- Released At: 12-05-2025
- Page Views:
- Downloads:
- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
|
|
|
H3C Switches and Servers |
|
Integration Guide |
|
|
|
|
Version: 6W100-20230317
Copyright © 2023 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Preface
This document provides examples for integrating H3C switches with servers and configuring related parameters.
This preface includes the following topics about the documentation:
· Audience
This documentation is intended for:
· Network planners.
· Field technical support and servicing engineers.
· Network administrators working with H3C switches.
The following information describes the conventions used in the documentation.
Symbols
|
Convention |
Description |
|
An alert that calls attention to important information that if not understood or followed can result in personal injury. |
|
|
An alert that calls attention to important information that if not understood or followed can result in data loss, data corruption, or damage to hardware or software. |
|
|
An alert that calls attention to essential information. |
|
|
NOTE: |
An alert that contains additional or supplementary information. |
|
An alert that provides helpful information. |
Network topology icons
|
Convention |
Description |
|
Represents a generic network device, such as a router, switch, or firewall. |
|
|
Represents a routing-capable device, such as a router or Layer 3 switch. |
|
|
Represents a generic switch, such as a Layer 2 or Layer 3 switch, or a router that supports Layer 2 forwarding and other Layer 2 features. |
|
|
Represents an access controller, a unified wired-WLAN module, or the access controller engine on a unified wired-WLAN switch. |
|
|
Represents an access point. |
|
|
Represents a wireless terminator unit. |
|
|
Represents a wireless terminator. |
|
|
Represents a mesh access point. |
|
|
Represents omnidirectional signals. |
|
|
Represents directional signals. |
|
|
Represents a security product, such as a firewall, UTM, multiservice security gateway, or load balancing device. |
|
|
Represents a security module, such as a firewall, load balancing, NetStream, SSL VPN, IPS, or ACG module. |
Examples provided in this document
Examples in this document might use devices that differ from your device in hardware model, configuration, or software version. It is normal that the port numbers, sample output, screenshots, and other information in the examples differ from what you have on your device.
This document is not restricted to specific software or hardware versions. Procedures and information in the examples might be slightly different depending on the software or hardware version of the device.
The configuration examples were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
You can e-mail your comments about product documentation to [email protected].
We appreciate your comments.
H3C switches and servers integration guide
Integrating an H3C switch with a Linux server through a bond interface
Connecting an H3C switch to a Linux server in bonding mode 1
Connecting an H3C switch to a Linux server in bonding mode 4
Integrating an H3C switch with a Linux server through LLDP/DCBX
Integrating an H3C switch with a BMP server
H3C switches and servers integration guide
Integrating an H3C switch with a Linux server through a bond interface
About bonding modes
Seven Linux bonding modes are available, each providing different load sharing and link backup policies.
· Mode 0 (balance-round robin)—This mode transmits packets through member ports one by one in sequence to realize load balancing.
· Mode 1 (active-backup)—Only one port in the bond is active. A different port in the bond becomes active only when the active port fails.
· Mode 2 (balance-xor)—This mode determines the port to transmit packets based on the formula of [(source MAC address XOR destination MAC address) % member port count].
· Mode 3 (broadcast)—This mode sends packets to all member ports.
· Mode 4 (802.3ad, dynamic link aggregation)—Creates an aggregation group that shares the same speed and duplex settings with all member ports. This mode requires the peer device to support 802.3ad.
· Mode 5 (adaptive transmit load balancing)—The outgoing traffic is distributed according to the transmit load on each member port.
· Mode 6 (adaptive load balancing)—Includes transmit load balancing and receive load balancing.
Interoperability analysis
|
H3C switch |
Linux server |
Interoperability |
|
No configuration required |
Bonding mode 1 (recommended) |
Yes |
|
Dynamic link aggregation mode |
Bonding mode 4 (recommended) |
Yes |
Configuration guidelines
ARP/ND
Network adapters (also called network ports) on the server operating in bonding mode 1 must support sending ARP/ND packets to the switch when a member port state changes between active and inactive. Based on the packets, the switch will refresh the ARP/ND entries and generate the host route.
Network adapters on the server operating in bonding mode 4 must support sending ARP/ND packets to the switch when the any member port in the aggregation group goes down or comes up. Based on the packets, the switch will refresh the ARP/ND entries and generate the host route.
FEC settings
Forward error correction (FEC) adds error correction information to packets at the transmit end and allows the receive end to use the information to correct error codes that are generated during data transmission. Although with some transmission latency, this technology can lower the channel error code ratio, improve signal quality, and extend the maximum transmission distance of physical media. If the FEC modes at the two ends do not match, the physical link cannot be connected. If the server adapter and switch do not match in the FEC mode, configure FEC settings for the server as follows:
· Execute the ethtool --show-fec <port name> command to view the current FEC mode on the port.
