- Released At: 08-05-2025
- Page Views:
- Downloads:
- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
|
|
|
SmartMC |
|
Technology White Paper |
|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2020 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Overview
Technical background
The expansion of networks requires an increasing number of access devices at network edges. Managing and maintaining such access devices can be very difficult and time-consuming.
Smart Management Center (SmartMC) provides a network management platform that integrates abundant management and maintenance functions for dispersed network devices at network edges, enabling simplified bulk device management. In a SmartMC network, only one device acts as the commander and the remaining devices all act as members.
SmartMC provides the following features:
· Smart management—Includes device role changing, network topology collection, outbound interface configuration, and automated Ethernet link aggregation.
· Smart operation and maintenance—Includes member upgrade, bulk backup of configuration files, one-key VLAN deployment, smart port identification, resource monitoring, and faulty device replacement.
· Management visibility—Includes network topology management, member adding, device list display, and device state display.
· Smart servicing—Includes user creation and activation.
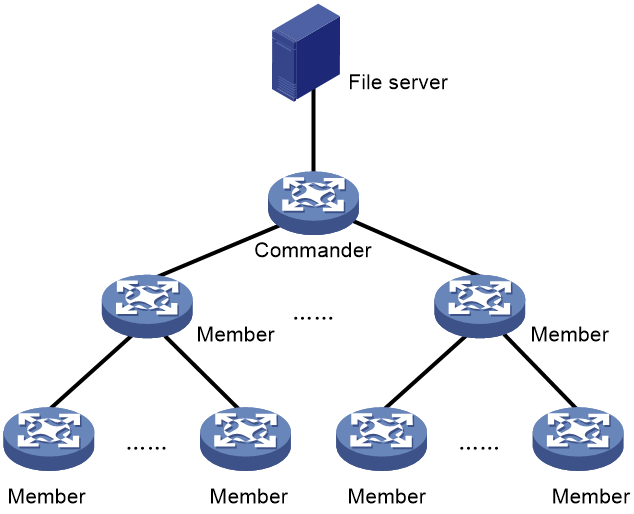
Figure 1 SmartMC network management platform
Benefits
SmartMC provides the following benefits:
· Ease of use—Allows operations from the Web interface without any software installation.
· Abundant features—Integrates abundant network management functions.
· Reduced cost—Reduces investment in network management and maintenance.
· Customization support—Allows users to customize platform functions as needed.
· Expandability—Supports expansion of platform functions.
SmartMC implementation
Network framework
Figure 2 shows the basic framework of a SmartMC network.
Figure 2 SmartMC network framework
The SmartMC network contains the following elements:
· Commander—Also called topology master (TM), which manages all members in the SmartMC network.
· Member—Also called topology client (TC), which is managed by the commander.
· File server—Stores startup software images and configuration files for the commander and members. Members obtain the required files from the server according to commands issued by the commander. The file server can be an independent server or co-located with the commander or a member. As a best practice to reduce workloads on the commander or member, deploy an independent file server.
SmartMC network topology management
SmartMC network establishment
A SmartMC network can be established automatically or manually.
Automatic network establishment
With SmartMC enabled, the commander scans the Layer 2 network for members, collects and saves member neighbor relations, and displays the topology on the Web interface. A member that starts up without loading any configuration automatically obtains the automatic configuration file from the DHCP server, loads the obtained configurations, and joins the SmartMC network.
To enable automatic network establishment:
1. Log in to the commander with an account that has the network-admin user role
2. Access the SmartMC > Configuration Wizard page.
3. Configure the following parameters:
¡ Management IP address—Specifies the IP address of VLAN-interface 1 on the commander. The SmartMC network will be established in VLAN 1.
¡ Management user—Specifies the local user of the commander. The user account is used for internal communications of the commander.
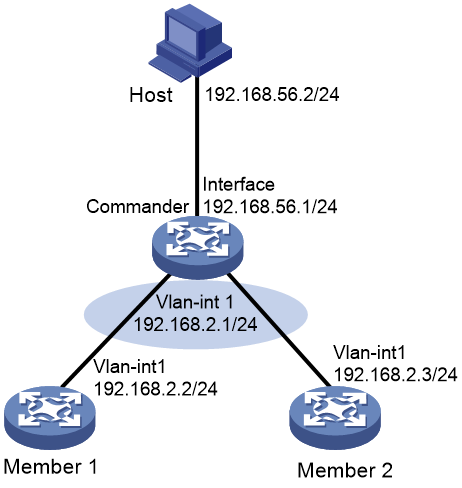
¡ Outgoing interface—Allows hosts connecting to an outgoing interface to access all the members in a SmartMC network. As shown in Figure 3, the host is connected to the uplink interface (192.168.56.0/24) on the commander and member 1 and member 2 are in a different network segment than the host. The host can access the Web interface of the commander but cannot access the Web interface of any member.
