- Products and Solutions
- Industry Solutions
- Services
- Support
- Training & Certification
- Partners
- About Us
- Contact Sales
- Become a Partner
-
 Login
Login
Country / Region
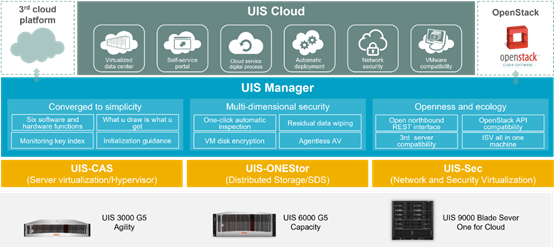
H3C UIS 3000 G5 Hyper Converged Infrastructure
H3C UIS HCI system 7.0 is an innovative future-oriented product for enterprises and industry data centers. In compliance with the open architecture standards, H3C UIS seamlessly integrates software technologies such as compute virtualization, storage virtualization, network security virtualization, O&M and monitoring management, and cloud service delivery on x86 and ARM servers. This integration streamlines data centers and IT operations, drives management efficiency, and reduces the TCO.
The H3C UIS system is available as a configure-to-order system that contains HCI servers and HCI kernel and management software that have been fully tuned, verified, and installed before delivery. The HCI servers can be up and running straight out of the box, simplifying deployment and accelerating service delivery.
UIS CAS is data center oriented virtualization software, providing powerful virtualization and resource pooling capabilities. UIS CAS has unique data acceleration capabilities and multi-queue block storage, which greatly improves the efficiency of services running on VMs. It provides dynamic resource eXtension (DRX) and cloud rainbow features. UIS CAS had an excellent performance in SPECvirt tests.
As a leading software-defined storage product in the industry, UIS ONEStor provides unified block storage, file storage, and object storage services for upper-layer applications. UIS ONEStor provides flexible protection mechanisms in multiple dimensions, including volume-based data redundancy, erasure coding, and multiple replicas. These mechanisms enable fast data restoration without hot backup disks. UIS ONEStor offers rich enterprise-class features to ensure user data consistency and data reliability and security. UIS ONEStor is capable of deduplication & compression* with a maximum deduplication compression ratio of 8:1. Deduplication & compression functionality is for all data transactions, including writing to volume disks, backups, tiering of unfrequently used data, etc.
UIS Sec provides tenants with virtual network security services through NFV, including vFW, vRouter, vLB, vNGFW, and vWAF. It offers VM access control and protection, automatic deployment of network devices in a cloud computing environment, and isolation in a multi-tenant environment. UIS Sec supports three-level HA to ensure continuity of customer services.
H3C UIS Manager provides a unified portal for users to access the infrastructure of the data center. Through SSO, H3C UIS Manager enables unified management of servers, VMs, networks, storage, and upper-layer services in the data center. H3C UIS Manager offers a full-screen dashboard, health check, one-click inspection, resource statistics reports, and topology-based deployment for visualized, automated, and intelligent Ops through in one Web interface. In addition, UIS Manager allows for unified management of multiple clusters and tenants and request of virtual resources through a self-service portal in large-scale deployment or RBRO scenarios.
* Deduplication & compression feature should be evaluated case by case.
The H3C UIS 3000 G5 HCI server uses Intel Xeon 3rd-generation scalable processors, enabling a performance improvement of up to 52% for floating point operations and 42% kernel number increase. With eight-channel 3200MT/s DDR4 memory, this server guarantees a bandwidth improvement of up to 60%. With 14 PCIe 4.0 expansion slots and 41 disks, the server has excellent system expansion capabilities. The power conversion efficiency of the server is 96%, and its standard operating temperature is 5 to 45°C (41 to 113°F), which provides users with high energy efficiency.
The following contents are complex, and it is recommended to browse on PC.
Enter c.h3c.com.cn on the PC browser and operate according to the page to synchronize to the PC and continue browsing.
Continue by mobile
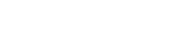
Innovative Engines
Cloud-native engine - With the built-in K8s APIs, the cloud-native engine offers unified orchestration and management of VMs, containers, and functions to help you build an application-centric cloud data center. Featuring small size and fast speed the cloud-native engine greatly improves resource usage
 .
.
Multi-role engine - With an adaptive architecture, UIS Manager enables you to perform unified management of x86 and ARM resources. It is compatible with physical nodes with different chips, models, settings, and capabilities and supports virtual nodes, distributed storage nodes, hybrid nodes, AI accelerated nodes, and bare metal nodes.
Convergence and Simplicity
Management convergence - Unifies the management of compute, storage, network, security, monitoring, and cloud service software capabilities to provide cloud capabilities out of the box.
Kernel convergence - Seamlessly integrates virtualized kernel and IPv6 capabilities, high-performance vSwitches, SR-IOV NIC driver, and GPU driver for system efficiency, reliability, and stability.
Storage convergence - Virtualizes the local disks into a resource pool to provide unified block, file, and object storage services to accommodate structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data.
Simplified service deployment - Integrates one-click auto migration tools that support P2V and V2V migration to help you quickly migrate traditional services to the cloud.
Visual and simplified O&M - Provides a flat, adaptive, and scalable platform for agile service delivery. The dashboard display, one-click operation, system health model, visual deployment, and quick access features enable you to perform visual, digital, automatic, and intelligent management, operations, and maintenance.
Virtualization Performance
UIS CAS performs well in the SPECvirt test and provides innovative features such as DRX, application HA, and cloud rainbow.
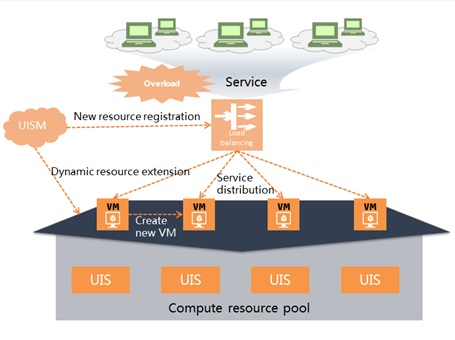
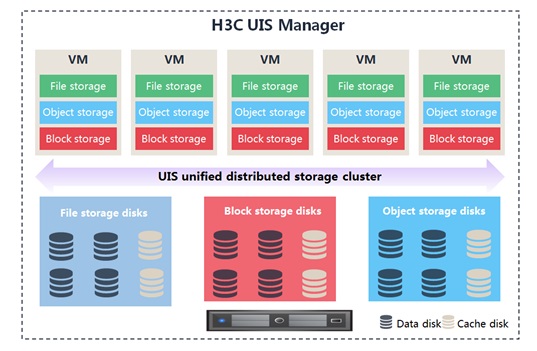
Unified Distributed Storage
UIS ONEStor uses a unified distributed storage architecture to ensure high performance, scalability, and security of the storage system and support automatic O&M.
