- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 03-Telemetry stream configuration | 139.51 KB |
Contents
Restrictions and guidelines: Telemetry stream configuration
Telemetry stream tasks at a glance
Configuring basic telemetry stream functions
Configuring telemetry stream timestamping
Display and maintenance commands for telemetry stream
Configuring telemetry stream
About telemetry stream
Telemetry stream is a network monitoring technology used to collect data from devices. It continuously streams data to a collector.
Telemetry stream supports collecting the input interface, timestamp, and output interface of traffic.
How telemetry stream works
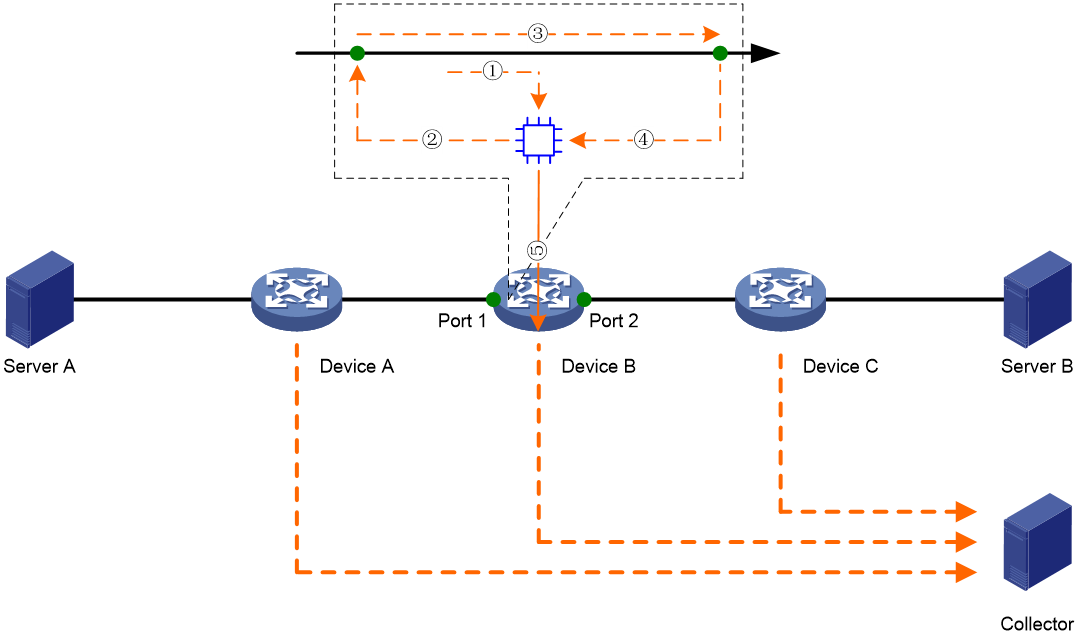
As shown in Figure 1, the working mechanism of telemetry stream is as follows:
1. Telemetry stream samples a matching packet on the input interface and copies it to the telemetry stream processor in the device. The telemetry stream processor adds the input interface information to the packet.
2. The telemetry stream processor loops the packet back to a service loopback group.
3. The interface in the service loopback group identifies the looped-back packet, adds the timestamp information, and forwards it to the output interface according to the routing table.
4. The output interface identifies the looped-back packet, adds the output interface and timestamp information to it, and sends it to the telemetry stream processor.
5. The telemetry stream processor encapsulates the packet and routes it to the collector.
The collector can calculate the path and delay information according to the collected data from multiple nodes.
Telemetry stream timestamping
With this function enabled, the device carries the timestamp in its packets sent to the collector. The collector can calculate the delay introduced when a node forwards packets. Additionally, the collector can use the timestamp information collected from multiple nodes to calculate the delay introduced when packets are forwarded along the path.
Restrictions and guidelines: Telemetry stream configuration
Telemetry stream can be deployed only in underlay networks.
Telemetry stream is mutually exclusive with the following features:
· NetStream.
· IPv6 NetStream.
· NetAnalysis.
· Mirroring configured with sampling.
· INT.
· MOD.
For more information about NetStream, IPv6 NetStream, mirroring, and NetAnalysis, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Telemetry stream tasks at a glance
To configure telemetry stream, perform the following tasks:
1. Configuring basic telemetry stream functions
2. (Optional.) Configuring telemetry stream timestamping
Prerequisites
Configure routing to make sure the devices can reach each other.
Configuring basic telemetry stream functions
About this task
The device copies an original packet on the input interface and sends the copy to the telemetry stream processor in the device. The telemetry stream processor adds the input and output interface information to the packet, encapsulates it, and routes it to the collector.
Too many original packets will overwhelm the Telemetry processor and even cause it to drop packets. To address this problem, you can use an ACL or sampler on the input interface to reduce the packets sent to the collector. Only packets matching a permit ACL rule or sampled packets are sent to the collector.
If the data portion of original packets is large, you can enable the truncation function to save the link bandwidth consumed between the device and the collector and reduce the parsing load of the collector. The truncation function truncates the packets before sending them to the collector. The truncated packets retain complete input interface, output interface, and timestamp information.
