- Products and Solutions
- Industry Solutions
- Services
- Support
- Training & Certification
- Partners
- About Us
- Contact Sales
- Become a Partner
-
 Login
Login
Country / Region
H3C CR16000-F High-End Routers
The CR16000-F is a high-end router series independently developed by H3C. It utilizes distributed hardware forwarding, and non-blocking switching technology. It adopts an advanced CLOS architecture with a separate control plane and forwarding plane. It supports high-density FE/GE, 10GE, 25GE, 40GE, 50GE, 100GE, 400GE interfaces, with flexible single-slot performance expansion to meet different network position requirements. It supports the advanced Comware 7 network operating system, which perfectly integrates with the CR16000-F in multiple aspects such as multi-core CPU support, distributed computing, modular design, high availability architecture, virtualization, and openness. It uses mature virtualization technology to improve network reliability while reducing device maintenance workload. It supports powerful BRAS functionality and carrier-grade CGN, meeting the development needs of multi-service edge MSE devices for operators and core devices for campus networks. It supports various network protection technologies and 1588v2 synchronous Ethernet, serving as an ER router to meet the IPRAN networking needs of operators. It supports the SR/SRv6, FlexE, iFIT, and NETCONF technologies, and has comprehensive SDN capabilities. Combined with the AD-WAN controller, it can achieve automatic business distribution, flexible network scheduling, multi-dimensional business assurance, and intelligent network O&M. With the support of IPSec VPN technology, it can meet users' demands for a trusted network.
The following contents are complex, and it is recommended to browse on PC.
Enter c.h3c.com.cn on the PC browser and operate according to the page to synchronize to the PC and continue browsing.
Continue by mobile
Comprehensive SDN capabilities
With the rapid development of the intelligent era, businesses are becoming increasingly complex and diverse, and traffic is growing rapidly. Traditional wide area network (WAN) issues are becoming more prominent, such as uncontrollable forwarding paths, invisible services, and difficult maintenance. It is necessary to introduce SDN and intelligent technologies to achieve unified resource management, full utilization, automatic application deployment, rapid deployment, dynamic business perception, proactive adaptation, differentiated protection, and visible quality.
CR16000-F provides the following benefits:
Supports SR/SRv6+EVPN technology, simplifying network configuration and achieving manageable and controllable network paths.
Supports sub-interface slicing, FlexE, and other hard isolation technologies, reserving broadband resources and ensuring high reliability for high-priority services.
Supports iFIT + Telemetry deep flow detection technology, proactively monitoring network health and transforming passive maintenance into proactive maintenance.
Supports NETCONF and YANG, providing configuration APIs to achieve network configuration automation and accelerate network device and service deployment.
Supports CBTS functionality, selecting different tunnel paths based on different business priorities to achieve differentiated forwarding services.
Supports EVPN/VXLAN, learning MAC addresses and routing information remotely to implement Layer 2 and Layer 3 VPN based on VXLAN.
The CR16000-F, combined with the AD-WAN controller, achieves comprehensive network management, control, and analysis. It can work with SDN components to achieve centralized management, control, and analysis of the wide area network, supporting unified management and control, single-domain, multi-domain, and cross-layer business automation.
Powerful BRAS functions
Traditional SR routers carry telecom services such as Mobile, Business, and IPTV, and BRAS serves as the access gateway for broadband network applications, performing user authentication and management. The CR16000-F combines SR and BRAS functions, improving the efficiency of user network device utilization and saving user investment. It provides the following benefits:
Supports Intelligent Target Account (iTA), which distinguishes business types by destination address, realizing billing, bandwidth control, and QoS for different types of user businesses, providing users with differentiated business operation solutions.
Supports unified wired and wireless authentication, simplifying user management costs. It meets the needs of massive user terminal access through high-capacity BRAS, while also meeting the mobility and seamless authentication needs of wireless terminals.
Supports BRAS IRF hot backup, avoiding single point of failures while simplifying operations, maintenance, and management.