Unified distributed storage architecture - Provides unified block, file, and object storage services without requiring independent metadata servers. Distributed global caching greatly improves read and write performance.
High availability - Supports replication redundancy policies with two to six replicas and erasure coding redundancy policies of N+1 to N+4 levels to fully protect data. UIS ONEStor provides replication, snapshot, clone, copy, failure domain, and protection domain features.
High reliability - Uses a fully redundant network to eliminate single point of failure and ensure uninterrupted services upon disk or node failures. UIS ONEStor automatically reconstructs data upon disk or node failures, and you can adjust the reconstruction priority. Nodes and disks can be added or deleted without interrupting services, and auto data balancing is supported.
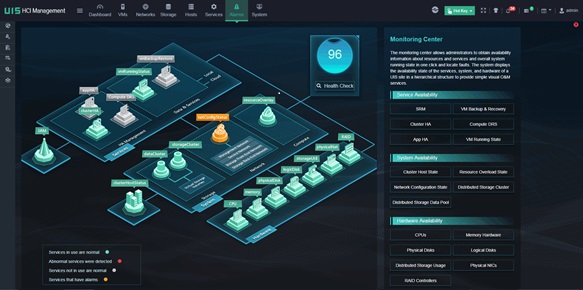
Reliability Monitoring Center
UIS Manager provides visual and simplified operations and maintenance. Administrators can obtain resource information and service state at one click and quickly locate specific issues. Hierarchical display of service, system, and hardware reliability states and one-click health inspection help improve O&M efficiency.
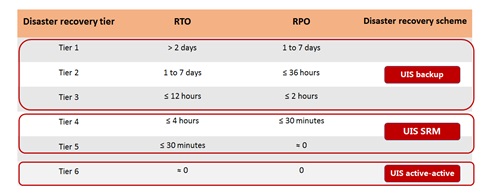
Multidimensional Data Protection
UIS provides service protection at three levels: UIS backup, UIS disaster recovery, and UIS active-active schemes to cover the six disaster recovery tiers defined in information security technology-disaster recovery specifications for information system.
Flexible redundancy policy - The distributed storage component integrated in UIS supports volume-based replication and erasure coding redundancy policies, providing data reconstruction without requiring hot backup disks and ensuring data integrity,supports 2-6 copies, storage cluster up to 256 Nodes.
Multiscenario backup - The agentless backup feature enables you to perform differential, full, and incremental backup of VMs without additional costs. Continuous data protection is supported.
SRM - Disaster recovery schemes such as async remote replication meets the disaster recovery requirements of both heterogeneous and homogeneous sites,support sending data copies to the DR site in the future by adding an HCI cluster at the DR site without having to upgrade the original license.
Active-active - Provides data center disaster recovery to ensure continuous running of critical services.
Cloud-managed Services
IaaS capabilities - Provides abundant IaaS services, including self-service resource delivery, hierarchical privilege management, multitenant management, workflow and support ticket management, and heterogeneous virtual resource incorporation.
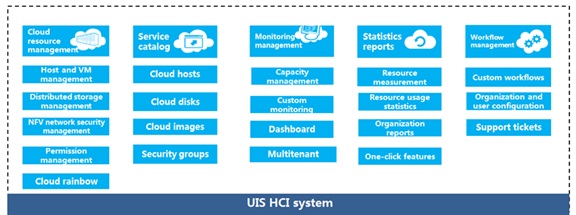
Open REST APIs - Provides standard REST APIs and is compatible with OpenStack H/J/K/L/M/P plug-ins and interfaces.
Open platform - Compatible with 200+ guest operating systems and 20+ open-source and commercial VNFs.
Open cooperation - Open cooperation in verticals such as security, backup, industry-specific applications, and cloud management platform.
CPU | 2 x 3rd generation Intel® Xeon® Ice Lake SP series (each processor up to 40 cores and maximum 270W power consumption) |
Memory | 32 x DDR4 DIMM slots , maximum 12.0 TB Up to 3200 MT/s data transfer rate, support RDIMM or LRDIMM Up to 16 Intel ® Optane™ DC Persistent Memory Module PMem 200 series ( Barlow Pass) |
Storage controller | Embedded RAID controller (SATA RAID 0, 1, 5, and 10) Standard PCIe HBA controller or storage controller, depending on model |
FBWC | 8 GB DDR4 cache, depending on model, support supercapacitor protection |
Storage | Up to front 12LFF bays, internal 4LFF bays , Rear 4LFF+4SFF bays* Up to front 25SFF bays, internal 8SFF bays , Rear 4LFF+4SFF bays* Front/Internal SAS/SATA HDD/SSD/NVMe Drives, maximum 28 x U.2 NVMe Drives SATA or PCIe M.2 SSDs, 2 x SD card kit, depending on model |
Network | 1 x onboard 1 Gbps management network port 2 x OCP 3.0 slots for 4 x 1GE or 2 x 10GE or 2 x 25GE NICs PCIe Standard slots for 1/10/25/40/100/200GE/IB Ethernet adapter |
PCIe slots | 14 x PCIe 4.0 standard slots |
Ports | VGA ports (Front and Rear) and serial port (RJ-45) 6 x USB 3.0 ports (2 front, 2,rear, 2 internal) 1 dedicated management Type-C port |
GPU | 14 x single-slot wide or 4 x double-slot wide GPU modules |
Optical drive | External optical disk drive, optional |
Management | HDM OOB system (with dedicated management port) and H3C iFIST/FIST, LCD touchable smart model |
Security | Chassis Intrusion Detection TPM2.0 Silicon Root of Trust Two-factor authorization logging |
Power supply | 2 x Platinum 550W/800W/850W/1300W/1600W/2400W (1+1 redundancy), depending on model 800W –48V DC power supply (1+1 Redundancy) Hot swappable redundant fans |
Standards | CE,UL , FCC,VCCI,EAC, etc. |
Operating temperature | 5°C to 45°C (41°F to 113°F) The maximum operating temperature varies by server configuration. For more information, see the technical documentation for the device. |
Dimensions (H × W × D) | 2U Height Without a security bezel: 87.5 x 445.4 x 748 mm (3.44 x 17.54 x 29.45 in) With a security bezel: 87.5 x 445.4 x 776 mm (3.44 x 17.54 x 30.55 in) |
Infrastructure services
UIS licenses | |||||
Feature | H3C UIS Manager | H3C UIS-CAS | H3C UIS Manager Enhancement Package | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Standard Edition | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Enterprise Edition |
H3C UIS-CAS (H3C UIS infrastructure uses the server virtualization software developed based on the evolving open-sourced Linux KVM. On this basis, H3C deeply optimized and improved the platform kernel to enhance stability and performance while developing the necessary functions, manageability, and operability required by commercial virtualization products. In response to the network reconstruction strategies of carriers, H3C developed a carrier-class virtualization kernel that features real-time response, high availability, and high network forwarding throughput and fits the layered decoupling scenarios of carriers.) | Y | Y | |||
H3C ONEStor distributed storage system (H3C UIS infrastructure uses the storage virtualization system that aggregates disks on local servers into a distributed storage resource pool through the storage network to provide virtual storage infrastructure services to the upper-layer virtual machines. Block storage, file storage, and object storage services can be provided simultaneously by using the same resource pool.) | Y | Y | |||
H3C UIS Manager (H3C UIS Manager provides highly integrated computing virtualization, storage virtualization, network virtualization, virtualization security, and O&M monitoring and management of physical and virtual resources. It uses a unified Web configuration interface, eliminating isolated configuration, fragmented management, and low deployment efficiency issues in a traditional multi-layer software and hardware structure. The platform enables the rapid deployment and simplified O&M of IT infrastructure, and helps users complete IT construction and perform O&M for data centers at a speed much higher than the current possible speed.) | Y | ||||
Interoperability and compatibility
UIS licenses | |||||
Feature | H3C UIS Manager | H3C UIS-CAS | H3C UIS Manager Enhancement Package | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Standard Edition | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Enterprise Edition |
