- Released At: 27-04-2022
- Page Views:
- Downloads:
- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
H3C Doctor AP Technology White Paper
Copyright © 2022 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Overview
Background
As WLAN network issues grow with deployment of WLANs, fast network failure restoration and lowering Ops costs have become a great concern.
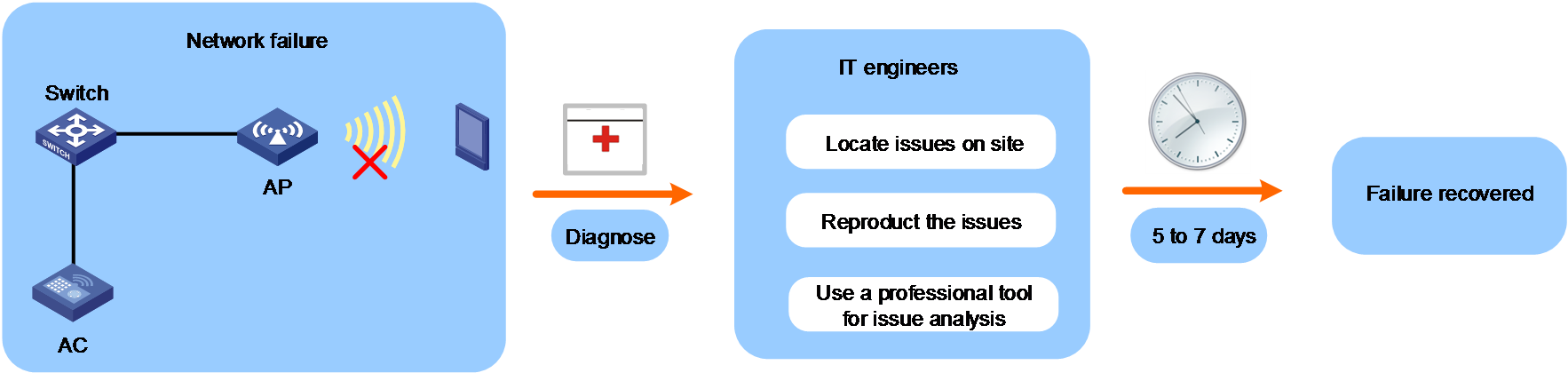
Traditional network Ops
Traditional network Ops requires network maintenance engineers to locate issues on site when network failures occur, which increases cost and maintenance period. In addition, traditional network issue location methods only locate network issues by AP rather than by client, and cannot reflect the network access behaviors of clients.
Figure 1 Traditional network Ops
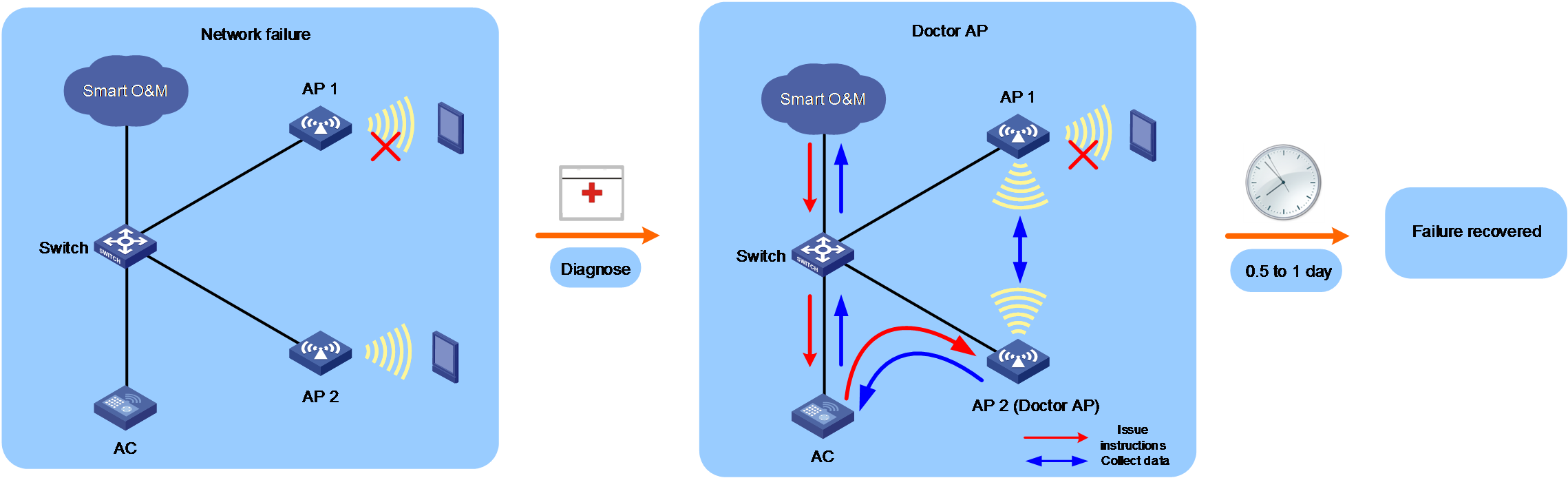
Doctor AP
The Doctor AP feature uses an online AP to simulate client association process to check the network health, including WLAN access, network connectivity, and app performance.