Mobile carrier network IP RAN
Traditional mobile operator base station backhaul networks are built on TDM/SDH. However, with the deployment and development of 3G and LTE services, data services have become the main carrier, and the demand for bandwidth is rapidly increasing. The traditional SDH TDM exclusive channel network expansion model is difficult to support, and the construction of a packetized backhaul network is an irreversible trend. IP RAN has become the mainstream solution in the mobile backhaul network field. The CR16000-F provides powerful functionality for IP RAN:
Supports various link detection and protection technologies, including: IP FRR, LDP FRR, Bypass PW, BFD For PW, and Y.1731.
Supports the 1588V2 clock synchronization protocol, achieving more accurate frequency synchronization and time synchronization.
Supports Ethernet clock synchronization, with clock recovery quality reaching 0.01 ppm.
Industry-leading network operating system
The control plane of the CR16000-F adopts multi-core and SMP symmetric multiprocessing technology, running the advanced Comware 7 operating system. Each software module has an independent operating space and can be dynamically loaded and separately upgraded.
Comware 7 supports distributed computing and global services such as MPLS and BGP. It can run on the designated MPU CPU system and distribute the main programs of each global service to different MPU systems, effectively balancing the pressure on each CPU and improving the overall performance of the system. A global service can be further split into sub-functions and the system distributes them to different MPU CPU systems, achieving distributed computing for a global service.
Technical Specifications
CR16003E-F | CR16006-F | CR16005E-F | CR16010-F | CR16010E-F | CR16010H-F | CR16018-F | |
Switching Capacity | 6.4T | 2.56T | 3.2T | 6.4T | 19.2T | 25.6T | 51.2T |
Forwarding Performance | 1,449.60 Mpps | 579.84 Mpps | 724.80 Mpps | 1,449.60 Mpps | 4,348.80 Mpps | 5,798.40 Mpps | 11,596.80 Mpps |
Maximum Board capacity | 1.6T | 320G | 400G | 400G | 1.6T | 1.6T | 1.6T |
MPU slots | 2 (1+1 redundancy) | 2 (1+1 redundancy) | 2 (1+1 redundancy) | 2 (1+1 redundancy) | 2 (1+1 redundancy) | 2 (1+1 redundancy) | 2 (1+1 redundancy) |
Subcard slots | 8 | 16 | 16 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 64 |
Line card slots | 2 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
Switch fabric modules | 2 (1+1 redundancy) | 4 (N+M redundancy) | 2 (1+1 redundancy) | 4 (N+M redundancy) | 2+2 (N+M redundancy) | 5 (N+M redundancy) | 5 (N+M redundancy) |
Total number of slots (LPUs + MPUs + independent switch fabric modules) | 4 | 10 | 6 | 14 | 12 | 15 | 23 |
Chassis | Integrated chassis, which can be installed in a 19-inch rack | ||||||
Power module system | 4 × AC or DC power supplies (N+M redundancy) and built-in AC power supplies | 4 × AC or DC power supplies (N+M redundancy) and built-in AC power supplies | 4 × AC or DC power supplies (N+M redundancy) and built-in AC power supplies | 6 × AC or DC power supplies (N+M redundancy) and built-in AC power supplies | 6 × AC or DC power supplies (N+M redundancy) and built-in AC power supplies | 8 × AC or DC power supplies (N+M redundancy) and built-in AC power supplies | 16 × AC or DC power supplies (N+M redundancy) and built-in AC power supplies |
Dimensions (H × W × D) | 219mm×440mm ×600mm(8.62×17.32 ×23.70 in) (5RU) | 353 × 440 × 660 mm (13.90 × 17.32 × 25.98 in) (8RU) | 264 × 440 × 600 mm (10.39 × 17.32 × 23.62 in) (6RU) | 930 × 440 × 660 mm (36.61 × 17.32 × 25.98 in) (21RU) | 575 × 440 × 600 mm (22.64 × 17.32 × 23.70 in) (13RU) | 931 × 440 × 640 mm (36.65 × 17.32 × 25.20 in) (21RU) | 1687 × 440 × 640 mm (66.42 × 17.32 × 25.20 in) (38RU) |
Weight in Full Configuration | <70 kg (154.32 lb) | <85 kg (187.39 lb) | <70 kg (154.32 lb) | <154 kg (339.51 lb) | <130 kg (286.60 lb) | <165 kg (363.76 lb) | <350 kg (771.62 lb) |
