- Released At: 12-05-2025
- Page Views:
- Downloads:
- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
|
|
|
|
|
RBAC Technology White Paper |
|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2021 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
This document provides generic technical information, some of which might not be applicable to your products.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Overview
Role-based access control (RBAC) controls access to items and system resources in a network device based on user roles. Examples of items are commands, Web pages, XML elements, and MIB nodes. Examples of system resources include interfaces, VLANs, VPN instances, security zones, and locations. This document describes basic ideas and H3C implementation of RBAC.
Technical background
Modern networks are typically virtualized, unified, and complex. They require more granular and flexible control of access to network devices than traditional user-based access control management.
In the traditional access control model, the network system is predefined with a set of user levels, with each level mapped to a set of access permissions. Users are assigned a user level to gain access permissions. This access control model is rigid and cannot provide the granular role-based access control required on modern networks.
RBAC improves user access control efficiency and reduce permission management and maintenance costs. It assigns access permissions to user roles that are created for different job responsibilities. Users are given permission to access a set of items and resources based on their user roles.
Benefits
RBAC delivers the following benefits:
· Flexibility in permission and privilege assignment—By separating permissions from users, RBAC enables easy permission authorization management. You only need to change user role permissions, remove user roles, or assign new user roles when the job responsibilities of users change.
· Control of access to system resources—RBAC uses resources access policies to specify which interfaces, VLANs, VPNs, security zones, and locations are accessible to user roles.
RBAC implementation
Concepts
Account
With Comware, you create user accounts and assign attributes to the accounts for user authentication and authorization. User accounts include the following types:
· Device management account—Users use a device management account to log in to the network device for device configuration and management.
· Network access account—Users use this account to access network resources through the device.
RBAC controls access to devices by managing device management accounts.
Action
An operation performed by a user on the system. For example, the user configures a feature from the CLI or an SNMP manager, or display device running status from the Web interface.
Command types
The following are types of commands in Comware:
· Read—Commands that display configuration and running information.
· Write—Commands that configure the system.
· Execute—Commands that execute specific functions. Examples include the ping command and the ftp command. Such commands do not affect system running status.
Feature
A set of commands related to a function. For example, OSPF feature contains all OSPF configuration, displaying, and debugging commands.
Feature group
A set of features. Use feature groups to bulk assign command access permissions to sets of features.
Role
A user role with permission assigned includes a set of rules and resource access policies. The rules specify commands, Web pages, XML elements, and MIB nodes accessible or inaccessible to the role. The policies specify which interfaces, VLANs, VPNs, security zones, and locations are accessible to the role.
Rule
User role rules permit or deny access to commands, Web pages, XML elements, and MIB nodes. You can define the following types of rules for different access control granularities:
· Command rule.
· Feature rule.
· Feature group rule.
· Web menu rule.
· XML element rule.
· OID rule.
For more information, see "Access control granularities."
A user role can have multiple rules uniquely identified by rule numbers. The set of permitted commands, Web pages, XML elements, and MIB nodes in these rules are accessible to the user role.
The following guidelines apply to non-OID rules:
· If two user-defined rules of the same type conflict, the rule with the higher ID takes effect. For example, a user role can use the tracert command but not the ping command if the user role contains rules configured by using the following commands:
¡ rule 1 permit command ping
¡ rule 2 permit command tracert
¡ rule 3 deny command ping
· If a predefined user role rule and a user-defined user role rule conflict, the user-defined user role rule takes effect.
The following guidelines apply to OID rules:
· The system compares an OID with the OIDs specified in user role rules, and it uses the longest match principle to select a rule for the OID. For example, a user role cannot access the MIB node with OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.141.3.0.1 if the user role contains rules configured by using the following commands:
¡ rule 1 permit read write oid 1.3.6
¡ rule 2 deny read write oid 1.3.6.1.4.1
¡ rule 3 permit read write oid 1.3.6.1.4
· If the same OID is specified in multiple rules, the rule with the higher ID takes effect. For example, a user role can access the MIB node with OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.141.3.0.1 if the user role contains rules configured by using the following commands:
¡ rule 1 permit read write oid 1.3.6
¡ rule 2 deny read write oid 1.3.6.1.4.1
Resource access policy
Resource access policies control access of user roles to system resources and include the following types:
· Interface policy—Controls access to interfaces.
· VLAN policy—Controls access to VLANs.
· VPN instance policy—Controls access to VPNs.
