| Title | Size | Downloads |
|---|---|---|
| H3C All-Optical Network Technology White Paper-6W100-book.pdf | 1.35 MB |
- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| book | 1.35 MB |
|
|
|
H3C |
|
All-Optical Network Technology White Paper |
|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2023 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is for generic use, some of which may not apply to the product you have purchased.
Contents
H3C all-optical (iOptic) network solution
iOptic Ethernet network solution
EPON-based iOptic POL network solution
iOptic PON+Ethernet integrated network solution
iOptic GPON-based POL network solution
iOptic network deployment cases
iOptic PON+Ethernet network deployment in a high-school dormitory
iOptic Ethernet network deployment for smart classrooms
iOptic Ethernet network deployment in a smart hospital
About all-optical networks
Technical background
As the development of network technologies is driving the growth of the digital economy, all-optical networks are gradually becoming widespread. All-optical networks use optical signals to complete all network communication functions, eliminating the need for optical-electrical conversion within the network, thereby bypassing the challenge of improving the information processing rate of electronic devices. Compared to traditional copper cable networks, all-optical networks offer significantly improved performance. Furthermore, copper cables come with drawbacks such as subpar transmission performance, high costs, and complicated wiring. As a result, copper cable networks are progressively being rendered inadequate for managing the traffic generated by various emerging network applications like the Internet of Things, cloud services, and Wi-Fi 6.
Over the past decade, China has been progressively phasing out copper cable networks in favor of fiber through the copper-to-fiber transition project. There is growing support for all-optical network construction from departments at all levels. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has clearly stated in the issued Dual-Gigabit Network Collaborative Development Action Plan (2021-2023) that China aims to build a dual-Gigabit network infrastructure that will cover all urban areas and eligible towns within three years, thereby achieving "Gigabit to the household" capabilities on both fixed and mobile networks. The term “Dual Gigabit" refers to the Gigabit optical network and the 5G network, with the all-optical network being a vital part of it.
Application scenarios
The all-optical network solution can be widely applied in smart campuses, smart hospitals, hotels, and general parks.
· Smart campus—Research and teaching services.
· Smart hospital—Supporting healthcare service systems such as HIS, EMR, LIS, PACS, RIS, and telemedicine.
· Smart Hotel—One room multiple services, integrating broadband, Wi-Fi, TV, and telephone into one network.
· Universal campus applications—Network-wide roaming, security isolation, portal authentication, and operation billing.
Technical benefits
High transmission performance
All-optical networks use fiber as the transmission medium, which features long transmission distance, high speed, low attenuation, strong anti-interference capability, and long life cycle. It is an ideal material for improving the network speed.
· Long transmission distance—The transmission distances of Category 5 and Category 6 cables are typically within 100 m (328.08 ft), and single-mode fibers on 10 gigabit transceiver modules can achieve a transmission distance of up to 80 km (49.71 miles). This significantly longer transmission distance greatly broadens the scope of network connectivity.
· Low attenuation—For example, at a distance of 100 m (328.08 ft), the signal loss of a fiber optic is only 3% of the original signal strength, while the signal loss of a Category 6A copper cable at the same distance is approximately 94% of its original signal strength. The transmission loss of copper cables will also increase rapidly with the increase of signal frequency. Because of low attenuation, optical fibers are widely used for long-distance transmissions and remote backbone networks.
· High transmission rate—The transmission rate of optical fibers can achieve a single-wavelength transmission rate of over 1 Tbps, which is more than 1000 times that of Category 6 network cables (1 Gbps).
· Strong anti-interference capabilities and higher security—Ordinary network cables are significantly affected by electromagnetic interference.
· Long lifespan—The lifespan of optical fibers is typically 30 years, 3 to 4 times that of ordinary Ethernet cables.
Simple network structure, easy to maintain
The traditional network architecture is complex, typically with multiple networks in one campus. Ordinary copper cables have poor transmission performance, requiring additional network devices every hundred meters, weak current rooms, and air conditioning systems, making the network structure more complex and difficult to manage in the future.
All-optical networks have a simple architecture, and can offer the following benefits:
· Various services such as video, data, wireless, and voice can be transported on the same network, because fibers can transmit data of different rates and protocols.
· Fibers have a long transmission distance and wide coverage area, reducing use of relay devices, weak current rooms, and air conditioning systems.
· All-optical networks provide unified management and monitoring, with simple fault diagnosis and one-click replacement of faulty devices.
· Optical link and transceiver module fault diagnosis and transceiver module lifecycle prediction enable timely prediction and handling of transceiver module failures for easy management and maintenance.
Convenient deployment and upgrade
Traditional networks are slow in service provisioning and require a lengthy onboarding process. Deploying and maintaining various devices with different vendors and models and cables of varying thickness, weight, and transmission distance incur high costs. As network traffic grows, some cables might require frequent upgrades because of insufficient bandwidth.