OS compatibility (H3C UIS supports various unmodified Guest OSs, including: · Some common OSs: Windows, Red Hat, CentOS, Oracle Linux, Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, FreeBSD, Solaris, SUSE, openSUSE, and Ubuntu · Domestic OSs: NeoKylin, Kylin, Red Flag Linux, Deepin, LINX-TECH Rocky, StartOS, Puhua, YM, EulerOS, and NewStart OS · Commercial OS and open-sourced NFV OSs: Cisco CSR1000v, Cisco ASAv, Brocade vRouter, H3C vBRAS, H3C SecPath VMSG VFW1000, VyOS, DD-WRT, m0n0wall, and pfSense) | Y | Y | |||
OVF (H3C UIS provides standard OVF format encapsulation, allowing importing exported OVF VMs back to H3C UIS. It also supports formatting the OVF templates of another virtualization vendor to run the VMs on H3C UIS.) | Y | Y | |||
Heterogeneous OVF/OVA VM template import and automated conversion (H3C UIS supports importing OVF/OVA VMs running on third-party virtualization platforms, such as VMware vSphere, Oracle VirtualBox, Citrix XenServer, and ZTE ZXCLOUD iECS, and can automatically convert these imported VMs to manage them.) | Y | Y | |||
Mainstream hardware compatibility (Compatible with x86/ARM hardware from mainstream manufacturers in the industry) | Y | Y | |||
Computing virtualization
UIS licenses | |||||
Feature | H3C UIS Manager | H3C UIS-CAS | H3C UIS Manager Enhancement Package | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Standard Edition | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Enterprise Edition |
VM lifecycle management (H3C UIS supports common lifecycle management operations, such as creating, starting, suspending, resuming, hibernating, restarting, safely shutting down, forcibly shutting down, and deleting VMs.) | Y | Y | |||
Virtualization Management Redundancy (Provides High Availability / Redundancy for Virtualization Management Platform. Virtualization management system nodes provide active and standby redundancy to ensure the availability of the platform.) | Y | Y | |||
Heterogeneous Platform Support (Supports the installation of hyper-converged software on general x86 and arm architecture servers, supports mainstream ARM platforms such as Kunpeng, and can be mixed with the original X86 system for deployment and unified management.) | Y | Y | |||
Resource Capacity Prediction (Support resource capacity prediction service, built-in time series model, management platform to automatically realize data prediction, provide users with easy-to-use data prediction service, the service supports display the data of CPU, memory and storage capacity resource usage in real-time. Based on AI Machine learning algorithms, predict and analyze early warning time points to help users do resource expansion, cost budgets, etc., and improve business reliability.) | Y | Y | |||
Real Time Monitoring (The visual real-time monitoring center provides a unified visual monitoring and management center for the failure of HCI of the overall software and hardware, reduces the operation and maintenance difficulty and workload. The visual real- time monitoring center can provide hardware reliability (including CPU, memory, disk, physical network card and raid card),system reliability (including cluster host, distributed storage, cluster network configuration status and cluster resource overload state), service reliability (including SRM, cluster reliability HA, application HA, computing resource DRS, virtual machine operation status and virtual machine backup) these three-levels real-time monitoring and hierarchical display. The operation and maintenance personnel can directly view the overall operation of the cluster and can quickly diagnose the health status of the cluster. Supports one click to analyze the usage of historical resources of virtual machine, host, and support for planning and decision-making. Support one click to analyze invalid image files on back-end storage, and provide one-click clean and free storage space capabilities.) | Y | Y | |||
Migration (Provide P2V, V2V migration tool. It supports the industry's mainstream operating systems, public cloud platforms, and virtualization platforms. The different platforms includes but not limited to the migration from VMware, Huawei, Hyper-V and other platforms.) | Y | ||||
Hardware Management (Monitor the hardware platform including power supply, fan, temperature sensor, CPU, memory, hard disk and other hardware platform information of HCI and also Provides Web Bowser based HCI Management Console. Also, provides complete visibility and centralized management / control of the Virtualization Platform) | Y | ||||
Scalability of Nodes (Provides capability to scale up to 128 nodes) | Y | ||||
HA Function (Provides highly redundant capability for the VMs to restart on another node in case of any Node failure in the Cluster.) | Y | ||||
Health Monitoring Function (The virtualization platform has a built-in virtualization system health evaluation model.) | Y | ||||
User Roles and Permissions (Supports to create and manage local Users with Role Based Access and Permission Control) | Y | ||||
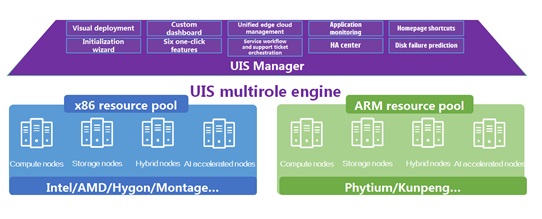
Topology Diagram (Supports draw topology and power on the VMs and Virtual Switch based on the draw diagram in the HCI Management GUI. This is for IT administrators’ ease to maintain the HCI cluster.) | Y | ||||
Multi-Role Cluster (Support different roles on different nodes. The host role can be designated as storage type, computing type, and hyper- converged type. The three types of hosts in the same cluster can be combined arbitrarily to meet various application scenarios of users and help to deal with unbalanced use of user resources better.) | Y | Y | Y | ||
Resource Expansion and Contraction (Supports flexible configuration of resource expansion and contraction strategies and can dynamically clone or delete virtual machines based on virtual machine CPU, memory, connection number, storage capacity, disk IO and other parameters to meet the requirements of "use more virtual machine to provide services and use less virtual machines to provide services according to the business. The entire process does not require manual intervention. At the same time, it supports unified load monitoring and load status display of the business virtual machine set) (a minimum of 5 user certificate of use) | Y | Y | |||
3rd-Party Platform Management (Supports Management for Existing Virtual Machines on VMware and management of VMs which are migrated from 3rd-party platform like Hyper-V, Huawei, and other platforms for single window management.) | Y | ||||
CPU hot add (Supports adding CPUs for VMs without service interruption or shutdown. Each VM supports a maximum of 128 vCPUs, but the actual supported quantity cannot exceed the total number of physical CPU cores on the physical host. Support for CPU hot adding also depends on the VM OS.) | Y | ||||
Memory hot add (Supports adding memory resources for VMs without service interruption or shutdown. Each VM supports a maximum of 1TB memory, but the actual supported memory size cannot exceed the physical memory capacity on the physical host. Support for memory hot adding also depends on the VM OS.) | Y | ||||
Hardware Health Check Capability (Provides Hardware Health Check capability to Monitor CPU, Memory, Network Interface Card, Hard Drive and RAID Controller etc.) | Y | ||||
Application HA (Provides application-level HA functions, which can automatically detect and automatically repair application failures in the virtual machine without installing an agent inside the virtual machine, including but not limited to Apache Tomcat, JDK, Apache HTTP Server, MySQL, SQL Server, Applications such as SharePoint, and support user-defined scripts for application status monitoring.) | Y | ||||