· To change the FEC mode, execute the ethtool --set-fec <port name> encoding off/baser/rs/auto command. The configuration takes effect immediately and the previous settings are restored after a server reboot.
· To change the FEC mode and make the configuration to take effect after a server reboot, you can edit the rc.locl file. To edit the /etc/rc.d/rc.local file:
¡ Execute the ethtool --set-fec <port name> encoding off/baser/rs/auto command.
¡ Execute the systemctl enable rc-local command to enable the rc-local service
¡ Reboot the server.
|
|
NOTE: For more information about ARP/ND and FEC settings for the server, see the user guide for the server. |
Connecting an H3C switch to a Linux server in bonding mode 1
Network configuration
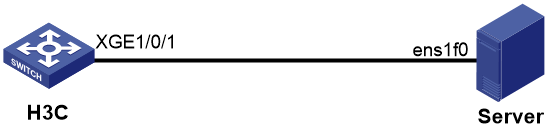
As shown in Figure 1, two network ports on the Linux server are connected to two different ports on the H3C switch. Configure the two network ports on the server to operate in active/standby mode, so the other port becomes active when the active port fails.
Configuration analysis
· Use port ens7f3 as the management port and configure bonding mode 1 on port ens1f0 and port ens1f1.
· Install the Linux system on the server directly. If a Linux VM is deployed based on VMware EXSI, the network ports of the Linux server are connected to the vSwitch deployed based on VMware EXSI instead of the switch directly. This might not realize the expected effect.
· No configuration is required on the switch.
Procedures
# View server information.
|
Item |
Description |
|
Server model |
H3C R4900 G5 |
|
Operating system |
Kernel version: Linux version 4.18.0-305.25.1 Operating system version: CentOS Linux release 8.4.2105 |
|
Network adapter model |
· 18:00.0 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT2894 Family [ConnectX-6 Lx] · 18:00.1 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT2894 Family [ConnectX-6 Lx] |
|
Network adapter driver version |
MLNX_OFED_LINUX-5.4-3.2.7.2.3-rhel8.4-x86_64 |
|
Network adapter firmware version |
driver: mlx5_core version: 5.4-3.2.7.2.3 firmware-version: 26.31.2006 (MT_0000000531) expansion-rom-version: bus-info: 0000:18:00.0 bus-info: 0000:18:00.1 |
|
Dependency package |
yum -y install zlib-devel bzip2-devel yum -y install openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel gdbm-devel db4-devel libpcap-devel xz-devel --skip-broken yum -y install createrepo pciutils gcc gcc-c++ flex bison yum -y install gtk2 atk cairo tcl tcsh tk yum -y install tcl tcsh gcc-gfortran tk python36 perl yum -y install -y kernel-modules-extra yum remove pcp-pmda-infiniband |
# Create virtual network adapter bond0 and file ifcfg-bond0.
[root@server4 /] vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-bond0
: wq
# Edit file ifcfg-bond0 and write network adapter settings to the file.
Note that the IP address of the bond port is a data network IP address.
vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-bond0
BONDING_OPTS="mode=1 miimon=100 updelay=100 downdelay=100"
TYPE=Bond
BONDING_MASTER=yes
PROXY_METHOD=none
BROWSER_ONLY=no
BOOTPROTO=none
IPADDR=55.50.129.129
PREFIX=25
GATEWAY=55.50.129.252
DEFROUTE=no
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6INIT=yes
IPV6_AUTOCONF=no
IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6_PRIVACY=no
IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy
IPV6ADDR=200::5/64
IPV6_DEFAULTGW=200::1
NAME=bond0
DEVICE=bond0
ONBOOT=yes
# Edit file ifcfg-ens1f0 and write network adapter settings to the file.
[root@server4 /]# more ifcfg-ens1f0
DEVICE=ens1f0
TYPE=Ethernet
ONBOOT=yes
SLAVE=yes
MASTER=bond0
BOOTPROTO=none
# Edit file ifcfg-ens1f1 and write network adapter settings to the file. Save the configuration and exist.
[root@server4 /]# more ifcfg-ens1f1
DEVICE=ens1f1
TYPE=Ethernet
ONBOOT=yes
SLAVE=yes
MASTER=bond0
BOOTPROTO=none
# Reboot network services.
# ifdown bond0
# ifup bond0
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that bond0 has two member ports that act in active/backup mode.