All-optical network deployment is simple, with plug-and-play devices that enable automated deployment. Optical fibers offer high transmission bandwidth, low cost, and use only one-fifth of the volume of Ethernet cables, resulting in low deployment costs. Optical fibers have a long service life and can meet network bandwidth demands for the next 30 years with just one upgrade. Network upgrade can be done simply by replacement with modules that have higher interface rates or even transceiver modules, allowing for easy expansion.
H3C all-optical (iOptic) network solution
H3C has developed four solutions in response to the development trend of all-optical networks: iOptic Ethernet network solution, iOptic Passive Optical LAN (POL) network solution based on the Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON) technology, iOptic PON+Ethernet network solution, and iOptic POL network solution based on Gigabit-Capable Passive Optical Networks (GPON) technology. These solutions provide high bandwidth and low latency and make the networks easy to maintain and easy to scale. They enhance user experience with a simple network architecture and support further upgrades of the networks in the future.
iOptic Ethernet and iOptic POL networking solutions each have their own advantages. The iOptic PON+Ethernet network solution achieves integrated networking with both Ethernet switches and PON, allowing flexible deployment in various scenarios according to specific needs. All four solutions are designed to deliver substantial value to customers by meeting the demands of various services for high bandwidth, enhanced security, and high availability.
iOptic Ethernet network solution
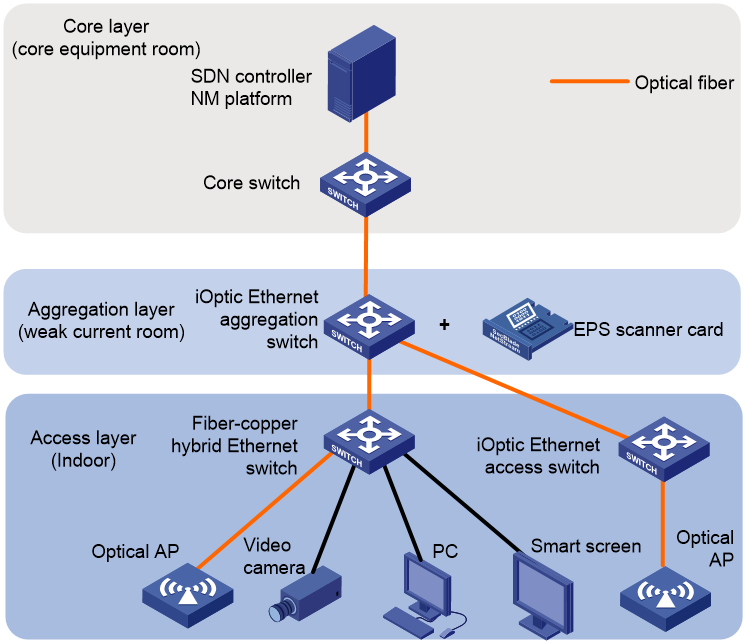
Figure 1 Typical iOptic Ethernet network
As shown in Figure 1, the iOptic Ethernet network solution provides high-bandwidth, low-latency network access services in scenarios such as classrooms, offices, hotel rooms, factory workshops, and dormitories.
· The all-in-one SDN appliance provides unified management of the all-optical network. By attaching an EPS scanner module to the iOptic Ethernet aggregation switch, you can view the network operations and endpoint access conditions from the information center and implement unified operation and maintenance. The unified operation and maintenance system can intelligently diagnose faults, analyze link quality, predict the lifecycle of transceiver modules, and ultimately enhance network quality.
· The iOptic Ethernet aggregation switch provides an uplink bandwidth of 10G/40G/100G, meeting the upstream bandwidth requirements in scenarios such as teaching.
· All-optical devices and optical APs can be deployed at the access side to provide wireless network access.
· Users can deploy also copper Ethernet switches according to their needs to enable mixed access of optical and copper endpoints.
· Access layer switches and APs are centrally powered, safe and reliable. This can ensure uninterrupted network service even in the event of a power outage in scenarios such as dormitories.