Disk hot expansion (Supports expanding the disk capacity for VMs without service interruption or shutdown. Each VM supports a maximum of 64TB disk size, but the actual supported size cannot exceed the maximum available size of the physical disk or LUN where the virtual disk file exists. After hot expanding the disk capacity, disk expansion must be formatted manually in the VM OS.) | Y | ||||
Disk hot add (Supports adding disks for VMs without service interruption or shutdown. Each VM supports a maximum of 16 virtual disks. After hot adding a disk, it must be formatted the disk manually in the VM OS.) | Y | ||||
NIC hot add (Supports adding NICs for VMs without service interruption or shutdown. Each VM supports a maximum of 12 vNICs.) | Y | ||||
Cluster Support (Supports clustering of multiple physical servers, and can perform dynamic resource scheduling based on CPU, memory, network traffic, storage capacity, disk IO and other resource utilization.) | Y | ||||
Computing resource priority (By default, CPU and memory resources of a physical host is fairly allocated to all VMs on the host. In case of a resource shortage, computing resource priority allows the system to ensure the highest level of CPU and memory scheduling opportunities for business-critical VMs.) Provides the dynamic load balancing function of virtual machine storage. The storage characteristics are used to determine the optimal location of virtual machine data when it is created and used. Non-disruptive automatic migration based on performance parameters and capacity of storage volume IO and IOPS can be eliminated to eliminate Storage risks. | Y | Y | |||
Computing resource reservation and limitation (In case of a computing resource shortage, this feature reserves computing resources for business critical VMs to guarantee the minimum resources required for maintaining the service quality. Computing resources available for non-critical services are limited to isolate services in resource competition and guarantee the user experience.) | Y | Y | |||
Security Access Control (Support virtual machine inbound, outbound, and inbound-outbound security access control functions, and can set access rules based on IP, MAC, port number, time period, etc.) | Y | ||||
vCPU and physical CPU binding (Assigns a physical CPU core for each vCPU to reduce performance loss caused by CPU core switchover.) | Y | Y | |||
CPU isolation (Supports removing the specified CPUs from the multi-core balanced scheduling policy of the host. The system will not assign tasks to isolated CPUs automatically. Isolated CPUs are dedicated to VM CPU binding and DPDK CPU binding, reserving CPU resources for DPDK enabling and critical VMs to prevent slow service processing if the host CPUs are busy.) | Y | Y | |||
Huge Pages (Supports 2MB and 1GB huge pages to reduce TLB miss risks and save performance cost caused by page table access for processes that require a large amount or memory, such as optimization of Oracle or any other large-scale database.) | Y | ||||
Host NUMA (Configures VMs to first obtain memory resources from the specified NUMA node and access a remote NUMA node only when the local memory resources are insufficient. Accessing local resources provides shorter latency and higher bandwidth than accessing remote resources.) | Y | Y | |||
Guest NUMA (Simulates the vCPU NUMA topology for VMs to distribute memory into different vNodes according to the vCPU configuration, and displays the mapping relationship between vCPU and memory in VMs.) | Y | Y | |||
Interrupt affinity (Configures all the interrupts that support setting the affinity on the specified CPU for all the interrupt processing programs to run on a specific CPU. As a best practice, specify a non-isolated CPU to avoid affecting the real-time performance of tasks running on the isolated CPU.) | Y | Y | |||
VM online migration (Migrates an operating VM from a server to another without service interruption or shutdown.) Provides the dynamic load balancing function of virtual machine storage. The storage characteristics are used to determine the optimal location of virtual machine data when it is created and used. Non-disruptive automatic migration based on performance parameters and capacity of storage volume IO and IOPS can be eliminated to eliminate Storage risks. | Y | Y | |||
VM storage online migration (Migrates the disk files on an operating VM from a storage location to another without service interruption or shutdown.) | Y | Y | |||
Disk IOPS (Supports setting read and write limits for virtual machine disk IOPS and I / O rates.) | Y | ||||
VM cold migration (Migrates a shutdown VM from one server to another or migrates the disk files on a shutdown VM from one storage array to another.) | Y | Y | |||
VM migration history (Supports displaying VM migration history from GUI. Available information includes the cause, time, source, and destination of each migration task.) | Y | Y | |||
VM template (Clones online or offline VMs or converts a VM into a template. A VM template has the same virtual resource configuration as the original VM, allowing the network administrator to deploy VMs in bulk based on the template.) | Y | Y | |||
VM bulk deployment (Deploys multiple VMs in bulk by using a VM template. You can deploy all the VMs on a specific physical host or allow the system to automatically deploy them on hosts in the cluster in a balanced manner.) | Y | Y | |||
VM snapshot (Creates VM snapshots that copy VM data at a specific time for test, backup, and restoration/revert back purposes to reduce backup time ranges and improve application availability. supports setting manual and periodic snapshots to save virtual machine disk files and memory status information to image files.) | Y | Y | |||
VM clone (Clones online or offline VMs to create new VMs. A cloned VM has exactly the same OS, application system, and data as the original VM but different vNIC MAC address and UUID. This ensures that no conflicts exist even if cloned VMs and the original VMs are deployed in the same network.) | Y | Y | |||
Scheduled startup and shutdown policy (Starts or shuts down the specified VMs at the specified time. This feature is applicable to desktop applications where scheduled power-on or power-off is required.) | Y | Y | |||
VM affinity (Configures specific VMs to stay on the same physical host for traffic between service systems that require frequent interaction (Web server and database for example) to be transmitted within a physical host instead of over a Layer 2 network. This prevents service congestion because of Layer 2 network issues. With this feature configured, even if DRS is triggered, the corresponding service systems are migrated along with the VMs.) | Y | Y | |||
VM anti-affinity (Allows CPU- or memory-intensive services to be deployed on different hosts to balance loads in the cluster.) | Y | Y | |||
VM view (Classifies and manages VMs as directories based on information such as department or service type, and supports setting VM boot priorities and boot delay in VM view. For example, for three VMs installed with the database, middleware, and Web Service software respectively, you can set their boot priorities for the VMs to start up in a specific order.) | Y | Y | |||
GPU pass-through (Passes through physical GPUs to a VM for the VM to use the GPUs exclusively. The pass-through VM sessions are established by using the H3C UIS virtualization kernel without virtualization simulation of Hypervisor, which provides better graphics displaying performance on VMs.) | Y | ||||
GPU virtualization (Virtualizes a physical GPU into multiple vGPUs for several VMs to share the same physical GPU. To use this feature, both the virtualization kernel and physical GPU support GPU virtualization.) | Y | ||||