[root@server4 /]# cat /proc/net/bonding/bond0
Ethernet Channel Bonding Driver: v4.18.0-305.25.1.el8_4.x86_64
Bonding Mode: fault-tolerance (active-backup)
Primary Slave: None
Currently Active Slave: ens1f0
MII Status: up
MII Polling Interval (ms): 100
Up Delay (ms): 100
Down Delay (ms): 100
Peer Notification Delay (ms): 0
Slave Interface: ens1f0
MII Status: up
Speed: 25000 Mbps
Duplex: full
Link Failure Count: 0
Permanent HW addr: 10:70:fd:7f:da:a6
Slave queue ID: 0
Slave Interface: ens1f1
MII Status: up
Speed: 25000 Mbps
Duplex: full
Link Failure Count: 0
Permanent HW addr: 10:70:fd:7f:da:a7
Slave queue ID: 0
# View the incoming traffic on the H3C switch.
<H3C> display counters rate inbound interface
Usage: Bandwidth utilization in percentage
Interface Usage (%) Total (pps) Broadcast (pps) Multicast (pps)
XGE1/0/1 25 2825519 -- --
XGE1/0/2 0 0 -- --
# Verify that when you shut down Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 on the H3C switch, the incoming traffic is transmitted to Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
<H3C> display counters rate inbound interface
Usage: Bandwidth utilization in percentage
Interface Usage (%) Total (pps) Broadcast (pps) Multicast (pps)
XGE1/0/1 0 0 -- --
XGE1/0/2 100 2825703 -- --
# Verify that when the Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 restores to normal on the H3C switch, the incoming traffic is still transmitted to Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/2, because port ens1f0 has become the backup interface after Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 goes down.
<H3C> display counters rate inbound interface
Usage: Bandwidth utilization in percentage
Interface Usage (%) Total (pps) Broadcast (pps) Multicast (pps)
XGE1/0/1 0 0 -- --
XGE1/0/2 100 2825508 -- --
Connecting an H3C switch to a Linux server in bonding mode 4
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, two network ports on the Linux server are connected to two different ports on the H3C switch. Configure link aggregation for the two ports of the Linux server to improve port usage and realize load balancing.
Configuration analysis
· Use port ens7f3 as the management port and configure bonding mode 4 for port ens1f0 and port ens1f1.
· Install the Linux system on the server directly. If a Linux VM is deployed based on VMware EXSI, the network ports of the Linux server are connected to the vSwitch deployed based on VMware EXSI instead of the switch directly. This might not realize the expected effect.
· Configure dynamic link aggregation on the switch.
Procedures
· Configure the H3C switch.
# Create Layer 2 aggregate port 1 and configure the port to operate in dynamic aggregation mode.
<H3C> system-view
[H3C] interface bridge-aggregation 1
[H3C-Bridge-Aggregation1] link-aggregation mode dynamic
# Configure the port as an edge port.
[H3C-Bridge-Aggregation1] stp edged-port
[H3C-Bridge-Aggregation1] quit
# Assign Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to aggregation group 1.
[H3C] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[H3C-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-aggregation group 1
[H3C-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[H3C] interface ten-gigabitEthernet 1/0/2
[H3C-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 1
[H3C-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
· Configure the Linux server.
# View the server information.
|
Item |
Description |
|
Server model |
H3C R4900 G5 |
|
Operating system |
Kernel version: Linux version 4.18.0-305.25.1 Operating system version: CentOS Linux release 8.4.2105 |
|
Network adapter model |
· 18:00.0 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT2894 Family [ConnectX-6 Lx] · 18:00.1 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT2894 Family [ConnectX-6 Lx] |
|
Network adapter driver model |
MLNX_OFED_LINUX-5.4-3.2.7.2.3-rhel8.4-x86_64 |
|
Network adapter firmware version |
driver: mlx5_core version: 5.4-3.2.7.2.3 firmware-version: 26.31.2006 (MT_0000000531) expansion-rom-version: bus-info: 0000:18:00.0 bus-info: 0000:18:00.1 |
|
Dependency package |
yum -y install zlib-devel bzip2-devel yum -y install openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel gdbm-devel db4-devel libpcap-devel xz-devel --skip-broken yum -y install createrepo pciutils gcc gcc-c++ flex bison yum -y install gtk2 atk cairo tcl tcsh tk yum -y install tcl tcsh gcc-gfortran tk python36 perl yum -y install -y kernel-modules-extra yum remove pcp-pmda-infiniband |
# Create virtual network adapter bond0 and file ifcfg-bond0.
[root@server4 /] vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-bond0
: wq
# Edit file ifcfg-bond0 and write network adapter settings to the file.
Note that the bonding port IP address is a data network IP address.
vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-bond0
BONDING_OPTS="mode=4 miimon=100 updelay=100 downdelay=100 xmit_hash_policy=layer3+4"