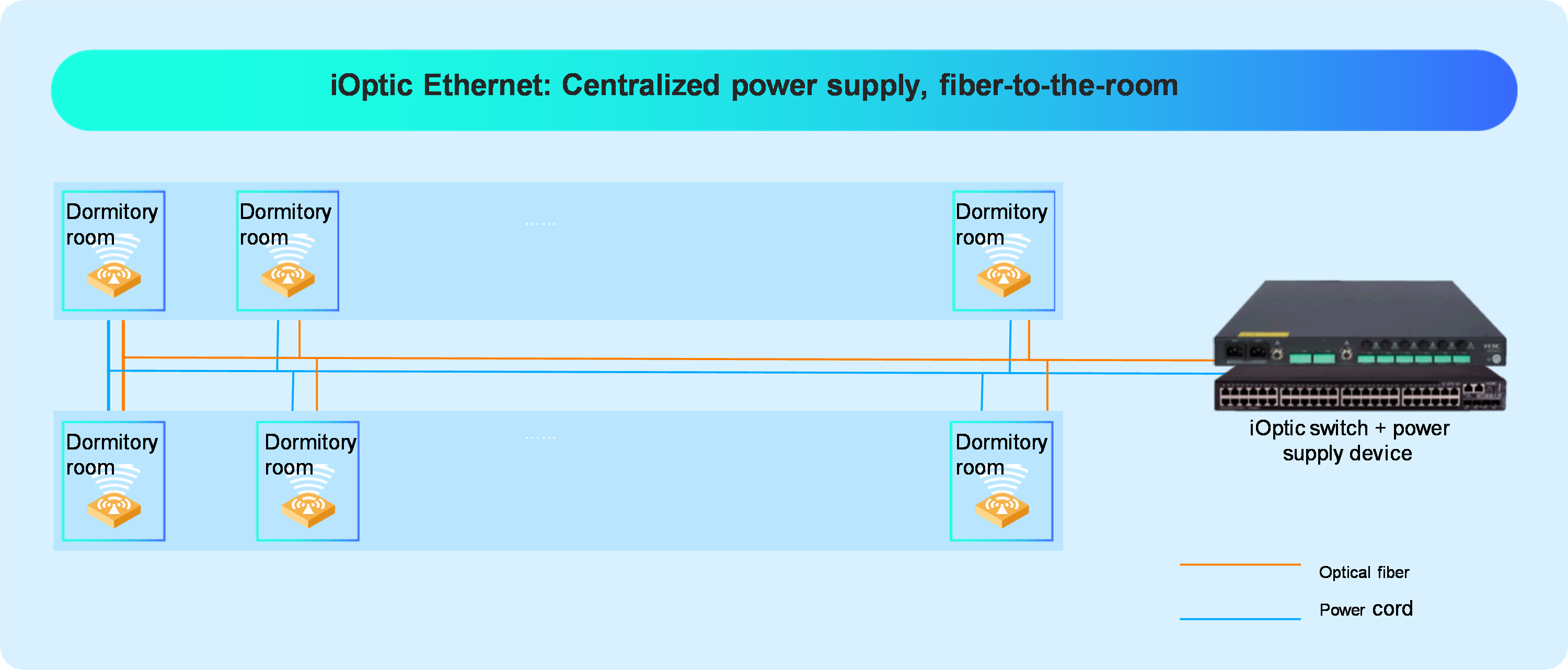
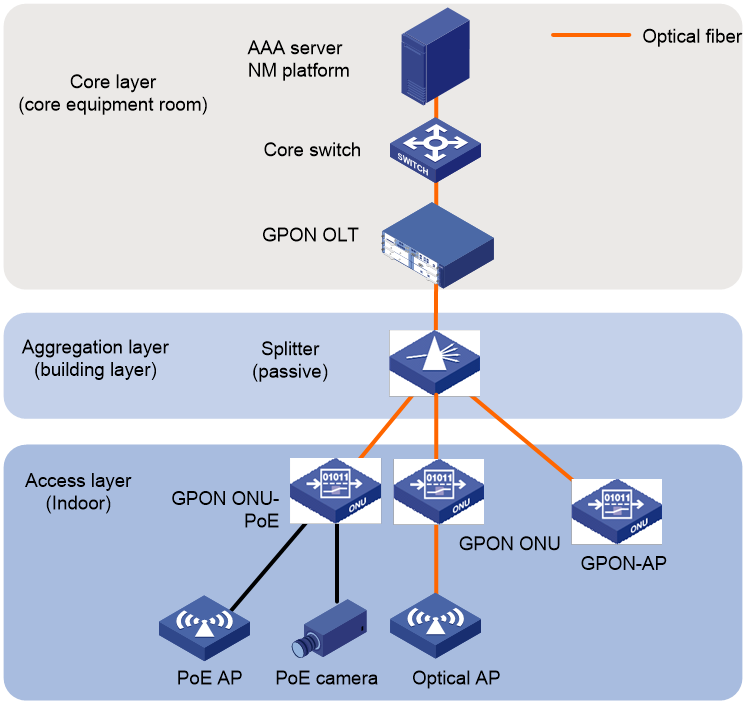
In a scenario such as a campus dormitory building where there is a high concentration of people and insufficient network resources, it is necessary to deploy an all-optical network. If the dormitory building faces issues such as limited space in the weak current room, limited power supply capacity, excessive building length, and tight space for the cable trays, you can deploy the iOptic Ethernet network as shown in Figure 2. Deploy a centralized power supply device to power iOptic switches and APs throughout the entire building and install iOptic APs in each room
Figure 2 IOptic Ethernet network solution with centralized power supply
EPON-based iOptic POL network solution
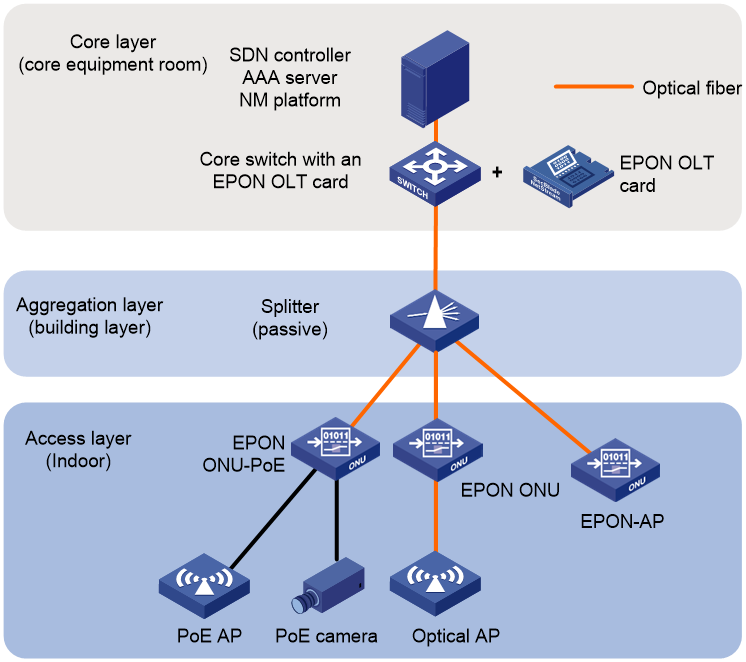
Figure 3 Typical EPON-based POL network solution
As shown in Figure 3, in the typical EPON-based POL network, the splitter does not require power supply and there is no need for air conditioning between devices. This solution is suitable for the deployment environments where the weak current room is small and difficult to reconstruct, and power delivery is difficult. This solution provides the following benefits:
· This solution does not require centralized power supply for aggregation and access layer devices, nor occupy space in the floor distribution equipment room. It is highly secure. Compared to the iOptic Ethernet network solution, it is easier to deploy.
· With the optical fiber entering the room, the EPON ONUs and APs draw power locally, eliminating the need for power cord deployment for centralized power supply. Users can deploy EPON ONUs with PoE power supply capabilities based on their actual needs, for power delivery to PoE-powered devices such as cameras and APs. This enables mixed access of optical and copper endpoints.