If the uplink interface on the commander is configured as the outgoing interface, the system maps the IP address of each member to a new address. The new address contains the IP address of the outgoing interface and the member's port number (5000+member ID) in the format of IP address:Port number. This enables the host to access the Web interfaces of members from the Web interface of the commander. As shown in Figure 3, the new address for member 1 is 192.168.56.1:5001.
Figure 3 Automatic network establishment
After you enable SmartMC on the commander, the following settings will be configured on the commander automatically:
· Enable DHCP.
· Create a DHCP address pool named SmartMC.
· Configure an IP address range in the DHCP address pool for dynamic allocation.
· Specify the subnet that the VLAN interface of VLAN 1 is in as the subnet for dynamic allocation in the DHCP address pool.
· Apply the address pool to the VLAN interface of VLAN 1.
· Specify an automatic configuration file for members.
· Set the lease duration in the DHCP address pool to unlimited.
After the configuration, the commander and members use the following procedure to establish a SmartMC network:
1. The commander broadcasts a SmartMC packet at an interval of 15 seconds to detect members in the network.
2. When a member receives the packet, it records the commander information, and returns a response packet to the commander.
3. When the commander receives the response packet, it initiates a NETCONF session to the member with the default username admin and the default password admin. The commander then obtains detailed information about the member through the session, including LLDP neighbor information.
4. The commander establishes a connection to the member for tracking the liveliness of the member, and adds the member to the SmartMC network.
5. Based on the LLDP neighbor information obtained from all members, the commander forms a SmartMC topology.
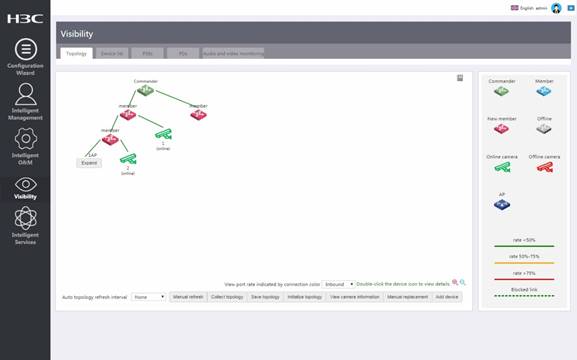
You can access the SmartMC > Visibility > Topology page to view the topology.
Manual SmartMC network establishment
If a device cannot join the network automatically as a member, you can manually add the device to the network from the Web interface of the commander.
Before manually adding a device, make sure you have performed the following tasks on the device:
· Enable HTTP and HTTPS.
· Enable Telnet.
· Enable HTTP-based NETCONF over SOAP.
· Enable LLDP globally.
· Create local user admin, set its password to admin, add the Telnet, HTTP, and HTTPS service types, and set the RBAC role to network-admin.
· Specify scheme authentication for VTY user lines.
· Configure the device to support SNMPv2c and set the read-only community string to public.
To manually add a device, access the SmartMC > Visibility > Topology page, click Add device, and enter the IP address, username, and password of the member. The members can join the network without exchanging SmartMC packets with the commander.
After you specify the information of a member on the commander, the commander performs the following operations to add the member to the network:
· Verify that the member can be accessed through Telnet.
· Obtain basic member information through NETCONF, including LLDP neighbor information.
· Obtain hardware information through SNMP Get operations.
Network topology maintenance
After the SmartMC network is established, the commander and members check for the existence of each other by exchanging SmartMC packets.
· When a member receives a SmartMC broadcast packet from the commander, it compares the bridge MAC address in the packet with the recorded bridge MAC address. If the two bridge MAC addresses are the same, the member returns a response packet to the commander. If the member does not receive a broadcast packet from the commander within the limit time, the member determines that the commander does not exist in the network anymore. Then, the member clears the commander information.
· When the commander receives a response packet from a member, it compares the bridge MAC address in the packet with the recorded bridge MAC address. If the two bridge MAC addresses are the same, the commander determines that the member still exists in the network. If the commander does not receive a response packet from a member within 150 seconds, the commander determines that the member is offline. Then, the commander sets the status of the member to offline.
Faulty member replacement
About faulty member replacement
You can use the following methods to replace a faulty member:
· Automatic replacement—To automatically replace a faulty member, first enable automatic replacement, and then install the new member at the location where the faulty member was installed and connect all cables. When the commander discovers that a new member has physically replaced the faulty member, it compares the new member with the faulty one. The commander performs a replacement if the following requirements are met:
¡ The commander obtains the same LLDP information from the new member for three consecutive times.