TYPE=Bond
BONDING_MASTER=yes
PROXY_METHOD=none
BROWSER_ONLY=no
BOOTPROTO=static
IPADDR=55.50.129.129
PREFIX=25
GATEWAY=55.50.129.252
DEFROUTE=no
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6INIT=yes
IPV6_AUTOCONF=no
IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no
IPV6_PRIVACY=no
IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy
IPV6ADDR=200::5/64
IPV6_DEFAULTGW=200::1
NAME=bond0
DEVICE=bond0
ONBOOT=yes
# Edit file ifcfg-ens1f0 and write network adapter settings to the file.
[root@server4 /]# more ifcfg-ens1f0
DEVICE=ens1f0
TYPE=Ethernet
ONBOOT=yes
SLAVE=yes
MASTER=bond0
BOOTPROTO=none
# Edit file ifcfg-ens1f1 and write network adapter settings to the file.
[root@server4 /]# more ifcfg-ens1f1
DEVICE=ens1f1
TYPE=Ethernet
ONBOOT=yes
SLAVE=yes
MASTER=bond0
BOOTPROTO=none
# Restart network services.
# ifdown bond0
# ifup bond0
Verifying the configuration
# View the aggregation status on the H3C switch.
<H3C> display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Aggregate Interface: Bridge-Aggregation1
Creation Mode: Manual
Aggregation Mode: Dynamic
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
System ID: 0x6e, 2001-0000-0018
Local:
Port Status Priority Index Oper-Key Flag
XGE1/0/1(R) S 32768 16391 40101 {ACDEF}
Remote:
Actor Priority Index Oper-Key SystemID Flag
XGE1/0/2 255 1 21 0xffff, 1070-fd7f-dac2 {ABCDEF}
# Verify that bond0 has two member ports that act in dynamic link aggregation mode and carry LACP information.
[root@server4/]# cat /proc/net/bonding/bond0
Ethernet Channel Bonding Driver: v4.18.0-305.25.1.el8_4.x86_64
Bonding Mode: IEEE 802.3ad Dynamic link aggregation
Transmit Hash Policy: layer3+4 (1)
MII Status: up
MII Polling Interval (ms): 100
Up Delay (ms): 100
Down Delay (ms): 100
Peer Notification Delay (ms): 0
802.3ad info
LACP rate: fast
Min links: 0
Aggregator selection policy (ad_select): stable
System priority: 65535
System MAC address: 10:70:fd:7f:da:a6
Active Aggregator Info:
Aggregator ID: 1
Number of ports: 2
Actor Key: 21
Partner Key: 40204
Partner Mac Address: 20:01:00:00:00:03
Slave Interface: ens1f0
MII Status: up
Speed: 25000 Mbps
Duplex: full
Link Failure Count: 1
Permanent HW addr: 10:70:fd:7f:da:a6
Slave queue ID: 0
Aggregator ID: 1
Actor Churn State: none
Partner Churn State: none
Actor Churned Count: 0
Partner Churned Count: 0
details actor lacp pdu:
system priority: 65535
system mac address: 10:70:fd:7f:da:a6
port key: 21
port priority: 255
port number: 1
port state: 63
details partner lacp pdu:
system priority: 110
system mac address: 20:01:00:00:00:03
oper key: 40204
port priority: 32768
port number: 16391
port state: 61
Slave Interface: ens1f1
MII Status: up
Speed: 25000 Mbps
Duplex: full
Link Failure Count: 4
Permanent HW addr: 10:70:fd:7f:da:a7
Slave queue ID: 0
Aggregator ID: 1
Actor Churn State: none
Partner Churn State: none
Actor Churned Count: 0
Partner Churned Count: 0
details actor lacp pdu:
system priority: 65535
system mac address: 10:70:fd:7f:da:a6
port key: 21
port priority: 255
port number: 2
port state: 63
details partner lacp pdu:
system priority: 110
system mac address: 20:01:00:00:00:03
oper key: 40204
port priority: 32768
port number: 32775
port state: 61
# View the incoming traffic on H3C switch.
<H3C> display counters rate inbound interface
Usage: Bandwidth utilization in percentage
Interface Usage (%) Total (pps) Broadcast (pps) Multicast (pps)
BAGG1 20 1011085 -- --
XGE1/0/1 20 1011085 -- --
XGE1/0/2 0 0 -- --
# Verify that when you shut down Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 on the H3C switch, the incoming traffic is transmitted to Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
<H3C> display counters rate outbound interface
Usage: Bandwidth utilization in percentage
Interface Usage (%) Total (pps) Broadcast (pps) Multicast (pps)
BAGG1 99 2809534 -- --
XGE1/0/1 0 0 -- --
XGE1/0/2 99 2809534 -- --
# Verify that when Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 restores to normal on the H3C switch, the incoming traffic is transmitted to Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<H3C> display counters rate inbound interface
Usage: Bandwidth utilization in percentage
Interface Usage (%) Total (pps) Broadcast (pps) Multicast (pps)
BAGG1 20 1011085 -- --
XGE1/0/1 20 1011085 -- --
XGE1/0/2 0 0 -- --
Integrating an H3C switch with a Linux server through LLDP/DCBX
Interoperability analysis
|
H3C switch |
Linux server |
Interoperability |
|
Support for integration with the Linux server in LLDP/DCBX |
Support for integration with the H3C switch in LLDP/DCBX |
Yes |
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, the H3C switch is connected to the Linux server. Configure PFC for 802.1p priorities to prevent packet loss for traffic with the specified priority between the H3C switch and the Linux server.
