- Products and Solutions
- Industry Solutions
- Services
- Support
- Training & Certification
- Partners
- About Us
- Contact Sales
- Become a Partner
-
 Login
Login
Country / Region
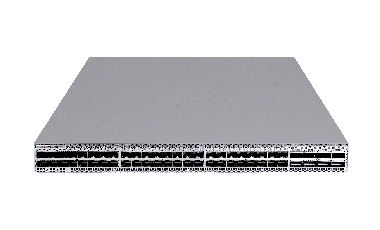
H3C S9855 DataCenter Switches
H3C S9855 series switches are a new generation of high-performance, high-density 400GE/100GE Ethernet switches launched by H3C for data centers. Provides high-density 400GE/200GE/100GE ports; S9855 series switches supports redundant and hot-swappable power supplies and fans. The S9855 can be used in the core and aggregation networking of the new generation data center. It connects to the S12500 series core switches through 400GE uplinks, and connects to 200GE/100GE servers in the downlink, providing high-bandwidth and large-capacity server access.
The S9855 switch series includes four models:
![]() H3C S9855-48CD8D: Supports 48*100G DSFP ports + 8 *400G QSFP-DD ports
H3C S9855-48CD8D: Supports 48*100G DSFP ports + 8 *400G QSFP-DD ports
![]() H3C S9855-24B8D: Supports 24 *200G QSFP56 ports + 8 *400G QSFP-DD ports
H3C S9855-24B8D: Supports 24 *200G QSFP56 ports + 8 *400G QSFP-DD ports
![]() H3C S9855-40B: Supports 40 *200G QSFP56 ports
H3C S9855-40B: Supports 40 *200G QSFP56 ports
![]() H3C S9855-32D:Supports 32 *400G QSFP-DD ports+2* SFP/ SFP+ ports(The 400G ports supports downward compatibility with 100G which support split into 4*10G or 4*25G. ).
H3C S9855-32D:Supports 32 *400G QSFP-DD ports+2* SFP/ SFP+ ports(The 400G ports supports downward compatibility with 100G which support split into 4*10G or 4*25G. ).
The following contents are complex, and it is recommended to browse on PC.
Enter c.h3c.com.cn on the PC browser and operate according to the page to synchronize to the PC and continue browsing.
Continue by mobile
High port density and powerful forwarding capacity
![]() The switch offers high-density 400G/200G/10G ports and a forwarding capacity as high as 16Tbps, which enables the switch to provide high-density server access in high-end data centers without oversubscriptions.
The switch offers high-density 400G/200G/10G ports and a forwarding capacity as high as 16Tbps, which enables the switch to provide high-density server access in high-end data centers without oversubscriptions.
Abundant Data Center Features
The switch supports abundant data center features, including:
![]() H3C S9855 series switches supports MP-BGP EVPN and VxLAN VTEP.
H3C S9855 series switches supports MP-BGP EVPN and VxLAN VTEP.
![]() H3C S9855 series switches support ROCEv2 network, based on Priority-based Flow Control (PFC), ECN Enhanced Transmission Selection (ETS). Which ensures low latency and lossless RDMA applications and high-speed computing services.
H3C S9855 series switches support ROCEv2 network, based on Priority-based Flow Control (PFC), ECN Enhanced Transmission Selection (ETS). Which ensures low latency and lossless RDMA applications and high-speed computing services.
Powerful visibility
![]() With the rapid development of data center, the scale of the data center expands rapidly, reliability, operation and maintenance become the bottleneck of data center for further expansion. H3C S9855 switch series conform to the trend of automated data operation and maintenance, and support visualization of data center. H3C S9855 switch series can send real-time resources information, statistics and alarm of RDMA information to the data center operation and maintenance platform through ERSPAN and GRPC protocols. This can allow the operation and maintenance center to perform real-time analysis in order to achieve network quality tracing, troubleshooting, risk warning and system optimization, etc. Visualization can even adjust network configuration automatically and reduce network congestion, which makes it possible to move to automated data center operation and maintenance.
With the rapid development of data center, the scale of the data center expands rapidly, reliability, operation and maintenance become the bottleneck of data center for further expansion. H3C S9855 switch series conform to the trend of automated data operation and maintenance, and support visualization of data center. H3C S9855 switch series can send real-time resources information, statistics and alarm of RDMA information to the data center operation and maintenance platform through ERSPAN and GRPC protocols. This can allow the operation and maintenance center to perform real-time analysis in order to achieve network quality tracing, troubleshooting, risk warning and system optimization, etc. Visualization can even adjust network configuration automatically and reduce network congestion, which makes it possible to move to automated data center operation and maintenance.
Powerful SDN Capability
![]() H3C S9855 series switches adopt the next-generation chip with more flexible Openflow flow Table, more resources and accurate ACL matching, which greatly improves the software-defined network (SDN) capabilities and meet the demand of data center SDN network.