· Deployment of the EPON-AP (ONU integrated with AP) achieves wired-wireless integration.
· The switch with an EPON OLT card at the core layer can provide OLT functionality, integrating Ethernet and POL networks.
The iOptic POL solution without requiring centralized power supply is applicable to the scenario such as a dormitory building with the following conditions:
· People are highly concentrated but the network resources are insufficient.
· Weak current renovation is hard to implement.
· Centralized power supply for endpoints cannot be realized.
With the iOptic POL network solution as shown in Figure 4, fiber optic is brought into the room and an EPON-AP is deployed in each room, achieving wired and wireless integration. The optical splitter is deployed in the telecommunications closet, eliminating the need for separate equipment room space and subsequent management and maintenance.
Figure 4 Typical POL network endpoints
iOptic PON+Ethernet integrated network solution
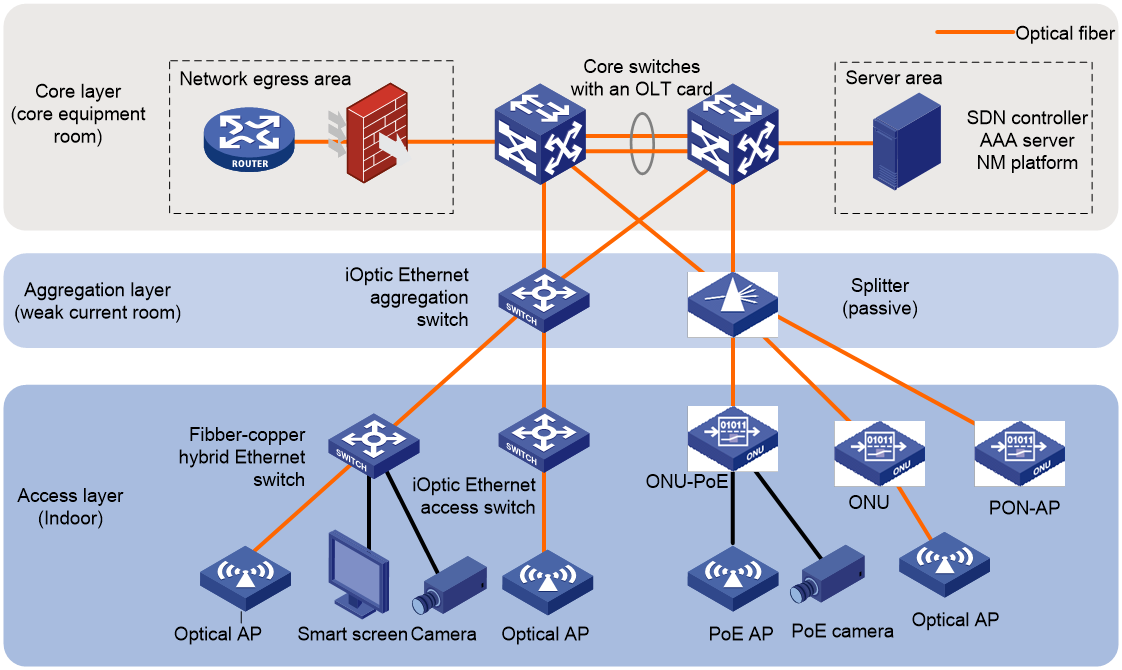
Figure 5 Typical iOptic PON+Ethernet integrated network solution
As shown in Figure 5, the typical iOptic PON+Ethernet integrated network solution features core switches that seamlessly integrate Ethernet and POL networks by installing a PON OLT card. This solution also incorporates comprehensive features such as security, SDN, and IoT, and more. The versatile nature of this solution makes it particularly suitable for a range of scenarios such as smart campuses, smart hospitals, hotels, and other campus scenarios. This solution has the following advantages:
· High network bandwidth—All-optical interconnection achieves ultra-wide networking.