Procedure
a. Enter system view.
system-view
b. Specify a device ID.
telemetry stream device-id address
By default, no device ID is specified.
2. Configure addressing parameters to encapsulate in the packets sent to the collector.
telemetry stream collector source source-address destination destination-address source-port source-port destination-port destination-port [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ truncation ]
By default, no addressing parameters are configured.
The destination IP address must be the IP address of the collector, and the outgoing interface for the destination IP address cannot be a management Ethernet interface. The destination port number must be the listening port number on the collector.
3. Configure a telemetry stream action on the input interface.
a. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
b. Configure a telemetry stream action on the interface.
telemetry stream action action-id [ acl [ mac | user-defined ] { acl-number | name acl-name } | sampler sampler-name ] *
By default, no telemetry stream action is configured.
c. Return to system view.
quit
For information about ACLs, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
For information about samplers, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
4. Enable telemetry stream.
telemetry stream enable
By default, telemetry stream is enabled.
Configuring telemetry stream timestamping
About this task
This feature allows the device to add the timestamp information when a packet enters and leaves it.
Procedure
1. Configure a service loopback group.
a. Create a service loopback group and specify its service type as telemetry-stream.
service-loopback group group-id type telemetry-stream
b. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
c. Assign the Layer 2 Ethernet interface to the service loopback group.
port service-loopback group group-id
By default, a Layer 2 Ethernet interface does not belong to any service loopback group.
d. Return to system view.
quit
A Layer 2 Ethernet interface assigned to a service loopback group will be solely used by the group and cannot be used for any other purposes. For more information about service loopback groups, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
2. Enable telemetry stream timestamping.
telemetry stream timestamp enable
By default, telemetry stream timestamping is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for telemetry stream
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display ACL configuration and match statistics. |
display acl [ mac | user-defined ] { acl-number | all | name acl-name } For more information about this command, see ACL and QoS Command Reference. |
|
Display the configuration of samplers. |
display sampler [ sampler-name ] [ slot slot-number ] For more information about this command, see Network Management and Monitoring Command Reference. |
|
Display information about service loopback groups. |
display service-loopback group [ group-id ] For more information about this command, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference. |
|
Display telemetry stream configuration. |
display telemetry stream |
Telemetry stream configuration examples
Example: Configuring telemetry stream
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, configure telemetry stream on Device B for the collector to calculate the delay when packets are forwarded by Device B.
Restrictions and guidelines
An interface assigned to a service loopback group will be solely used by the group and cannot be used for any other purposes.
Prerequisites
Assign IP addresses to interfaces and configure routing protocols. (Details not shown.)
Procedure
# Specify 10.0.0.1 as the device ID.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] telemetry stream device-id 10.0.0.1
# Configure addressing parameters to encapsulate in telemetry stream packets sent to the collector.
[DeviceB] telemetry stream collector source 20.0.0.2 destination 30.0.0.1 source-port 12 destination-port 14
# Create service loopback group 1, and specify its service type as telemetry-stream.
[DeviceB] service-loopback group 1 type telemetry-stream
# Assign Twenty-FiveGigE 1/0/2 to service loopback group 1.
[DeviceB] interface twenty-fivegige 1/0/2
[DeviceB-Twenty-FiveGigE1/0/2] port service-loopback group 1
All configurations on the interface will be lost. Continue?[Y/N]:y
[DeviceB-Twenty-FiveGigE1/0/2] quit
# Enable telemetry stream timestamping.
[DeviceB] telemetry stream timestamp enable
# Create sampler samp in random sampling mode, and set the sampling rate to 8. One packet from 256 (2 to the 8th power) packets is selected.
[DeviceB] sampler samp mode random packet-interval n-power 8
# Create IPv4 basic ACL 2000, and configure a rule to match packets with source IP address 192.168.1.2.
[DeviceB] acl basic 2000
[DeviceB-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.1.2 0
[DeviceB-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] quit
# Configure telemetry stream action 1 to use ACL 2000 and sampler samp on Twenty-FiveGigE 1/0/3.
[DeviceB] interface twenty-fivegige 1/0/3
[DeviceB-Twenty-FiveGigE1/0/3] telemetry stream action 1 acl 2000 sampler samp
[DeviceB-Twenty-FiveGigE1/0/3] quit
# Enable telemetry stream.
[DeviceB] telemetry stream enable
Verifying the configuration
# Display the telemetry stream configuration on Device B.
[DeviceB] display telemetry stream
Telemetry stream status : Enabled
Telemetry stream timestamp status: Enabled
Telemetry stream device-id : 10.0.0.1
Telemetry stream action:
Twenty-FiveGigE1/0/3:
Telemetry stream action 1:
ACL : 2000
Sampler: samp
Telemetry stream collector: (Configuration succeeded)
Source IP : 20.0.0.2
Destination IP : 30.0.0.1
Source port : 12
Destination port: 14