H3C S9855 series switches adopt the next-generation chip with more flexible Openflow flow Table, more resources and accurate ACL matching, which greatly improves the software-defined network (SDN) capabilities and meet the demand of data center SDN network.
![]() H3C S9855 series switches can interconnect with H3C SeerEngine-DC Controller for SeerFabric solutions.
H3C S9855 series switches can interconnect with H3C SeerEngine-DC Controller for SeerFabric solutions.
Rich QoS features
![]() H3C S9855 switch series support Layer 2 to Layer 4 packet filtering, which can provide traffic classification based on source MAC address, destination MAC address, source IP address, destination IP address, TCP/UDP port number, protocol type, and VLAN.
H3C S9855 switch series support Layer 2 to Layer 4 packet filtering, which can provide traffic classification based on source MAC address, destination MAC address, source IP address, destination IP address, TCP/UDP port number, protocol type, and VLAN.
![]() S9855 switch series supports five queuing modes include SP (Strict Priority), WRR (Weighted Round Robin), SP+WRR, WFQ, and SP+WFQ.
S9855 switch series supports five queuing modes include SP (Strict Priority), WRR (Weighted Round Robin), SP+WRR, WFQ, and SP+WFQ.
![]() S9855 switch series supports CAR (Committed Access Rate) function with a minimum granularity of 8Kbps, and port mirroring on both directions used to monitor packets on the specified port and forward the packets to the monitoring port for network detection and troubleshooting.
S9855 switch series supports CAR (Committed Access Rate) function with a minimum granularity of 8Kbps, and port mirroring on both directions used to monitor packets on the specified port and forward the packets to the monitoring port for network detection and troubleshooting.
Outstanding management capacity
The switch improves system management through the following ways:
![]() Provides multiple management interfaces, including the serial console port, mini USB console port, USB port, two out-of-band management ports, and two SFP ports. The SFP ports can be used as service ports or in-band data management ports, through which the sampled packets are encapsulated and sent to the controller or other management devices for in-depth analysis.
Provides multiple management interfaces, including the serial console port, mini USB console port, USB port, two out-of-band management ports, and two SFP ports. The SFP ports can be used as service ports or in-band data management ports, through which the sampled packets are encapsulated and sent to the controller or other management devices for in-depth analysis.
![]() Supports configuration and management from CLI or a mainstream network management platform and H3C IMC Intelligent Management Center.
Supports configuration and management from CLI or a mainstream network management platform and H3C IMC Intelligent Management Center.
![]() Supports multiple access methods, including SNMPv1/v2c/v3, Telnet, SSH 2.0, SSL, and FTP.
Supports multiple access methods, including SNMPv1/v2c/v3, Telnet, SSH 2.0, SSL, and FTP.
![]() Supports GRPC and provides a flexible programmable interface for customized development.
Supports GRPC and provides a flexible programmable interface for customized development.
Hardware Specification
Item | S9855-48CD8D | S9855-24B8D | S9855-40B | S9855-32D |
Dimensions (H × W × D) | 44×440×660 mm (1.73×17.32×25.98 in) | 44×440×660 mm (1.73×17.32×25.98 in) | 44×440×550 mm (1.73×17.32×21.65 in) | 44 × 440 × 660 mm |
Weight(Full loaded) | ≤ 12.2 kg (26.90 lb) | ≤ 12.2 kg (26.90 lb) | ≤ 12.2 kg (26.90 lb) | ≤ 15 kg (33.07 lb) |
Serial console port | 1*RJ-45 | |||
Out-of-band management port | 1* 10/100/1000BASE-T | |||
USB port | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
SFP+ | - | - | - | 2 |
200G QSFP56 port | / | 24 | 40 | - |
DSFP port | 48 | / | / | - |
QSFP-DD port | 8 | 8 | / | 32 |
Power module slot | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
Fan tray slot | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
Air flow direction | From front to rear | From front to rear From rear to front | From front to rear | From front to rear |
Minimum power consumption | Single AC input: 125 W Dual AC inputs: 140 W | Single AC input: 133 W Dual AC inputs: 146 W | Single AC input: 131 W Dual AC inputs: 146 W | Dual DC inputs: 234 W |
