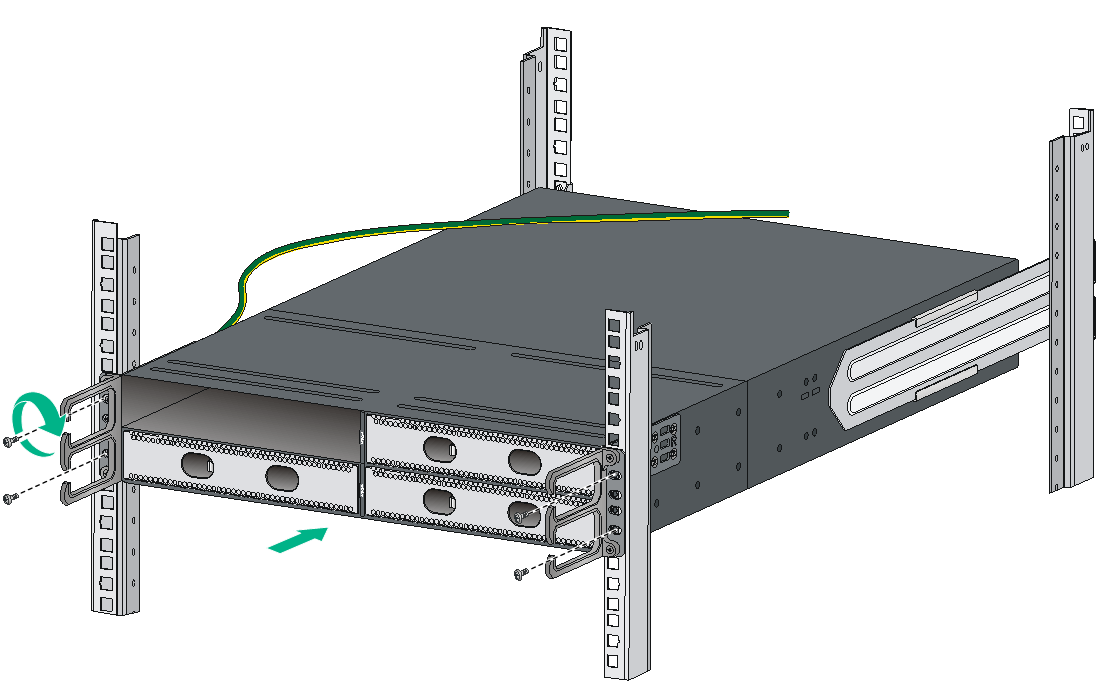
Rack-mounting procedures at a glance
Figure2-10 Rack-mounting procedure
|
|
NOTE: If a rack shelf is available, you can put the switch on the rack shelf, slide the switch to an appropriate location, and attach the switch to the rack with the mounting brackets. |
Follow these guidelines when you install the switch in a 19-inch rack:
· The rack must meet the requirements described in Table2-2.
· To secure the switch to the rack, you must install not only mounting brackets, but also chassis rails and slide rails.
|
Switch model |
Installation method |
Chassis dimensions |
Distance between the front and rear rack posts |
Rack requirements |
|
S6800-32Q |
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and slide rails |
· Height—43.6 mm (1.72 in)/1 RU · Width—440 mm (17.32 in) · Depth—688 mm (27.09 in) ¡ 28 mm (1.10 in) for the power module/fan tray handle ¡ 660 mm (25.98 in) for the chassis |
405 to 834 mm (15.94 to 32.83 in) |
· A minimum of 1.0 m (3.28 ft) in depth (recommended) · A minimum of 130 mm (5.12 in) between the front rack post and the front door · A minimum of 750 mm (29.53 in) between the front rack post and the rear door |
|
S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF and LS-6800-54QF-H1) |
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and long slide rails |
· Height—43.6 mm (1.72 in)/1 RU · Width—440 mm (17.32 in) · Depth—488 mm (19.21 in) ¡ 28 mm (1.10 in) for the power module/fan tray handle ¡ 460 mm (18.11 in) for the chassis |
621 to 854 mm (24.45 to 33.62 in) |
· A minimum of 800 mm (31.50 in) in depth (recommended) · A minimum of 130 mm (5.12 in) between the front rack post and the front door · A minimum of 550 mm (21.65 in) between the front rack post and the rear door |
|
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and slide rails |
401 to 634 mm (15.79 to 24.96 in) |
|||
|
S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3 and LS-6800-54QF-H5) |
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and long slide rails |
· Height—44 mm (1.73 in)/1 RU · Width—440 mm (17.32 in) · Depth—426 mm (16.77 in) ¡ 26 mm (1.02 in) for the power module/fan tray handle ¡ 400 mm (15.75 in) for the chassis |
621 to 793 mm (24.45 to 31.22 in) |
· A minimum of 600 mm (23.62 in) in depth (recommended) · A minimum of 130 mm (5.12 in) between the front rack post and the front door · A minimum of 470 mm (18.50 in) between the front rack post and the rear door |
|
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and super-short slide rails (narrow-spacing installation) |
330 to 505 mm (12.99 to 19.88 in) |
|||
|
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and super-short slide rails (wide-spacing installation) |
438 to 632 mm (17.24 to 24.88 in) |
|||
|
S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT and LS-6800-54QT-H1) |
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and slide rails |
· Height—43.6 mm (1.72 in)/1 RU · Width—440 mm (17.32 in) · Depth—688 mm (27.09 in) ¡ 28 mm (1.10 in) for the power module/fan tray handle ¡ 660 mm (25.98 in) for the chassis |
405 to 834 mm (15.94 to 32.83 in) |
· A minimum of 1.0 m (3.28 ft) in depth (recommended) · A minimum of 130 mm (5.12 in) between the front rack post and the front door · A minimum of 750 mm (29.53 in) between the front rack post and the rear door |
|
S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT-H3) |
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and long slide rails |
· Height—44 mm (1.73 in)/1 RU · Width—440 mm (17.32 in) · Depth—486 mm (19.13 in) ¡ 26 mm (1.02 in) for the power module/fan tray handle ¡ 460 mm (18.11 in) for the chassis |
621 to 854 mm (24.45 to 33.62 in) |
· A minimum of 800 mm (31.50 in) in depth (recommended) · A minimum of 130 mm (5.12 in) between the front rack post and the front door · A minimum of 550 mm (21.65 in) between the front rack post and the rear door |
|
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and slide rails |
401 to 634 mm (15.79 to 24.96 in) |
|||
|
S6800-54HF |
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and long slide rails |
· Height—43.6 mm (1.72 in)/1 RU · Width—440 mm (17.32 in) · Depth—488 mm (19.21 in) ¡ 28 mm (1.10 in) for the power module/fan tray handle ¡ 460 mm (18.11 in) for the chassis |
621 to 854 mm (24.45 to 33.62 in) |
· A minimum of 800 mm (31.50 in) in depth (recommended) · A minimum of 130 mm (5.12 in) between the front rack post and the front door · A minimum of 550 mm (21.65 in) between the front rack post and the rear door |
|
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and slide rails |
401 to 634 mm (15.79 to 24.96 in) |
|||
|
S6800-54HT |
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and slide rails |
· Height—43.6 mm (1.72 in)/1 RU · Width—440 mm (17.32 in) · Depth—688 mm (27.09 in) ¡ 28 mm (1.10 in) for the power module/fan tray handle ¡ 660 mm (25.98 in) for the chassis |
405 to 834 mm (15.94 to 32.83 in) |
· A minimum of 1.0 m (3.28 ft) in depth (recommended) · A minimum of 130 mm (5.12 in) between the front rack post and the front door · A minimum of 750 mm (29.53 in) between the front rack post and the rear door |
|
S6800-2C |
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and slide rails |
· Height—44.2 mm (1.74 in)/1 RU · Width—440 mm (17.32 in) · Depth—688 mm (27.09 in) ¡ 28 mm (1.10 in) for the power module/fan tray handle ¡ 660 mm (25.98 in) for the chassis |
520 to 769 mm (20.47 to 30.28 in) |
|
|
S6800-2C-FC |
Using mounting brackets, chassis rails, and slide rails |
· Height—44.2 mm (1.74 in)/1 RU · Width—440 mm (17.32 in) · Depth—688 mm (27.09 in) ¡ 28 mm (1.10 in) for the power module/fan tray handle ¡ 660 mm (25.98 in) for the chassis |
520 to 769 mm (20.47 to 30.28 in) |
|
|
S6800-4C |
Using mounting brackets (installed at the port side), chassis rails, and slide rails |
· Height—88.1 mm (3.47 in)/2 RU · Width—440 mm (17.32 in) · Depth—776 mm (30.55 in) ¡ 26 mm (1.02 in) for the power module/fan tray handle ¡ 660 mm (25.98 in) for the chassis ¡ 90 mm (3.54 in) for the mounting brackets |
518 to 858 mm (20.39 to 33.78 in) |
|
|
Using mounting brackets (installed at the power module side), chassis rails, and slide rails |
· Height—88.1 mm (3.47 in)/2 RU · Width—440 mm (17.32 in) · Depth—750 mm (29.53 in) ¡ 660 mm (25.98 in) for the chassis ¡ 90 mm (3.54 in) for the mounting brackets |
518 to 858 mm (20.39 to 33.78 in) |
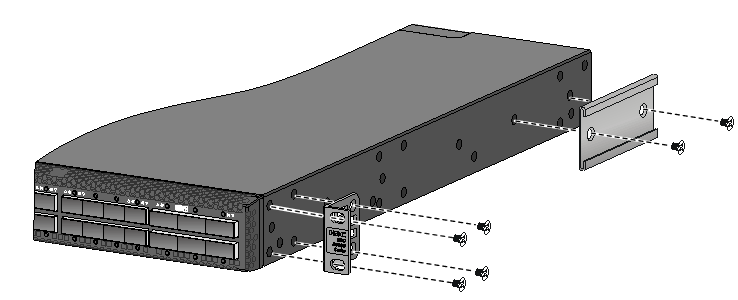
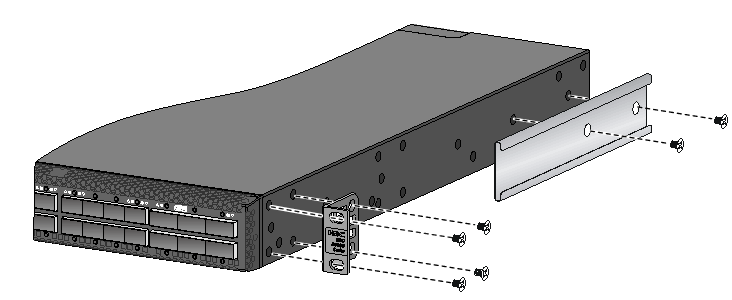
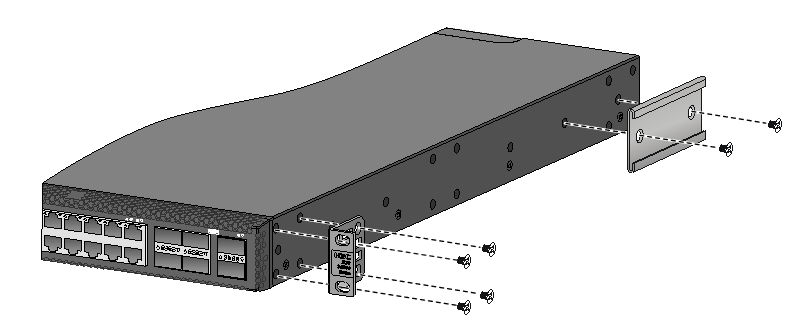
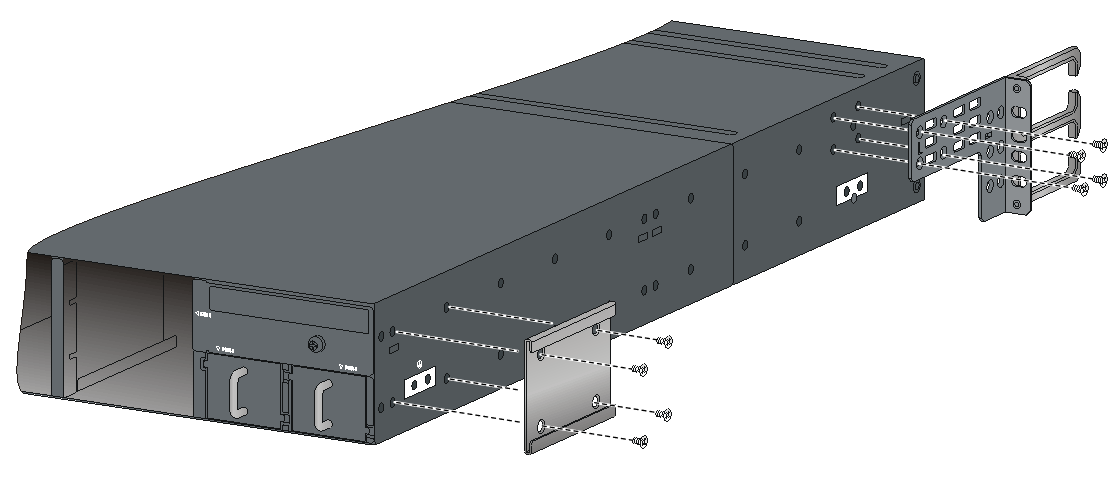
Attaching the mounting brackets, chassis rails, and grounding cable to the chassis
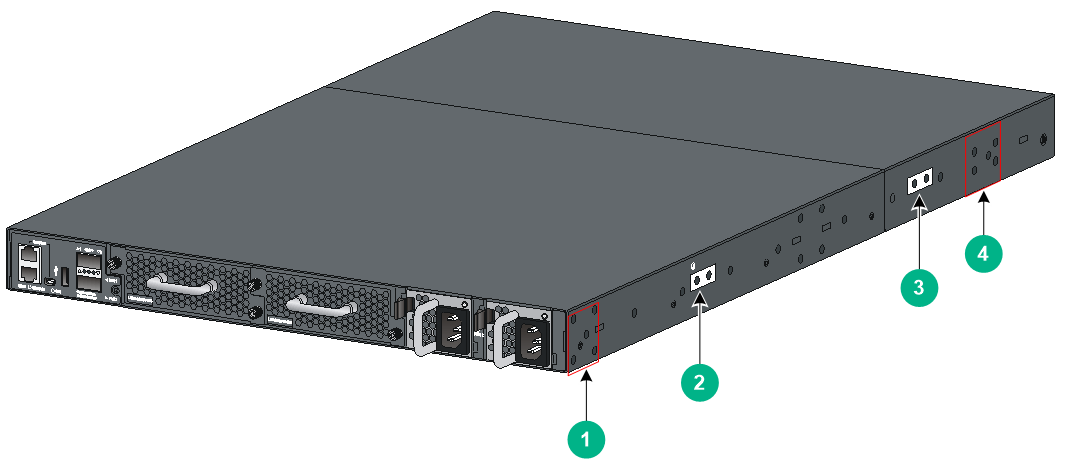
The switch has one mounting position near the network ports and one mounting position near the power modules for mounting brackets.