GPU resource pool (Constructs the physical GPU resource pool. VMs dynamically obtain GPU resources from the pool at startup and automatically release GPU resources at shutdown. This feature is applicable to non-linear editing, synthesis, and transcoding services in the broadcasting and television industry.) | Y | ||||
Network-based USB redirection (Allows VMs to use USB devices cross physical hosts like using a local physical USB device. In virtualization deployment, this feature resolves issues in VM dynamic migration scenarios as well as cross-physical host mapping of USB devices.) | Y | Y | |||
Backup Function (Virtualization software has a built-in backup module, which enables full, incremental, and differential backup of virtual machines without the need to install backup software separately. It has no impact on business operations during backup, and supports scheduled backup (day, week, and month) settings. Backup strategy can be refined to minutes) | Y | Y | |||
Cloud rainbow (A cloud rainbow is a bridge between two sets of H3C virtualization platforms, allowing VM migration from one platform with insufficient resources to the other without VM service interruption. Cloud rainbow requires the two sets of hyper-converged infrastructure to be deployed at the same Layer 3 network to avoid service interruption after migration.) | Y | ||||
Network virtualization
UIS licenses | |||||
Feature | H3C UIS Manager | H3C UIS-CAS | H3C UIS Manager Enhancement Package | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Standard Edition | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Enterprise Edition |
Standard virtual switch (Connects VMs on a host to the external network and can be used to create virtual networks on an H3C UIS CVK host. A virtual switch supports a maximum of 1024 virtual ports and each host supports a maximum of 256 virtual switches.) | Y | Y | |||
Distributed vSwitch (By providing a unified interface, the system simplifies virtual network connection establishment and management. It can create and manage a single distributed vSwitch configured with multiple distributed virtual port profiles. Port profiles enable network settings to automatically follow the VMs at VM migration.) | Y | Y | |||
vNIC (Each VM is configured with one or multiple vNICs. Each virtual network interface has its own IP address and MAC address, providing network properties consistent with those of a physical interface on a traditional physical NIC.) | Y | Y | |||
Port profiles/Port group (Uses port profiles available for multiple vNICs to simplify port configuration. Each port profile defines a set of network properties, including VLAN, QoS, ACL, and network priority.) | Y | Y | |||
Distributed vFirewall (Use the software-defined data center approach to define the trust relationships and move the data center security boarder down to the vSwitch level. Building a vNIC-based firewall provides different security policies for different vNICs, balances performance and flexibility, and allows security policies to follow VMs at VM migration between different physical nodes.) | Y | ||||
Network priority (Sets network priorities for VMs to ensure that critical services with a high priority can obtain as much network I/O resources as possible in case of physical NIC network congestion.) | Y | Y | |||
Network QoS (Sets the uplink and downlink rates for vNICs and limit the maximum vNIC throughput to control vNIC traffic within an acceptable range.) | Y | Y | |||
VLAN (Creates a virtual LAN over a physical LAN to isolate network traffic to enhance security performance and separate workloads. H3C UIS VLAN is compatible with IEEE 802.1Q and can be deployed without any change to network cabling or switch settings. VLANs confine broadcast traffic to VLANs, which reduces broadcast load on other switches and in the other subnets.) | Y | Y | |||
ACL (Controls VM access to protect service resources on VMs. ACL supports configuring packet matching rules based on criteria such as time ranges and source and destination MAC addresses, IP addresses, and ports.) | Y | Y | |||
IP and MAC binding (Configures VM IP and MAC bindings to resolve audit issues caused by IP or MAC address changes.) | Y | Y | |||
NetFlow (Specifies the IP address and port number of the NetFlow collector to which the vSwitch sends the received traffic in the NetFlow V5 format. The system identifies IPv4 flow based on the 5-Tuple (source IP, destination IP, source port, destination port, and protocol number). Packets with the same 5-Tuple are identified as traffic of the same flow.) | Y | Y | |||
Port mirroring (Copy messages received from the specified port to the port connected to the data monitoring device, allowing the device to analyze these copied messages for network monitoring and troubleshooting.) | Y | Y | |||
Policy Templates (Supports the creation of network policy templates and uses network policy templates that span multiple virtual ports to simplify port configuration. The template defines a set of network policy attributes, including VLAN, QoS, ACL, network priority, etc.) | Y | ||||
Link aggregation (Provides built-in network failover and load balancing capabilities for each VM in the network to provide higher hardware availability and fault tolerance.) | Y | Y | |||
DHCP server (vSwitches can act as DHCP servers to automatically assign IP addresses to VMs in the virtualization environment and display address allocation for an IP address pool in a graphic way.) | Y | Y | |||
NIC pass-through (Uses IOMMU to passes through physical NICs to a VM for the VM to use the NICs exclusively. The physical network card is transparently transmitted to a virtual machine on the host, the virtual machine monopolizes the physical network card, and fully owns the physical network card resources and performance.) | Y | Y | |||
Hardware SR-IOV (Virtualizes a physical NIC into multiple virtual function (VF) interfaces, with an independent virtual PCIe channel assigned to each interface. These virtual PCIe channels share the PCIe channel of the physical NIC. Each VM can use one or multiple VF interfaces, allowing VMs to directly access their own VF interfaces without the negotiation of Hypervisor. This greatly improves the network throughput performance.) | Y | ||||
DPDK (Provides a highly efficient function database for data packet processing in the user space. This feature makes high-efficiency packet forwarding possible in the x86 architecture by using the following technologies: kernel-bypass stack at the Environment Abstraction Layer (EAL), uninterrupted packet receiving and forwarding in polling mode, unlocked ring memory management, memory/cache/queue management optimization, load balancing based on NIC multi-queue and flow identification, HugePages, NUMA, and CPU isolation and binding.) | Y | ||||
Network visibility (Provides a visual description of network connections and data traffic in end-to-end network view. This helps users clearly understand VM connections to the entity network and the virtual network and better resolve network issues.) | Y | ||||
Storage virtualization
UIS Licenses | |||||
Feature | H3C UIS Manager | H3C UIS-CAS | H3C UIS Manager Enhancement Package | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Standard Edition | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Enterprise Edition |