Interface types | FE, GE, 10-GE (LAN/WAN), 25-GE, 40-GE, 50-GE, 100-GE, 400-GE, 155M POS, 622M POS, 2.5G POS, 10G POS, CPOS, 155M ATM, 622M ATM, E1/T1 400-GE to 100-GE interface switching 100-GE to 40-GE interface switching 155M POS, 622M POS, and GE interface switching ATM to POS interface switching 155M ATM to 622M ATM interface switching | ||||||
Unicast routing | IPv4/IPv6 dual stack Static routing, RIP, RIPv2, RIPng, OSPF, OSPFv3, IS-IS, IS-ISv6, BGP, BGP4+, and MP-BGP DHCP Server, DHCP Relay VRRP and VRRPv3 IPv6 neighbor discovery, PMTU discovery, TCP6, ping IPv6, traceroute IPv6, socket IPv6, static IPv6 DNS, specifying an IPv6 DNS server, and TFTP IPv6 client ICMPv6 MIB, UDP6 MIB, TCP6 MIB, and IPv6 MIB ECMP/UCMP Policy-based routing Routing policies Tunneling technologies such as GRE FRR for static routing, OSPF, IS-IS, BGP, and OSPFv3 Filtering routes based on IP address, AS path, and route tag | ||||||
Multicast | Routing protocols such as PIM-DM, PIM-SM, PIM-SSM, MSDP, MBGP, and anycast-RP IGMP v1/v2/v3 and IGMP snooping v1/v2/v3 IGMP Proxy and Snooping PIM6-DM, PIM6-SM, and PIM6-SSM MLD v1/v2 and MLD snooping v1 Multicast policies and multicast QoS BIER | ||||||
MPLS VPN | MPLS label distribution protocols such as LDP and RSVP-TE, and LDP label capacity greater than 512K P/PE functions, which comply with RFC2547bis Three inter-AS MPLS VPN methods (Option1/Option2/Option3) Hierarchy of PE (HoPE) Multi-role hosts BGP and LDP L2VPN, L3VPN, VPLS and inter-AS L2VPN/L3VPN EVPN VPLS/VPWS/L3VPN 6PE and 6vPE Distributed multicast VPN ACL-based traffic identification and redirection to different VPNs MPLS VPN troubleshooting features, including MPLS ping and MPLS traceroute L2VPN access to L3VPN VPLS access in QinQ mode MPLS TE FRR and LDP FRR | ||||||
BRAS service | PPPoE, PPPoEoVLAN, and PPPoEoQ access authentication methods PPPoX function, and PPPoA and PPPoEoA access authentication methods Layer 2 portal, Layer 3 portal, and QinQ portal access authentication methods IPoE, IPoEoVLAN, and IPoEoQ access authentication methods Subnet-/interface-/L2VPN-leased access authentication methods L2TP Layer 2 transparent access and Layer 3 transparent access Remote AAA based on RADIUS/TACACS+ RADIUS, TACACS, Intelligent target accounting (ITA), which differentiates services by destination addresses to perform accounting, bandwidth control, and QoS Unified wired and wireless authentication, which meets the access requirements of massive user endpoints through a high-capacity BRAS and meets the mobility requirements of wireless endpoints BRAS IRF, which offers redundancy and simplifies Ops | ||||||
IPsec on the following types of interfaces: high-speed link interfaces (FE, GE, 10-GE, 40-GE, 50-GE, 100-GE, 2.5G POS, and 10G POS) and low-speed link interfaces (155M POS, 622M POS, CPOS interface, 155M ATM, 622M ATM, and E1/T1) High-precision NAT: Carrier Grade NAT (CGN), Static NAT, Dynamic NAT, NAT44/NAT444, NAT64 1588 V2 | |||||||
Virtualization features | Virtualization technology, which virtualizes multiple physical devices into a logical device, manages devices and forwarding entries on a unified interface, and supports multi-chassis link aggregation | ||||||
ACL | IPv4/IPv6 standard ACLs and extended ACLs Layer 2/Layer 3/Layer 4-based ACLs Ingress/Egress ACLs Hardware ACLs | ||||||
QoS | Hierarchical QoS (HQoS) and queue scheduling mechanisms such as PQ, WFQ, and CBWFQ 5-level HQoS scheduling for granular service management Traffic shaping Congestion avoidance technologies such as tail drop (TD) and Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) Priority marking/remarking, and 802.1p, ToS, DSCP, and EXP priority mappings Congestion avoidance, traffic policing (CAR), and traffic shaping Packet marking based on IP address, port number, 802.1p priority, and DSCP value Multi-level queue scheduling mechanisms (including CQ, PQ, LLQ, and WFQ) for packets Multicast QoS QPPB, and QoS for MPLS TE | ||||||