1. During the association process, the Doctor AP will record the packet exchange duration.
2. After associating with an AC, the Doctor AP does some network detection operations such as app and webpage access.
3. After the test finishes, the Doctor AP reports the result to the cloud platform. You can troubleshoot the network based on the detection result.
The Doctor AP feature collects network failure information through the cloud platform and performs AI-powered analysis, helping fast restoration of the network with lost cost and short restoration period.
Figure 2 Doctor AP
Benefits
The Doctor AP feature offers the following benefits:
· Detects network issues and reports the detection results to the cloud platform for administrators to troubleshoot the network. No additional devices are required.
· Simulates Internet access behaviors and reports the behaviors to the cloud platform, which can display packet exchange latency, packet loss rate, and clients’ access to applications.
· Supports one-off or scheduled detection of the WLAN to provide better user experience.
· Supports both automatic and manual selection of a Doctor AP based on the network condition.
· Supports key AP configuration. After an AP is selected as a Doctor AP, clients associated with that AP will be disconnected. Key APs will not be selected as Doctor APs.
· With alarm pushing enabled, the system generates an alarm every time it detects a failed SSID.
· Supports custom diagnostic items for users to select as needed.
Implementation
Concepts
· Automatic detection—The cloud platform selects an idle AP as the Doctor AP, and the Doctor AP detects the APs within the specified range immediately or periodically. Alarm pushing and key AP configuration are supported.
· Manual detection—Includes intelligent mode and manual mode.
¡ Intelligent—The cloud platform selects an idle AP as the Doctor AP, and the Doctor AP detects the APs within the specified range immediately or periodically. Alarm pushing and key AP configuration are supported.
¡ Manual—You select a Doctor AP and performs network detection on the specified APs or SSIDs.
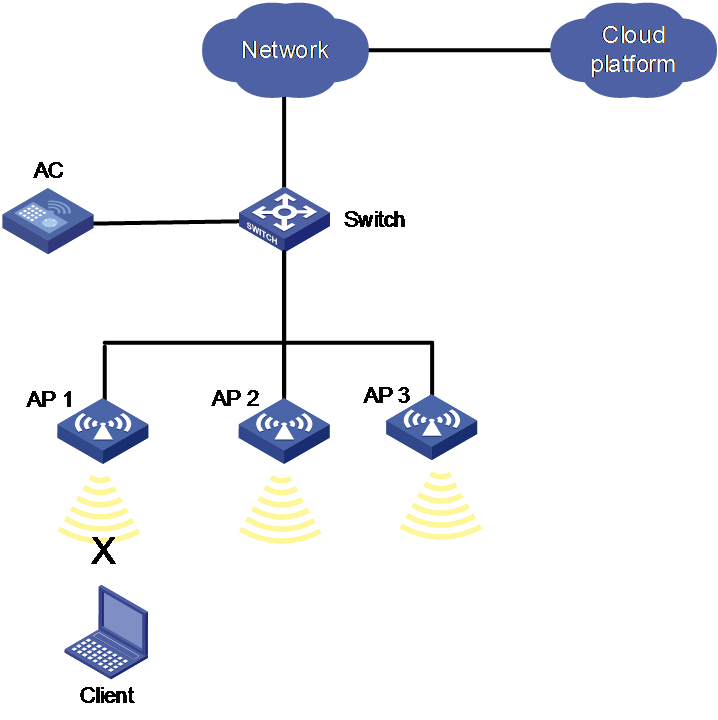
Application scenarios
As shown in Figure 3, if clients cannot associate with AP 1 or can associate with AP 1 but cannot access the WLAN, you can select AP 1 as the detected AP. The system will automatically select a neighbor AP as the doctor AP (for example, AP 2) to simulate client association to the WLAN and report the result to the cloud platform.
Alternatively, you can configure scheduled network inspection for the system to automatically detect the network health for all detected APs bound to the AC.
Procedure
When a network failure occurs, you can enable Doctor AP mode for an AP from the cloud platform for the AP to perform fault detection on wireless services and report the result to the cloud platform.