The S6800-32Q, S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF and LS-6800-54QF-H1), S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT and LS-6800-54QT-H1), and S6800-4C switches each provide three grounding points: primary grounding point (with a grounding sign), auxiliary grounding point 1, and auxiliary grounding point 2. The S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3 and LS-6800-54QF-H5), S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT-H3), S6800-54HF, S6800-54HT, S6800-2C, and S6800-2C-FC switches each provide two grounding points: primary grounding point (with a grounding sign) and auxiliary grounding point 1.
Figure2-11 Mounting and grounding positions on the S6800-32Q switch
|
(1) Auxiliary grounding point 2 |
(2) Power module-side mounting position |
|
(3) Primary grounding point |
(4) Auxiliary grounding point 1 |
|
(5) Port-side mounting position |
|
Figure2-12 Mounting and grounding positions on the S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF and LS-6800-54QF-H1) switch
|
(1) Auxiliary grounding point 2 |
(2) Power module-side mounting position |
|
(3) Primary grounding point |
(4) Auxiliary grounding point 1 |
|
(5) Port-side mounting position |
|
|
(1) Power module-side mounting position |
(2) Primary grounding point |
|
(3) Auxiliary grounding point 1 |
(4) Port-side mounting position |
Figure2-14 Mounting and grounding positions on the S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT-H3) switch
|
(1) Power module-side mounting position |
(2) Primary grounding point |
|
(3) Auxiliary grounding point 1 |
(4) Port-side mounting position |
Figure2-15 Mounting and grounding positions on the S6800-2C and S6800-2C-FC switches
|
(1) Power module-side mounting position |
(2) Primary grounding point |
|
(3) Auxiliary grounding point 1 |
(4) Port-side mounting position |
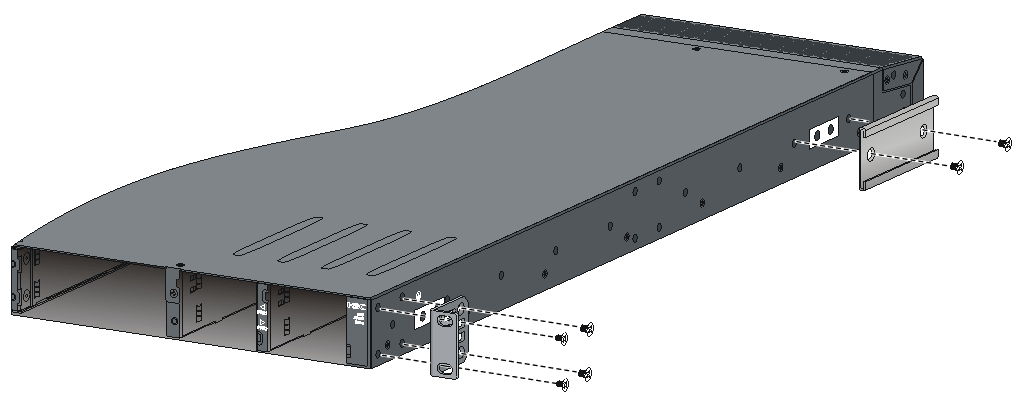
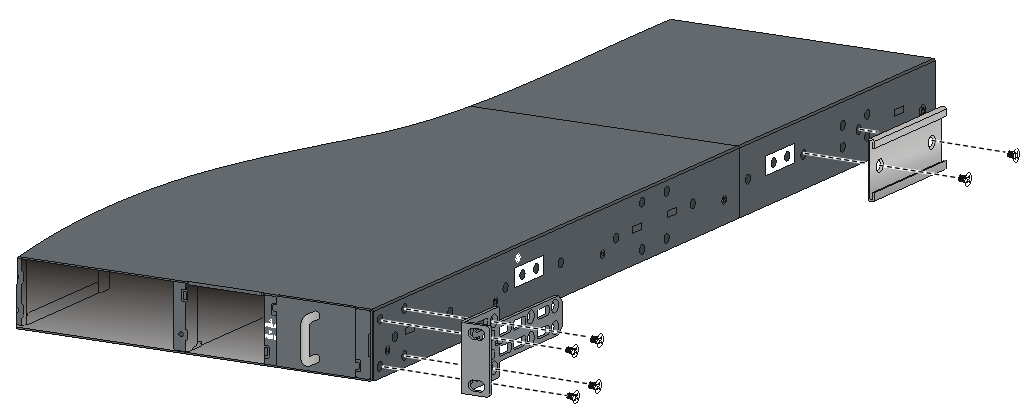
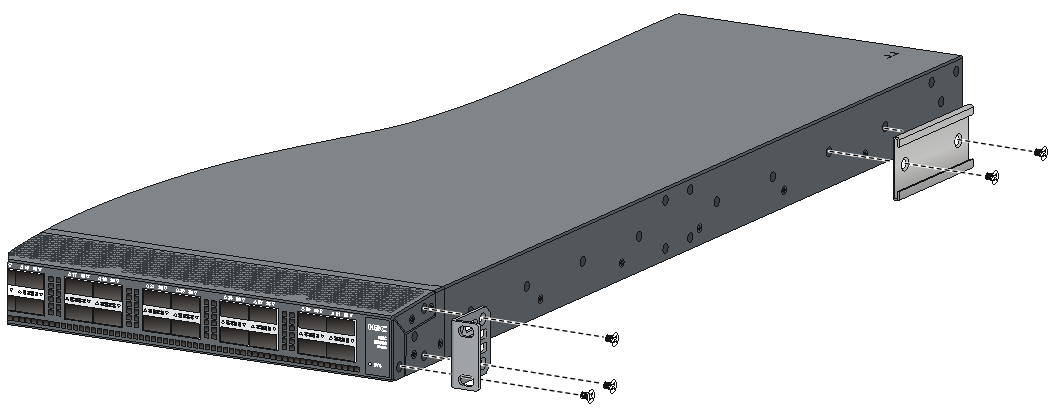
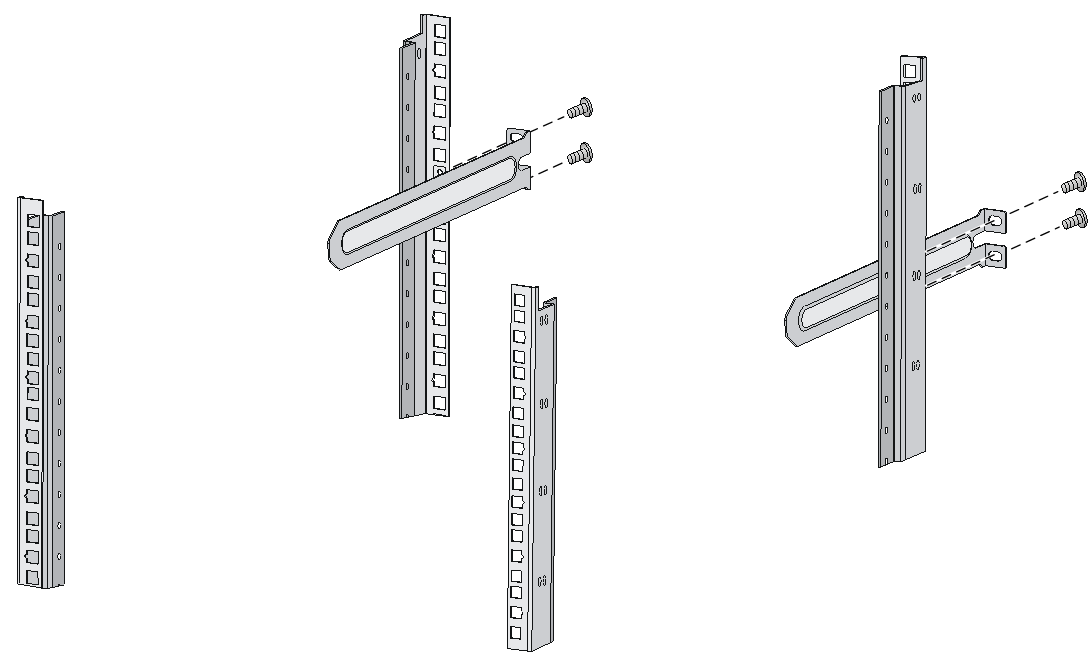
Attaching the mounting brackets and chassis rails to the chassis
The mounting bracket and chassis rail installation procedures are the same for the S6800-32Q, S6800-54QF, S6800-54QT, S6800-54HF, and S6800-54HT switches. For the S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3), S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H5) and S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT-H3), four screws are required for install a mounting bracket at the port side. For the other models, three screws are required.
For an S6800-2C, S6800-2C-FC, or S6800-4C switch, use the four screw holes nearest to the port side and nearest to the power module side to install the mounting brackets at the port side and at the power module side, respectively.
To attach the mounting brackets and chassis rails to the chassis:
1. Align the mounting brackets with the screw holes in the chassis. Use M4 screws (provided) to attach the mounting brackets to the chassis.
¡ To install the mounting brackets at the power module side, see Figure2-16, Figure2-17, and Figure2-18.
¡ To install the mounting brackets at the port side, see Figure2-19, Figure2-20, Figure2-21, Figure2-22, Figure2-23, Figure2-24, and Figure2-25.
2. Align the chassis rails with the rail mounting holes in the chassis:
¡ If the mounting brackets are in the power module-side mounting position, align the chassis rails with the screw holes at the front of the side panels (see Figure2-16, Figure2-17, and Figure2-18).
¡ If the mounting brackets are in the port-side mounting position, align the chassis rails with the screw holes at the rear of the side panels (see Figure2-19, Figure2-20, Figure2-21, Figure2-22, Figure2-23, Figure2-24, and Figure2-25).
3. Use M4 screws (provided) to attach the chassis rails to the chassis. As a best practice, use a torque of 12 kgf-cm (1.18 Nm) to fasten the M4 screws.
Secure the mounting brackets and chassis rails to both sides of the chassis in the same way.
To use super-short slide rails for the S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3 and LS-6800-54QF-H5), you can install the chassis rails through narrow-spacing or wide-spacing installation, depending on the distance between the front and rear rack posts, as shown in Figure2-21 and Figure2-22.
Figure2-16 Attaching the mounting brackets and chassis rails to an S6800-32Q switch (power module-side mounting position for the mounting brackets)
Figure2-20 Attaching the mounting brackets and chassis rails to an S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3 and LS-6800-54QF-H5) switch (port-side mounting position for the mounting brackets)
Figure2-21 Attaching the mounting brackets and chassis rails (narrow-spacing installation) to an S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3 and LS-6800-54QF-H5) switch (port-side mounting position for the mounting brackets)
Connecting the grounding cable to the chassis
|
CAUTION: · If the grounding cable length or terminal type cannot meet your requirement, make an applicable grounding cable or contact H3C Support. · If you use a grounding point on the side panel, connect the grounding cable to the grounding point before you mount the switch in the rack. |
The S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3 and LS-6800-54QF-H5), S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT-H3), S6800-54HF, S6800-54HT, S6800-2C, and S6800-2C-FC switches each provide two grounding points on the left side panel: primary grounding point and auxiliary grounding point 1. Use M5 grounding screws to attach the grounding cable that has a single-hole grounding lug or two-hole grounding lug to the switch. Choose the grounding point according to the mounting bracket installation positions. If you install the mounting brackets at the port side, use the grounding point near the ports. If you install the mounting brackets at the power module side, use the grounding point near the power modules.