Procedures
· Configure the H3C switch.
# Enable LLDP globally.
<H3C> system-view
[H3C] lldp global enable
# Enable LLDP and DCBX TLV advertisement on Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[H3C] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[H3C-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] lldp enable
[H3C-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] lldp tlv-enable dot1-tlv dcbx
# Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1 to trust the DSCP value in the incoming packets for priority mapping.
[H3C-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] qos trust dscp
# Enable PFC in auto mode on Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1 and enable PFC for 802.1p priority 5.
[H3C-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] priority-flow-control auto
[H3C-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] priority-flow-control no-drop dot1p 5
· Configure the Linux server.
|
|
NOTE: To prevent ECN to take effect before PFC, disable ECN before you configure the server. |
# View server information.
|
Item |
Description |
|
Server model |
H3C R4900 G5 |
|
Operating system |
Kernel version: Linux version 4.18.0-305.25.1 Operating system version: CentOS Linux release 8.4.2105 |
|
Network adapter model |
· 18:00.0 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT2894 Family [ConnectX-6 Lx] · 18:00.1 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT2894 Family [ConnectX-6 Lx] |
|
Network adapter driver version |
MLNX_OFED_LINUX-5.4-3.2.7.2.3-rhel8.4-x86_64 |
|
Network adapter firmware version |
driver: mlx5_core version: 5.4-3.2.7.2.3 firmware-version: 26.31.2006 (MT_0000000531) expansion-rom-version: bus-info: 0000:18:00.0 bus-info: 0000:18:00.1 |
|
Dependency packages |
yum -y install zlib-devel bzip2-devel yum -y install openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel gdbm-devel db4-devel libpcap-devel xz-devel --skip-broken yum -y install createrepo pciutils gcc gcc-c++ flex bison yum -y install gtk2 atk cairo tcl tcsh tk yum -y install tcl tcsh gcc-gfortran tk python36 perl yum -y install -y kernel-modules-extra yum remove pcp-pmda-infiniband |
# Enable LLDP and DCBX on the server.
For more information, see "Flow Control - MLNX_EN v5.4-3.6.8.1 LTS - NVIDIA Networking Docs."
# Enable MST.
[root@server4 /]# mst start
Starting MST (Mellanox Software Tools) driver set
Loading MST PCI module - Success
[warn] mst_pciconf is already loaded, skipping
Create devices
Unloading MST PCI module (unused) - Success
# View the MST status.
[root@server4 /]# mst status
MST modules:
------------
MST PCI module is not loaded
MST PCI configuration module loaded
MST devices:
------------
/dev/mst/mt4119_pciconf0 - PCI configuration cycles access.
domain:bus:dev.fn=0000:4b:00.0 addr.reg=88 data.reg=92 cr_bar.gw_offset=-1
Chip revision is: 00
/dev/mst/mt4127_pciconf0 - PCI configuration cycles access.
domain:bus:dev.fn=0000:18:00.0 addr.reg=88 data.reg=92 cr_bar.gw_offset=-1
Chip revision is: 00
# View the LLDP and DCBX status.
[root@server4 mst]# mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt4127_pciconf0 q
Device #1:
----------
Device type: ConnectX6LX
Name: MCX631102AN-ADA_Ax
Description: ConnectX-6 Lx EN adapter card; 25GbE ; Dual-port SFP28; PCIe 4.0 x8; No Crypto
Device: /dev/mst/mt4127_pciconf0
Configurations: Next Boot
MEMIC_BAR_SIZE 0
MEMIC_SIZE_LIMIT _256KB(1)
LLDP_NB_DCBX_P1 False(0)
LLDP_NB_RX_MODE_P1 OFF(0)
LLDP_NB_TX_MODE_P1 OFF(0)
LLDP_NB_DCBX_P2 False(0)
LLDP_NB_RX_MODE_P2 OFF(0)
LLDP_NB_TX_MODE_P2 OFF(0)
DCBX_IEEE_P1 True(1)
DCBX_CEE_P1 True(1)
DCBX_WILLING_P1 True(1)
DCBX_IEEE_P2 True(1)
DCBX_CEE_P2 True(1)
DCBX_WILLING_P2 True(1)
# Edit LLDP and DCBX parameters.
[root@server4 /]# mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt4127_pciconf0 set LLDP_NB_DCBX_P1=TRUE LLDP_NB_TX_MODE_P1=2 LLDP_NB_RX_MODE_P1=2 LLDP_NB_DCBX_P2=TRUE LLDP_NB_TX_MODE_P2=2 LLDP_NB_RX_MODE_P2=2
Device #1:
----------
Device type: ConnectX6LX
Name: MCX631102AN-ADA_Ax
Description: ConnectX-6 Lx EN adapter card; 25GbE ; Dual-port SFP28; PCIe 4.0 x8; No Crypto
Device: /dev/mst/mt4127_pciconf0
Configurations: Next Boot New
LLDP_NB_DCBX_P1 True(1) True(1)
LLDP_NB_TX_MODE_P1 OFF(0) ALL(2)
LLDP_NB_RX_MODE_P1 OFF(0) ALL(2)
LLDP_NB_DCBX_P2 False(0) True(1)
LLDP_NB_TX_MODE_P2 OFF(0) ALL(2)
LLDP_NB_RX_MODE_P2 OFF(0) ALL(2)
Apply new Configuration? (y/n) [n] : y
Applying... Done!