Network inspection by Doctor AP uses the following procedure:
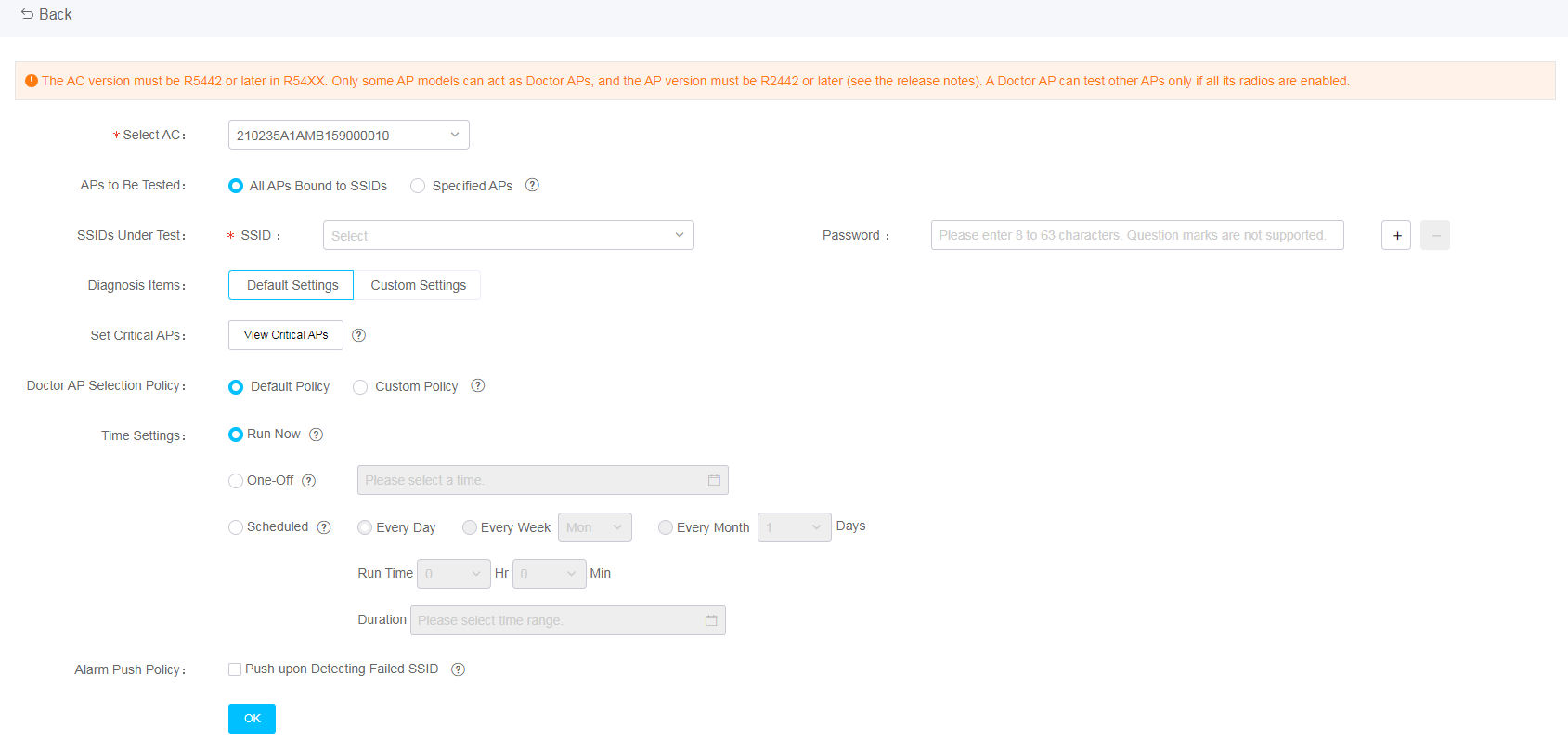
1. The network administrator configures basic test template information, including the test start time, SSID to be tested, and Doctor AP selection policy.
Figure 4 Configuring detection settings
2. After the AC is connected to the cloud platform, it selects an AP as the doctor AP based on the test template. A Doctor AP does not provide wireless services during the detection process, and it resumes providing services after the detection finishes.
3. The Doctor AP starts detection based on the deployed template, simulates client association, and records the packet type and latency during the association process. After associating with the AC, the Doctor AP starts application testing, records the test result, and reports the result to the cloud platform after the test finishes.
4. The network administrator performs the following operations:
a. On the Summary page, view the test result.
b. On the Auto Test Result or Manual
Test Result page, click ![]() to expand test
information. To view detailed test information, including WLAN access, DHCP,
DNS, Ping, and HTTP, click Details.
to expand test
information. To view detailed test information, including WLAN access, DHCP,
DNS, Ping, and HTTP, click Details.
- WLAN access—Checks authentication configuration and checks for available wireless service based on the time required to associate with WLAN, test details, and packet exchanges.
- DHCP—Checks DHCP server configuration based on the address allocation duration, test details, and packet exchanges.
- DNS—Checks the DNS server configuration based on the DNS duration, test details, and test result.
- Ping—Checks the ping destination host set in the diagnostics template and checks for network congestion caused by large number of broadcast packets based on the packet loss rate, test details, and test result.
- HTTP—Checks the HTTP destination host set in the diagnostics template based on the round trip delay, test details, and test result.