Ethernet | 802.1Q, VLAN Ethernet Virtual Circuits ( EVC) Layer2ProtocolTunneling 802.1Q VLAN trunk QinQ VLAN encapsulation QinQ termination 802.3d (STP), 802.3w (RSTP), and 802.3s (MSTP) IEEE 802.3ad (link aggregation), static link aggregation, and multi-card link aggregation Aggregation of interfaces at different rates Port mirroring (SPAN/RSPAN) and flow mirroring MACsec FlexE Subinterface channelization (slicing) On-demand channelization (slicing) | ||||||
SDN | VXLAN Layer 2 gateway and VXLAN Layer 3 gateway (distributed and centralized) EVPN VXLAN Layer 2 gateway and EVPN VXLAN Layer 3 gateway (distributed and centralized) PCEP Network information collection protocols such as BGP-LS NETCONF and YANG SR-BE, SR-TE and SR Policy, SR TI-LFA/Anti-micro-loop SRv6-BE, SRv6 TE policy CBTS OpenFlow v1.3 BGP FlowSpec Telemetry APN6 OSPFv3 over SRv6 and IS-IS over SRv6 L2VPN over SRv6, EVPN VPWS over SRv6 policy, and EVPN VPLS over SRv6 policy Color-based traffic steering and DSCP-based traffic steering by SRv6-TE policy Optimization capabilities based on latency, bandwidth, and packet loss rate by SRv6 policy Switchover to SRv6 BE path upon SRv6 policy path failure EVPN E-tree over SRv6 EVPN VPLS over SRv6 policy SR-MPLS BE, SR-MPLS TE, and SR-MPLS TE policy Ping, trace, and traffic statistics collection based on SR/SRv6 TE policy paths, and ping and trace based on SR BE 10 layers of SIDs in the header for SRv6 TE policy without affecting forwarding capabilities | ||||||
Network flow analysis | NetStream, which supports the v5/v8/v9 data export formats, sampling, and flow statistics collection Multiple log hosts Hardware-based network traffic application analysis IPv4/IPv6/MPLS traffic collection and analysis Traffic collection and analysis in the inbound and outbound directions of interfaces Abnormal traffic detection and monitoring | ||||||
Availability | Redundant backup for the key components, including the MPUs, switching fabric modules, power supplies, and fans MPU and LPU separation, and module plus submodule design Passive design for the backplane to prevent single point of failure Network processor (NP) architecture design, which prevents services from affecting forwarding capabilities Hot swapping for all components, and hot swapping of switching fabric modules without removing fan modules Intelligent fan rotation speed tuning Built-in DC and AC power supplies, not occupy service slots Stateful failover, NSF, NSR, and GR IP trunk, MP, and Ethernet interface aggregation IP/LDP/VPN/TE/VLL FRR NSR for OSPF/OSPFv3/ISIS/ISISv6/BGP/BGP4+/VRRP/IPv6 VRRP/PIM SM/PIM DM/LDP MPLS L3VPN/6VPE/MPLS TE primary/secondary switchover without packet loss TI-LFA FRR for SRv6 with switchover time no longer than 50ms PW redundancy, MPLS/Ethernet OAM, Y.1731, routing protocol/port/VLAN damping, and other protection mechanisms Hardware-based BFD, which supports fast failure detection for various protocols (with minimum packet interval of 3.3ms) and a failover time of less than 50ms BFD for VRRP, OSPF, IS-IS, BGP, LDP, TE, SR, VRRPv6, OSPFv3, ISISv6, BGP4+, PW(VCCV) Comprehensive FRR features: IP/IPv6/LDP/TE/VPNv4/VPNv6 FRR, with a service switchover time less than 50ms and a network availability of 99.999% RFC2544, which supports automatically sending packets to detect the throughput, delay, jitter, and packet loss rate of links | ||||||
OAM | In-situ flow information telemetry (iFIT), which can detect network failures in real time, troubleshoot the network failures, and implement visible management over performance data TWAMP, MPLS OAM, VRRP, Ethernet OAM (802.3ah, 802.1ag/Y.1731), LLDP, BFD for eth-trunk, Bit error detection | ||||||
