- Released At: 19-12-2020
- Page Views:
- Downloads:
- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
|
|
|
Dual-Link Backup |
|
Technology White Paper |
|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2020 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Overview
Background
In an AC+fit AP network, the AC is responsible for AP data maintenance, service calculation, and decision making, as well as data forwarding if centralized forwarding is configured. Failure of the AC can interrupt services in the entire network. To avoid single points of failure, you can deploy dual-link backup to provide AP-based link backup, AC failover, and service failback.
Benefits
Dual-link backup provides the following benefits:
· AC failover—Enables the backup AC to fast take over services upon a master AC failure. After the failed AC recovers, the AC can act as the new backup AC for the next master AC failure.
· Service failback—Enables APs to always prefer the AC that has a higher AP connection priority. This allows services to be automatically switched back to the recovered master AC after failover.
· Load balancing—Enables the two ACs to share AP management and traffic forwarding workloads, helping maintain the optimal AC performance and improve network stability and reliability. With load balancing configured, AC failover and service failback still take effect.
· Load migration—Allows you to fast migrate specific APs to the specified AC with a short service interruption when both ACs are operating correctly.
· Flexible expansion—Supports flexible expansion to up to five ACs, of which four provide wireless services and one acts as the backup.
· NAT traversal networking—Allows ACs and APs to be connected through the public network over NAT devices, freeing networking from physical location limits.
· License synchronization—Supports the following license synchronization methods:
¡ Direct license synchronization among ACs in the network.
¡ Unified license allocation through a license server.
Failure of an AC does not affect license synchronization among other ACs.
Dual-link backup implementation
Concepts
· AC role—Includes master AC and backup AC. The master AC is responsible for AP configuration deployment and AP management. An AC can act as the master AC for one AP and the backup AC for another AP.
· Master tunnel and backup tunnel—Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Point (CAPWAP) tunnels established between AP and AC to provide data encapsulation and transmission. The tunnel established with the master AC is the master tunnel and the tunnel established with the backup AC is the backup tunnel. An AP establishes a backup CAPWAP tunnel only after establishing the master tunnel.
Restrictions and guidelines
Make sure service settings, except for dual-link backup settings such as AP connection priority and backup AC IP address, are the same on the master AC and the backup AC.
Commands that require immediate AP processing do not take effect on the backup AC, for example, image downloading, file deletion, or log retrieval commands.
Backup tunnel establishment
To configure dual-link backup, you must specify a backup AC for the master AC.
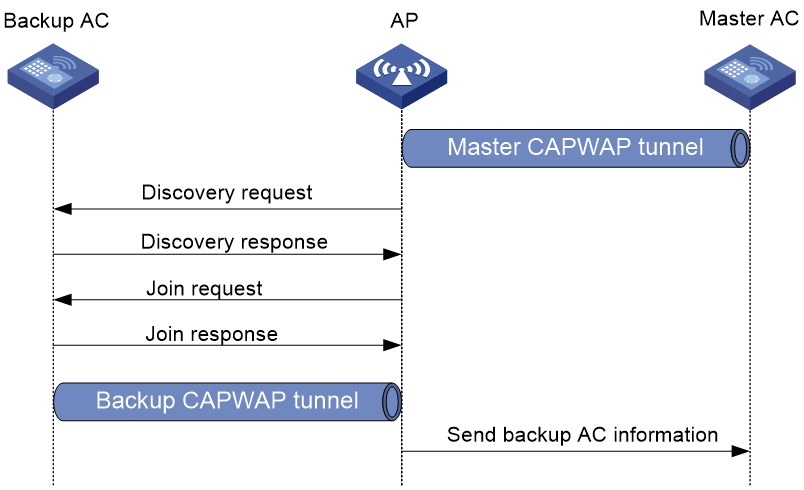
As shown in Figure 1, an AP establishes a backup tunnel as follows:
1. After establishing the master tunnel, the AP obtains the IP address of the specified backup AC from the master AC.
2. The AP exchanges discovery and join messages with the backup AC and then establishes a backup tunnel.
3. The AP sends backup AC information to the master AC.
Figure 1 Establishing a backup tunnel
You can view backup tunnel and AP information from the backup AC and configure AP settings. However, settings on the backup AC, except for CAPWAP tunnel settings, do not take effect until the backup AC becomes the master AC. APs are always managed by the master AC.