¡ The new member has the same LLDP information as the faulty member.
¡ The new member has the same model as the faulty member.
· Manual replacement—To manually replace a faulty member, first install the new member at the location where the faulty member was installed, connect all cables, and then perform manual replacement from the SmartMC > Visibility > Topology page. The commander performs a replacement if the new member has the same model as the faulty member.
The new member will download the configuration file of the faulty member from the file server and run the file to complete the replacement.
Restrictions and guidelines
If more than one adjacent member fails, automatic replacement does not take effect. You must perform manual replacement.
In an IRF fabric, to avoid IRF split, make sure the IRF configuration and cable connection are the same for the new member and faulty member.
Bulk member management
About bulk member management
SmartMC supports the following bulk management functions on the SmartMC > Intelligent O&M > Monitor resources page:
· Bulk upgrade—Upgrades device version and rolls back configurations in bulk.
· Bulk configuration management—Backs up configuration files and deploy configurations to members in bulk.
You can manage a specific member, members in a specific SmartMC group, or all members. Member grouping can be performed by device type, IP address, and MAC address.
The commander can obtain information from members through NETCONF, and deploy configurations to members through NETCONF, Telnet, or SmartMC Layer 2 packets.
Bulk upgrade
You can upgrade devices to a higher version or downgrade devices to a lower version. The system supports immediate upgrade, delayed upgrade, and scheduled upgrade.
Bulk upgrade operates as follows:
1. The commander notifies the specified members to download the image file at the specified upgrade time.
2. Members download the image file from the file server and perform upgrades.
3. Members send SmartMC unicast responses to the commander to report the upgrade results.
4. The commander sends confirm packets to the members.
Bulk management
|
CAUTION: Before deploying configurations to devices in bulk, make sure the configurations to deploy will not cause network flapping or affect SmartMC functions. For example, do not change the IP address of VLAN-interface 1 or disable Telnet on members. |
Bulk management includes the following functions:
· Bulk configuration file backup—You can use the following methods to back up the configuration file on the commander and members:
¡ Automatic backup—Enable this feature for the commander and all members in the network to immediately perform a backup. After that, the commander and members back up the configuration file at a user-specified interval.
¡ Manual backup—Manually trigger a backup on specified members.
During a backup, a member saves its running configuration to the local configuration file, uploads the file to the file server, and then deletes the local file.
· Bulk configuration deployment—Allows you to deploy multiple command lines to members from the commander, eliminating the need to log in to members and configure the commands one by one. The procedure is as follows:
a. The commander acts as a Telnet client and establishes Telnet connections to the members.
b. The commander deploys a batch file to the members through Telnet connections and records the deployment result. The batch file is created on the commander and contains command lines to be deployed.
Application scenarios
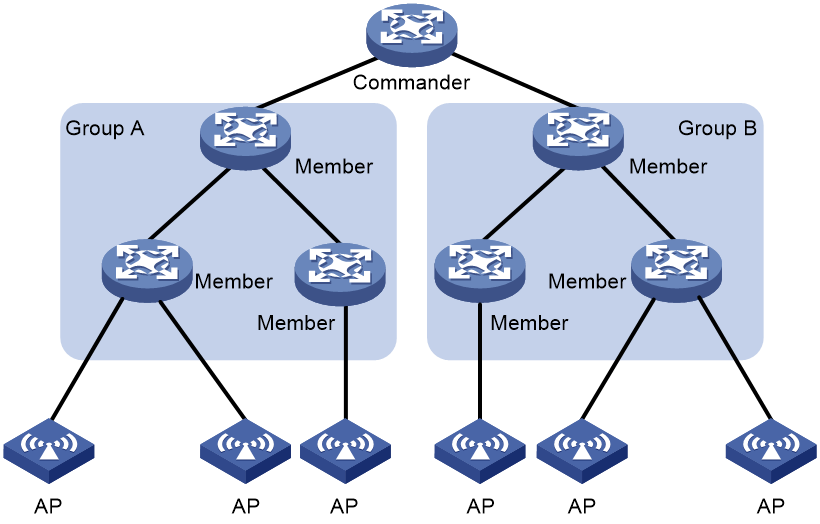
As shown in Figure 4, create SmartMC groups A and B, add member devices to the groups, and configure the commander to manage members by SmartMC group.
You can log in to the Web interface of the commander and perform the following tasks:
· View information about all members.
· Fast configure member settings, such as port authentication, VLAN settings, and resource monitoring.
· View wired and wireless devices in the SmartMC network on the SmartMC > Visibility > Topology page.
· Manage PoE power and basic wireless settings of the whole SmartMC network.