Security | Firewall modules High-performance SM-based encryption modules, which support SM2, SM3, and SM4 encryption algorithms AAA security authentication protocols (for example, RADIUS and TACACS+) Control plane attack defense Security authentication and accounting with primary-secondary RADIUS SSHv1/v2/v3, providing a secure encrypted channel for user login Standard and extended ACLs, which filter packets and prevent network attacks Defense against attacks by packets such as ARP, unknown multicast, broadcast, unknown unicast, local subnet route scanning, TCP SYN, packets with TTL 1, PADI, DHCP, portal, and protocol packets PADI, DHCP, and portal attack defense Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (uRPF), which prevents network attacks based on source address spoofing Plaintext and MD5 authentication for RIPv2, OSPF, IS-IS, BGP, OSPFv3, IS-ISv6, and BGP4+ protocols, and keychain feature that allows different keys to be active based on time ranges Secure network management through SNMPv3 | ||||||
System management | In-band management and out-of-band management CLI-based configuration through console/AUX modem/Telnet/SSH2.0 File upload/download through FTP, TFTP, XMODEM, and SFTP SNMP v1/v2c/v3 RMON v1/v2, which supports groups 1, 2, 3, and 9 NTP clock Network Quality Analyzer (NQA) Failure alarms and automatic recovery DHCP Data logs ICMP Syslog Traceroute Multi-threaded access to devices through Telnet Hot patching to achieve smooth software upgrade | ||||||
Operating temperature: | 0℃ to 45℃ (32°F to 113°F) | ||||||
Regulatory compliance | Directive2014/30/EU EN55032ClassA, EN 55024/EN 55035 EN 60950-1, EN61000-3-2, EN61000-3-3 IEC 60950-1 UL 60950-1 | ||||||
Application scenarios
As a high-end router with high processing performance, the CR16000-F can be applied in the core layer and backbone layer of large wide area networks, the core layer of large campus networks, and the core layer of metropolitan area networks. The following are examples of typical applications. Actual applications are not limited to specific industries.
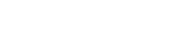
WAN SDN solution
Traditional wide area network traffic is forwarded according to the shortest path calculated by the routing protocol. Even if a certain path becomes congested, the traffic will not be switched to other backup paths. This problem is not very serious when the network traffic is not heavy and the service quality requirements are not high. However, with the widespread of the Internet, the business complexity grows, and the problems of traditional shortest path first routing are exposed.
The wide area network SDN solution can dynamically collect real-time link quality information such as link usage, delay, and jitter. The DPI function integrated into the device will report the business types in real time. The WAN APP dynamically selects the optimal end-to-end path for specific applications and delivers the optimal path policy to the router through NETCONF. By implementing a wide area network SDN solution, network management costs can be reduced, network resources can be fully scheduled, resources can be dynamically adjusted in the event of network congestion or severe jitter, and value-added services and additional businesses can be implemented.
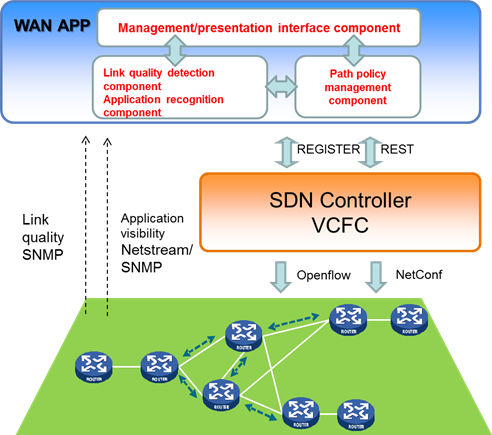
BRAS solution
H3C BRAS supports intelligent targeted accounting (iTA), which distinguishes business traffic by destination address and provides different bandwidth, accounting, and QoS policies, meeting the requirements of university users for accessing the campus network, Cernet, and the Internet with different rate and accounting policies. It provides a unified wired and wireless authentication solution, meeting the needs of massive user terminal access through high-capacity BRAS, while also meeting the mobility and seamless authentication needs of wireless terminals. The BRAS IRF function can simplify operations and maintenance while meeting the requirements for hot backup.