Master/backup switchover
APs send keepalive packets to the master AC at specific intervals to detect tunnel connectivity. Upon detecting network errors, the AP triggers a master/backup switchover. A network error can occur if the master AC fails or a user manually logs off the AP. The switchover operates as follows:
1. The AP notifies the backup AC of the master tunnel failure.
2. Upon receiving the notification, the backup AC synchronizes data between service modules, changes its role to master, and then notifies the AP of the switchover.
3. The AP destroys the master tunnel data block, uses the backup tunnel data block as the master tunnel data block, and synchronizes data between service modules.
4. After the switchover, the new master AC takes over services and issues configurations to the AP.
5. If the new master AC has a backup AC, the AP attempts to establish a backup tunnel with the backup AC.
Tunnel preemption
This feature enables a backup CAPWAP tunnel to become a master tunnel even if the master tunnel operates correctly. An AP prefers to establish a master tunnel with the AC that has a higher AP connection priority.
Master CAPWAP tunnel preemption operates as follows:
1. After establishing the backup CAPWAP tunnel, the AP compares the AP connection priority configured on the master AC and the backup AC. If the backup AC has a higher priority, the AP sends a disassociation request to the master AC.
2. The master AC destroys the tunnel data block, terminates the tunnel, and synchronizes data between service modules to log off the AP.
3. The AP triggers a master/backup switchover. For more information, see "Master/backup switchover."
Application scenarios
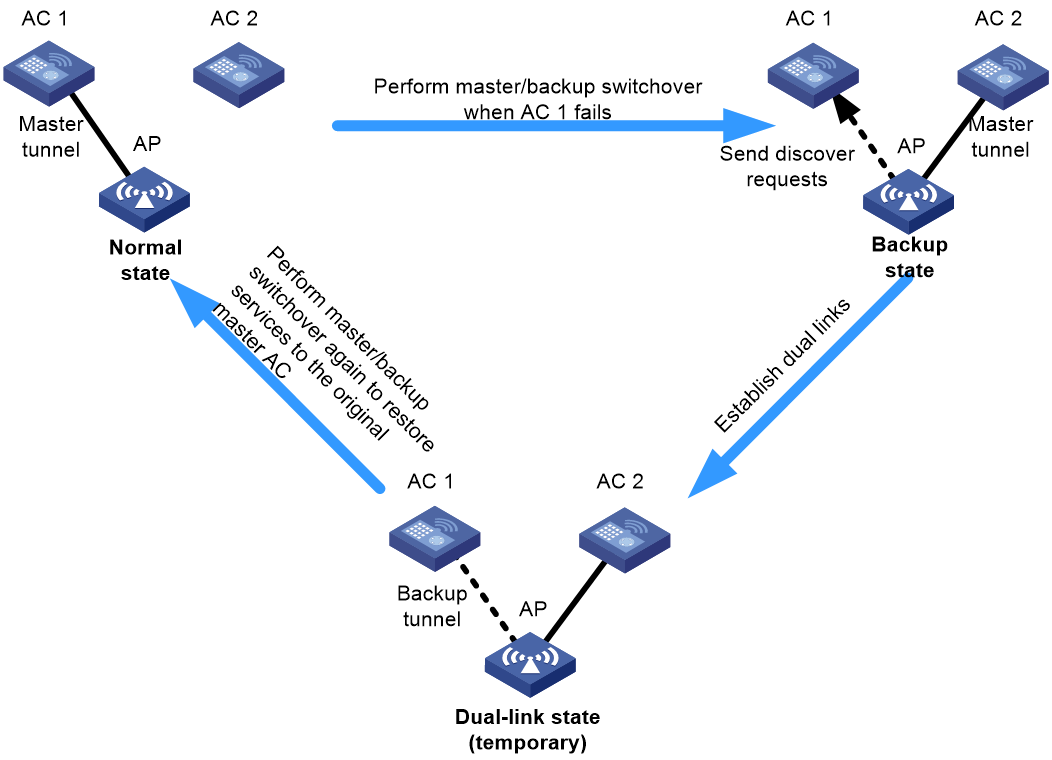
Master/backup
To provide high availability, deploy two ACs with one AC as the master and the other as the backup, specify a higher AP connection priority for the master AC, and enable tunnel preemption on the master AC.