The S6800-32Q, S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF and LS-6800-54QF-H1), S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT and LS-6800-54QT-H1), and S6800-4C switches each provide three grounding points. The primary grounding point and auxiliary grounding point 1 are on the side panel, and auxiliary grounding point 2 is on the rear panel. If you use a grounding cable that has a two-hole grounding lug, connect it to the primary grounding point or auxiliary grounding point 1. If you use a grounding cable that has a single-hole grounding lug, connect it to auxiliary grounding point 2. Use M5 grounding screws to attach the grounding cable to the switch. Choose the grounding point according to the mounting bracket installation positions.
This section uses the primary grounding point on the S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3) switch as an example.
To connect the grounding cable to a grounding point:
1. Unpack the grounding cable and grounding screws.
2. Align the single-hole grounding lug or two-hole grounding lug at one end of the cable with the grounding holes of the grounding point, insert the grounding screws into the holes, and tighten the screws with a screwdriver, as shown in Figure2-26 and Figure2-27. As a best practice, use a torque of 30 kgf-cm (2.94 Nm) to fasten the screws.
Attaching the slide rails to the rack
The procedures are the same for attaching 1U and 2U slide rails to the rack. This section uses the 1U slide rails as an example.
To attach the slide rails to the rack:
1. Identify the planned slide rail installation position in the rack.
Plan a 1U rack space for installation of 1U slide rails and a 2U rack space for installation of 2U slide rails. Figure2-28 shows a standard 1U rack space.
In a standard 1U rack space, there are three installation holes, one in the middle for auxiliary installation and one at either end for standard installation. The spacing between two adjacent standard installation holes is slightly smaller than the distance between a standard installation hole and the middle, auxiliary installation hole.
Figure2-28 1U rack space
2. Install cage nuts (user-supplied) in the mounting holes in the rack posts.
3. Align the screw holes in one slide rail with the cage nuts in the rack post on one side, and use M6 screws (user-supplied) to attach the slide rail to the rack, as shown in Figure2-29. As a best practice, use a torque of 30 kgf-cm (2.94 Nm) to fasten the M6 screws.
4. Repeat the preceding steps to attach the other slide rail to the rack post on the other side.
Keep the two slide rails at the same height so the slide rails can attach into the chassis rails.
Figure2-29 Installing the 1U slide rails
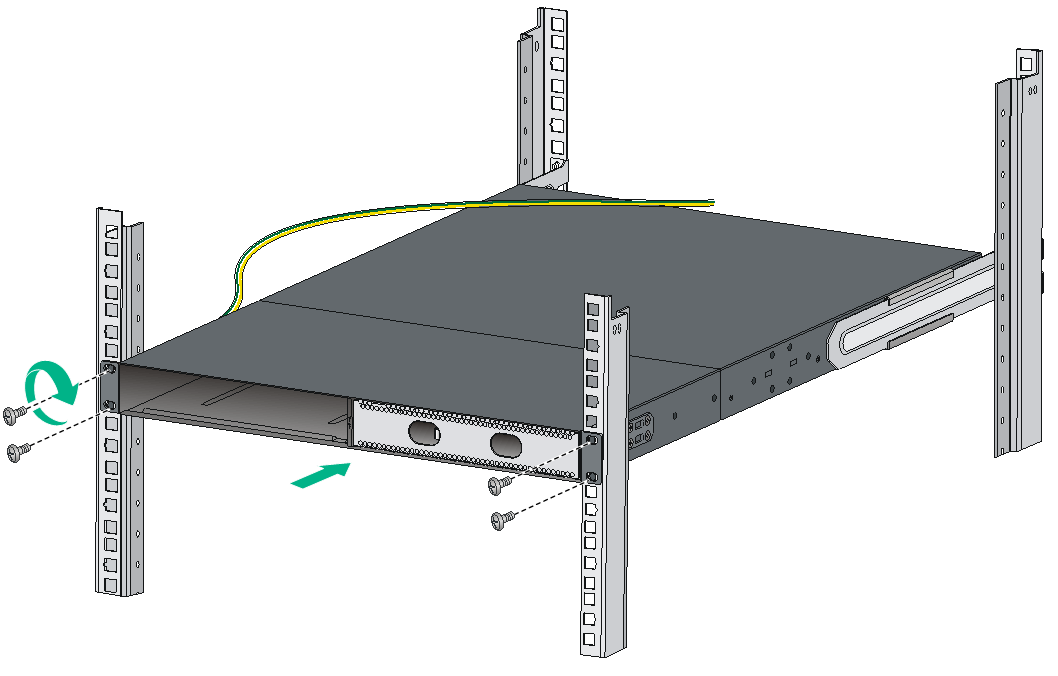
Mounting the switch in the rack
This task requires two people.
To mount the switch in the rack:
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Verify that the mounting brackets and chassis rails have been securely attached to the switch chassis.
3. Verify that the slide rails have been correctly attached to the rear rack posts.
4. Install cage nuts (user-supplied) to the front rack posts and make sure they are at the same level as the slide rails.
5. One person performs the following operations:
a. Supporting the bottom of the switch, aligns the chassis rails with the slide rails on the rack posts.
b. Pushes the switch slowly to slide the chassis rails along the slide rails until the mounting brackets are flush with the rack posts.
6. The other person uses M6 screws (user-supplied) to attach the mounting brackets to the rack. As a best practice, use a torque of 30 kgf-cm (2.94 Nm) to fasten the M6 screws.
If the slide rails or long slide rails are used, make sure the front ends of the slide rails or long slide rails reach out of the chassis rails. If the super-short slide rails are used, make sure the super-short slide rails slide a minimum length of 90 mm (3.54 in) into the chassis rails.
The rack-mounting procedures are the same for the S6800-32Q, S6800-54QF, S6800-54QT, S6800-54HF, S6800-54HT, S6800-2C-FC, and S6800-2C switches. The following figures use the S6800-2C switch as an example.
Figure2-31 Mounting the S6800-2C switch in the rack (port-side mounting position for the mounting brackets)
|
|
NOTE: To rack-mount the S6800-4C switch by using 2U high mounting brackets and slide rails, use two screws and two cage nuts to attach each mounting bracket to the rack. Determine the screw installation positions based on the distances between the square holes on the rack posts. The screw installation positions in Figure2-32 and Figure2-33 are for illustration only. |
Grounding the switch by using a grounding strip
|
CAUTION: · Correctly connecting the grounding cable is crucial to lightning protection and EMI protection. · Do not connect the grounding cable to a fire main or lightning rod. · To guarantee the grounding effect and avoid switch damage, use the grounding cable provided with the switch to connect the switch to a grounding strip in the equipment room. |
The power input end of the switch has a noise filter, whose central ground is directly connected to the chassis to form the chassis ground (commonly known as PGND). You must securely connect this chassis ground to the earth so the faradism and leakage electricity can be safely released to the earth to minimize EMI susceptibility of the switch.
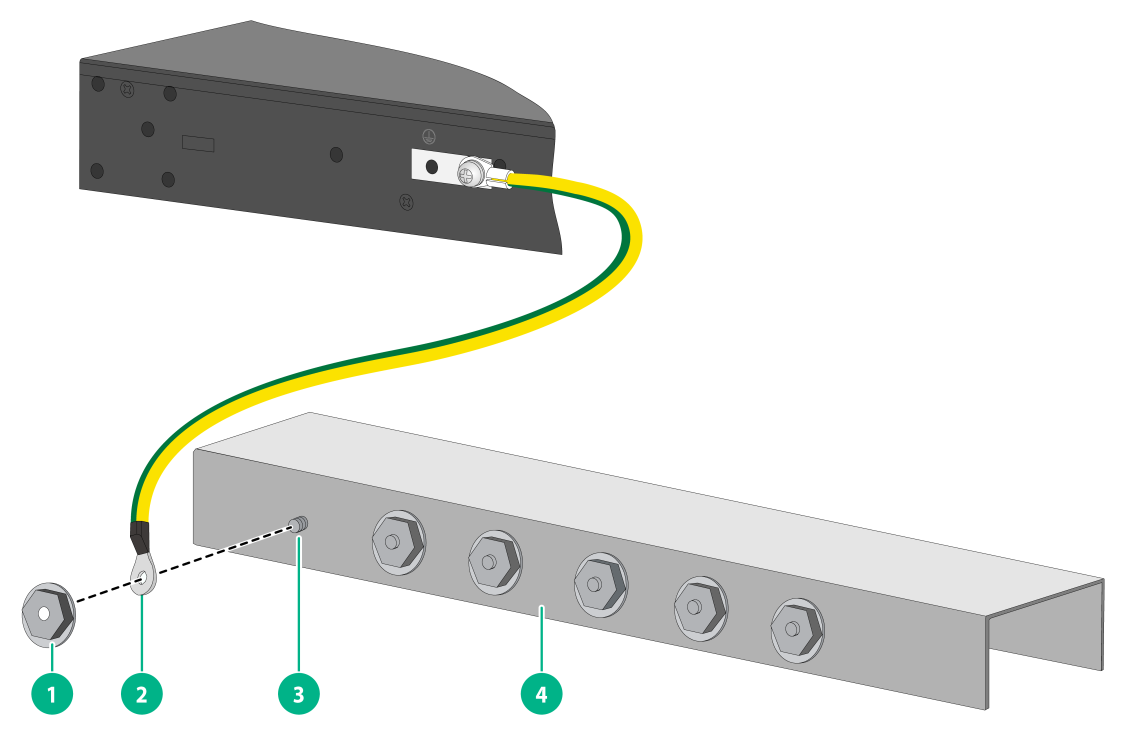
To ground the switch by using a grounding strip:
1. Select a grounding point on the switch as required.
2. Attach the single-hole grounding lug at one end of the grounding cable to the grounding point on the switch chassis. For more information, see "Connecting the grounding cable to the chassis."
3. Remove the hex nut of a grounding post on the grounding strip.
4. Attach the ring terminal at the other end of the grounding cable to the grounding post on the grounding strip, and secure the ring terminal to the grounding post with the hex nut.
Figure2-34 Connecting the grounding cable to a grounding strip
|
(1) Hex nut |
(2) Ring terminal |
|
(3) Grounding post |
(4) Grounding strip |
Installing and removing a fan tray
Follow these guidelines when you install or remove a fan tray:
· You must install fan trays of the same model on the switch.
· An S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT-H3) switch supports 4+1 fan tray redundancy. The switch can operate correctly with four fan trays. In the remaining fan tray slot, you can install a fan tray for 4+1 redundancy or a filler panel. On the other switch models, you must install a fan tray in each fan tray slot.
· Make sure all slots have a module or filler panel installed when the switch is operating.
· For an S6800-32Q, S6800-2C, or S6800-2C-FC switch, if both fan trays fail during the switch operation, replace the fan trays within two minutes one by one.
· For an S6800-4C, S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF), S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H1), S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT), S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT-H1), S6800-54HF, or S6800-54HT switch, if both fan trays fail during the switch operation, replace the fan trays within one minute.
· For an S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3), S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H5), or S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT-H3) switch, if more than one fan tray fail during the switch operation, replace the faulty fan trays one by one and finish replacing a fan tray within three minutes.
Installing a fan tray
|
CAUTION: To prevent damage to the fan tray or the connectors on the backplane, insert the fan tray gently. If you encounter a hard resistance while inserting the fan tray, pull out the fan tray and insert it again. |
Select appropriate fan trays as needed. For the optional fan trays and their specifications, see H3C S6800 Switch Series Hardware Information and Specifications.
Installing an LSWM1FANSC/LSWM1FANSCB/LSWM1HFANSC/LSWM1HFANSCB fan tray
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Unpack the fan tray and verify that the fan tray model is correct.
3. Grasp the handle of the fan tray with one hand and support the fan tray bottom with the other, and slide the fan tray along the guide rails into the slot until the fan tray seats in the slot and has a firm contact with the backplane (see callout 1 in Figure2-35).
4. Fasten the captive screw on the fan tray with a Phillips screwdriver until the fan tray is securely attached in the chassis (see callout 2 in Figure2-35).
If the captive screw cannot be tightly fastened, verify the installation of the fan tray.