· Security zone policy—Controls access to security zones.
· Location policy—Controls access to locations.
Mechanism
User role assignment
You assign access rights to a user by assigning a minimum of one user role.
Depending on the authentication method, user role assignment has the following methods:
· AAA authorization—If scheme authentication is used, the AAA module handles user role assignment.
¡ If the user passes local authorization, the device assigns the user roles specified in the local user account.
¡ If the user passes remote authorization, the remote AAA server assigns the user roles specified on the server.
· Non-AAA authorization—When the user accesses the device without authentication or by passing password authentication on a user line, the device assigns user roles specified on the user line.
Permission assignment
The users can use the collection of items and resources accessible to all user roles assigned to the user. The system obtains the system configuration based on the user role, and forms a user role rule table and a resource access policy table.
· A user role rule includes rule ID, permission (permit or deny), rule type (CLI, Web, XML, or SNMP), command type (read, write, or execute), and rule content.
· A resource access policy includes resource type (VLAN, interface, VPN, security zone, or location), permission (permit or deny), resource identification (VLAN ID, interface name, VPN name, security zone name, or location identifier).
A user that logs in with a user role has the two tables, and the collection of items and resources are accessible to the role assigned to the user.
To use a command related to a specific interface, VLAN, VPN, security zone, or location, a user role must have access to both the command and the interface, VLAN, VPN, security zone, or location. For example, a user role has access to the qos apply policy command and access only to interface Ethernet 1/1. When the user role is assigned, you can enter the interface view and use the qos apply policy command on the interface. However, you cannot enter the view of any other interface or use the command on any other interface. If the user role has access to any interface but does not have access to the qos apply policy command, you cannot use the command on any interface.
Role-based access control
When a user operates at the CLI or through other tools, the system looks up the user role rule table for the permissions assigned to the user. Both the user role rule table and the resource access policy table define the permissions to specific resources. The following describes the process:
1. The system detects that the user entered a command, for example, vlan 1.
2. The system performs a rule table lookup.
a. The lookup starts from the rule with the highest ID. The system does not stop searching until it finds a command rule.
b. The system compares vlan 1 with the regular expression of the rule content. If it matches, the system returns the permission to the user. If it does not match, it continues searching the next rule.
3. If the return permission is operation permitted, the system looks up the resource access policy table.
The vlan 1 command is to operate the VLAN resources, so the system checks the resource control entry of the VLAN type.
¡ If VLAN 1 is permitted, the vlan 1 command is permitted.
¡ If VLAN 1 is denied, the system denies executing the vlan 1 command, and it returns the message Permission denied.
4. If the return permission is operation denied, a message appears to notify the user of Permission denied.
Comware implementation of RBAC
Predefined user roles
The system provides multiple predefined user roles. All these user roles have access to all system resources (interfaces, VLANs, VPNs, security zones, and locations). However, their access permissions differ, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Predefined roles and permissions matrix
|
User role name |
Permissions |
|
network-admin |
Accesses all features and resources in the system, except for the security log file management-related commands. |
|
network-operator |
· Accesses the display commands for all features and resources in the system, except for some display commands (including display history-command all and display security-logfile summary). To display all accessible commands of the user role, use the display role command. · Changes between MDC views. · Enables local authentication login users to change their own passwords. · Accesses the command used for entering XML view. · Accesses all read-type Web menu items. · Accesses all read-type XML elements. · Accesses all read-type MIB nodes. |
|
mdc-admin |
Accesses all features and resources in the administered MDC, except for the following features: · Commands for security log file management. · Features available only on the default MDC. |
|
mdc-operator |
· Accesses the display commands for all features and resources available in the administered MDC, except for some display commands (including the display history-command all and display security-logfile summary commands and the display commands available only on the default MDC). To display all accessible commands of the user role on the managed MDC, use the display role command. · Enables local authentication login users to change their own passwords. · Accesses the command used for entering XML view. · Accesses all read-type Web menu items. · Accesses all read-type XML elements. · Accesses all read-type MIB nodes. |
|
level-n (n = 0 to 15) |