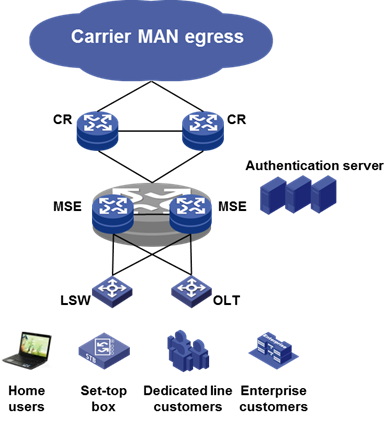
Nation-grade WAN solution
Due to the vast geographical coverage of the national wide area network, the reliability and security requirements for network devices are extremely high. The CR16000-F can serve as the national core and provincial aggregate nodes. To ensure network security, the design architecture of the national core and provincial nodes separates the uplink and downlink devices. The provincial and city nodes also serve as metropolitan area network aggregate access, dedicated line aggregate, and narrowband access.
This solution is suitable for the construction, expansion, and renovation of large-scale industry backbone networks such as operators, governments, taxation, finance, and electricity. The entire network supports MPLS VPN.
PID | Description |
CR16003E-F | H3C CR16003E-F core router chassis |
CR16005E-F | H3C CR16005E-F core router chassis |
CR16006-F | H3C CR16006-F core router chassis |
CR16010-F | H3C CR16010-F core router chassis |
CR160010E-F | H3C CR160010E-F core router chassis |
CR16010H-F | H3C CR16010H-F core router chassis |
CR16018-F | H3C CR16018-F core router chassis |
Power module | |
PSR2400-12D | DC 2400W power module |
PSR2500-12A | AC 2500W power module |
PSR1600B-12A-B | AC 1600W power module |
PSR2000-12D-B | DC 2000W power module |
MPU module | |
CSR05SRP1L1 | H3C CR16000-F Management and Route Process Unit(1L1) |
CSR05SRP1L3 | H3C CR16000-F Management and Route Process Unit(1L3) |
CSR05SRP1P1 | H3C CR16000-F Main Processing Unit(1P1) |
CSR05SRP1P3 | H3C CR16000-F Main Processing Unit(1P3) |
CSR05SRP1R3 | H3C CR16000-F Main Processing Unit(1R3) |
CSR05SRP051E3-G | H3C CR16005E-F Main Processing Unit (051E3-G) |
CSR05SRP101E3-G | H3C CR16010E-F Main Processing Unit (101E3-G) |
Switching fabric module | |
CSFC-04B | H3C CR16006-F Switch Fabric Card(B Type) |
CSFC-04D | H3C CR16006-F Switch Fabric Card(D Type) |
CSFC-08B | H3C CR16010-F Switch Fabric Card(B Type) |
CSFC-08D | H3C CR16010-F Switch Fabric Card(D Type) |
CSFC-08E | H3C CR16010-F Fabric Module(E Type) |
CSFC-08E1 | H3C CR16010H-F Fabric Module(E Type) |
CSFC-08T | H3C CR16010H-F Fabric Module(T Type) |
CSFC-16E | H3C CR16018-F Fabric Module(E Type) |
CSFC-16T | H3C CR16018-F Fabric Module(T Type) |
CSFC-10T-G | H3C CR16010E-F Fabric Module (T Type) |
CSFC-10E-G | H3C CR16010E-F Fabric Module (E Type) |
Sec Module | |
IM-MSUX | H3C CR16000-F Universal Line Processing Unit (IM-MSUX) |
IM-MSEX-B | Service Processing Unit (IM-MSEX-B) |
IM-SP-B | Universal Expansion Service Processing Module (IM-SP-B) |
IM-SFMX | Network Data Encryption Service Processing Unit (IM-SFMX) |
IO Module | |
CEPC-XP4LX | H3C CR16000-F 4-port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Line Processing Unit Module (SFP+, LC) |
CEPC-XP48RX | H3C CR16000-F 48-Port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Module (SFP+, LC) |
CEPC-CP4RX | H3C CR16000-F 4-Port 100GBASE Ethernet Optical Interface Module (CFP2) |
CEPC-CP4RX-L | H3C CR16000-F 4-port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Line Processing Unit (QSFP28, LC) |