Figure2-35 Installing an LSWM1HFANSC fan tray for an S6800-32Q switch
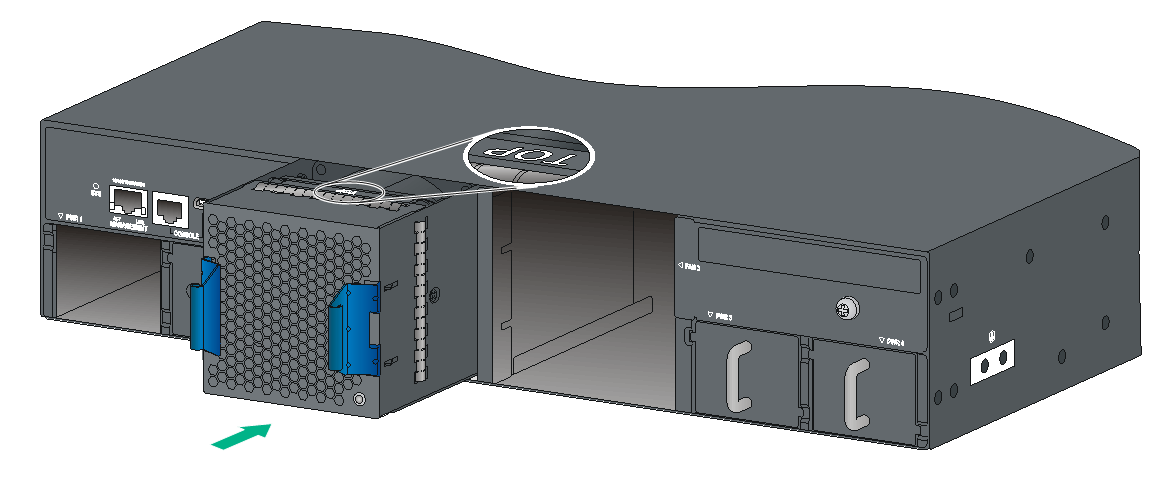
Installing an LSWM1BFANSC, LSWM1BFANSC-SN, LSWM1BFANSCB, or LSWM1BFANSCB-SN fan tray
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Unpack the fan tray and verify that the fan tray model is correct.
3. Orient the fan tray with the "TOP" mark on the top. Grasp the handle of the fan tray with one hand and support the fan tray bottom with the other, and slide the fan tray along the guide rails into the slot until the fan tray is fully seated in the slot and has a firm contact with the backplane.
Figure2-36 Installing an LSWM1BFANSC fan tray
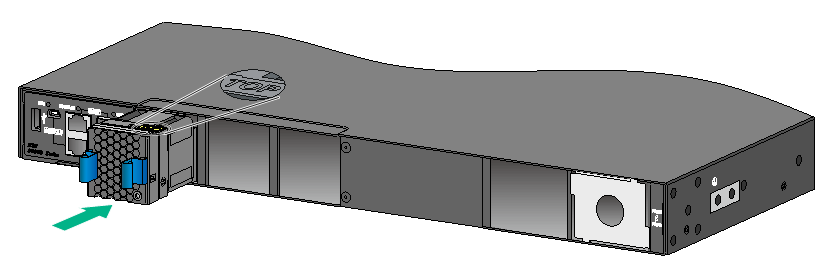
Installing an LSPM1FANSA, LSPM1FANSA-SN, LSPM1FANSB, or LSPM1FANSB-SN fan tray
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Unpack the fan tray and verify that the fan tray model is correct.
3. Orient the fan tray with the "TOP" mark on the top. Grasp the handle of the fan tray and slide the fan tray along the guide rails into the slot until the fan tray is fully seated in the slot and has a firm contact with the backplane.
Figure2-37 Installing an LSPM1FANSA fan tray
Removing a fan tray
|
WARNING! · Ensure electricity safety and never touch the rotating fans when you hot-swap a fan tray. · To prevent an unbalanced fan from causing loud noise, do not touch the fans, even if they are not rotating. · Do not touch any bare wires and terminals on a fan tray. · Do not place a fan tray in a moist location or let liquid flow into it. · Contact H3C Support if the circuits or components on a fan tray are faulty. Do not remove any fan tray components. |
Removing an LSWM1FANSC/LSWM1FANSCB/LSWM1HFANSC/LSWM1HFANSCB fan tray
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Loosen the captive screw of the fan tray with a Phillips screwdriver until it is fully disengaged from the switch chassis.
3. Grasp the handle of the fan tray with one hand and pull the fan tray part way out of the slot. Support the fan tray bottom with the other hand, and pull the fan tray slowly along the guide rails out of the slot.
4. Place the removed fan tray in an antistatic bag.
Removing an LSWM1BFANSC, LSWM1BFANSC-SN, LSWM1BFANSCB, or LSWM1BFANSCB-SN fan tray
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Grasp the fan tray handle with one hand to pull the fan tray part way out. Support the fan tray bottom with the other and pull out the fan tray slowly along the guide rails.
3. Place the removed fan tray in an antistatic bag.
Figure2-38 Removing an LSWM1BFANSC fan tray
Removing an LSPM1FANSA, LSPM1FANSA-SN, LSPM1FANSB, or LSPM1FANSB-SN fan tray
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Grasp the fan tray handle and pull out the fan tray slowly along the guide rails.
3. Place the removed fan tray in an antistatic bag.
Figure2-39 Removing an LSPM1FANSA fan tray
Installing and removing a power module
|
WARNING! · In power redundancy mode, you can replace a power module without powering off the switch but must strictly follow the installation and procedures in Figure2-40 and Figure2-41 to avoid any bodily injury or damage to the switch. · Provide a separate circuit breaker for each power module. |
|
CAUTION: Do not install power modules with different models on the same switch. |
The switches, except for the S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3), S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H5) and S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT-H3), come with the power module slots empty and filler panels for the power module slots as accessories. The LS-6800-54QF-H3, LS-6800-54QF-H5 and LS-6800-54QT-H3 came with power module slot 1 empty and a filler panel installed in power module slot 2.
For more information about the power modules available for the switches, see H3C S6800 Switch Series Hardware Information and Specifications.
Figure2-40 Installation procedure
Safety guidelines
To prevent device damage and even bodily injury, follow these restrictions and guidelines when you install or remove a power module:
· Always wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure the strap makes good skin contact.
· Before installing a power module, make sure the voltage of the power source is as required by the power module, and the output voltage of the power module is as required by the device.
· Do not touch any bare cables or terminals on the power module.
· Do not place the power module in a wet area, and prevent liquid from entering the power module.
· To avoid power module damage, do not open the power module. When an internal circuit or component of the power supply fails, contact H3C Support.
Installing a power module
|
CAUTION: · Follow the forward inertia of the power module when inserting it into the chassis, and make sure the power module has firm contact with the connectors on the backplane. · To prevent damage to the connectors inside the switch chassis, insert the power module gently. If you encounter a hard resistance while inserting the power module, pull out the power module and insert it again. · As a best practice for heat dissipation, make sure each empty power module slot is installed with a filler panel. |
The power module installation procedures are the same for the S6800 switches. This section uses the S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3 and LS-6800-54QF-H5) switch as an example.
To install a power module:
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Remove the filler panel from the target power module slot, if any, as shown in Figure2-42.
Figure2-42 Removing the filler panel from a power module slot
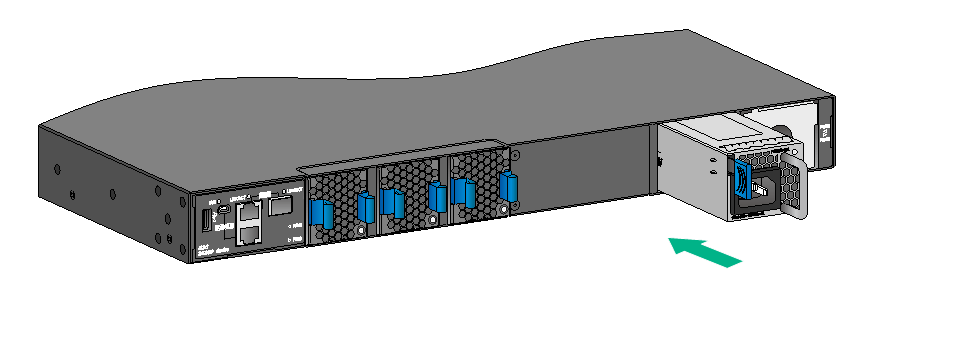
3. Unpack the power module and verify that the power module model is correct.
4. Correctly orient the power module with the power module slot (see Figure2-43), grasp the handle of the power module with one hand and support its bottom with the other, and slide the power module slowly along the guide rails into the slot.
The slot is foolproof. If you cannot insert the power module into the slot, re-orient the power module rather than use excessive force to push it in.
Figure2-43 Installing a power module
Removing a power module
|
CAUTION: · When an S6800-32Q, S6800-54QF, S6800-54QT, S6800-54HF, S6800-54HT, S6800-2C, or S6800-2C-FC switch has two power modules in 1+1 redundancy mode, removing one power module does not affect the operation of the switch. When the switch has only one power module installed, removing the power module powers off the switch. · When an S6800-4C switch has four power modules in 2+2 redundancy mode, removing one or two power modules does not affect the operation of the switch. When the switch has only two power module installed, removing a power module might power off the switch or cause power insufficiency. |
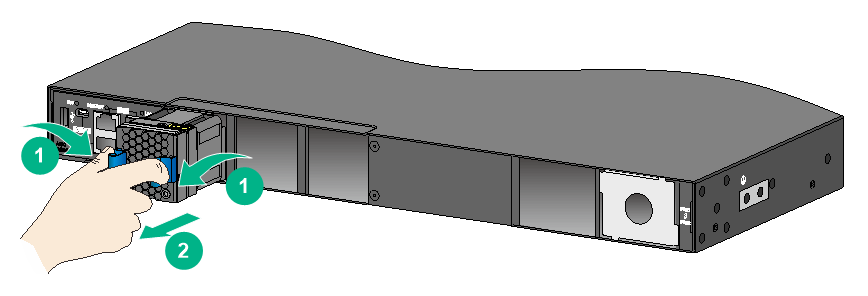
Removing an LSVM1AC300/LSVM1AC650/PSR250-12A/PSR250-12A1/PSR450-12A/PSR450-12A1 power module
The removal procedure is the same for the LSVM1AC300, LSVM1AC650, PSR250-12A/PSR250-12A1, and PSR450-12A/PSR450-12A1 power modules. This procedure uses an LSVM1AC300 power module on an S6800-32Q switch as an example.
To remove an LSVM1AC300 power module:
1. Remove the power cord.
2. Hold the handle on the power module with one hand, pivot the latch on the power module to the right with your thumb, and pull the power module part way out of the slot, as shown in Figure2-44.
3. Supporting the power module bottom with one hand, slowly pull the power module out with the other hand.
4. Put away the removed power module in an antistatic bag for future use.
Figure2-44 Removing an LSVM1AC300 power module
|
(1) Pivot the latch to the right with your thumb |
(2) Pull the power module out |
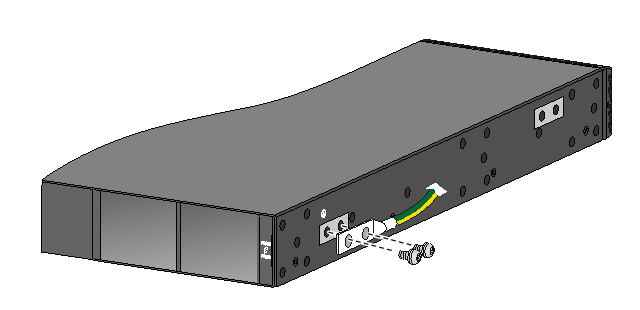
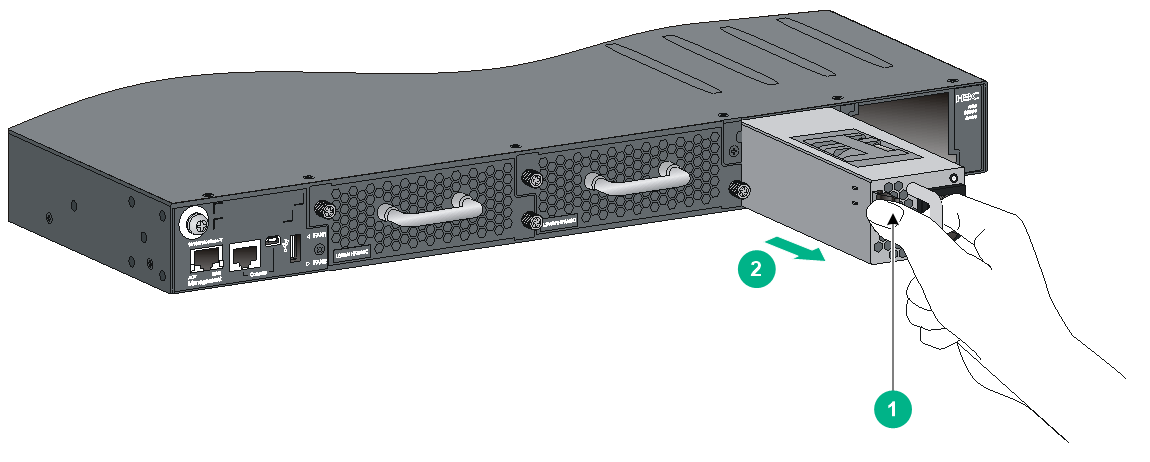
Removing an LSVM1DC300/LSVM1DC650/PSR450-12D power module
1. Remove the power cord from the power module.
¡ For an LSVM1DC300 or LSVM1DC650 power module, squeeze the tabs on the power cord connector with your thumb and forefinger, and pull the connector out of the power module. See Figure2-45.