Typical power consumption | Single AC input: 238 W Dual AC inputs: 250 W | Single AC input: 251 W Dual AC inputs: 263 W | Single AC input: 258 W Dual AC inputs: 263 W | Dual DC inputs: 476 W |
Maximum power consumption | Single AC input: 713 W Dual AC inputs: 719 W | Single AC input: 739 W Dual AC inputs: 748 W | Single AC input: 709 W Dual AC inputs: 748 W | Dual DC inputs: 1265 W |
CPU | 2.9GHz@4core | 2.9GHz@4core | 2.9GHz@4core | 2.9GHz@4core |
Flash/SDRAM | 240G/16G | 240G/16G | 240G/16G | 240G/16G |
Latency | <1.2μs | <1.2μs | <1.2μs | <1μs |
Switching capacity | 16Tbps | 16Tbps | 16Tbps | 25.6Tbps |
Forwarding capacity | 2680Mpps | 2680Mpps | 2680Mpps | 5346.7Mpps |
Buffer(byte) | 82M | 82M | 82M | 132M |
Operating temperature | 0°C to 40°C | 0°C to 40°C | 0°C to 40°C | 0°C to 40°C |
Operating humidity | 5% to 95%, noncondensing | 5% to 95%, noncondensing | 5% to 95%, noncondensing | 5% to 95%, noncondensing |
MTBF(year) | 49.3 | 34.9 | 34.9 | 56.07 |
MTTR(hour) | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 |
Software Specification
Item | Feature description |
Device Virtualization | M-LAG(DRNI) |
S-MLAG | |
Network Virtualization | BGP-EVPN |
VxLAN | |
VxLAN | L2 VxLAN gateway |
L3 VxLAN gateway | |
Distributed VxLAN gateway | |
Centralized VxLAN gateway | |
EVPN VxLAN | |
manual configured VxLAN | |
IPv4 VxLAN tunnel | |
IPv6 VxLAN tunnel | |
QinQ VxLAN access | |
SDN | H3C SeerEngine-DC for SeerFabric |
Lossless network | PFC and ECN |
DCBX | |
RDMA and ROCE | |
PFC deadlock watchdog | |
ROCE stream analysis | |
Programmability | Openflow1.3 |
Netconf | |
Python//TCL/Restful API to realize DevOps automated operation and maintenance | |
Traffic analysis | Sflow |
VLAN | Port-based VLANs |
QINQ | |
MAC address | Dynamic learning and aging of mac address entries |
Dynamic,static and blackhole entries | |
IPv4 routing | OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) v1/v2 |
ISIS(Intermediate System to Intermediate system) | |
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) | |
Routing policy | |
VRRP | |
PBR | |
IPv6 routing | OSPFv3 |
IPv6 ISIS | |
BGP4+ | |
Routing policy | |
VRRP | |
PBR | |
MPLS | MPLS label number |
MPLS label depth | |
MPLS interface number | |
Static LSP number | |
Maximum number of LSPs supported | |
ECMP LSP | |
LDP local peer number | |
LDP remote peer number | |
MPLS LSP tracert | |
MPLS LSP ping | |
Reliability | LACP |
LLDP | |
STP/RSTP/MSTP protocol | |
STP Root Guard and BPDU Guard | |
BFD for OSPF/OSPFv3, BGP/BGP4, IS-IS/IS-ISv6 and Static route | |
QOS | Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) and tail drop |
Flexible queue scheduling algorithms based on port and queue, including strict priority (SP), Weighted Deficit Round Robin (WDRR), Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ), SP + WDRR, and SP + WFQ. | |
Traffic shaping | |
Packet filtering at L2 (Layer 2) through L4 (Layer 4); flow classification based on source MAC address, destination MAC address, source IP (IPv4/IPv6) address, destination IP (IPv4/IPv6) address, port, protocol, and VLAN to apply qos policy,including mirroring,redirection,priority remark etc. | |
Committed access rate (CAR) | |
Account by packet and byte | |
COPP | |
Telemetry | Real-time telemetry |
Telemetry Stream | |
INT | |
Packet capture | |
Configuration and maintenance | Console telnet and SSH terminals |
SNMPv1/v2/v3 | |
ZTP | |
System log | |
File upload and download via FTP/TFTP, BootRom update and remote update | |
NQA | |
ping,tracert | |
NTP | |
Security and management | Hierarchical management and password protection of users |
AAA /RADIUS/HWTACACS | |
SSH 2.0 | |
HTTPS | |
Boot ROM access control (password recovery) | |
RMON | |
EMC | FCC Part 15 Subpart B CLASS A ICES-003 CLASS A VCCI CLASS A CISPR 32 CLASS A EN 55032 CLASS A AS/NZS CISPR32 CLASS A CISPR 24 EN 55024 EN 61000-3-2 EN 61000-3-3 ETSI EN 300 386 GB/T 9254 YD/T 993 |
Safety | UL60950-1 EN60950-1 IEC60950-1 GB4943 |
Standards and Protocols Compliance
Organization | ID | Name |
IEEE | 1588-2008 | Timing and Synchronization for Time-Sensitive Applications in Bridged Local Area Networks |
IEEE | 802.1 | LAN/MAN Bridge and Management |
IEEE | 802.17-2011 | Part 17: Resilient packet ring (RPR) access method and physical layer specifications |
IEEE | 802.1AB-2005 | IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks Station and Media Access Control Connectivity Discovery |