Distributed storage cluster size (Integrates local disks on multiple servers into a distributed storage resource pool and provides upper-layer VMs with industry-standard SCSI, iSCSI, and object access interfaces for obtaining the resources. The local storage spaces on compute nodes are scheduled and managed by the distributed storage cluster software. The more nodes in the cluster, the more complex the inter-node information exchange tasks and the algorithm for data synchronization when a disk fails. Three nodes support the deployment of three copies. It is not required to add additional hard disks (groups), capacity, or nodes to satisfy the replication strategy and it makes full use of the resources of each disk and each node.) | 3~32 | 3~32 | |||
Minimum expansion unit (Minimum number of compute nodes that must be added in one expansion operation. Online horizontal expansion of computing and storage capabilities is an advantage of distributed storage, and is also the method to resolve future data center expansion issues. The smaller the minimum expansion unit, the simpler the expansion, and the lower the cost per investment.) | 1 | 1 | |||
Number of replicas/Copies (Replication is a basic method of providing fault tolerance to distributed storage. Data replicas are evenly distributed on multiple compute nodes in the distributed storage system for the nodes to share access request processing tasks. This reduces the response time and eliminates the risk of data loss in case of node failure. A group of hard disk pools (groups) can support both 2-copy and 3-copy strategies and can be selected arbitrarily to maximize the use of disk capacity. There is no need to use additional disk groups to carry two different strategies, which greatly reduces customer costs. In addition, support for "online" adjustment of virtual machine disk redundancy strategy greatly facilitates operation and maintenance and avoids interruption of business.) | 2~5 | 2~5 | |||
Full flash support (Uses only SSDs as local disks for distributed storage construction. This greatly improves IOPS performance with reduced read/write latency. As the price of SSDs declines, the all-flash architecture has become an application trend in the North American market. In the domestic market, hyper-convergence that uses the all-flash architecture is gradually entering the vision of users in high-value industries, such as finance.) | Y | Y | |||
SSD cache (In hybrid deployment of HDDs and SSDs, local SSD cache is often used to improve the read/write performance of distributed storage. Before writing data to the persistent local storage, the system first writes the data into the SSD cache that provides a higher access speed. When a VM attempts to read data, it first searches through the hot data in the SSD cache before accessing the local persistent storage. Provide SSD based Read Caching and Write Buffer capability to improve the performance of the I/O) | Y | Y | |||
Erasure coding (EC) (The distributed storage system uses replicas to protect data and provide availability of the highest level. When data failure occurs, the system restores the data directly from a replica instead of computing and reading it from another storage location. However, the storage cost is very high because full replication is required. To resolve the issue, H3C UIS 7.0 supports using EC for data coding. Similar to RAID 5, EC gets the parity bit through calculation. It codes data block strips on different nodes and calculates the parity bits. When a host or disk fails, the corresponding parity bit can be used to restore the missing data block. Supports the erasure code protection for file storage from N + 1 to N + 4, and support the failure of any 4 nodes without data loss and system shutdown) | Y | Y | |||
Automatic data reconstruction (Allows the system to automatically detect data failures by comparing replicas on different nodes when a storage cluster node or disk fails and then start self-healing to restore the lost replica to ensure complete fault tolerance. Provides Automated Data Rebuilding capability to restore redundancy in case of any Disk or Node Failure.) | Y | Y | |||
QoS Function (Support storage QoS policy, specify service priority according to business pressure; support volume QoS, data recovery QoS, support setting data recovery policy with hard disk pool as granularity.) | Y | ||||
Disk Replacement (Supports disk replacement wizard, provides a graphical and wizard-based interface, supports hot-swappable replacement of hard disks, and brings more efficient maintainability) | Y | ||||
Automatic data balancing (The data replica distribution algorithm balances data storage among nodes in the storage cluster, enabling replicas to be stored on different nodes, disks or cabinets to avoid single point of failure. At node scale-up or scale-down, the data recovery and construction algorithm can ensure workload balancing among nodes after data construction. The Striped data multi copy mechanism is adopted to ensure the data reliability. The storage software divides the physical hard disk into chunks of 4MB size to save the data. The redundancy mode of RAID1 is not allowed. Independent hot spare is not needed in the storage node. Supports to automatically balance the data when it is placed, and it is not required to delay the balance or choose another balance time and strategy. This can ensure the smooth operation of customer services, otherwise it will take up bandwidth and affect the business by finding another time to balance it.) | Y | Y | |||
Storage thin provisioning (Assigns physical disk space on demand to maximize storage resource usage and resolve the over-provisioning issue. For example, if 1TB disk space is pre-allocated to a VM, but the VM uses only 200GB, the system assigns only 200GB to the VM.) | Y | Y | |||
Unified storage (One node can support virtualization and three storage functions at the same time, which allows a cluster that contains a minimum of three nodes to provide virtualization, distributed block storage, object storage, and file storage services. Note that object storage and file storage services must be provided by a host. One node can support virtualization and 3 types of storage functions (block, file, object) at the same time. At least 3 node cluster can provide virtualization, distributed block, object, and file storage services at the same time. Among them, object and file services are provided on the host machine. File storage support protocols include FTP, CIFS, NFS, HTTP; Provides a variety of NAS value-added service functions including authority management, snapshot management (WORM), shared directory management, etc. NAS services can adopt multi-service nodes for high availability and support load balancing. Object storage, compatible with S3 and other interfaces, supporting management through HTTP or cli) | Y | Y | |||
Snapshot (Block storage supports snapshotting, writable snapshots based on read-only snapshots, scheduled snapshotting, and volume consistency group snapshotting.) | Y | ||||
Volume copy (Volumes of block storage support offline volume copy.) | Y | ||||
Asynchronous remote replication (Supports asynchronous remote replication and the SRA plugin.) | Y | ||||
Virtualization security
UIS licenses | |||||
Feature | H3C UIS Manager | H3C UIS-CAS | H3C UIS Manager Enhancement Package | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Standard Edition | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Enterprise Edition |
Storage QoS (Sets the upper limit of read and write IOPS for a VM or each VM disk file, eliminating the read and write adjacent bit interference (ABI) between multiple VMs in the same storage LUN, and satisfying the Service-Level-Agreement (SLA) of performance from the disk file granularity aspect.) | Y | Y | |||