¡ For a PSR450-12D power module, use a flat-head screwdriver to loosen the screws on the power cord connector, and then pull the connector out of the power module. See Figure2-46.
2. Hold the handle on the power module with one hand, pivot the latch on the power module to the right with your thumb, and pull the power module part way out of the slot, as shown in Figure2-44.
3. Supporting the power module bottom with one hand, slowly pull the power module out with the other hand.
4. Put the removed power module in an antistatic bag for future use.
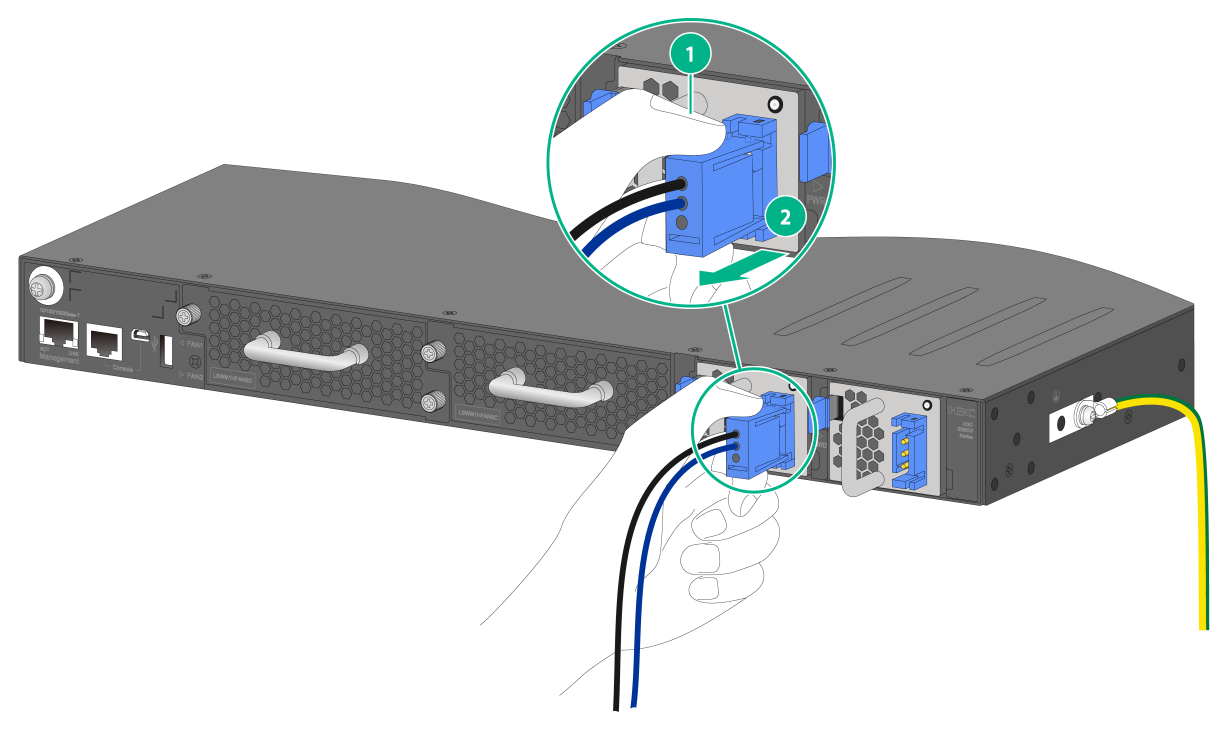
Figure2-45 Removing the power cord from an LSVM1DC300/LSVM1DC650 power module
|
(1) Press the tabs on the power cord connector with your thumb and forefinger |
|
(2) Pull the power cord connector out |
Figure2-46 Removing the power cord from a PSR450-12D power module
|
(1) Use a flat-head screwdriver to loosen the screws on the power cord connector |
|
(2) Pull the power cord connector out |
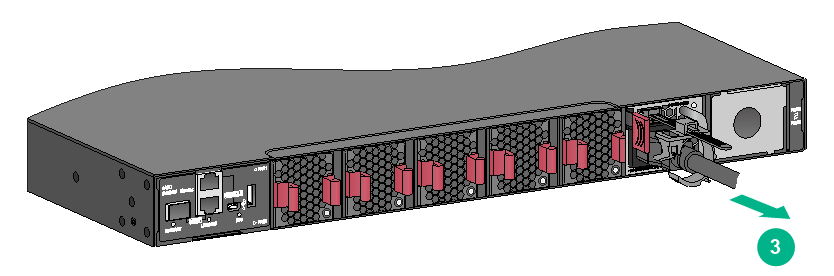
Removing a PSR450-12AHD power module
To remove a PSR450-12AHD power module:
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Open the cable clamp (see Figure2-47), and then remove the power cord connector from the power module (see Figure2-48).
Figure2-47 Opening the cable clamp
Figure2-48 Removing the power cord from the power module
3. Hold the handle of the power module with one hand, press the latch on the power module to the right with your thumb, and pull the power module part way out of the slot. Supporting the power module bottom with one hand, slowly pull the power module out of the slot along the guide rails with the other.
Place the removed power module in an antistatic bag.
Connecting the power cord
|
WARNING! Provide a circuit breaker for each power input. When you connect a power cord, make sure the circuit breaker is switched off. |
Connecting the power cord for an LSVM1AC300/LSVM1AC650/PSR250-12A/PSR250-12A1/PSR450-12A/PSR450-12A1 power module
1. Insert the female connector of the power cord supplied with the power module into the power receptacle on the power module.
2. Use a cable tie to secure the power cord to the handle of the power module, as shown in Figure2-49.
3. Connect the other end of the power cord to a power source.
Figure2-49 Connecting the power cord for an LSVM1AC300/LSVM1AC650/PSR250-12A/PSR250-12A1/PSR450-12A1 power module
|
(1) Releasable cable tie |
|
(2) Tighten the releasable cable tie to secure the power cord to the handle of the power module |
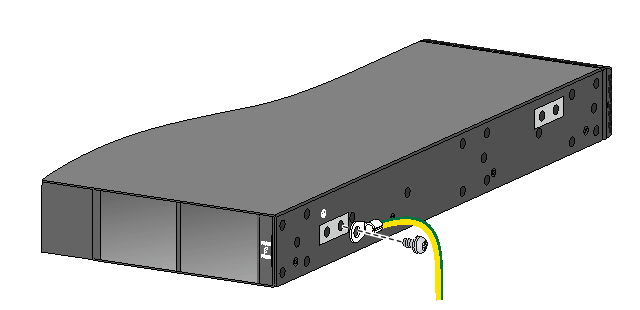
Connecting the power cord for an LSVM1DC300/LSVM1DC650 power module
1. Unpack the DC power cord, identify the plug for connecting to the power module, orient the plug with the power receptacle on the power module, and insert the plug into the receptacle.
The receptacle is foolproof. If you cannot insert the plug into the receptacle, re-orient the plug rather than use excessive force to push it in.
2. Use a cable tie to secure the power cord to the handle of the power module, as shown in Figure2-49.
3. Connect the other end of the power cord to a DC power source.
Figure2-50 Connecting the power cord for an LSVM1DC300 or LSVM1DC650 power module
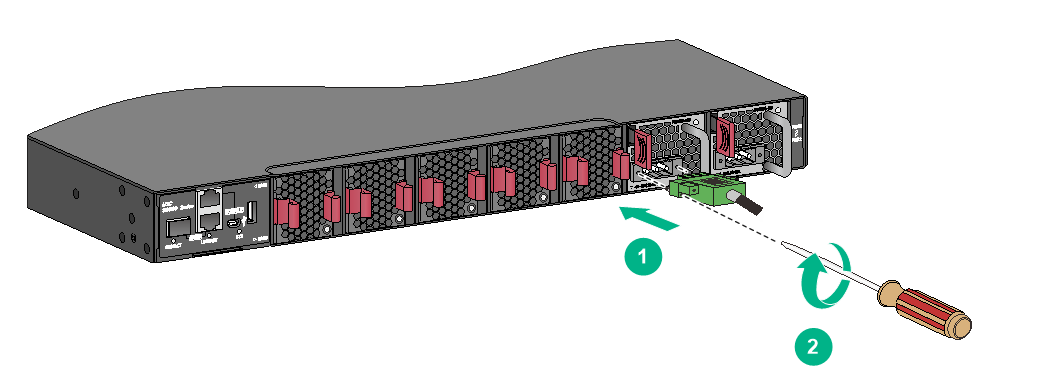
Connecting the power cord for a PSR450-12AHD power module
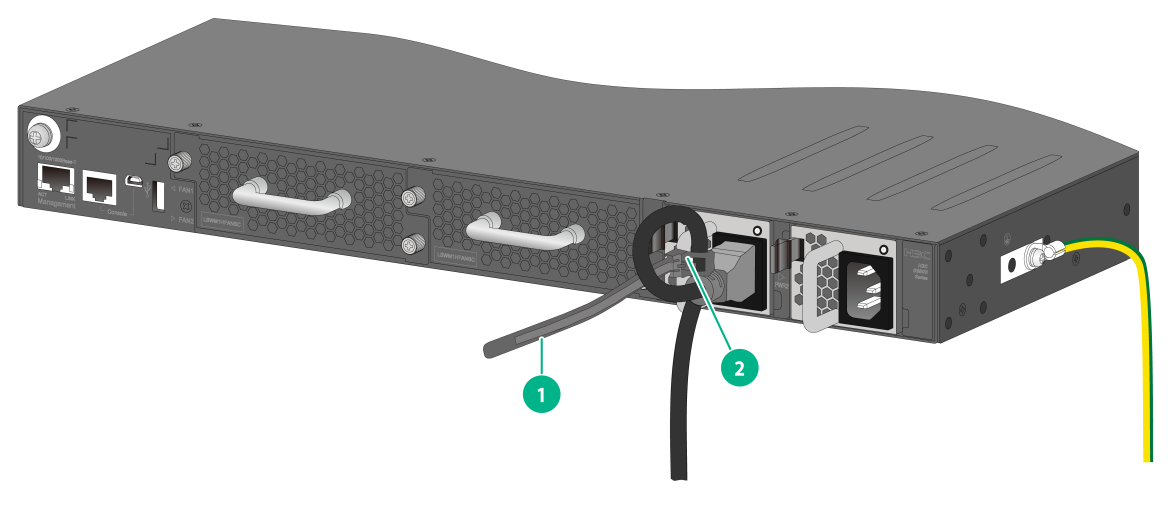
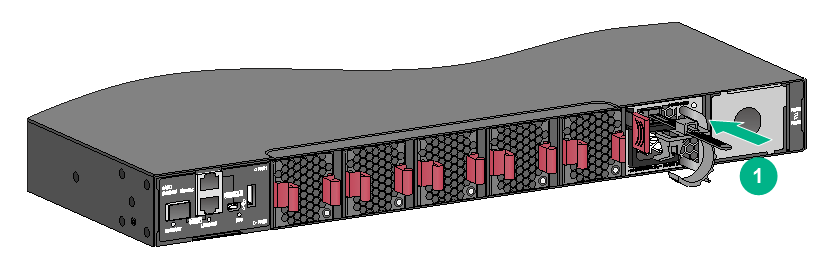
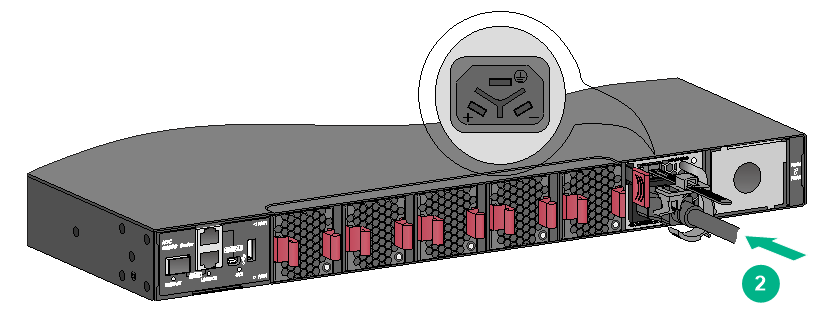
1. Slide the cable clamp onto the tie mount on the power module, as shown in Figure2-51.
2. Connect the female connector of the power cord to the power receptacle on the power module, as shown in Figure2-52
3. Close the cable clamp and slide it forward until it is flush against the edge of the female connector, as shown in Figure2-53.
4. Connect the other end of the power cord to an AC or DC power source.
Figure2-51 Connecting the power cord for a PSR450-12AHD power module (1)
Figure2-52 Connecting the power cord for a PSR450-12AHD power module (2)
Figure2-53 Connecting the power cord for a PSR450-12AHD power module (3)
Connecting the power cord for a PSR450-12D power module
1. Correctly orient the DC power cord plug and insert the plug into the power receptacle on the power module.
If you orient the DC power cord plug upside down, you cannot insert the plug into the power receptacle.