In this network, the maximum number of supported APs depends on the AC that has the lower AP capacity.
Figure 2 Master/backup
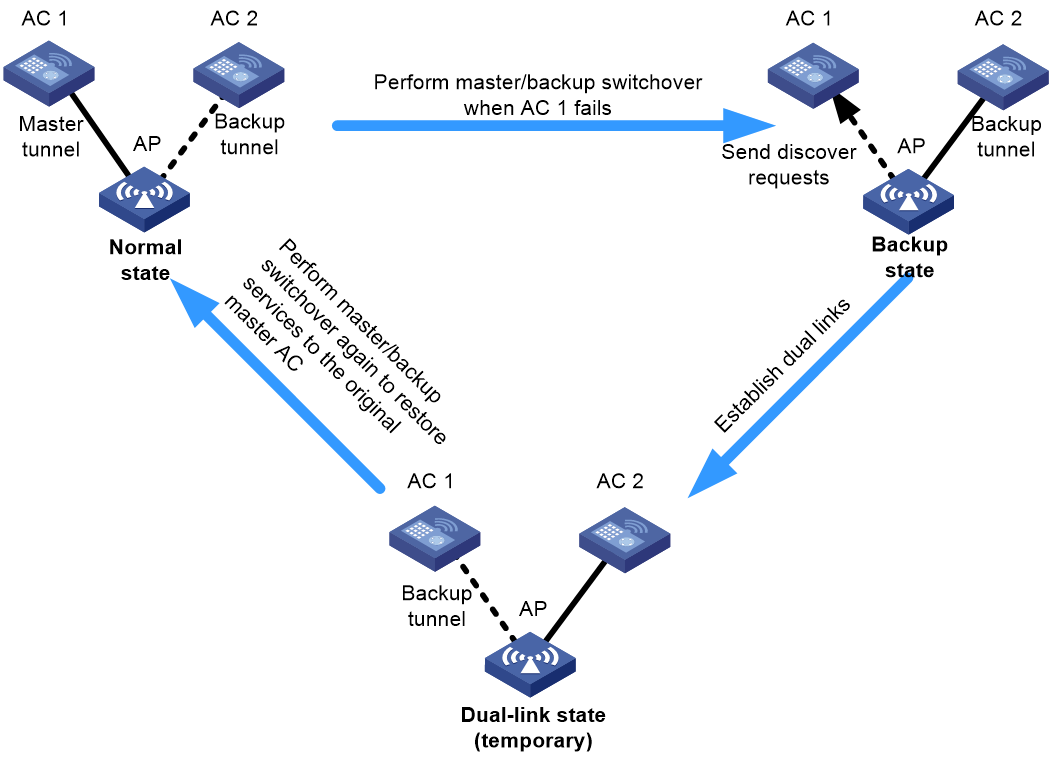
Active/active failover
To provide high availability and improve the AC failover speed, deploy two ACs and configure them to back up each other. Specify a higher AP connection priority on one AC (AC 1 in this example) and enable tunnel preemption on the AC.
In this network, the maximum number of supported APs depends on the AC that has the lower AP capacity.