Virtual resource isolation (Uses the following technologies to isolate virtual resources: · Hardware-assisted virtualization technologies such as Intel VT-x and AMD-V—Isolates vCPU register instructions and state control information. · Mapping of hardware physical memory and VM logical memory—Isolates the virtual memory spaces of different VMs. This allows memory pages to automatically clear the physical bits at VM shutdown or deletion to ensure the non-recoverability of memory data. · vSwitch integrated at the Hypervisor layer—Used to exchange and isolate traffic between VMs. · Distributed lock mechanism of the cluster file system—Enforces exclusive VM access to virtual disk files.) | Y | Y | |||
Boot process integrity check (Checks the integrity of product components at startup, and performs self-recovery if the integrity is damaged. This prevents attackers from compromising the security baseline integrity of the virtualization system.) | Y | Y | |||
VM backup (Backs up VMs manually or as scheduled. Full backup, incremental backup, and differential backup are supported. It supports collaboration with backup schemes of other professional vendors.) | Y | Y | |||
VM disk backup (Uses disk-level data backup and restoration to provide fast and simple data protection for VMs. This feature supports automatic scheduled backup and manually triggered immediate backup, full, incremental, and differential backup, as well as backup management and restoration.) | Y | Y | |||
VM anti-virus (Cooperates with mainstream anti-virus vendors in the industry, such as Trend Micro and Qihoo 360, to support both light agent and agentless methods to ensure that existing virus can be detected and killed during VM data read or write.) | Y | Y | |||
VM recycle bin (VMs in the recycle bin cannot be displayed from the H3C UIS, but their image and configuration files are retained. The HA, DRS, affinity, and anti-affinity rules do not take effect on VMs in the recycle bin.) | Y | Y | |||
User-defined roles and permissions (Allows administrators to create user-defined roles and configure privileges and permissions for the roles to limit access to resource pools, servers, and VMs.) | Y | Y | |||
Management service access security (Supports configuring IP segments allowed or forbidden to access the virtualization management platform, setting the maximum login failures and lockdown duration, and specifying the Web idle timeout.) | Y | Y | |||
User authentication (Supports password authentication. LDAP authentication, and dual-factor authentication based on USB key and password.) | Y | Y | |||
Password complexity policy (Supports configuring the user password complexity requirements and the password change interval.) | Y | Y | |||
VM template integrity check and source tracing (Uses checksums to prevent malicious tampering with VM template files, and traces the source of VM templates and VM template deployment records.) | Y | Y | |||
Secure erasure of data residue (Erases VM disk and memory data residue generated by VM destroying or VM shutdown to prevent sensitive data leakage.) | Y | Y | |||
Security audit (Audits the event object, content description, result, time, risk level, category, behavior, and reserved fields of administrator system operation logs, administrator resource access behaviors, and local configuration operations on server, storage, or other physical resources. This feature adopts the UTF-8 encoding format and supports using Syslog and Web Service to connect to a third-party log management platform. Audit log integrity protection and regular automatic log dumping are also available.) | Y | Y | |||
High reliability and high availability
UIS licenses | |||||
Feature | H3C UIS Manager | H3C UIS-CAS | H3C UIS Manager Enhancement Package | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Standard Edition | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Enterprise Edition |
Management platform fast recovery (Supports online export of management platform configuration and database. When the management platform fails, you can import the exported data to quickly restore the platform.) | Y | Y | |||
Management platform HA (Supports cluster deployment, allowing a maximum of (n-1)/2 nodes to fail without affecting the platform services. n is the total number of nodes in the management cluster.) | Y | Y | |||
Host and VM HA (Uses the cost-efficient and easy-to-configure UIS cluster function to provide high availability. H3C UIS 7.0 HA can automatically detect host and VM failures and then restart the VMs on another physical host in the cluster in the shared storage environment.) | Y | Y | |||
OS HA (Uses CAStools installed in the VM OS to monitor VM OS operation regularly and restart or migrate the VM in case of VM BSOD or panic.) | Y | Y | |||
Application HA (Uses CAStools installed in the VM OS to monitor the application operation in the VM OS regularly and restart the application or VM in case of application failure.) | Y | ||||
Service network HA (Automatically detects the status of the physical NIC through which a VM provides services to the external network, and migrates the VM to another compute node in the cluster when the service NIC fails to ensure service continuity as much as possible.) | Y | Y | |||
VM boot priority (Specifies the VM boot order at host restart to ensure that service-critical VMs can start up first. For example, if Web frontend, middleware, and database VMs exist on the same host, you can specify the priorities for the database VM to start up first.) | Y | Y | |||
Host maintenance mode (Automatically migrates operating and closed VMs to an operating host in the cluster and then shuts down the physical host if the original host is to be shut down for maintenance (adding memory for example).) | Y | Y | |||
DRS (Regularly calculates the loads of computing resources such as CPU and memory on the cluster hosts, and automatically adjusts VMs on the hosts for all the virtualization hosts in the cluster to have balanced loads.) | Y | Y | |||
DRX (Industry-first solution for dynamic resource scaling. It monitors service system resource usage and load in real time, provides automated awareness of service system performance, and can automatically scale up or down virtual resources. Together with load balancing devices, DRX provides the service system with flexible and expansible resource pools to improve the service access experience.) | Y | ||||
Hyper-converged management and O&M capabilities
UIS licenses | |||||
Feature | H3C UIS Manager | H3C UIS-CAS | H3C UIS Manager Enhancement Package | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Standard Edition | H3C UIS-ONEStor Block Enterprise Edition |
Centralized control and operation and visibility (Adopts the mainstream B/S architecture and HTML5 to comprehensively present the status and hierarchical relationship of managed objects, and allows all operations related to virtualization functions to be managed and monitored from the Web interface.) | Y | ||||
Flexible selection of cluster node types (Allows users to specify the host role as storage, computing, or hyper-converged, and supports flexible combination of the three types of hosts in a cluster to meet requirements in various scenarios and better respond to flexible resource scaling in case of unbalanced resource usage.) | Y | ||||
Unified management of x86 and ARM (H3C UIS can manage hyper-converged systems built on x86 and ARM in a unified way.) | Y | ||||
One-key health check of the hyper-converged environment (Monitors the health status of VMs, nodes, and disks with more than 220 check items, and uses fully automated machine-based patrol and fault diagnosis instead of manual item-by-item analysis and fault location, reducing O&M time from 1 hour to 5 minutes.) | Y | ||||