IEEE | 802.1AB-2009 | IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks Station and Media Access Control Connectivity Discovery |
IEEE | 802.1ad-2005 | Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks |
IEEE | 802.1AE-2006 | IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks—Port-Based Network Access Control Part 9:MACsec Key Agreement protocol (MKA) |
IEEE | 802.1ag-2007 | Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks Amendment 5: Connectivity Fault Management |
IEEE | 802.1ak-2007 | Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks—Amendment 7: Multiple Registration Protocol |
IEEE | 802.1AS-2011 | Timing and Synchronization for Time-Sensitive Applications in Bridged Local Area Networks |
IEEE | 802.1AX-2008 | Link Aggregation |
IEEE | 802.1D-2004 | Media Access Control (MAC) Bridges |
IEEE | 802.1p | Traffic Class Expediting and Dynamic Multicast Filtering |
IEEE | 802.1Q-2005 | Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks |
IEEE | 802.1Q-2011 | IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks——Media Access Control (MAC) Bridges and Virtual Bridge Local Area Networks |
IEEE | 802.1Qaz-2011 | Draft Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks Amendment 18: Enhanced Transmission Selection for Bandwidth Sharing Between Traffic Classes |
IEEE | 802.1Qbb-2011 | Media Access Control (MAC) Bridges and Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks—Amendment 17: Priority-based Flow Control |
IEEE | 802.1s-2002 | Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks—Amendment 3: Multiple Spanning Tree |
IEEE | 802.1v-2001 | Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks—Amendment 2: VLAN Classification by Protocol and Port |
IEEE | 802.1w-2001 | Part 3:Media Access Control (MAC) Bridges—Amendment 2: Rapid Reconfiguration |
IEEE | 802.1X-2001 | Standard for Port based Network Access Control |
IEEE | 802.1X-2010 | IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks—Port-Based Network Access Control Part 9:MACsec Key Agreement protocol (MKA) |
IEEE | 802.2 | Logical Link Control |
IEEE | 802.3 | Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) access method and physical layer specifications |
IEEE | 802.3ad-2000 | Link Aggregation Control Protocol |
IEEE | 802.3ah-2004 | IEEE Standard for |
IETF | RFC0768 | User Datagram Protocol |
IETF | RFC0791 | Internet Protocol |
IETF | RFC0792 | Internet Standard Subnetting Procedure |
IETF | RFC0793 | Transmission Control Protocol |
IETF | RFC0826 | Ethernet Address Resolution Protocol: Or Converting Network Protocol Addresses to 48.bit Ethernet Address for Transmission on Ethernet Hardware |
IETF | RFC0854 | Telnet Protocol Specification |
IETF | RFC0855 | Telnet Option Specifications |
IETF | RFC0856 | Telnet Binary Transmission |
IETF | RFC0857 | Telnet Echo Option |
IETF | RFC0858 | Telnet Suppress Go Ahead Option |
IETF | RFC0862 | Character Generator Protocol |
IETF | RFC0864 | Character Generator Protocol |
IETF | RFC0894 | A Standard for the Transmission of IP Datagrams over Ethernet Networks |
IETF | RFC0919 | Broadcasting Internet Datagrams |
IETF | RFC0922 | Broadcasting Internet Datagrams in the Presence of Subnets (IP_BROAD) |
IETF | RFC0950 | Internet Standard Subnetting Procedure |
IETF | RFC0959 | FILE TRANSFER PROTOCOL (FTP) |
IETF | RFC1002 | Protocol Standard For a NetBIOS Service on a TCP/UDP Transport: Detailed Specifications |
IETF | RFC1034 | Domain names - implementation and specification |
IETF | RFC1035 | Domain names - implementation and specification |
IETF | RFC1112 | Host Extensions for IP Multicasting |
IETF | RFC1119 | Network Time Protocol (version 2) specification and implementation |
IETF | RFC1155 | Structure and identification of management information for TCP/IP-based internets |
IETF | RFC1212 | Concise MIB definitions. |
IETF | RFC1213 | Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-II |
IETF | RFC1350 | Trivial File Transfer Protocol(TFTP). |
IETF | RFC1661 | The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) |
IETF | RFC1662 | PPP in HDLC-like Framing |
IETF | RFC1722 | RIP Version 2 Protocol Applicability Statement |
IETF | RFC1723 | RIP Version 2 Carrying Additional Information |
IETF | RFC2085 | HMAC-MD5 IP Authentication with Replay Prevention |
IETF | RFC2228 | FTP Security Extensions |
IETF | RFC2328 | OSPF Version 2 |
IETF | RFC2453 | RIP Version 2 |
IETF | RFC2578 | Structure of Management Information Version 2 (SMIv2). |
IETF | RFC2579 | Textual Conventions for SMIv2. |