Figure 3 Active/active failover
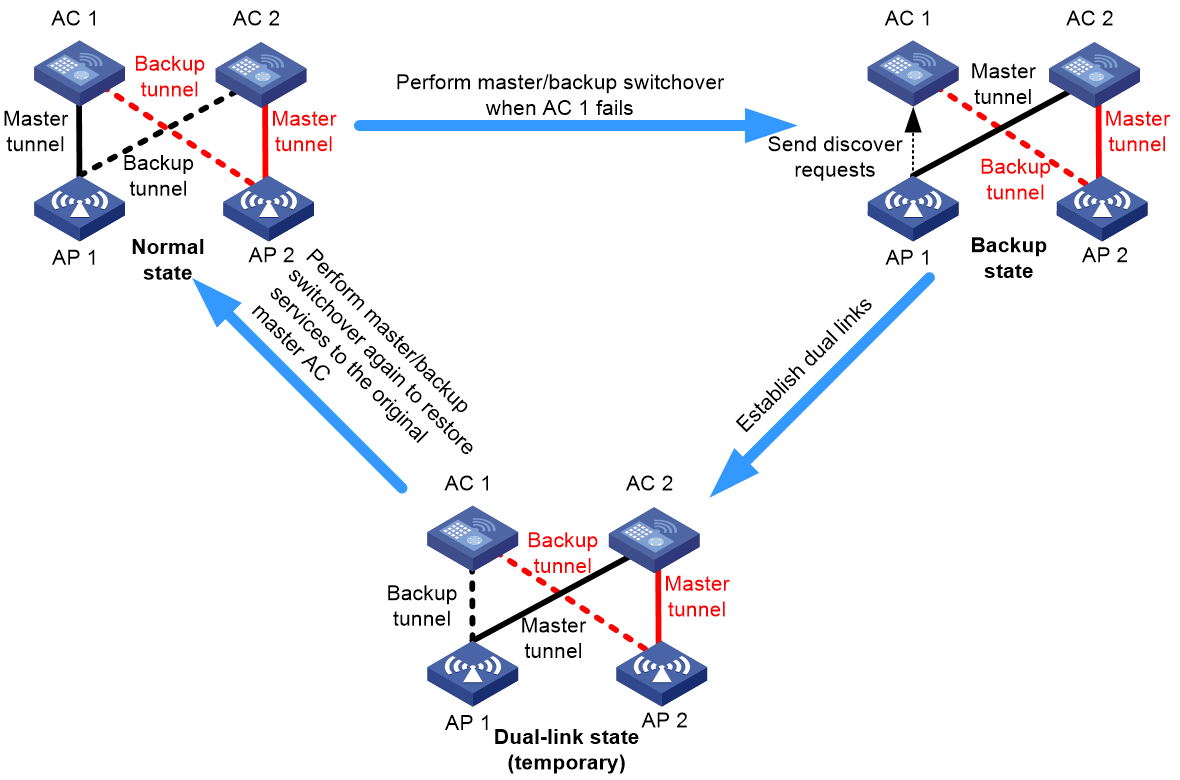
Load sharing
To provide high availability and load balancing, configure two ACs to back up each other, create two AP groups, and specify a higher AP connection priority for one group on AC 1 and a higher priority connection for the other group on AC 2. Enable tunnel preemption on both ACs.
In this network, the maximum number of supported APs depends on the AC that has the lower AP capacity.