· level-0—Has access to diagnostic commands, including ping, tracert, ssh2, telnet, and super. Level-0 access rights are configurable. · level-1—Has access to the display commands of all features and resources in the system except display history-command all. The level-1 user role also has access rights of the user role level-0. Level-1 access rights are configurable. · level-2 to level-8, and level-10 to level-14—Have no access rights by default. Access rights are configurable. · level-9—Has access to all features and resources except those in the following list. If you are logged in with a local user account that has a level-9 user role, you can change the password in the local user account. Level-9 access rights are configurable. ¡ RBAC non-debugging commands. ¡ Local users. ¡ MDCs. ¡ File management. ¡ Device management. ¡ The display history-command all command. · (MDC- and context-incapable devices.) level-15—Has the same rights as network-admin. · (MDC-capable devices.) level-15—Has the same rights as network-admin on the default MDC, and has the same rights as mdc-admin on non-default MDCs. (Context-capable devices.) level-15—Has the same rights as network-admin on the default context, and has the same rights as context-admin on non-default contexts. |
|
security-audit |
Security log manager. The user role has the following access rights to security log files: · Accesses to commands for security log file management. · Accesses to commands for security log file operations. For example, use the more, dir, and mkdir commands to operate security log files. Only the security-audit user role has access to security log files. Other user roles cannot access security log files. You cannot assign the security-audit user role to non-AAA authentication users. |
|
guest-manager |
Accesses only guest-related web pages, and has no access to commands. |
|
Accesses all features and resources in the managed context, except for the commands for security log file management. |
|
|
· Accesses the display commands for features and resources available in the administered context, except for some display commands (including display history-command all and display security-logfile summary). To display all accessible commands of the user role, use the display role command. · Enables local authentication login users to change their own passwords. · Accesses the command used for entering XML view. · Accesses all read-type Web menu items. · Accesses all read-type XML elements. · Accesses all read-type MIB nodes. |
|
|
system-admin |
System manager. The user role has the following access permissions: · Has read, write, and execute access permissions to the Web menus under the Summary category. · Has read, write, and execute access permissions to the System Logs Web menu under the Monitoring category. · Has the following access permissions under the System category: ¡ Has read access permissions to the Administrators and Roles Web menus. ¡ Has read, write, and execute access permissions to other Web menus. · Accesses the ping and tracert commands. To display detailed information about the access permissions of this user role, use the display role command. You cannot assign the system-admin user role to non-AAA authentication users. |
|
security-admin |
Security manager. The user role has the following access permissions: · Has read, write, and execute access permissions to Web menus under the Policies, Objects, and Network categories. · Has the following access permissions under the Monitoring category: ¡ Has no access permissions to the System Logs and Operation Logs Web menus. ¡ Has read, write, and execute access permissions to other Web menus. · Accesses the ping and tracert commands. To display detailed information about the access permissions of this user role, use the display role command. You cannot assign the security-admin user role to non-AAA authentication users. |
|
audit-admin |
Audit manager. The user role has the following access permissions: · Has read, write, and execute access permissions to the Operation Logs Web menu under the Monitoring category. · Accesses the ping and tracert commands. To display detailed information about the access permissions of this user role, use the display role command. You cannot assign the audit-admin user role to non-AAA authentication users. |
Flexible access control
Access control granularities
Command rule
A command rule controls access to a command or a set of commands that match a regular expression.
The permit or deny keyword specifies the access permission and the command-string argument specifies a command or a set of commands.
Feature rule
A feature rule controls access to the commands of a feature by command type.
The permit or deny keyword specifies the access permission. The feature-name argument specifies a feature. The execute, read, or write keyword specifies the execute, read, or write command of a feature. If no feature is specified, you specify all the features in the system.
Feature group rule
A feature group rule controls access to commands of a group of features by command type.
The permit or deny keyword specifies the access permission. The feature-group-name argument specifies a feature group. The execute, read, or write keyword specifies the execute, read, or write command of a feature group.
Use feature groups to bulk assign command access permissions to sets of features.
Web menu rule
A Web menu rule controls access to the Web pages used for configuring the device. These Web pages are called Web menus.
The permit or deny keyword specifies the access permission. The web-menu argument specifies the ID path of the Web menu. The execute, read, or write keyword specifies the execute, read, or write operation of the menu. If no Web menu is specified, you specify all Web menus in the system.
XML element rule
An XML element rule controls access to the XML elements used for configuring the device.
The permit or deny keyword specifies the access permission. The xml-path argument specifies the Xpath of an XML element. The execute, read, or write keyword specifies the execute, read, or write operation of an XML element. If no path is specified, you specify all XML elements in the system.
OID rule
An OID rule controls SNMP access to a MIB node and its child nodes.