H3C CR16000-F 8-Port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Line Processing Unit(QSFP28,LC) | |
CEPC-CQ16L1 | H3C CR16000-F 16-Port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Line Processing Unit (QSFP28,LC) |
CEPC-CDQ2L | H3C CR16000-F 2-Port 400G Ethernet Optical Interface Line Processing Unit(QSFP28-DD,LC) |
Service Engine module | |
CSPEX-1304X | H3C CR16000-F Service Processing Unit(1304X) |
CSPEX-1404X | H3C CR16000-F 4-Port Multi-Service Processing Engine1404X |
CSPEX-1504X | H3C CR16000-F 4-Port Multi-Service Processing Engine1504X |
RX-SPE200 | H3C RX8800,SR0MRLN2EQ1,Service Processing Unit(SPE200) |
CSPEX-1602X | H3C CR16000-F Service Processing Unit(1602X) |
CSPEX-1802X | H3C CR16000-F Service Processing Unit(1802X) |
CSPEX-1804X | H3C CR16000-F Service Processing Unit(1804X) |
CSPEX-2314X-G1 | H3C CR16000-F Service Processing Unit (2314X-G1) |
Sub-card module | |
MIC-GP4L | H3C CR16000-F 4-Port 1000BASE-X/1000BASE-T Combo Interface Card |
MIC-GP10L-V2 | H3C CR16000-F 10-Port 1000BASE-X Ethernet Optical Interface Card(SFP,LC) |
MIC-GP20L | H3C CR16000-F 20-Port 1000BASE-X Ethernet Optical Interface Card,(SFP,LC) |
MIC-GT20L | H3C CR16000-F 20-Port 1000BASE-X Ethernet Electrical Interface Card(RJ45) |
MIC-XP2L-LAN | H3C CR16000-F 2-port 10GBASE-R Ethernet Optical Interface Card(SFP+,LC)-LAN |
MIC-XP2L | H3C CR16000-F 2-port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Card(SFP+,LC) |
MIC-XP4L1 | H3C CR16000-F 4-port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Card 1(SFP+,LC) |
MIC-XP5L1 | H3C CR16000-F 5-port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Card(SFP+,LC) |
MIC-XP5L2 | H3C CR16000-F 5-port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Card(SFP+,LC) |
MIC-QP1L | H3C CR16000-F 1-port 40G Ethernet Optical Interface Card(QSFP+,LC) |
MIC-XP20L | H3C CR16000-F 20-port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Card(SFP+,LC) |
MIC-CP2L | H3C CR16000-F 2-port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Card(CFP2,LC) |
MIC-CQ2L | H3C CR16000-F 2-port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Card(QSFP28) |
MIC-CP1L-V2 | H3C CR16000-F 1-port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Card(CFP2,LC) |
MIC-CP2L-V2 | H3C CR16000-F 2-port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Card(QSFP28) |
MIC-SP8L | H3C CR16000-F 8-Port OC-3c/STM-1c POS Optical Interface Card,(SFP,LC) |
MIC-SP4L | H3C CR16000-F 4-Port OC-3c/STM-1c POS/ATM or 1-Port OC-12c/STM-4c POS/ATM Optical Interface Card,(SFP,LC) |
NIC-GT20L | H3C CR16000-F 20-port 1000BASE-T Ethernet Copper Interface Card(RJ45)(NIC) |
MIC-CLP2L | H3C CR16000-F 2-Port OC-3/STM-1 Channelized POS Optical Interface Card, (SFP, LC) |
MIC-CLP4L | H3C CR16000-F 4-Port OC-3/STM-1 Channelized POS Optical Interface Card, (SFP, LC) |
MIC-ET16L | H3C CR16000-F 16-Port E1 Electrical Interface Card (HM96 Male Connector) |
MIC-CQ1L1 | H3C CR16000-F 1-port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Card (QSFP28) |
H3C CR16000-F 20-Port 1000BASE-T Ethernet Copper Interface Card (RJ45) | |
MIC-GP10L2 | H3C CR16000-F 10-Port 1000BASE-X Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP, LC) |
