- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-Flow group configuration | 62.66 KB |
Configuring flow groups
About flow groups
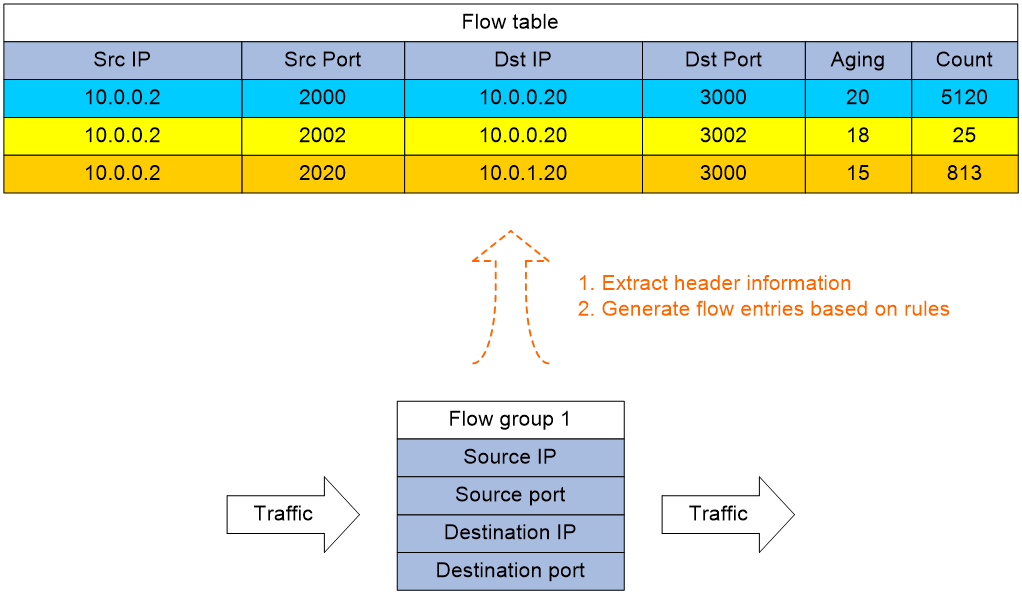
A flow group allows you to identify flows based on flow generation rules. The device extracts traffic characteristics (for example, 5-tuples in the packet header) and generates flow entries according to the header fields specified in a flow generation rule.
A flow group can use an ACL to limit the traffic for which flow entries are generated. A flow entry is aged out if no matching packets are received before the aging timer expires.
Figure 1 Flow entry generation
The flow entries generated by a flow group can be used by other features. A flow group can be in one of the following modes:
· Common MOD mode—Used by MOD. This mode occupies hardware resources but has a lower burden on the CPU. For more information about MOD, see Telemetry Configuration Guide.
· Simple MOD mode—Used by MOD. This mode has a higher burden on the CPU but saves hardware resources.
· Elephant/mice flow mode—Used by the elephant and mice flows distinguishing feature (see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide).
Restrictions and guidelines: Flow group configuration
A flow group can reference only one IPv4 ACL. An ACL referenced by a flow group supports only the 5-tuple (source IP address, destination IP address, source port number, destination port number, and protocol) and DSCP priority match items.
Because a flow can belong to only one flow group, make sure the same flow is not assigned to more than one flow group when specifying ACLs. For information about ACLs, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
To delete an applied flow group, first remove the application and then delete the flow group.
Only one flow group can be applied.
For a flow group in MOD mode or elephant/mice flow mode to work correctly, you must set the hardware resource operating mode to EM by using the hardware-resource switch-mode command (see device management commands in Fundamentals Command Reference).
Procedure
system-view
2. Create a flow group and enter its view.
telemetry flow-group group-id [ name group-name ] [ mode { simple-mod | mice-elephant-flow } ]
3. Specify an ACL.
if-match acl { acl-number | name acl-name }
By default, no ACL is specified.
4. Configure the header fields used for generating flow entries.
template { destination-ip | destination-port | protocol | source-ip | source-port | vxlan { inner-destination-ip | inner-destination-port | inner-protocol | inner-source-ip | inner-source-port | vxlan-id } * } *
By default, no header fields are used for generating flow entries.
5. Return to system view.
quit
6. (Optional.) Set the aging time for flow entries.
telemetry flow-group aging-time [ msec ] aging-time
The default setting is 10 milliseconds for the elephant/mice flow mode and 15 minutes for other modes.
7. (Optional.) Set the maximum rate of packets sent to the CPU to limit the flow entry generation rate.
telemetry flow-group rate-limit pps
By default, the rate of packets sent to the CPU is not limited.
8. (Optional.) Set the maximum number of flow entries generated.
telemetry flow-group max-entry max-entries
By default, the number of flow entries is not limited.
9. Apply the flow group.
telemetry apply flow-group { group-id | name group-name }
By default, no flow group is applied.
Display and maintenance commands for flow group
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the configuration and application status of flow groups. |
display telemetry flow-group [ group-id | name group-name ] [ slot slot-number ] |
|
Display flow entries. |
display telemetry flow-group flow-table [ [ group-id | name group-name ] | mod | mice-elephant-flow ] [ destination-ip { dst-ipv4 | dst-ipv6 } | destination-port dst-port | protocol protocol | source-ip { src-ipv4 | src-ipv6 } | source-port src-port | vxlan [ inner-destination-ip { dst-ipv4 | dst-ipv6 } | inner-destination-port dst-port | inner-protocol protocol | inner-source-ip { src-ipv4 | src-ipv6 } | inner-source-port src-port | vxlan-id vxlan-id ] * ] * { slot slot-number } |