IETF | RFC2580 | Conformance Statements for SMIv2. |
IETF | RFC2819 | Remote Network Monitoring Management Information Base |
IETF | RFC2981 | Event MIB |
IETF | RFC3019 | Multicast Listener Discovery Protocol MIB used for managing MLD version 1. |
IETF | RFC3411 | An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management Frameworks. |
IETF | RFC3412 | Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). |
IETF | RFC3413 | Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Applications. |
IETF | RFC3414 | User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3). |
IETF | RFC3415 | View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). |
IETF | RFC3416 | Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). |
IETF | RFC3417 | Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). |
IETF | RFC3418 | Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework. |
IETF | RFC3489 | STUN - Simple Traversal of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Through Network Address Translators (NATs) |
IETF | RFC3576 | Dynamic Authorization Extensions to Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) |
IETF | RFC3925 | Vendor-Identifying Vendor Options for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 4 (DHCPv4) |
IETF | RFC3947 | Negotiation of NAT-Traversal in the IKE. |
IETF | RFC3961 | Encryption and Checksum Specifications for Kerberos 5 |
IETF | RFC3962 | Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Encryption for Kerberos 5 |
IETF | RFC3970 | A Traffic Engineering (TE) MIB |
IETF | RFC4120 | The Kerberos Network Authentication Service (V5) |
IETF | RFC4121 | The Kerberos Version 5 Generic Security Service Application Program Interface (GSS-API) Mechanism: Version 2 |
IETF | RFC4822 | RIPv2 Cryptographic Authentication |
IETF | RFC5250 | The OSPF Opaque LSA Option |
IETF | RFC5311 | Simplified Extension of Link State PDU (LSP) Space for IS-IS |
IETF | RFC5329 | Traffic Engineering Extensions to OSPF Version 3 |
IETF | RFC5396 | Textual Representation of Autonomous System (AS) Numbers |
IETF | RFC5424 | The Syslog Protocol |
IETF | RFC5427 | Textual Conventions for Syslog Management |
IETF | RFC5575 | Clarification of the Flowspec Redirect Extended Community |
IETF | RFC5603 | Ethernet Pseudowire (PW) Management Information Base (MIB) |
IETF | RFC5642 | Dynamic Hostname Exchange Mechanism for OSPF |
IETF | RFC5643 | Management Information Base for OSPFv3 |
IETF | RFC5647 | AES Galois Counter Mode for the Secure Shell Transport Layer Protocol |
IETF | RFC5656 | Elliptic Curve Algorithm Integration in the Secure Shell Transport Layer |
IETF | RFC5675 | Mapping Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Notifications to SYSLOG Messages |
IETF | RFC5676 | Definitions of Managed Objects for Mapping SYSLOG Messages to Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Notifications |
IETF | RFC5709 | OSPFv2 HMAC-SHA Cryptographic Authentication |
IETF | RFC5880 | Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) |
IETF | RFC5881 | Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for IPv4 and IPv6 (Single Hop) |
IETF | RFC5882 | Generic Application of Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) |
IETF | RFC5883 | Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for Multihop Paths |
IETF | RFC5884 | Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for MPLS Label Switched Paths (LSPs) |
IETF | RFC5885 | Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for the Pseudowire Virtual Circuit Connectivity Verification (VCCV) |
IETF | RFC6074 | Provisioning, Auto-Discovery, and Signaling in Layer 2 Virtual Private Networks (L2VPNs) |
IETF | RFC6146 | Stateful NAT64 Network Address and Protocol Translation |
IETF | RFC6165 | Extensions to IS-IS for Layer-2 Systems |
IETF | RFC6242 | Using the NETCONF Protocol over Secure Shell (SSH) |
IETF | RFC6391 | Flow-Aware Transport of Pseudowires over an MPLS Packet Switched Network |
IETF | RFC6445 | Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Traffic Engineering Management Information Base for Fast Reroute |
IETF | RFC6470 | Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) Base Notifications |
IETF | RFC6536 | Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) Access Control Model |
IETF | RFC6620 | FCFS SAVI: First-Come, First-Served Source Address Validation Improvement for Locally Assigned IPv6 Addresses |
IETF | RFC6810 | BGP Prefix Origin Validation |