· Intelligent O&M—Intelligent diagnosis of optical links to guarantee link quality in real time, diagnosis, analysis, and lifecycle prediction for transceiver modules, network self-healing, visual wireless assurance, device status view in real time, and one-click replacement of faulty devices.
· Simple deployment—All devices are plug-and-play and can onboard automatically.
· Integrated networking, centralized control—The iOptic Ethernet network and the POL network are integrated and managed by SDN. PON functionalities are integrated into the leaf switch in the form of an OLT card, eliminating the need for a separate OLT device.
· High availability—The wired network architecture with a dual-core redundant design and core switches support for IRF setup enable millisecond-level switching in case of a single device failure.
· Ultimate experience—Fiber-to-the-room addresses high-bandwidth access requirements. In classrooms, dormitories and other scenarios, multi-rate silent switches and silent ONUs can be deployed to satisfy users' network experience.
iOptic GPON-based POL network solution
Figure 6 Typical GPON-based POL network solution
The typical GPON-based POL network solution as shown in Figure 6, similar to the EPON-based iOptic POL network solution, provide high-performance all-optical networks. The passive splitter at the aggregation layer doesn't take up space in the floor convergence room. This solution eliminates the need for a centralized power supply for convergence layer and access layer devices. This makes the network more secure and easier to deploy. GPON OLT primarily focuses on conversion from PON to Ethernet, and its capabilities in Ethernet forwarding and switching are relatively limited. In contrast, the EPON-based POL solution leverages the EPON OLT's enhanced Ethernet forwarding and switching capabilities.
iOptic network devices
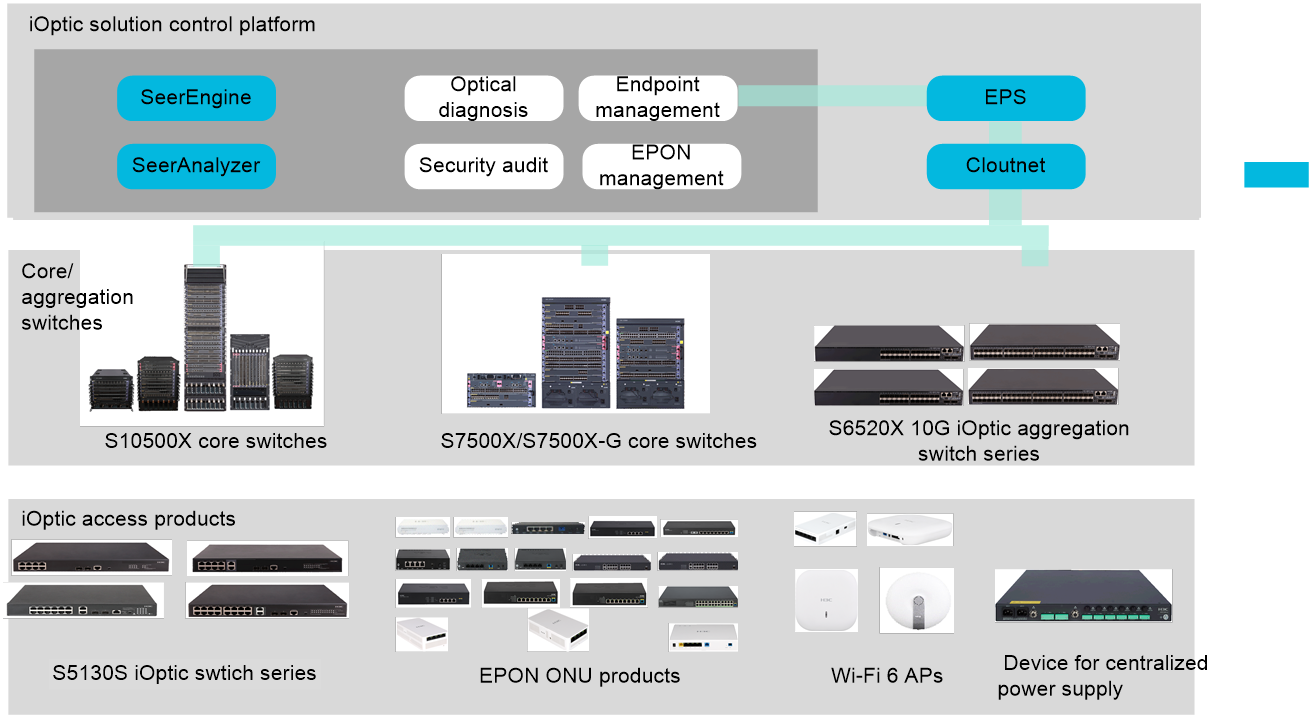
H3C provides an extensive array of iOptic Ethernet switches and PON network devices, encompassing all categories of all-optical network devices from core to access. This enables customers to tailor the deployment of all-optical network devices in line with their specific network requirements, thereby ensuring an optimal and efficient networking solution.