-I- Please reboot machine to load new configurations.
# Verify that LLDP and DCBX settings are changed successfully.
[root@server4 /]# mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt4127_pciconf0 q
Device #1:
----------
Device type: ConnectX6LX
Name: MCX631102AN-ADA_Ax
Description: ConnectX-6 Lx EN adapter card; 25GbE ; Dual-port SFP28; PCIe 4.0 x8; No Crypto
Device: /dev/mst/mt4127_pciconf0
Configurations: Next Boot
MEMIC_BAR_SIZE 0
MEMIC_SIZE_LIMIT _256KB(1)
LLDP_NB_DCBX_P1 True(1)
LLDP_NB_RX_MODE_P1 ALL(2)
LLDP_NB_TX_MODE_P1 ALL(2)
LLDP_NB_DCBX_P2 True(1)
LLDP_NB_RX_MODE_P2 ALL(2)
LLDP_NB_TX_MODE_P2 ALL(2)
DCBX_IEEE_P1 True(1)
DCBX_CEE_P1 True(1)
DCBX_WILLING_P1 True(1)
DCBX_IEEE_P2 True(1)
DCBX_CEE_P2 True(1)
DCBX_WILLING_P2 True(1)
# Restart firmware.
[root@server4 /]# mlxfwreset -d /dev/mst/mt4127_pciconf0 --level 3 reset
Requested reset level for device, /dev/mst/mt4127_pciconf0:
3: Driver restart and PCI reset
Continue with reset?[y/N] y
-I- Sending Reset Command To Fw -Done
-I- Stopping Driver -Done
-I- Resetting PCI -Done
-I- Starting Driver -Done
-I- Restarting MST -Done
-I- FW was loaded successfully.
# Change the DCBX mode to firmware.
DCBX mode: Firmware controlled
Priority trust state: pcp
default priority:
Receive buffer size (bytes): 0,156096,0,0,0,0,0,0,
Cable len: 7
PFC configuration:
priority 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
enabled 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
buffer 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
tc: 1 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 0
tc: 0 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 1
tc: 2 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 2
tc: 3 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 3
tc: 4 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 4
tc: 5 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 5
tc: 6 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 6
tc: 7 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 7
[root@server4 /]# mlnx_qos -i ens1f0 -d fw
DCBX mode: Firmware controlled
Priority trust state: pcp
default priority:
Receive buffer size (bytes): 0,156096,0,0,0,0,0,0,
Cable len: 7
PFC configuration:
priority 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
enabled 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
buffer 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
tc: 1 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 0
tc: 0 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 1
tc: 2 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 2
tc: 3 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 3
tc: 4 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 4
tc: 5 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 5
tc: 6 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 6
tc: 7 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 7
# Configure port ens1f0 to trust the DSCP value in the packets.
[root@server4 /]# mlnx_qos -i ens1f0 --trust dscp
DCBX mode: Firmware controlled
Priority trust state: dscp
dscp2prio mapping:
prio:0 dscp:07,06,05,04,03,02,01,00,
prio:1 dscp:15,14,13,12,11,10,09,08,
prio:2 dscp:23,22,21,20,19,18,17,16,
prio:3 dscp:31,30,29,28,27,26,25,24,
prio:4 dscp:39,38,37,36,35,34,33,32,
prio:5 dscp:47,46,45,44,43,42,41,40,
prio:6 dscp:55,54,53,52,51,50,49,48,
prio:7 dscp:63,62,61,60,59,58,57,56,
default priority:
Receive buffer size (bytes): 0,156096,0,0,0,0,0,0,
Cable len: 7
PFC configuration:
priority 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
enabled 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
buffer 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
tc: 1 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 0
tc: 0 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 1
tc: 2 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 2
tc: 3 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 3
tc: 4 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 4
tc: 5 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 5
tc: 6 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 6
tc: 7 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: vendor
priority: 7
Verifying the configuration
# View the LLDP neighbor information of the H3C switch.
<H3C> display lldp neighbor-information list
Chassis ID : * -- -- Nearest nontpmr bridge neighbor
# -- -- Nearest customer bridge neighbor
Default -- -- Nearest bridge neighbor
Local Interface Chassis ID Port ID System Name
XGE1/0/1 ec0d-9ad4-48fa ec0d-9ad4-48f8 -
# Verify that PFC is enabled in auto mode for 802.1p priority 5 on the server.
[root@server4 ~]# mlnx_qos -i ens1f0
DCBX mode: Firmware controlled
Priority trust state: dscp
dscp2prio mapping:
prio:0 dscp:07,06,05,04,03,02,01,00,
prio:1 dscp:15,14,13,12,11,10,09,08,
prio:2 dscp:23,22,21,20,19,18,17,16,
prio:3 dscp:31,30,29,28,27,26,25,24,
prio:4 dscp:39,38,37,36,35,34,33,32,
prio:5 dscp:47,46,45,44,43,42,41,40,
prio:6 dscp:55,54,53,52,51,50,49,48,
prio:7 dscp:63,62,61,60,59,58,57,56,
default priority:
Receive buffer size (bytes): 20016,156096,0,0,0,0,0,0,
Cable len: 7
PFC configuration:
priority 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
enabled 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
buffer 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
tc: 0 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: ets, bw: 2%
priority: 0
tc: 1 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: ets, bw: 4%
priority: 1
tc: 2 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: ets, bw: 6%
priority: 2
tc: 3 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: ets, bw: 8%
priority: 3
tc: 4 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: ets, bw: 9%
priority: 4
tc: 5 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: ets, bw: 17%
priority: 5
tc: 6 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: ets, bw: 25%
priority: 6
tc: 7 ratelimit: unlimited, tsa: ets, bw: 29%
priority: 7
# View QoS queue statistics on the H3C switch.
<H3C> display qos queue-statistics interface Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 outbound
Interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Direction: outbound
Forwarded: 24731576 packets, 26864670580 bytes
Dropped: 0 packets, 0 bytes
Queue 0
Forwarded: 0 packets, 0 bytes, 0 pps, 0 bps
Dropped: 0 packets, 0 bytes
Current queue length: 0 packets
Queue 1
Forwarded: 0 packets, 0 bytes, 0 pps, 0 bps
Dropped: 0 packets, 0 bytes
Current queue length: 0 packets
Queue 2
Forwarded: 0 packets, 0 bytes, 0 pps, 0 bps
Dropped: 0 packets, 0 bytes
Current queue length: 0 packets
Queue 3
Forwarded: 0 packets, 0 bytes, 0 pps, 0 bps
Dropped: 0 packets, 0 bytes
Current queue length: 0 packets
Queue 4
Forwarded: 0 packets, 0 bytes, 0 pps, 0 bps
Dropped: 0 packets, 0 bytes
Current queue length: 0 packets
Queue 5
Forwarded: 24731572 packets, 26864670088 bytes, 2822493 pps, 24527467704 bps
Dropped: 0 packets, 0 bytes
Current queue length: 5 packets
Queue 6
Forwarded: 0 packets, 0 bytes, 0 pps, 0 bps
Dropped: 0 packets, 0 bytes
Current queue length: 0 packets
Queue 7
Forwarded: 4 packets, 492 bytes, 0 pps, 0 bps
Dropped: 0 packets, 0 bytes
Current queue length: 0 packets
Integrating an H3C switch with a BMP server
About BMP
BGP can only record the current status of BGP sessions and BGP routes, but cannot directly collect statistics about the process of session status changes and route updates. To resolve this issue, you can configure the BGP Monitoring Protocol (BMP) feature. The BMP server monitors the operation status of BGP sessions in the network in real time, including the adding and deleting of BGP peers and route updates. This helps the network administrator learn more about the operation status of BGP sessions.
Interoperability analysis
|
H3C switch |
BMP server |
Interoperability |
|
Support for integration with the BMP server |
Support for integration with the H3C switch |
Yes |
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 4, establish BGP sessions between Switch A and Switch B. Configure BMP on Switch B to monitor the BGP operation status and route updates, and report the BMP information to the BMP server.
Procedures
· Configure Switch A.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchA-vlan-interface10] ip address 10.200.1.1 255.255.255.0
[SwitchA] bgp 45090
[SwitchA-bgp-default] peer 10.200.1.2 as-number 45090
[SwitchA-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[SwitchA-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.200.1.2 enable
[SwitchA-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[SwitchA-bgp-default] quit
· Configure Switch B.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchB-vlan-interface10] ip address 10.200.1.2 255.255.255.0
[SwitchB] bgp 45090
[SwitchB-bgp-default] peer 10.200.1.1 as-number 45090
[SwitchB-bgp-default] peer 10.200.1.1. bmp server 1
[SwitchB-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[SwitchB-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.200.1.1 enable
[SwitchB-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[SwitchB-bgp-default] quit
[SwitchB] bmp server 1
[SwitchB-bmpserver-1] server address 16.1.1.2 port 5000
[SwitchB-bmpserver-1] server connect-interface loopback0
[SwitchB-bmpserver-1] route-mode adj-rib-out
[SwitchB-bmpserver-1] route-mode loc-rib
[SwitchB-bmpserver-1] statistics-interval 10
· Configure the BMP server.