IETF | RFC6860 | Hiding Transit-Only Networks in OSPF |
IETF | RFC6939 | Client Link-Layer Address Option in DHCPv6 |
IETF | RFC7348 | Virtual eXtensible Local Area Network (VXLAN): A Framework for Overlaying Virtualized Layer 2 Networks over Layer 3 Networks |
IETF | RFC7431 | Multicast-Only Fast Reroute |
IETF | RFC7432 | BGP MPLS-Based Ethernet VPN |
IETF | RFC7490 | Remote Loop-Free Alternate (LFA) Fast Reroute (FRR) |
IETF | RFC7513 | Source Address Validation Improvement (SAVI) Solution for DHCP |
IETF | RFC7637 | NVGRE: Network Virtualization Using Generic Routing Encapsulation |
IETF | RFC7674 | Clarification of the Flowspec Redirect Extended Community |
IETF | RFC7684 | OSPFv2 Prefix/Link Attribute Advertisement |
IETF | RFC7770 | Extensions to OSPF for Advertising Optional Router Capabilities |
IETF | RFC7854 | BGP Monitoring Protocol (BMP) |
IETF | RFC7911 | IEEE 802.1x |
IETF | RFC8102 | Remote-LFA Node Protection and Manageability |
IETF | RFC8202 | IS-IS Multi-Instance |
IETF | RFC8214 | Virtual Private Wire Service Support in Ethernet VPN |
IETF | RFC8231 | Path Computation Element Communication Protocol (PCEP) Extensions for Stateful PCE |
IETF | RFC8281 | Path Computation Element Communication Protocol (PCEP) Extensions for PCE-Initiated LSP Setup in a Stateful PCE Model |
IETF | RFC8362 | OSPFv3 Link State Advertisement (LSA) Extensibility |
IETF | RFC8365 | A Network Virtualization Overlay Solution Using Ethernet VPN (EVPN) |
IETF | RFC8408 | Conveying Path Setup Type in PCE Communication Protocol (PCEP) Messages |
IETF | RFC8664 | Path Computation Element Communication Protocol (PCEP) Extensions for Segment Routing |
IETF | RFC8697 | Path Computation Element Communication Protocol (PCEP) Extensions for Establishing Relationships between Sets of Label Switched Paths (LSPs) |
IETF | RFC8745 | Path Computation Element Communication Protocol (PCEP) Extensions for Associating Working and Protection Label Switched Paths (LSPs) with Stateful PCE |
IETF | RFC8754 | IPv6 Segment Routing Header (SRH) |
IETF | RFC8986 | SRv6 Network Programming |
ITU | G.8032 | Ethernet ring protection switching |
ITU | X.509 | Public-key and attribute certificate frameworks |
ITU-T | G.8261/Y.1361 | Timing and synchronization aspects in packet networks |
ITU-T | G.8275.1/Y.1369.1 | Precision time protocol telecom profile for phase/time synchronization with full timing support from the network |
ITU-T | G.8275.2 | PTP profile for phase/time synchronization with partial timing support from the network |
ITU-T | Q.921 | ISDN user network interface-Data Link Layer specification |
ITU-T | Q.931 | ISDN user network interface-Layer 3 specification for basic call control |
ITU-T | Y.1731 | OAM functions and mechanisms for Ethernet based networks |
Performance and scalability
Item | Description | |
Virtualization | M-LAG device number | 2 |
ACL | max number of ingress ACLs | S9855-48CD8D/ S9855-24B8D/S9855-40B: |
max number of ingress Car | S9855-48CD8D/ S9855-24B8D/S9855-40B: 512*2 S9855-32D: 512*4 | |
max number of ingress Counter | 24k-2 | |
max number of egress ACLs | S9855-48CD8D/ S9855-24B8D/S9855-40B: S9855-32D: 2K-1@160bit/pipe,4 pipes | |
max number of egress Car | S9855-48CD8D/ S9855-24B8D/S9855-40B: 128*2 S9855-32D: 128*4 | |
max number of egress Counter | 4K-2 | |
Forwarding table | Jumbo frame length(byte) | 9216 |
Mirroring group | 4 | |
max number of MACs per switch | routing mode:32K mac mode:224K | |
max number of ARP entries IPv4 | 28K-3 | |
max ND table size for IPv6 | 28K-3 | |
max number of unicast routes IPv4 | 980000(24B) 1000000(32B) | |
max number of unicast routes IPv6 | 1000000(80B/128B) | |
LAGG group | 1000 | |
LAGG member per group | 128 | |
ECMP group | Max Group:4095 | |
ECMP member per group | 2-128 | |
VRF | 4K | |
Interface | Loopback interface number | 1K |
L3 sub interface number | 4K | |
SVI interface number | 4K | |
VxLAN AC number | 14K-10 | |
VxLAN VSI number | 8K-1 | |
VxLAN tunnel number | 4095 | |
VSI interface number | 4K | |
VLAN number | 4094 | |
Performance | RIB | 4M |
MSTP instance | 64 | |
VRRP VRID | 255 | |
VRRP group | 4096 | |
NQA group | 32 | |
Static table | static mac-address | 16K |
static ARP | 28K-3 | |
static ND | 28K-3 | |
static IPv4 routing table | same as FIB | |
static IPv6 routing table | same as FIB | |
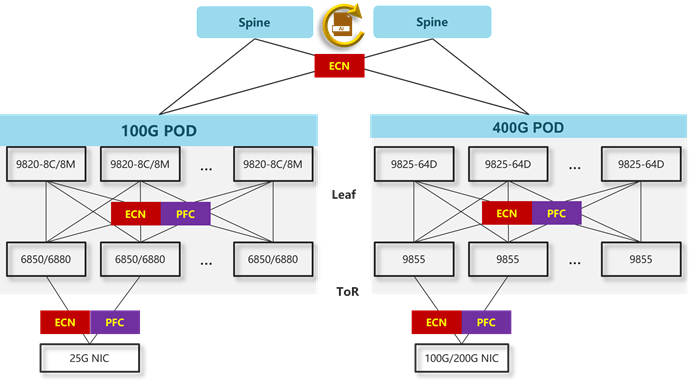
The typical data center application for S9855 is ROCE scenarios.