Figure 7 iOptic network solution control platform and some devices
The following table lists the device models that support the iOptic networks currently. More products will support iOptic networks in the future.
Table 1 iOptic network solution product models
|
Product category |
Access layer |
Aggregation layer |
Core layer |
|
iOptic Ethernet switch |
S5130S-28F-SI S5130S-28F-EI S5130S-52F-EI S5560S-28F-EI S5560S-52F-EI S5170-36F-EI S5570S-36F-EI S5570S-54F-EI E500C-F (with centralized power supply capability in E552C-X-PS-F) |
S5560X-30F-EI S5560X-54F-EI S5560X-30F-HI S5560X-54F-HI S6520X-SI/EI/HI series |
S10500X core switches S7500X switch series |
|
EPON |
ET304-A ET304-A ET304-C-A ET354-A ET354-P ET358-P ET358-POTS ET904-IW ET904-A ET904-H ET904-H-P ET916-A ET916-H-A ET908-H-P ET908-H-PQ ET908-H-PD ET908-H-P-W ET924-H-POE WA6320H-XEPON (PON and AP integrated) |
12-port 10G EPON OLT card 24-port EPON OLT card 8-port EPON OLT card Fixed-port OLTS3210-16 Fixed-port OLTS3210-08 |
N/A |
|
GPON |
EGT354 EGT354-P EGT302 EGT358-P EGT358-POTS |
Modular OLT P3500 16-port GPON OLT card 8-fixed port GPON OLT P3108 16-fixed port GPON OLT P3116 |
N/A |
|
Wireless product |
WIFI6 AP WA6320H-XEPON |
N/A |
N/A |
iOptic network deployment cases
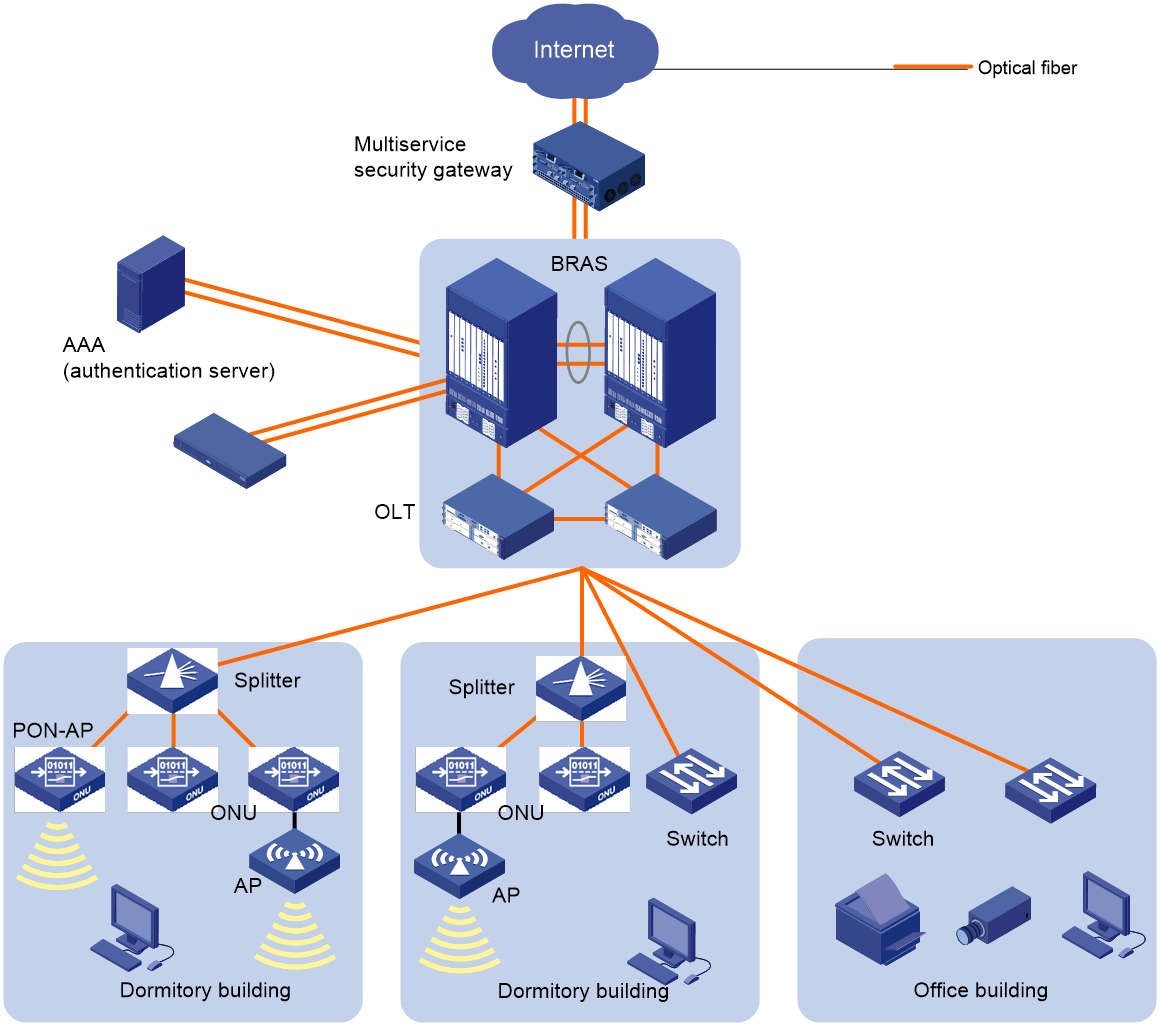
iOptic PON+Ethernet network deployment in a high-school dormitory
Figure 8 iOptic PON+Ethernet network deployment in a high-school dormitory
The construction time of the network infrastructure in areas such as the student dormitories of a university is early, and the network bridges and cable trays are almost all fully loaded, and are unable to support new services and high-bandwidth access. Multiple carriers deploy their own networks in the dormitories, and the Internet data in the student dormitories are not forwarded through the campus network, which results in complex authentication process and difficult O&M and management and brings threats to network information security.