The permit or deny keyword specifies the access permission. The oid-string argument represents the OID. The execute, read, or write keyword specifies the execute, read, or write operation of a MIB node.
Access control to file system
You can configure a feature rule with the filesystem keyword to control access to the file system at the CLI.
Access to the file system commands is controlled by both the file system command rules and the system feature rules.
Access control of read and write to the file system affects the upload and download operation permission for FTP users.
A command with output redirection to the file system is permitted only when the command type write is assigned to the file system feature.
User role assignment methods
Assigning user roles to remote AAA authentication users
An AAA authentication user must have a minimum of one user role to log in to the device.
The default user role feature enables a remote AAA authenticated user that has not been assigned any user role to log in with a default user role. The default user role is configurable.
User roles are configured on the authentication server. For information about configuring user roles for RADIUS users, see the RADIUS server documentation. For HWTACACS users, the role configuration must use the roles="role-1 role-2 … role-n" format, where user roles are space separated. For example, configure roles="level-0 level-1 level-2" to assign level-0, level-1, and level-2 to an HWTACACS user.
Assigning user roles to local AAA authentication users
Configure user roles for local AAA authentication users in their local user accounts. Every local user has a default user role. If this default user role is not suitable, delete it.
Assigning user roles to non-AAA authentication users on user lines
Specify user roles for the following types of login users on the user lines:
· Users that use password authentication or no authentication.
· SSH clients that use publickey or password-publickey authentication. User roles assigned to these SSH clients are specified in their local management user accounts.
Temporary user role authorization
Temporary user role authorization allows you to obtain a temporary user role without reconnecting to the device. This feature is useful when you want to use a user role temporarily to configure a feature.
Temporary user role authorization is effective only on the current login. It does not change the user role settings in the user account that you have been logged in with. The next time you are logged in with the user account, the original user role settings take effect.
Application scenario
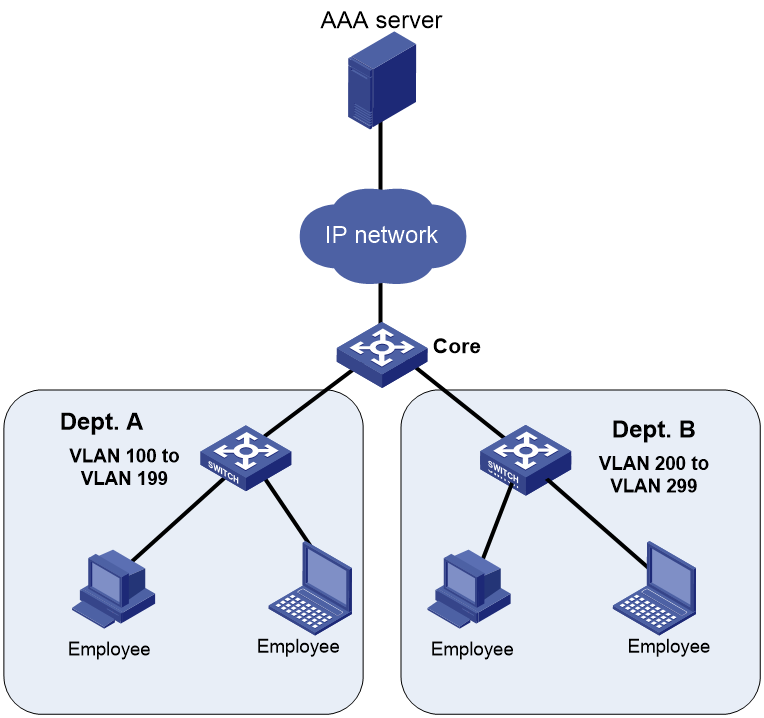
As shown in Figure 1, the core switch uses a FreeRADIUS server to provide AAA service for login users. Department A and Department B are in different VLANs.
Configure RBAC to make sure the department network administrators can deploy QoS polices for traffic control on the core device.
· Configure user roles that have different access permissions on the core device.
· Use the AAA server to assign the user roles to the department network administrators.
The user roles have the following access permissions:
· Network administrator user role depart-admin can configure traffic control policies on the core device.
· Resource control user role departA-resource of Department A can configure VLAN 100 to VLAN 199.
· Resource control user role departB-resource of Department B can configure VLAN 200 to VLAN 299.
On the AAA server, assign user roles depart-admin and departA-resource to the network administrator for Department A, and assign user roles depart-admin and departB-resource to the network administrator for Department B.