- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-MOD configuration | 94.31 KB |
Restrictions and guidelines: MOD configuration
Example: Configuring common MOD to send packets through UDP
Configuring MOD
Overview
Mirror On Drop (MOD) can detect packet drops during the forwarding process on the device. When a packet is dropped, MOD can send the packet drop reason and the characteristics of the dropped packet to the collector.
Restrictions and guidelines: MOD configuration
On the S9855 series switches, MOD takes effect only on packets matching ACLs referenced by flow groups.
On the S9825 series switches, MOD takes effect on all packets and sends only packets with the specified drop reasons to the collector.
Only packets matching the ACL referenced by a flow group carry a flow group ID. The flow group ID in packets that do not match the ACL is 0.
Configuring common MOD
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MOD view.
telemetry mod
3. Configure the device ID for MOD.
device-id address
By default, no device ID is configured for MOD.
4. Enable sampling for MOD.
sampler sampler-name
By default, sampling is disabled for MOD.
5. Configure the encapsulation information for packets sent to the collector by MOD.
collector source-ip source-address destination-ip destination-address source-port source-port destination-port destination-port [ vlan vlan-id ]
By default, the encapsulation information for packets sent to the collector by MOD is not configured.
6. Configure the packet drop reason list monitored by MOD.
reason-list { reason-list | all }
By default, no packet drop reasons is configured, and the device does not monitor packet drops.
For more information about the packet drop reason list, see the reason-list command in Telemetry Command Reference.
Verifying and maintaining MOD
To verify the MOD configuration, execute the following command in any view:
· Display MOD configuration.
display telemetry mod [ slot slot-number ]
MOD configuration examples
Example: Configuring common MOD to send packets through UDP
Network configuration
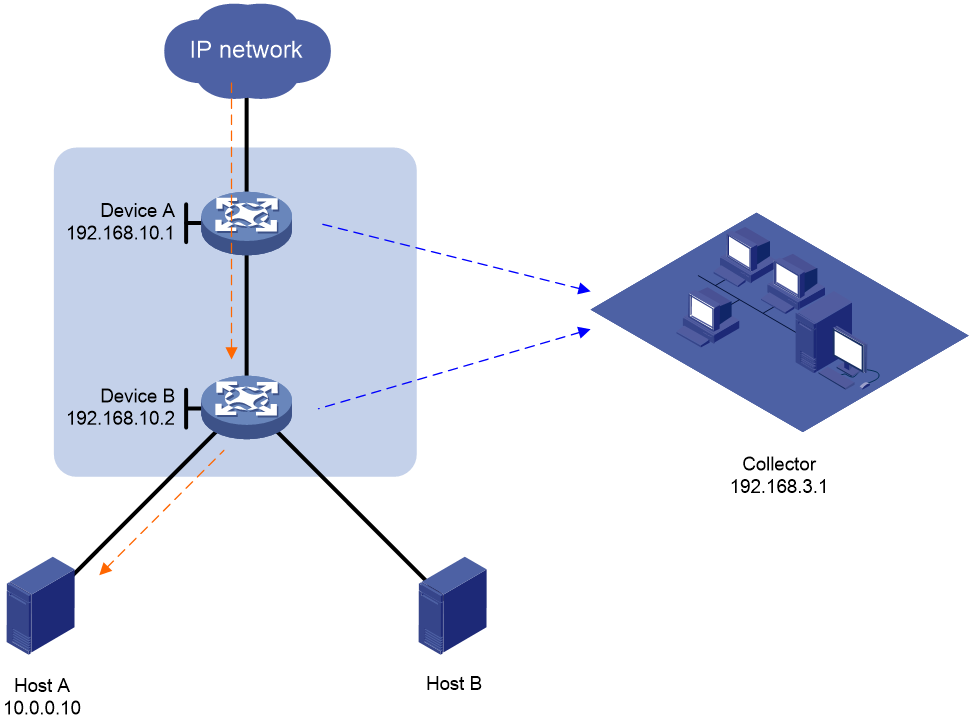
As shown in Figure 1, Host A and Host B access the external network through Device A and Device B. Some packets from the external network are missing on Host A. Configure MOD on the access device and aggregation device to identify whether packets are dropped during the forwarding process on the two devices.
Prerequisites
Configure IP addresses for devices, and make sure they can reach each other at Layer 3.
Procedure
1. Configure Device A:
a. Configure a flow group:
# Create advanced IPv4 ACL 3000, and configure a rule to match packets with destination IP address 10.0.0.10 for the ACL.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] acl advanced 3000
[DeviceA-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] rule permit ip destination 10.0.0.10 0
[DeviceA-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] quit
# Create flow group 1 and configure it to reference ACL 3000.
[DeviceA] telemetry flow-group 1
[DeviceA-telemetry-flow-group-1] if-match acl 3000
# Configure the flow group to generate flow entries based on the destination IP address.
[DeviceA-telemetry-flow-group-1] template destination-ip
[DeviceA-telemetry-flow-group-1] quit
# Apply flow group 1.
[DeviceA] telemetry apply flow-group 1
b. Configure MOD:
# Configure the device ID for MOD as 192.168.10.1.
[DeviceA] telemetry mod
[DeviceA-telemetry-mod] device-id 192.168.10.1
[DeviceA-telemetry-mod] quit
# Create sampler samp, set the sampling mode to random, and set the sampling rate to 2 to the 8th power.
[DeviceA] sampler samp mode random packet-interval n-power 8
# Enable sampling for MOD, and reference sampler samp.
[DeviceA] telemetry mod
[DeviceA-telemetry-mod] sampler samp
# Encapsulate the packets sent to the collector by MOD with the following information: source IP address 192.168.10.1, destination IP address 192.168.3.1, source port number 1000, and destination port number 2333.
[DeviceA-telemetry-mod] collector source-ip 192.168.10.1 destination-ip 192.168.3.1 source-port 1000 destination-port 2333
# Configure MOD to monitor all packet drop reasons.
[DeviceA-telemetry-mod] reason-list all
[DeviceA-telemetry-mod] quit
2. Configure Device B.
Configure Device B in the same way Device A is configured except the device ID for MOD and the source IP address encapsulated in the packets sent to the collector.
Verifying the configuration
1. Verify the configuration on Device A:
# Display the ACL configuration.
<DeviceA> display acl 3000
Advanced IPv4 ACL 3000, 1 rule,
ACL's step is 5, start ID is 0
rule 0 permit ip destination 10.0.0.10 0
# Display the flow group configuration.
<DeviceA> display telemetry flow-group 1
Flow group 1 (Successful)
ACL : 3000
Template :
destination-ip
# Display the MOD configuration.
<DeviceA> display telemetry mod
Status : Successful
Drop reason list:
denied-vlan
higig-header-error
invalid-tpid
ip-multicast-error
ipv4-dip-miss
…Omitted…
Sampler : samp
Device ID : 192.168.10.1
Transport protocol : udp
Collector
Source IP : 192.168.10.1
Destination IP : 192.168.3.1
Source port : 1000
Destination port : 2333
VLAN ID : 20
Output interface : HundredGigE1/0/1
Destination MAC : 0011-0200-0211
2. Verify the configuration on Device B.
The configuration on Device B is the same as the configuration on Device A except the device ID for MOD and the source IP address encapsulated in the packets sent to the collector. (Details not shown.)
3. Verify the configuration on the collector.
When a packet destined for IP address 10.0.0.10 is dropped during the forwarding process on Device A and Device B, the collector can receive the packet drop reason and the characteristics of the dropped packet from the devices.