2. Use a flat-head screwdriver to fasten the screws on the power cord connector, as shown in Figure2-54.
3. Connect the other end of the power cord to a DC power source.
Figure2-54 Connecting the DC power cord for a PSR450-12D power module
Installing and removing an expansion module
|
CAUTION: · Never touch the components on the expansion module surface. · Do not use excessive force. · Do not install or remove an expansion module during startup of the switch. The expansion modules are hot swappable when the switch is operating correctly. |
The S6800-2C and S6800-2C-FC switches each provide two expansion slots. The S6800-4C switch provides four expansion slots. For the available expansion modules, see H3C S6800 Switch Series Hardware Information and Specifications.
The expansion module installation and removal procedures are the same. This section uses the LSWM18QC interface module as an example.
Installing an expansion module
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure the wrist strap makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. (Optional.) If the target expansion slot has a filler panel installed, remove the filler panel. Figure2-55 uses the S6800-2C switch as an example.
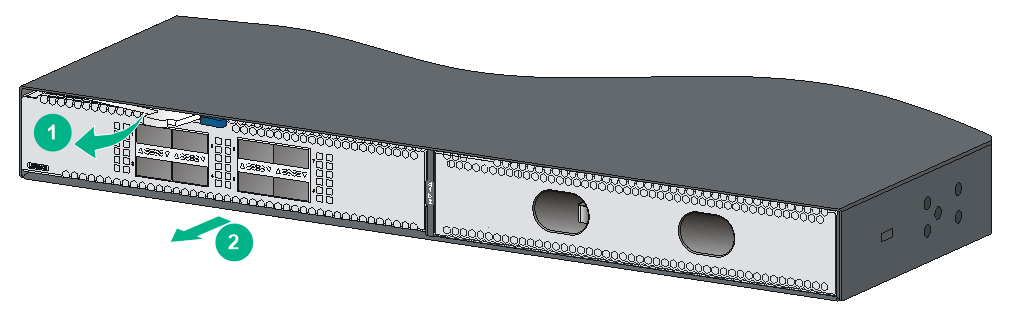
a. Use your thumb and forefinger to hold the filler panel through the two holes.
b. Push right the metal tab in the left hole and pull out the filler panel along the guide rails.
Figure2-55 Removing the filler panel from the expansion slot
Keep the removed filler panel secure for future use.
3. Unpack the expansion module.
Figure2-56 LSWM18QC interface module
|
(1) Ejector lever |
(2) Latch |
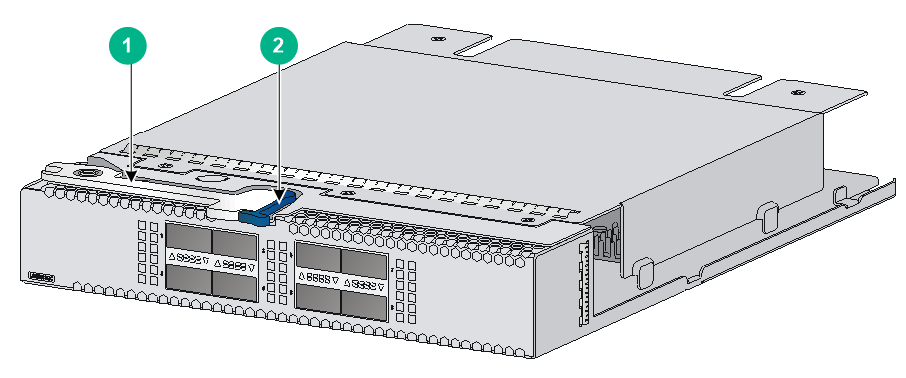
4. Press the latch on the expansion module to release the ejector lever.
5. Insert the expansion module slowly into the slot along the guide rails, as shown by callout 1 in Figure2-57.
6. Rotate inward the ejector lever as shown by callout 2 in Figure2-57 until the latch locks the ejector lever in place.
Figure2-57 Installing an LSWM18QC interface module
Removing an expansion module
|
CAUTION: · Before you remove an expansion module, remove the cable from it to avoid cable damage. · If you are not to install a new expansion module after removing the original one, install the filler panel in the slot to prevent dust and ensure good ventilation in the device. |
To remove an expansion module:
1. Prepare an anti-static bag.
2. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure the wrist strap makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
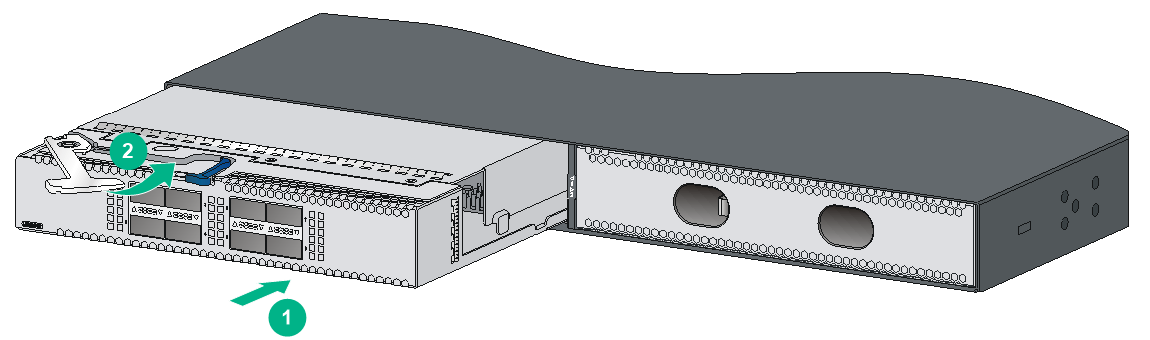
3. Press the latch to release the ejector lever
4. Rotate outward the ejector lever as shown by callout 1 in Figure2-58.
5. Pull out the expansion module slowly out of the expansion slot, as shown by callout 2 in Figure2-58.
6. Place the removed expansion module in the anti-static bag.
Figure2-58 Removing an LSWM18QC interface module
Verifying the installation
After you complete the installation, verify that:
· There is enough space for heat dissipation around the switch, and the rack is stable.
· The grounding cable is securely connected.
· The correct power source is used.
· The power cords are correctly connected.
· All the interface cables are cabled indoors.
3 Accessing the switch for the first time
Setting up the configuration environment
An S6800 switch supports the following ways to connect the configuration terminal:
· Through the console port by using the serial console cable
The switch comes with the serial console cable. This way is preferred.
· Through the Mini USB console port by using the user-supplied USB mini console cable
Do not use the two ways together on the same S6800 switch.
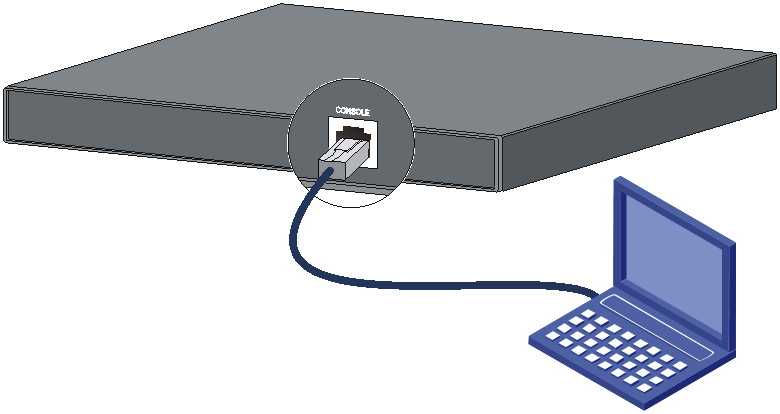
The example uses a console cable to connect a console terminal (PC) to the serial console port on the switch.
Figure3-1 Connecting the serial console port to a terminal
Connecting the console cable
Serial console cable
A serial console cable is an 8-core cable, with a crimped RJ-45 connector at one end for connecting to the serial console port of the switch, and a DB-9 female connector at the other end for connecting to the serial port on the console terminal.
Figure3-2 Serial console cable
Table3-1 Serial console cable pinout
|
RJ-45 |
Signal |
DB-9 |
Signal |
|
1 |
RTS |
8 |
CTS |
|
2 |
DTR |
6 |
DSR |
|
3 |
TXD |
2 |
RXD |
|
4 |
SG |
5 |
SG |
|
5 |
SG |
5 |
SG |
|
6 |
RXD |
3 |
TXD |
|
7 |
DSR |
4 |
DTR |
|
8 |
CTS |
7 |
RTS |
USB mini console cable
A USB mini console cable has a USB mini-Type B connector at one end to connect to the Mini USB console port of the switch, and a standard USB Type A connector at the other end to connect to the USB port on the configuration terminal.
Connection procedure
To connect a terminal (for example, a PC) to the switch by using the serial console cable:
1. Plug the DB-9 female connector of the serial console cable to the serial port of the PC.
2. Connect the RJ-45 connector to the serial console port of the switch.
|
|
NOTE: · Identify the mark on the console port and make sure you are connecting to the correct port. · The serial ports on PCs do not support hot swapping. If the switch has been powered on, connect the serial console cable to the PC before connecting to the switch, and when you disconnect the cable, first disconnect from the switch. |
To connect to the configuration terminal through the USB mini console cable:
1. Connect the standard USB Type A connector to the USB port of the configuration terminal.
2. Click the following link, or copy it to the address bar on the browser to log in to download page of the USB console driver, and download the driver.
http://www.h3c.com/en/home/USB_Console/,
3. Run Installer to preinstall the driver. After the preinstallation finishes, the system pops up a dialog box to indicate a successful preinstallation.
4. Connect the USB mini-Type B connector to the Mini USB console port on the switch. The system installs the driver automatically.
Setting terminal parameters
To configure and manage the switch through the console port, you must run a terminal emulator program, HyperTerminal or PuTTY, on your configuration terminal. You can use the emulator program to connect a network device, a Telnet site, or an SSH site. For more information about the terminal emulator programs, see the user guides for these programs
The following are the required terminal settings:
· Bits per second—9600.
· Data bits—8.
· Stop bits—1.
· Parity—None.
· Flow control—None.
Powering on the switch
Before powering on the switch, verify that the following conditions are met:
· The power cord is correctly connected.
· The input power voltage meets the requirement of the switch.
· The console cable is correctly connected.
· The configuration terminal (a PC, for example) has started, and its serial port settings are consistent with the console port settings on the switch.
Power on the switch. During the startup process, you can access Boot ROM menus to perform tasks such as software upgrade and file management. The Boot ROM interface and menu options differ with software versions. For more information about Boot ROM menu options, see the software-matching release notes for the device.
After the startup completes, you can access the CLI to configure the switch.
For more information about the configuration commands and CLI, see H3C S6800 Switch Series Configuration Guides and H3C S6800 Switch Series Command References.
4 Setting up an IRF fabric
You can use H3C IRF technology to connect and virtualize S6800 switches into a large virtual switch called an "IRF fabric" for flattened network topology, and high availability, scalability, and manageability.
The S6800 switches are divided into the following groups. Only members in the same group can form an IRF fabric.
· S6800-54HF, S6800-54HT, S6800-2C-FC, S6800-32Q (LS-6800-32Q-H1), S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H1, LS-6800-54QF-H3 and LS-6800-54QF-H5), S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT-H1 and LS-6800-54QT-H3), S6800-2C (LS-6800-2C-H1), and S6800-4C (LS-6800-4C-H1).
· S6800-32Q (LS-6800-32Q), S6800-2C (LS-6800-2C), S6800-4C (LS-6800-4C), S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF), and S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT).
To set up IRF links between two switches, use the 10-GE, 40-GE, or 100-GE ports.
IRF fabric setup flowchart
Figure4-1 IRF fabric setup flowchart
To set up an IRF fabric:
|
Step |
Description |
|
1. Plan IRF fabric setup. |
Plan the installation site and IRF fabric setup parameters: · Planning IRF fabric size and the installation site · Identifying the master switch and planning IRF member IDs · Planning IRF topology and connections |
|
2. Install IRF member switches. |
|
|
3. Connect ground wires and power cords. |
See "Grounding the switch by using a grounding strip" and "Connecting the power cord." |
|
4. Power on the switches. |
N/A |
|
5. Configure basic IRF settings. |
N/A |
|
6. Connect the physical IRF ports. |
Connect the physical IRF ports on switches. Use SFP+, QSFP+, or QSFP28 transceiver modules and fibers for long-distance connection. Use twisted pair cables or SFP+, QSFP+, or QSFP28 cables for short-distance connection. All switches except the master switch automatically reboot, and the IRF fabric is established. |
Planning IRF fabric setup
This section describes issues that an IRF fabric setup plan must cover.
Planning IRF fabric size and the installation site
Choose switch models and identify the number of required IRF member switches, depending on the user density and upstream bandwidth requirements. The switching capacity of an IRF fabric equals the total switching capacities of all member switches.