The deployment of iOptic PON+ Ethernet network solution helps the university improve the network bandwidth, simplify O & M, and reduces expenditure.
· Simplified O&M—The network structure is simplified, and ONUs plug and play and can be onboarded immediately without configuration, reducing the O&M pressure of the university.
· Integrated wired and wireless management—The core switch integrates AC functions, supports the latest Wi-Fi 6 APs, provides higher rates and concurrent connections, and achieves integrated wired and wireless networking.
· Saving investment—The optical splitter is passive, and no special installation environment is required in the aggregation layer and access layer, which saves costs for equipment rooms, power supply, and horizontal cabling.
· Ultra broadband interconnection—The network renovation adopts 10G PON peer-to-peer Fibre (Fiber) To The Home (FFTH), with an uplink interface bandwidth that can reach 10G/40G/100G, eliminating any potential bottlenecks in forwarding. The downlink supports flexible network configurations as needed, with Gigabit and 10 Gigabit ONUs.
· Unified authentication—Networks in all areas are centrally controlled and uniformly authenticated, ensuring network information security.
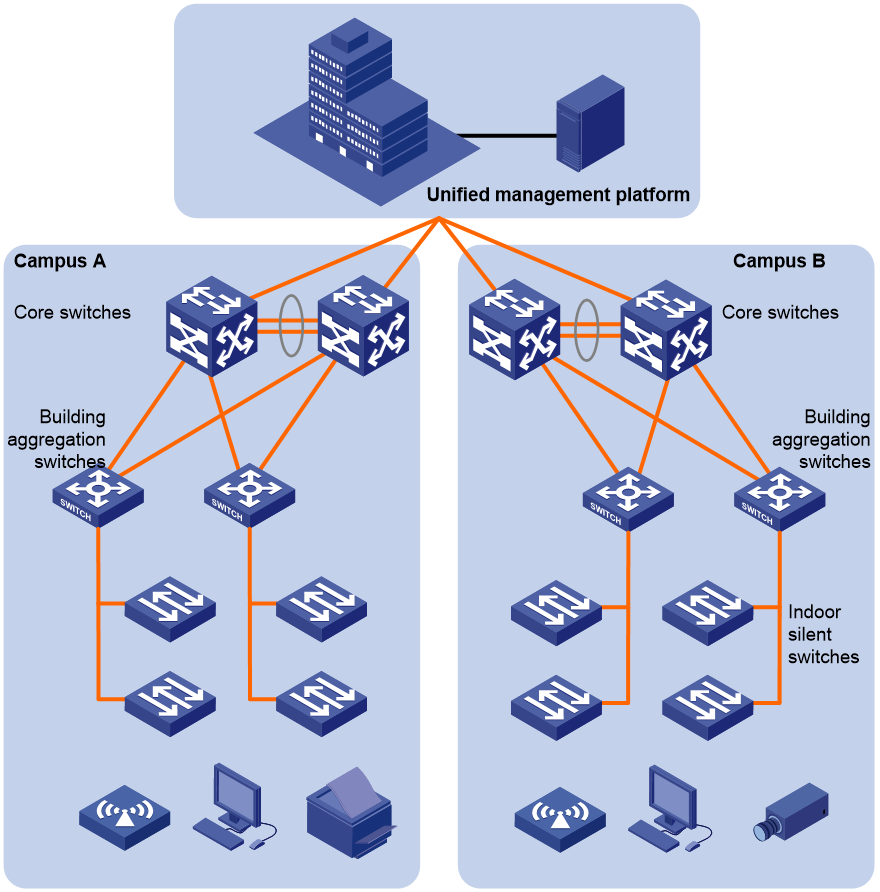
iOptic Ethernet network deployment for smart classrooms
Figure 9 iOptic Ethernet network deployment for smart classrooms
As the advancement of educational informatization deepens, smart classrooms have become an essential support for educational reform. This project aims to create a high-speed, reliable, and integrated smart classroom network to meet the development needs of various applications in schools. The customer's existing network faces challenges such as coexistence of multiple networks, complex management, chaotic cabling, difficult fault troubleshooting, and difficulties in bandwidth expansion and upgrade.