PID | Description |
LS-9855-24B8D | H3C S9855-24B8D L3 Ethernet Switch with 24 200G QSFP56 Ports and 8 400G QSFP-DD Ports |
LS-9855-48CD8D | H3C S9855-48CD8D L3 Ethernet Switch, with 2 AC Power Supplies and 6 Fan Modules |
LS-9855-40B | H3C S9855-40B 40 Port 200G QSFP56 Switch |
LS-9855-32D | H3C S9855-32D Ethernet Switch with 32*400G QSFP-DD Ports |
LS-Z+A2+M6-5 | H3C S9855-24B8D L3 Ethernet Switch,with 2 AC Power Supplies and 6 Fan Modules |
LS-Z+A2+M6-2 | H3C S9855-48CD8D-W1 L3 Ethernet Switch,with 2 AC Power Supplies and 6 Fan Modules |
LS-Z+A2+F6-1 | H3C S9855-32D Ethernet Switch with 32*400G QSFP-DD Ports, 2 AC Power Supplies and 6 Fan Modules |
LS-Z+A2+M6-11 | H3C S9855-40B L3 Ethernet Switch,with 2 AC Power Supplies and 6 Fan Modules |
Power |
|
PSR1600C-12A-B | 1600W AC Power Supply Module (Power Panel Side Exhaust Airflow) |
PSR1300-12A-C-A | H3C 1300W AC Power Supply Module (Power Panel Side Exhaust Airflow |
Fan |
|
FAN-40B-1-C | Fan Module (Fan Panel Side Exhaust Airflow, Electronic Label Supported) |
FAN-40F-1-D | H3C Fan Module(Fan Panel Side Intake Airflow) |
FAN-40B-1-H | Fan Module(Fan Panel Side Exhaust Airflow,SN Code Supported) |
Transceiver |
|
QSFP-100G-LR4-WDM1300 | 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Module(1310nm,10km,LR4,WDM,LC) |
QSFP-100G-LR4L-WDM1300 | 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,2km,LR4L,CWDM4,LC) |
QSFP-100G-PSM4-SM1310 | 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,500m,PSM4,MPO/APC) |
QSFP-100G-eSR4-MM850 | 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,300m OM4,eSR4,MPO) |
QSFP-100G-SWDM4-MM850 | 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,100m OM4,SWDM4,LC) |
QSFP-100G-SR4-MM850 | 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,100m OM4,SR4,MPO) |
QSFPDD-400G-FR4-WDM1300 | 400G QSFPDD Optical Transceiver Module(1300nm,2km,FR4,LC) |
QSFPDD-400G-SR8-MM850 | 400G QSFPDD Optical Transceiver Module(850nm,100m OM4,SR8,MPO16/APC) |
QSFP-40G-LR4-WDM1300 | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,10km,LR4,LC) |
QSFP-40G-BIDI-SR-MM850 | QSFP+ 40GBASE BIDI Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,100m,SR) |
QSFP-40G-BIDI-WDM850 | QSFP+ 40GBASE BIDI Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,300m) |
QSFP-40G-LR4L-WDM1300 | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,2km,LR4L,LC) |
QSFP-40G-ER4-WDM1300 | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,40km,ER4,LC) |
QSFP-40G-LR4-PSM1310 | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,10km,MPO/APC,LR4,Parallel Single Mode) |
QSFP-40G-LR4-PSM1310-A | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,10km,MPO/APC,LR4,Parallel Single Mode) |
QSFP-40G-SR4-MM850 | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,100m,SR4,Support 40G to 4*10G) |
QSFP-40G-CSR4-MM850 | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,300m,CSR4,Support 40G to 4*10G) |
QSFP-40G-LR4-WDM1300 | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,10km,LR4,LC) |
QSFP-40G-CSR4-MM850 | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,300m,CSR4,Support 40G to 4*10G) |
QSFP-40G-SR4-MM850 | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,100m,SR4,Support 40G to 4*10G) |
QSFP-40G-LR4-PSM1310 | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,10km,MPO/APC,LR4,Parallel Single Mode) |
QSFP-100G-SR4-MM850 | 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,100m OM4,SR4,MPO) |
QSFP-40G-BIDI-WDM850 | QSFP+ 40GBASE BIDI Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,300m) |
QSFP-40G-LR4L-WDM1300 | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,2km,LR4L,LC) |