Physical machine management (Monitor the physical host status of each hyper-converged compute/storage node, as well as the status indicators for CPU, memory, fan, power, temperature, and other key parameters.) | Y | ||||
Dashboard (Homepage of H3C UIS, displaying the overall operation status, resource usage, alarms, and other critical information in the hyper-converged environment.) | Y | ||||
Dashboard in full-screen display (Displays main performance indicators and resource status in the hyper-converged environment in full-screen mode.) | Y | ||||
Dashboard customization (Allows users to customize the performance metrics and resource status for full-screen display as needed. Customizable metrics include host performance, VM performance, shared storage performance, overall system health, host health, CPU allocation ratio, memory allocation ratio, storage allocation ratio, system alarms, Top 5 hosts by CPU or memory usage, Top 5 VMs by CPU or memory usage, and host and VM status statistics.) | Y | ||||
One-key analysis of recent resource usage (Supports automatic analysis of VM, host, and cluster history resource usage through one click to help network planning and decision making.) | Y | ||||
One-key storage cleanup (Supports invalid image file detection in local and shared storage as well as invalid image cleanup through one click to free up storage space.) | Y | ||||
One-key export (Supports exporting cluster, host, and VM configuration and status information through one click on H3C UIS.) | Y | ||||
One-key VM restoration (Supports restoring the VM configuration at a specific time point through one click.) | Y | ||||
One-key zombie VM management (A zombie VM represents a shutdown VM that has not been used for a long time. H3C UIS supports displaying, starting up, deleting zombie VMs through one click.) | Y | ||||
Alarm management (Collects alarm information in the virtualization environment at a specific interval, monitors information about key resources, including computing, storage, and network resources, and supports notifying the system administrator through emails or short messages.) | Y | ||||
Syslog server (Sends the collected operation logs to the specified Syslog server.) | Y | ||||
Host reports (Displays critical performance information of hosts during the specified period of time. Available information includes CPU usage, memory usage, disk read rate, disk write rate, disk I/O throughput, network total traffic, network read traffic, network write traffic, network read rate, and network write rate.) | Y | ||||
VM reports (Displays critical performance information of VMs during the specified period of time. Available information includes CPU usage, memory usage, disk read rate, disk write rate, disk I/O throughput, network total traffic, network read traffic, network write traffic, network read rate, and network write rate.) | Y | ||||
TopN host performance reports (Displays information about the TopN hosts collected during the specified period of time by CPU usage, memory usage, disk I/O throughput, network total traffic, network read traffic, and network write traffic.) | Y | ||||
TopN VM performance reports (Displays information about the TopN VMs collected during the specified period of time by CPU usage, memory usage, disk I/O throughput, network total traffic, network read traffic, and network write traffic.) | Y | ||||
Cluster resource statistics (Displays the state, density, total CPU cores, CPU allocation rate, total memory capacity, and memory allocation rate information of VMs in all or the specified cluster, and supports exporting the information in PDF format.) | Y | ||||
Host resource statistics (Displays the host model, CPU model, physical CPU cores, memory capacity, VM running summary, host running state, continuous running time, CPU usage, memory usage, and local disk space information of all or the specified hosts, and supports exporting the information in PDF format.) | Y | ||||
VM resource statistics (Displays the VM running state, CPU cores, CPU usage, memory capacity, memory usage, VM OS, and host (compute node) information of all or the specified VMs, and supports exporting the information in PDF format.) | Y | ||||
IP allocation statistics (Displays the IP address, MAC address, CAStools version, and VM OS information of all or the specified VMs, and supports exporting the information in PDF format.) | Y | ||||
Virtualization topology (Supports graphic display of the relationship between cluster, host, VM, network, and storage. Available topologies include virtual computing topology, virtual network topology, and virtual storage topology that centered on computing resources, vSwitches, and storage LUNs, respectively.) | Y | ||||
Drag-and-drop service topology (Supports fast service logic topology generation through drag and drop and editing. The topology shields the complex logic of the underlying computing, network, and storage infrastructure, helping users quickly, simply and intuitively understand the logical topology required by each service in the data center.) | Y | ||||
Interface customization (Supports customization of login page background, system title, logo, copyright information, copyright logo, product logo, and homepage header background.) | Y | ||||
Migration tools (H3C UIS is built in with online p2v and v2v migration tools that support mainstream operating systems, public cloud platforms, and virtualization platforms in the industry, including VMware, Huawei, Hyper-V, and other platforms. This enhances the platform universality, reduces the difficulty of service onboard, and reduces the O&M workload.) | Y | ||||
AI-driven resource capacity prediction (Built-in with a time series model, H3C UIS supports automated data retrieval and prediction to provide easy-to-use data prediction services. The platform displays real-time CPU, memory, and storage usage data, and gives tips on the warning time point based on prediction and analysis performed by using the AI machine learning algorithm. This helps users in resource capacity expansion and cost budgeting improve service reliability.) | Y | ||||
SSD life detection (Supports displaying SSD remaining life in percentage in real time to remind users to replace hard disks in time and ensure service continuity.) | Y | ||||
Management of VMware (Supports heterogeneous management of VMware VMs and provides full life-cycle management and O&M for the VMs.) | Y | ||||
Backup Features (Provides the capability to take full / Incremental level VM Backups. Provides Automated Scheduling for Backups based on Hourly, Daily, weekly etc. scheduling. Supports to configure Internal Virtual Storage, External SAN or NAS to be Backup repository for Storing Virtual Machine Backups. Supports Industry’s common storage protocols such as iSCSI, FC or Network File Sharing (NFS). It does not limit to specific number of VMs and supports unlimited number of VMs for future scalability). | Y | ||||
DCIG TOP 5 Enterprise HCI Providers
Click the button below to download the 2023-24 DCIG TOP 5 Enterprise HCI Providers Report.
Resource Center
- Cloud & AI
- InterConnect
- Intelligent Computing
- Intelligent Storage
- Security
- SMB Products
- Intelligent Terminal Products
- Product Support Services
- Technical Service Solutions
Product Support Services
Technical Service Solutions
- Resource Center
- Policy
- Online Help
- Technical Blogs
Resource Center
Policy
Online Help
- Become A Partner
- Partner Policy & Program
- Global Learning
- Partner Sales Resources
- Partner Business Management
- Service Business
Global Learning
- Profile
- News & Events
- Online Exhibition Center
- Contact Us

 Products and Solutions
Products and Solutions