Plan the installation site depending on your network solution as follows:
· Place all IRF member switches in one rack for centralized high-density access.
· Distribute the IRF member switches in different racks to implement the top-of-rack (ToR) access solution for a data center.
As your business grows, you can plug H3C S6800 switches into the IRF fabric to increase the switching capacity without any topology change or replacement.
Identifying the master switch and planning IRF member IDs
Determine which switch you want to use as the master for managing all member switches in the IRF fabric. An IRF fabric has only one master switch. You configure and manage all member switches in the IRF fabric at the command line interface of the master switch.
|
|
NOTE: IRF member switches will automatically elect a master. You can affect the election result by assigning a high member priority to the intended master switch. For more information about master election, see H3C S6800 Switch Series IRF Configuration Guide or H3C S6800 Switch Series Virtual Technologies Configuration Guide, depending on the software version. |
Prepare an IRF member ID assignment scheme. An IRF fabric uses member IDs to uniquely identify and manage its members, and you must assign each IRF member switch a unique member ID.
Planning IRF topology and connections
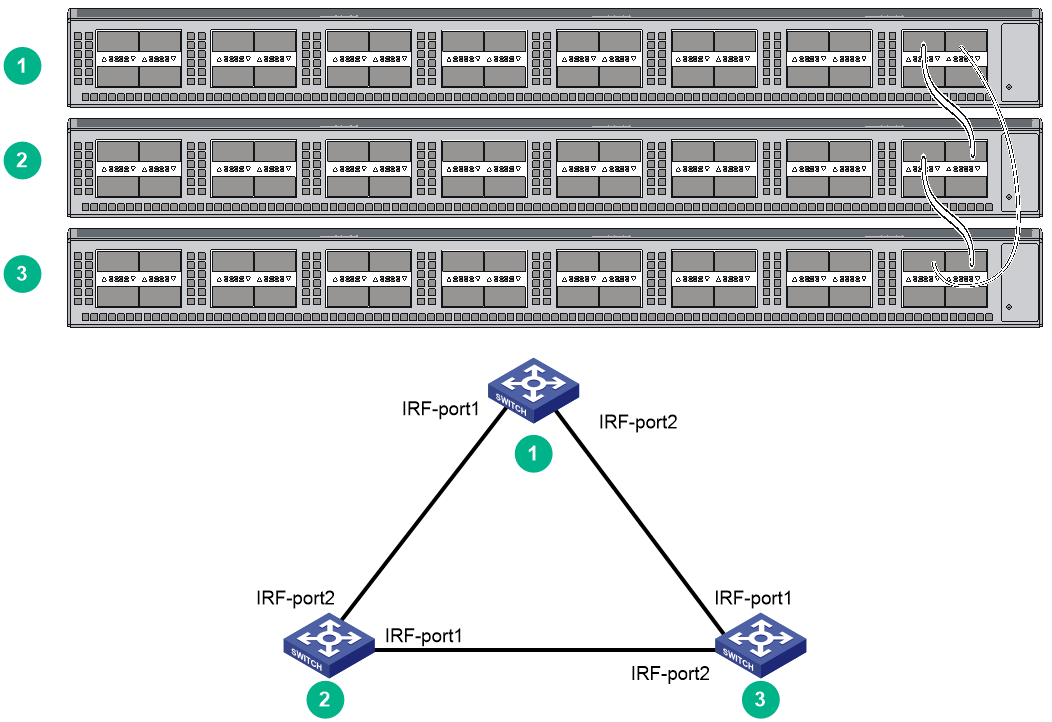
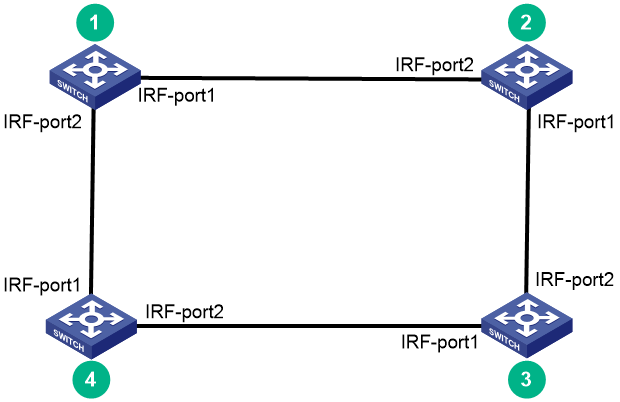
You can create an IRF fabric in daisy chain topology, or more reliably, ring topology. In ring topology, the failure of one IRF link does not cause the IRF fabric to split as in daisy chain topology. Rather, the IRF fabric changes to a daisy chain topology without interrupting network services.
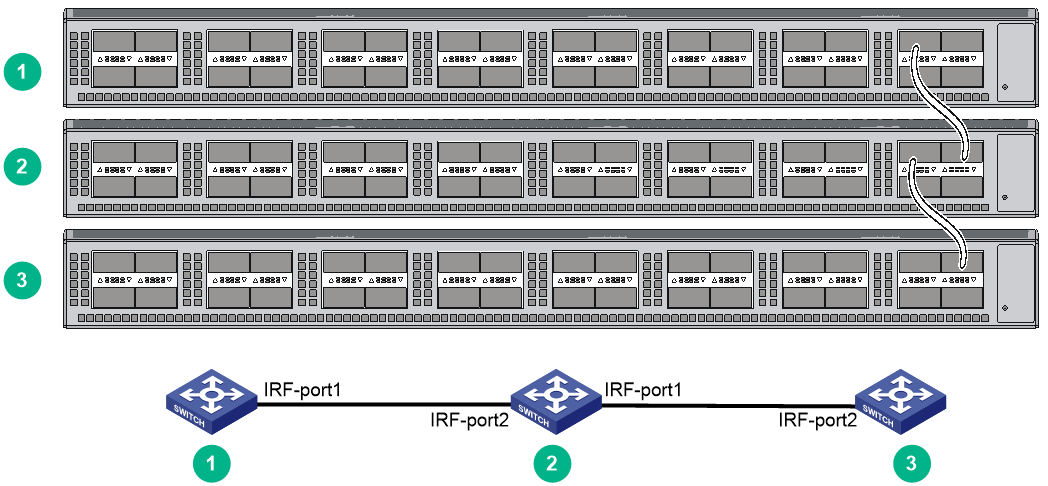
You connect the IRF member switches through IRF ports, the logical interfaces for the connections between IRF member switches. Each IRF member switch has two IRF ports: IRF-port 1 and IRF-port 2. To use an IRF port, you must bind at least one physical port to it.
When connecting two neighboring IRF member switches, you must connect the physical ports of IRF-port 1 on one switch to the physical ports of IRF-port 2 on the other switch.
The IRF port connections in the two figures are for illustration only, and more connection methods are available.
Figure4-2 IRF fabric in daisy chain topology
Figure4-3 IRF fabric in ring topology
You can provide the following IRF physical connections between S6800 switches:
· 10-GE IRF physical connection by connecting 10GBase-T Ethernet ports or SFP+ ports.
· 40-GE IRF physical connection by connecting QSFP+ ports.
· 100-GE or 40-GE IRF physical connection by connecting QSFP28 ports.
· IRF physical connection by using a 40G QSFP+ to 4 × 10G SFP+ cable to connect a QSFP+ port and four SFP+ ports.
You can bind several ports to an IRF port for increased bandwidth and availability.
Identifying physical IRF ports on the member switches
Identify the 10GBase-T Ethernet ports, SFP+ ports, QSFP+, and QSFP28 ports to be used for IRF connections on the member switches according to your topology and connection scheme.
All the 10GBase-T Ethernet ports, SFP+ ports, QSFP+ ports, and QSFP28 ports on the S6800 switch can be used for IRF connections.
When you use QSFP+ cables to connect physical IRF ports, follow these guidelines:
· Make sure the two ports on an IRF link are both fixed ports or ports on interface modules.
· If you use ports on interface modules as physical IRF ports, make sure the interface modules on an IRF link are the same model.
Planning the cabling scheme
You can use twisted pair cables, SFP+/QSFP+/QSFP28 cables, or SFP+/QSFP+/QSFP28 transceiver modules and optical fibers to connect the switches for IRF connections. If the IRF member switches are far away from one another, choose the SFP+/QSFP+/QSFP28 transceiver modules and optical fibers. If the IRF member switches are all in one equipment room, choose twisted pair cables or SFP+/QSFP/QSFP28 cables. For more information about available transceiver modules and cables, see H3C S6800 Switch Series Hardware Information and Specifications.
The following subsections describe several H3C recommended IRF connection schemes, and all these schemes use a ring topology.
Connecting the IRF member switches in one rack
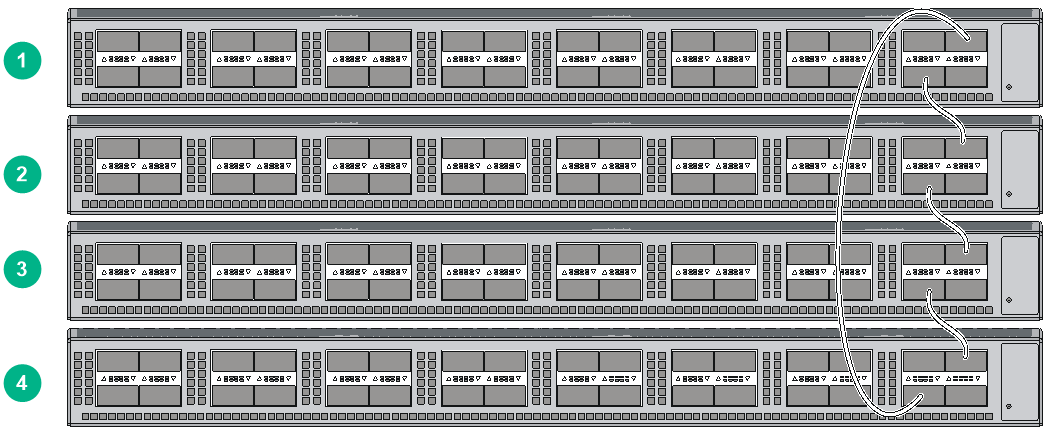
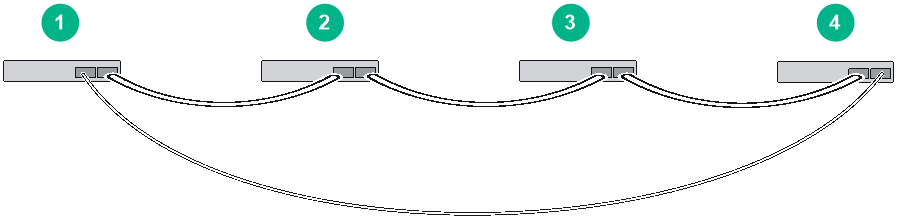
Figure4-4 shows an example for connecting four IRF member switches in a rack by using QSFP+ cables and QSFP+ transceiver modules and optical fibers. The switches in the ring topology (see Figure4-5) are in the same order as connected in the rack.
Figure4-4 Connecting the switches in one rack
Connecting the IRF member switches in a ToR solution
You can install IRF member switches in different racks side by side to deploy a top of rack (ToR) solution.
Figure4-6 shows an example for connecting four top of rack IRF member switches by using QSFP+ cables and QSFP+ transceiver modules and optical fibers. The topology is the same as Figure4-5.
Configuring basic IRF settings
After you install the IRF member switches, power on the switches, and log in to each IRF member switch (see H3C S6800 Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide) to configure their member IDs, member priorities, and IRF port bindings.
Follow these guidelines when you configure the switches:
· Assign the master switch higher member priority than any other switch.
· Bind physical ports to IRF port 1 on one switch and to IRF port 2 on the other switch. You perform IRF port binding before or after connecting IRF physical ports depending on the software release.
· Execute the display irf configuration command to verify the basic IRF settings.
For more information about configuring basic IRF settings, see H3C S6800 Switch Series IRF Configuration Guide or H3C S6800 Switch Series Virtual Technologies Configuration Guide, depending on the software version.
Connecting the physical IRF ports
|
CAUTION: Wear an ESD wrist strap when you connect cables or transceiver modules and optical fibers. For more information, see the installation guide for the transceiver modules. |
Use cables or transceiver modules and optical fibers to connect the IRF member switches as planned.
Accessing the IRF fabric to verify the configuration
To verify the basic functionality of the IRF fabric after you finish configuring basic IRF settings and connecting IRF ports:
1. Log in to the IRF fabric through the console port of any member switch.
2. Create a Layer 3 interface, assign it an IP address, and make sure the IRF fabric and the remote network management station can reach each other.
3. Use Telnet or SNMP to access the IRF fabric from the network management station. (See H3C S6800 Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide.)