Figure 4 Load sharing
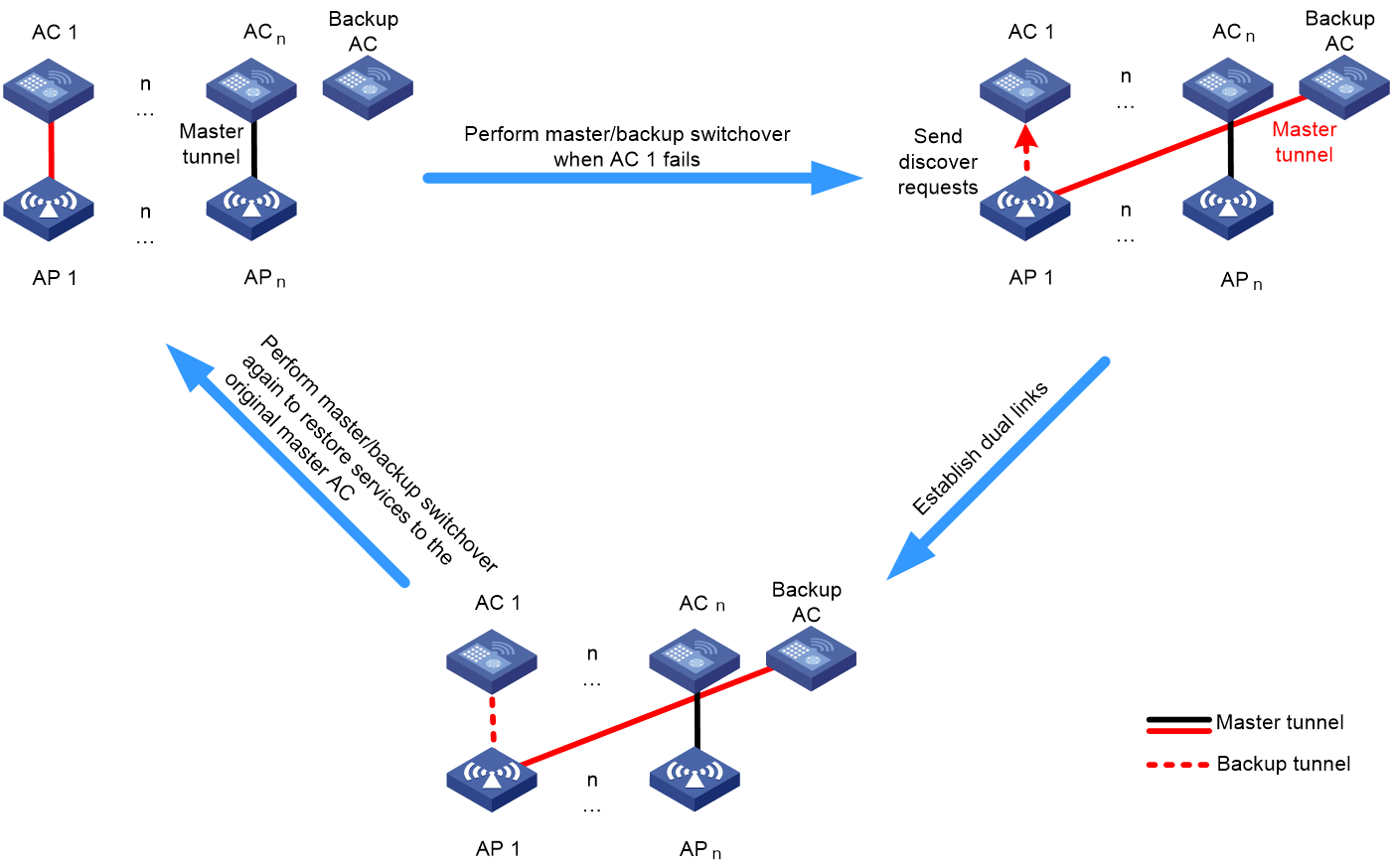
N+1 backup
In a network with three to five ACs, you can configure N+1 AC backup to provide load balancing and high availability.
N+1 backup allows only one AC to act as the backup AC and the other ACs to act as master ACs. Make sure the number of associated APs on each master AC does not exceed the maximum number of supported APs on the backup AC.
To configure N+1 backup:
1. Create an AP group on each master AC, and specify the highest AP connection priority for one master AC. Enable tunnel preemption on the ACs.
2. On the backup AC, configure all APs and AP groups. For an AP group, specify its master AC as the backup AC and set the connection priority to be smaller than the priority on the master AC. This enables APs to switch back to the master AC after the master AC recovers.
Figure 5 N+1 backup