QSFP-40G-BIDI-SR-MM850 | QSFP+ 40GBASE BIDI Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,100m,SR) |
QSFP-100G-LR4-WDM1300 | 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Module(1310nm,10km,LR4,WDM,LC) |
QSFP-40G-ER4-WDM1300 | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,40km,ER4,LC) |
QSFP-100G-SWDM4-MM850 | 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,100m OM4,SWDM4,LC) |
QSFP-100G-PSM4-SM1310 | 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,500m,PSM4,MPO/APC) |
QSFP-100G-LR4L-WDM1300 | 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,2km,LR4L,CWDM4,LC) |
QSFP-100G-eSR4-MM850 | 100G QSFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,300m OM4,eSR4,MPO) |
QSFP-40G-LR4-PSM1310-A | QSFP+ 40GBASE Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,10km,MPO/APC,LR4,Parallel Single Mode) |
QSFP56-200G-SR4-MM850 | 200G QSFP56 Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,100m OM4,SR4,MPO12/UPC) |
QSFPDD-400G-LR8-WDM1300 | 400G QSFP-DD Optical Transceiver Module (1300nm,10km,LR8,LC) |
Cable | |
QSFP-100G-D-AOC-10M | 100G QSFP28 to 100G QSFP28 10m Active Optical Cable |
QSFP-100G-D-CAB-1M | 100G QSFP28 to 100G QSFP28 1m Passive Cable |
QSFP-100G-D-AOC-20M | 100G QSFP28 to 100G QSFP28 20m Active Optical Cable |
QSFP-100G-D-CAB-3M | 100G QSFP28 to 100G QSFP28 3m Passive Cable |
QSFP-100G-D-CAB-5M | 100G QSFP28 to 100G QSFP28 5m Passive Cable |
QSFP-100G-D-AOC-7M | 100G QSFP28 to 100G QSFP28 7m Active Optical Cable |
LSWM1QSTK0 | 40G QSFP+ Cable 1m |
LSWM1QSTK1 | 40G QSFP+ Cable 3m |
LSWM1QSTK2 | 40G QSFP+ Cable 5m |
QSFP-40G-D-AOC-3M | 40G QSFP+ to 40G QSFP+ 3m Active Optical Cable |
QSFP-40G-D-AOC-10M | 40G QSFP+ to 40G QSFP+ 10m Active Optical Cable |
QSFP-40G-D-AOC-20M | 40G QSFP+ to 40G QSFP+ 20m Active Optical Cable |
QSFP-40G-D-AOC-7M | 40G QSFP+ to 40G QSFP+ 7m Active Optical Cable |
LSWM1QSTK3 | 40G QSFP+ to 4x10G SFP+ Cable 1m |
LSWM1QSTK4 | 40G QSFP+ to 4x10G SFP+ Cable 3m |
LSWM1QSTK5 | 40G QSFP+ to 4x10G SFP+ Cable 5m |
LSWM1QSTK0 | 40G QSFP+ Cable 1m |
LSWM1QSTK1 | 40G QSFP+ Cable 3m |
LSWM1QSTK2 | 40G QSFP+ Cable 5m |
LSWM1QSTK3 | 40G QSFP+ to 4x10G SFP+ Cable 1m |
LSWM1QSTK4 | 40G QSFP+ to 4x10G SFP+ Cable 3m |
LSWM1QSTK5 | 40G QSFP+ to 4x10G SFP+ Cable 5m |
QSFP-40G-D-AOC-7M | 40G QSFP+ to 40G QSFP+ 7m Active Optical Cable |
QSFP-40G-D-AOC-10M | 40G QSFP+ to 40G QSFP+ 10m Active Optical Cable |
QSFP-40G-D-AOC-20M | 40G QSFP+ to 40G QSFP+ 20m Active Optical Cable |
QSFP-100G-D-CAB-1M | 100G QSFP28 to 100G QSFP28 1m Passive Cable |
QSFP-100G-D-CAB-3M | 100G QSFP28 to 100G QSFP28 3m Passive Cable |
QSFP-100G-D-AOC-7M | 100G QSFP28 to 100G QSFP28 7m Active Optical Cable |
QSFP-100G-D-AOC-10M | 100G QSFP28 to 100G QSFP28 10m Active Optical Cable |
QSFP-100G-D-AOC-20M | 100G QSFP28 to 100G QSFP28 20m Active Optical Cable |
QSFP-100G-D-CAB-5M | 100G QSFP28 to 100G QSFP28 5m Passive Cable |
QSFP-40G-D-AOC-3M | 40G QSFP+ to 40G QSFP+ 3m Active Optical Cable |
Resource Center
- Cloud & AI
- InterConnect
- Intelligent Computing
- Intelligent Storage
- Security
- SMB Products
- Intelligent Terminal Products
- Product Support Services
- Technical Service Solutions
Product Support Services
Technical Service Solutions
- Resource Center
- Policy
- Online Help
- Technical Blogs
Resource Center
Policy
Online Help
- Become A Partner
- Partner Policy & Program
- Global Learning
- Partner Sales Resources
- Partner Business Management
- Service Business
Global Learning
- Profile
- News & Events
- Online Exhibition Center
- Contact Us

 Products and Solutions
Products and Solutions