# View the server information.
|
Item |
Description |
|
Server model |
H3C R4900 |
|
Physical server OS |
Vmware ESXi 6.0 |
|
VM OS |
Linux kernel version: 3.10.0-693.5.2.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Fri Oct 20 20:32:50 UTC 2017 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux |
|
CentOS version |
CentOS Linux release 7.4.1708 (Core) |
|
BMP software version |
openbmpd (www.openbmp.org) version: 0.14.0-0 |
# Make sure the BMP server are Switch B reachable to each other. (Details not shown.)
# Install OPENBMP on the BMP server:
¡ Install the OVA file.
¡ Execute the docker run -d --name=openbmp_aio \ -e KAFKA_FQDN=localhost \ -v /var/openbmp/mysql:/data/mysql \ -v /var/openbmp/config:/config \ -p 3306:3306 -p 2181:2181 -p 9092:9092 -p 5000:5000 -p 8001:8001 \ openbmp/aio command to run Docker.
|
|
NOTE: The command must be issued in one line without any line breaks. |
Verifying the configuration
# View BMP server information on Switch B.
<SwitchB> display bgp bmp server 1
BMP server number: 1
Server VPN instance name: --
Server address: 16.1.1.2 Server port: 5000
Client address: 16.1.1.1 Client port: 34481
BMP server state: Connected Up for 00h09m42s
TCP source interface has been configured
Message statistics:
Total messages sent: 285751
INITIATION: 1
TERMINATION: 0
STATS-REPORT: 464
PEER-UP: 15
PEER-DOWN: 0
ROUTE-MON: 285271
BMP monitor BGP peers:
10.200.1.1
# View received messages on the BMP server when BGP peers are added or deleted.
[root@openbmp ~]# docker exec openbmp_aio tail -f /var/log/openbmpd.log
2022-12-22T04:01:48.223803 | INFO | runServer | Initializing server
2022-12-22T04:01:49.328034 | INFO | runServer | Ready. Waiting for connections
2022-12-22T04:01:59.480328 | INFO | runServer | Accepted new connection; active connections = 1
2022-12-22T04:01:59.480373 | INFO | runServer | Client Connected => 1.1.1.1|:12815, sock = 10
2022-12-22T04:02:02.588530 | INFO | ClientThread | Thread started to monitor BMP from router 1.1.1.1| using socket 10 buffer in bytes = 15728640
2022-12-22T04:02:02.589027 | INFO | ReadIncomingMsg | 1.1.1.1|: Init message received with length of 208
2022-12-22T04:02:02.589083 | INFO | handleInitMsg | Init message type 1 and length 162 parsed
2022-12-22T04:02:02.589098 | INFO | handleInitMsg | Init message type 1 = H3C Comware Platform Software, Software Version 7.1.070, Feature 2809
H3C S12508X-AF
Copyright (c) 2004-2021 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
2022-12-22T04:02:02.589107 | INFO | handleInitMsg | Init message type 2 and length 7 parsed
2022-12-22T04:02:02.589115 | INFO | handleInitMsg | Init message type 2 = kalia-2
2022-12-22T04:02:02.589123 | INFO | handleInitMsg | Init message type 0 and length 27 parsed
2022-12-22T04:02:02.589131 | INFO | handleInitMsg | Init message type 0 = bgp instance name:
default
2022-12-22T04:02:02.589138 | INFO | ReadIncomingMsg | Router ID hashed with hash_type: 1
2022-12-22T04:02:19.431566 | INFO | ReadIncomingMsg | 1.1.1.1|: PEER UP Received, local addr=:::0 remote addr=:::0 -------------A BGP peer relationship has been established between Switch A and Switch B.
2022-12-22T04:02:19.431647 | NOTICE | parsePeerUpInfo | Peer info message type 0 is not implemented
2022-12-22T04:02:19.431875 | INFO | ReadIncomingMsg | 1.1.1.1|: PEER UP Received, local addr=10.200.1.2:179 remote addr=10.200.1.1:55674
2022-12-22T04:02:29.437774 | INFO | ReadIncomingMsg | 1.1.1.1|: PEER UP Received, local addr=:::0 remote addr=:::0
2022-12-22T04:02:29.437845 | NOTICE | parsePeerUpInfo | Peer info message type 0 is not implemented
2022-12-22T04:02:29.438906 | NOTICE | parseAttr_AsPath | 10.200.1.1 rtr=1.1.1.1|: Could not parse the AS PATH due to update message buffer being too short when using ASN octet size 4 (4 > 2)
2022-12-22T04:02:29.438934 | NOTICE | parseAttr_AsPath | 10.200.1.1: rtr=1.1.1.1|: switching encoding size to 2-octet
2022-12-22T04:02:46.083438 | NOTICE | parsePeerDownEventHdr | sock=16 : 10.200.1.1: BGP peer down notification with reason code: 3 -------------The BGP peer relationship between Switch A and Switch B has been down.