This project uses the iOptic Ethernet network solution, which addresses the needs of the school for network access, O & M, and unified management, ensuring the user experience of smart classrooms. Fiber into the room ensures high-bandwidth access of endpoints. The indoor switch features a 24-port fanless silent design, ensuring a good interactive experience for teachers and students. The networks of multiple campuses are centrally managed on a unified management platform, allowing view of the network operation status in real-time.
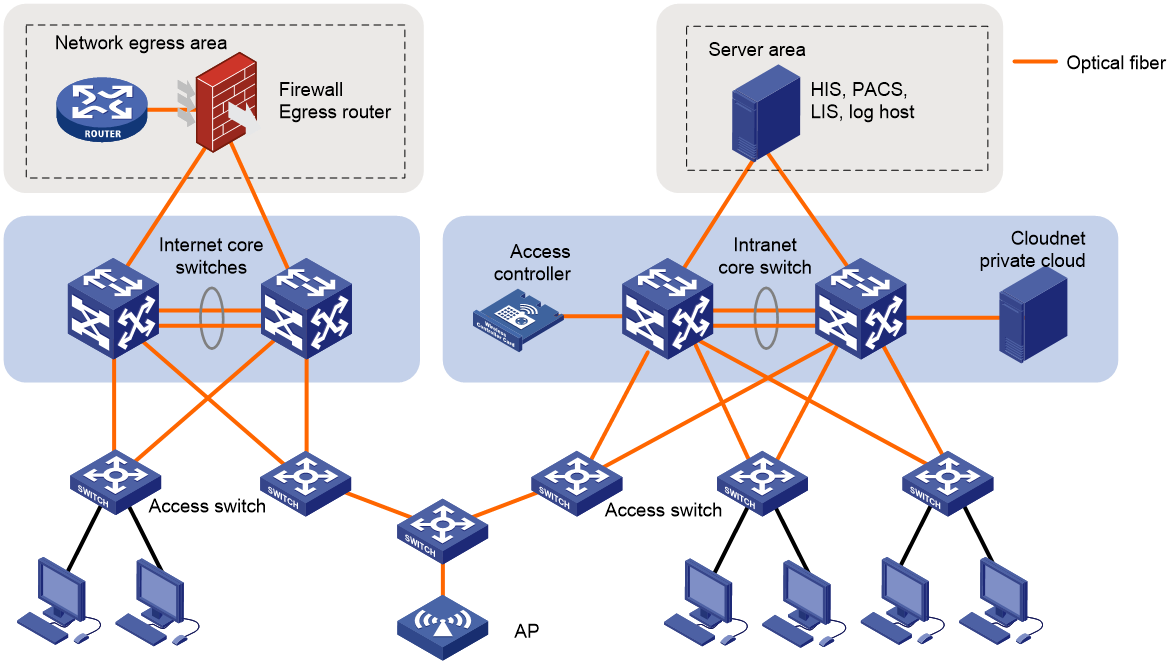
iOptic Ethernet network deployment in a smart hospital
Figure 10 iOptic Ethernet network deployment in a smart hospital
With the application of electronic medical record systems, medical order systems, and PACS systems in many hospitals, clinical applications such as doctors' mobile rounds and nurses' mobile bedside care are no longer limited to "paper talks". Building a digital medical system, improving the level of digital applications in hospitals, optimizing the quality of medical care, ensuring medical safety, and better serving patients are the development trends of the medical scene network, and also the construction goal of this project. With the feature of high availability, reliability, and performance, the iOptic Ethernet network solution enables high-speed connections and access to the hospital's HIS, PACS, LIS systems, thereby meeting the needs of various services in hospitals.
Appendix Acronyms
|
Acronym |
Full spelling |
|
PON |
Passive Optical Network |
|
POL |
Passive Optical LAN |
|
SDN |
Software Defined Network |
|
PoE |
Power over Ethernet |
|
ONU |
Optical Network Unit |
|
AP |
Access Point |
|
OLT |
Optical Line Terminal |
|
FTTH |
Fibre (Fiber) To The Home |
|
EPON |
Ethernet Passive Optical Network |
|
GPON |
Gigabit-Capable Passive Optical Networks |