4. Verify that you can manage all member switches as if they were one node.
5. Display the running status of the IRF fabric by using the commands in Table4-1.
Table4-1 Displaying and maintaining IRF configuration and running status
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display information about the IRF fabric. |
display irf |
|
Display all members' IRF configurations. |
display irf configuration |
|
Display IRF fabric topology information. |
display irf topology |
|
|
NOTE: To avoid IP address collision and network problems, configure at least one multi-active detection (MAD) mechanism to detect the presence of multiple identical IRF fabrics and handle collisions. For more information about MAD detection, see H3C S6800 Switch Series IRF Configuration Guide or H3C S6800 Switch Series Virtual Technologies Configuration Guide, depending on the software version. |
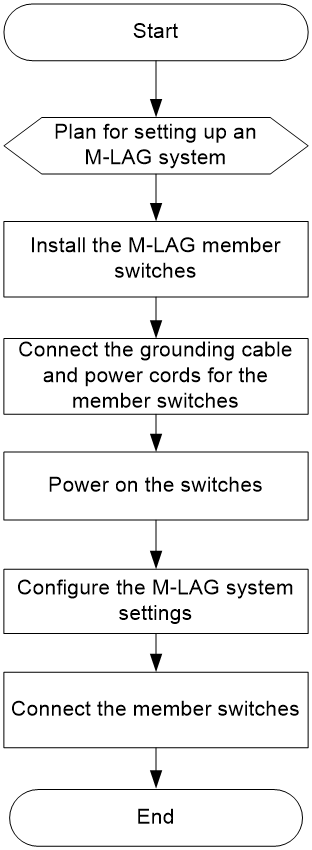
5 Setting up an M-LAG system
Multichassis Link Aggregation (M-LAG) virtualizes two physical devices into one system through multichassis link aggregation to provide device-class high availability and load sharing.
Compared to IRF, M-LAG offers higher network reliability and shorter service interruption during upgrade.
You cannot configure IRF and M-LAG on the same network.
|
IMPORTANT: · In Release 2702 and earlier, M-LAG is called DRNI and uses the DRNI set of command keywords in the CLI. · In Release 6710 and later, the device supports both the M-LAG set and DRNI set of command keywords in the CLI by default. The two sets of commands are consistent in the service configuration methods, functions, and output, with only differences in the command keywords. For the differences in the command keywords, see M-LAG configuration in H3C S6800 & S6860 Switch Series Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide. |
M-LAG system setup flowchart
Figure5-1 M-LAG system setup flowchart
To set up an M-LAG system:
|
Step |
Description |
|
1. Plan for setting up the M-LAG system. |
Plan for setting up the M-LAG system based on the network and device conditions: · Determine the installation locations of the switches. · Reserve physical ports for M-LAG connections. · Plan the cable connection scheme. For more information, see "Planning for setting up an M-LAG system." |
|
2. Install M-LAG member switches. |
|
|
3. Connect grounding cable and power cords for the member switches. |
See "Attaching the mounting brackets, chassis rails, and grounding cable to the chassis" and "Connecting the power cord." |
|
4. Power on the switches. |
N/A |
|
5. Configure the M-LAG system settings. |
For detailed information about M-LAG, see M-LAG configuration in H3C S6800 & S6860 Switch Series Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide. |
|
6. Connect the member switches. |
Select cables or transceiver modules and optical fibers matching the rate of the physical ports of the peer link and keepalive link for connection. |
Planning for setting up an M-LAG system
Determining device installation locations
An M-LAG system can be set up with only two devices. Reserve sufficient space in the rack for installation of the devices.
You can place the two switches in one cabinet. Alternatively, you can install the switches in two cabinets if you're seeking a top-of-rack access solution in the data center.
Reserving physical ports for M-LAG connection
To set up an M-LAG system, you must establish a peer link and a keepalive link between the two devices.
The M-LAG member devices exchange protocol packets and transmit data traffic over the peer link. An M-LAG system has only one peer link. You can create a peer-link interface on each M-LAG member device, and the link between the two peer-link interfaces is the peer link.
The M-LAG member devices exchange keepalive packets over the keepalive link to detect multi-active collisions when the peer link is down.
Peer link
In addition to protocol packets, the peer link also transmits data packets between the M-LAG member devices when an uplink fails. When you set up the peer link, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· Configure the peer-link aggregation group as follows:
¡ If an M-LAG member device is a fixed-port device with interface expansion modules, assign ports from multiple interface expansion modules to the aggregation group for the peer-link interface. Make sure at least one member port resides on a different slot than the uplink interfaces.
¡ If an M-LAG member device is a fixed-port device, assign at least two physical interfaces to the aggregation group for the peer-link interface.
· The member ports in the aggregation group for the peer-link interface must have the same speed.
· If an M-LAG system is attached to a large number of servers by using non-M-LAG interfaces, take the size of the traffic sent among those servers into account when you determine the bandwidth of the peer link.
Keepalive link
As a best practice, establish a dedicated direct link between two M-LAG member devices as a keepalive link. Do not use the keepalive link for any other purposes. Make sure the M-LAG member devices have Layer 2 and Layer 3 connectivity to each other over the keepalive link.
You can use management Ethernet interfaces, Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces, Layer 3 aggregate interfaces, or interfaces with a VPN instance bound to set up the keepalive link.
As a best practice, do not use VLAN interfaces for keepalive link setup. If you have to use VLAN interfaces, remove the peer-link interfaces from the related VLANs to avoid loops.
On a device with interface expansion modules, do not use the same module to provide interfaces for setting up the keepalive link and peer link.
Planning the cable connection scheme
Select cables or transceiver modules and optical fibers matching the rate of physical ports of the peer link and the keepalive link for connection.
Cables are short but with high performance and stability, suitable for short-distance connections in the equipment room. Transceiver modules and optical fibers can be combined flexibly and is suitable for longer distance connections.
For information about the transceiver modules and cables supported by the switch, see H3C S6800 Switch Series Hardware Information and Specifications.
This following section describes several cable connection schemes that use 40G physical ports for the peer link connection and the keepalive link connection, with matching cables or transceiver module and optical fibers.
|
|
NOTE: The physical port locations in the following figures are for illustration only. |
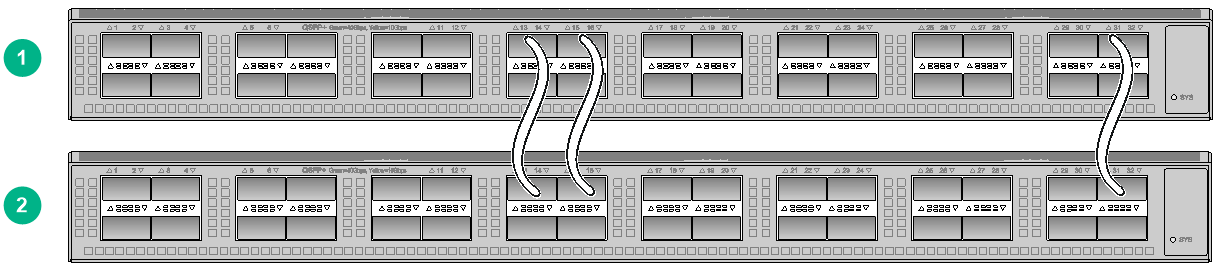
Connecting the member switches in one rack
If two M-LAG member devices are installed in the same rack, use the following connection method to connect them as a best practice.
Figure5-2 Connecting two M-LAG member devices are installed in the same rack
Figure5-3 Connection topology of two M-LAG member devices in the same rack
Top of rack connection scheme
You can install M-LAG member switches in two different racks side by side to deploy a top of rack (ToR) solution as shown in Figure5-4. Use transceiver modules and optical fibers for connection if a large distance exists between the member switches.
Figure5-4 Top of rack connection scheme
Configuring the M-LAG system settings
After you install the M-LAG member switches, start and log in to each member switch to configure basic M-LAG system settings, including:
· M-LAG system MAC address.
· M-LAG system ID.
· M-LAG system priority.
· Peer-link interface settings.
· Keepalive parameters.
For information about logging in to the switch, see H3C S6800 & S6860 Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
For information about configuring the M-LAG system settings, see M-LAG configuration in H3C S6800 Ethernet Switch Series Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
Restrictions and guidelines
You can set up an M-LAG system with only two member devices. For the M-LAG member devices to be identified as a single M-LAG system, you must configure the same M-LAG system MAC address and M-LAG system priority for them. To distinguish between the two member devices, assign them different M-LAG system IDs.
Make sure the MAC address of the M-LAG system is unique.
For correct packet forwarding, delete M-LAG configuration from an M-LAG member device if it leaves its M-LAG system.
When you bulk shut down physical interfaces on an M-LAG member device for service changes or hardware replacement, shut down the physical interfaces used for keepalive detection prior to the physical member ports of the peer-link interface. If you fail to do so, link flapping will occur on the member ports of M-LAG interfaces.
You must configure the keepalive link interfaces (including physical ports and logical interfaces) as M-LAG reserved interfaces. This ensures that these interfaces will not be MAD down when the peer link fails.
For more configuration restrictions and guidelines and typical configuration examples for the M-LAG system, see H3C Data Center Switches M-LAG Configuration Guide.
Connecting the M-LAG member switches
|
CAUTION: Wear an ESD wrist strap when you connect the M-LAG member switches. Make sure the strap makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded. |
Connect the M-LAG member switches based on the network topology and cable connection scheme. For the installation method and restrictions and guidelines for connecting cables or transceiver modules and optical fibers, see the installation guide for them.
Verifying the configuration
To verify the running status of the M-LAG system:
1. Create a Layer 3 interface on a member device, assign it an IP address, and make sure the device and the remote network management station can reach each other.
2. Use Telnet or SNMP to access the device remotely. For more information, see H3C S6800 & S6860 Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
3. Display the running status of the M-LAG system by using the display commands in any view.
Table5-1 Displaying and maintaining M-LAG system configuration and running status
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display M-LAG member device role information. |
display m-lag role |
|
Display M-LAG interface summary information. |
display m-lag summary |
|
Display M-LAG system information. |
display m-lag system |
|
Display detailed information about M-LAG interfaces. |
display m-lag verbose [ interface interface-number ] |
|
CAUTION: · In an M-LAG system, all management Ethernet ports on the primary and secondary devices are available for use. From the perspective of the network management system, the two devices in the M-LAG system are independent and you must log in and manage them separately. · To prevent network failures caused by M-LAG system splitting, configure HA after the M-LAG system is set up. For more information, see H3C Data Center Switches M-LAG Configuration Guide. |
6 Maintenance and troubleshooting
Power module failure
You can use the LEDs on the power module to identify a power module failure. For more information about the LEDs on a power module, see H3C S6800 Switch Series Hardware Information and Specifications.
The LEDs on the power module are steady green (active) or flashing green (standby) while the power module system is correctly operating. If the LEDs behave in any other way, verify the following items:
· The switch power cord is correctly connected.
· The power source meets the requirement.
· The operating temperature of the switch is in the normal range and the power module has good ventilation.
If the issue persists, contact the H3C technical support for help.
To replace a power module, see "Installing and removing a power module."
Fan tray failure
When an LSWM1FANSC, LSWM1FANSCB, LSWM1HFANSC, or LSWM1HFANSCB fan tray is faulty, the system status LED on the switch is steady red and the system outputs alarm messages.
When an LSWM1BFANSC, LSWM1BFANSC-SN, LSWM1BFANSCB, or LSWM1BFANSCB-SN fan tray is faulty, the Alarm LED on the fan tray is steady yellow and the system outputs alarm messages.
When an LSPM1FANSA, LSPM1FANSA-SN, LSPM1FANSB, or LSPM1FANSB-SN fan tray is faulty, the fan tray LED is steady yellow and the system outputs alarm messages.
To replace a failed fan tray, see "Installing and removing a fan tray."
Follow these guidelines when you install or remove a fan tray:
· For an S6800-32Q, S6800-2C, or S6800-2C-FC switch, if both fan trays fail during the switch operation, replace the fan trays within two minutes.
· For an S6800-4C, S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF or LS-6800-54QF-H1), S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT or LS-6800-54QT-H1), S6800-54HF, or S6800-54HT switch, if both fan trays fail during the switch operation, replace the fan trays within one minute.
· For an S6800-54QF (LS-6800-54QF-H3 or LS-6800-54QF-H5) or S6800-54QT (LS-6800-54QT-H3) switch, if more than one fan tray fail during the switch operation, replace the faulty fan trays one by one and finish replacing a fan tray within three minutes.
Configuration terminal issues
If the configuration environment setup is correct, the configuration terminal displays booting information when the switch is powered on. If the setup is incorrect, the configuration terminal displays nothing or garbled text.
No display on the configuration terminal
The configuration terminal has no display when the switch is powered on.
To resolve the issue:
1. Verify that the power system is operating correctly.
2. Verify that the console cable has been connected correctly and no fault occurs on the console cable.
3. Verify that the following settings are configured for the terminal:
¡ Baud rate—9600.
¡ Data bits—8.
¡ Stop bits—1.
¡ Parity—None.
¡ Flow control—None.
4. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.
Garbled display on the configuration terminal
The configuration terminal displays garbled text.
To resolve the issue:
1. Verify that the following settings are configured for the terminal:
¡ Baud rate—9600.
¡ Data bits—8.
¡ Stop bits—1.
¡ Parity—None.
¡ Flow control—None.
2. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.