MIC-CQ1L2 | H3C CR16000-F 1-Port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Card 2 (QSFP28, LC) |
MIC-XP10L-LAN | H3C CR16000-F 10-Port 10GBASE-R Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP+, LC)-LAN |
NIC-GP20L | H3C CR16000-F 20-port 1000BASE-X Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP, LC) (NIC) |
NIC-XP20L | H3C CR16000-F 20-port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP+, LC) (NIC) |
NIC-CC1L | H3C CR16000-F 1-port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Card (CFP2, LC) (NIC) |
NIC-XP5L | H3C CR16000-F 5-port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP+, LC) (NIC) |
NIC-XP10L | H3C CR16000-F 10-port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP+, LC) (NIC) |
NIC-CQ1L | H3C CR16000-F 1-port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Card (QSFP28) (NIC) |
NIC-GP24L | H3C CR16000-F 24-port 1000BASE-X Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP, LC) (NIC) |
NIC-GP24L1 | H3C CR16000-F 24-Port 1000BASE-X Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP, LC) (NIC) |
NIC-CQ2L | H3C CR16000-F 2-port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Card (QSFP28) (NIC) |
RX-NIC-YGS4L | H3C CR16000-F 4-port 25G Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP28, LC) (RX-NIC) |
RX-NIC-LGQ2L | H3C CR16000-F 2-port 50G Ethernet Optical Interface Card (QSFP28, LC) (RX-NIC) |
RX-NIC-LGQ4L | H3C CR16000-F 4-port 50G Ethernet Optical Interface Card (QSFP28, LC) (RX-NIC) |
RX-NIC-CQ1LF | H3C CR16000-F 1-port 100G Flexible Ethernet Optical Interface Card (QSFP28, LC) (RX-NIC) |
RX-NIC-CQ2LF | H3C CR16000-F 2-port 100G Flexible Ethernet Optical Interface Card (QSFP28, LC) (RX-NIC) |
GIC-GP12L-G | H3C CR16000-F 12-Port 1000BASE-X Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP,LC)(GIC) |
GIC-XP6L-G | H3C CR16000-F 6-Port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP+,LC)(GIC) |
GIC-XP4L-G | H3C CR16000-F 4-Port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP+,LC)(GIC) |
GIC-XP12L-G | H3C CR16000-F 12-Port 10GBASE-R/W Ethernet Optical Interface Card (SFP+,LC)(GIC) |
GIC-CQ1L-G | H3C CR16000-F 1-Port 100G Ethernet Optical Interface Card (QSFP28,LC)(GIC) |
GIC-ET16L-G | H3C CR16000-F 16-Port E1 Copper Interface Card (HM96 Male Connector)(GIC) |
GIC-TCP8L-G | H3C CR16000-F 8-Port OC-3c/OC-12c (622M/155M) POS/GE Optical Interface Card (SFP,LC)(GIC) |
GIC-CLP2L-G | H3C CR16000-F 2-Port OC-3/STM-1 (155M) Channelized POS Optical Interface Card (SFP,LC)(GIC) |
Resource Center
- Cloud & AI
- InterConnect
- Intelligent Computing
- Intelligent Storage
- Security
- SMB Products
- Intelligent Terminal Products
- Product Support Services
- Technical Service Solutions
Product Support Services
Technical Service Solutions
- Resource Center
- Policy
- Online Help
- Technical Blogs
Resource Center
Policy
Online Help
- Become A Partner
- Partner Policy & Program
- Global Learning
- Partner Sales Resources
- Partner Business Management
- Service Business
Global Learning
- Profile
- News & Events
- Online Exhibition Center
- Contact Us

 Products and Solutions
Products and Solutions