- Products and Solutions
- Industry Solutions
- Services
- Support
- Training & Certification
- Partners
- About Us
- Contact Sales
- Become a Partner
-
 Login
Login
Country / Region
H3C S5590-EI Series Converged Hybrid Multigiga Switches
H3C S5590-EI series switches are a new generation of high-performance, high-port density, high-security Layer 3 Ethernet switches developed by H3C Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as H3C) using industry-leading ASIC technology, supporting IPv4/IPV6 Dual-stack management and forwarding, support static routing protocols and routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF, BGP, ISIS, etc., and support rich management and security features. It is a Gigabit Layer 3 Ethernet switch product for converged service networks.
In the campus network, H3C S5590-EI series switches can be used as aggregation layer equipment, or as the core of small and medium-sized enterprises; downward can provide high-density GE and MultiGiga ports, upward through 10G/25G/40G/100G fiber or link aggregation is aggregated to the core switch to build a high-performance end-to-end IP network solution together with other H3C products.
H3C S5590-EI series switches include the following models:
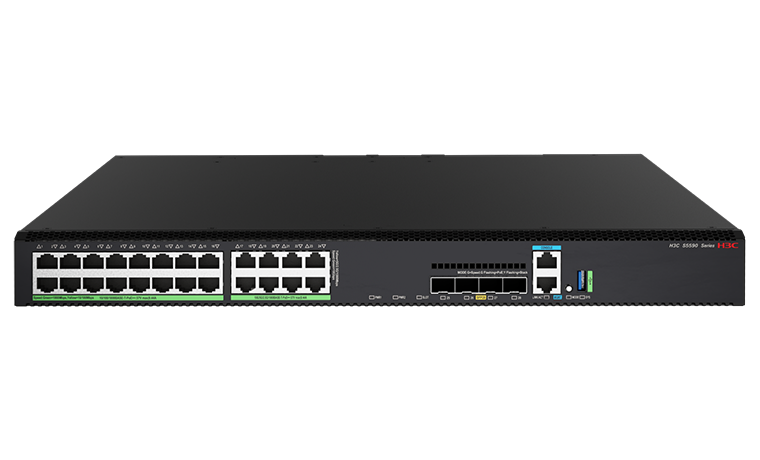
![]() S5590-24UXM4YC-EI: 16*10/100/1000Base-T Ports (PoE++), 8*10M/100M/1G/2.5G/5G/10G Base-T Ports (PoE++), 4*1G/10G/25GBase-X SFP28 Ports, and 1 Slot;
S5590-24UXM4YC-EI: 16*10/100/1000Base-T Ports (PoE++), 8*10M/100M/1G/2.5G/5G/10G Base-T Ports (PoE++), 4*1G/10G/25GBase-X SFP28 Ports, and 1 Slot;
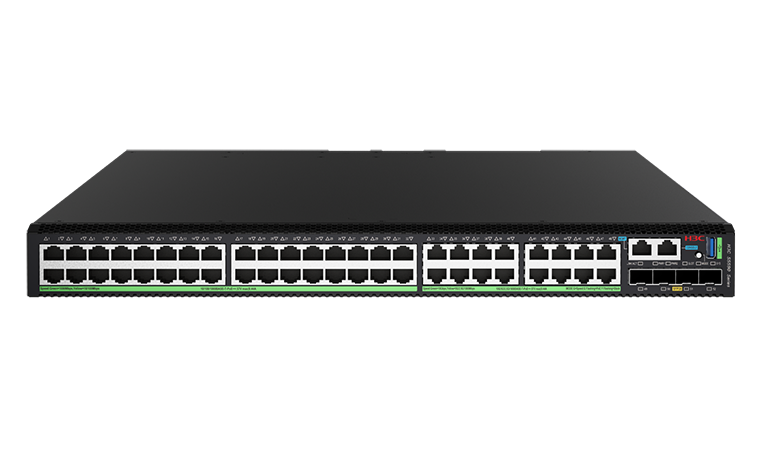
![]() S5590-48UXM4YC-EI: 32*10/100/1000Base-T Ports (PoE++), 16*10M/100M/1G/2.5G/5G/10G Base-T Ports (PoE++), 4*1G/10G/25GBase-X SFP28 Ports, and 1 Slot;
S5590-48UXM4YC-EI: 32*10/100/1000Base-T Ports (PoE++), 16*10M/100M/1G/2.5G/5G/10G Base-T Ports (PoE++), 4*1G/10G/25GBase-X SFP28 Ports, and 1 Slot;
The following contents are complex, and it is recommended to browse on PC.
Enter c.h3c.com.cn on the PC browser and operate according to the page to synchronize to the PC and continue browsing.
Continue by mobile
SmartMC (Smart Management Center)
As the network scale increases, a large number of access devices are required at the network edge, which makes the management of these devices very cumbersome. The main purpose of SmartMC is to solve the problem of centralized management of a large number of scattered network devices. It is designed to solve the switch-based operation and maintenance tasks of small enterprises. SmartMC realizes unified operation, maintenance and management of the network by means of built-in equipment and graphical operation.
SmartMC simplify the operation, maintenance and management of small and medium-sized parks:
![]() Smart management: It mainly includes device role selection, FTP server configuration, global configuration and network management port configuration, etc.
Smart management: It mainly includes device role selection, FTP server configuration, global configuration and network management port configuration, etc.
![]() Intelligent operation and maintenance: Mainly include group management, equipment or group upgrade backup, monitoring and equipment failure replacement, etc.
Intelligent operation and maintenance: Mainly include group management, equipment or group upgrade backup, monitoring and equipment failure replacement, etc.
![]() Visualization: Includes networking topology visualization and management, device list display, device ports display, etc.
Visualization: Includes networking topology visualization and management, device list display, device ports display, etc.
![]() Smart business: Mainly includes user management, etc.: After network access users are created and successfully activated, these users can access the SmartMC network through the port of one- key arming.
Smart business: Mainly includes user management, etc.: After network access users are created and successfully activated, these users can access the SmartMC network through the port of one- key arming.
H3C S5590-EI series switches can be used as the management device of SmartMC. You can log in to the SmartMC network through the S5590 - EI to manage the entire network in a unified manner.
Multi-Service Integration
Based on H3C's Open Service Architecture (OAA), H3C S5590-EI series switches can not only provide the functions of traditional switches, but also integrate security module cards including FW, IPS, and load balancing, mini-iMC cards, and Eagle Vision cards. etc., making the S5590-EI series switches a converged multi-service bearing platform.
High-Performance IPv4/IPv6 Service Capability
H3C S5590-EI series switches implement a hardware-based IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack platform, support multiple tunnel technologies, rich IPv4 and IPv6 Layer 3 routing protocols, multicast technologies and policy routing mechanisms, providing users with complete IPv4/IPv6 solution.
IRF2 (Second Generation Intelligent Resilience Architecture)
H3C S5590-EI series switches support IRF2 (Second Generation Intelligent Resilient Architecture) technology, which is to connect multiple physical devices to each other to make it virtual as a logical device, that is to say, users can regard these multiple devices as one Manage and use a single device. IRF can bring the following benefits to users:
![]() Simplified management: IRF architecture is formed, it can be connected to any port of any device to log in to a unified logical device. By configuring a single device, it can manage the entire intelligent elastic system and all member devices in the system. There is no need to physically connect to each member device to configure and manage them individually.
Simplified management: IRF architecture is formed, it can be connected to any port of any device to log in to a unified logical device. By configuring a single device, it can manage the entire intelligent elastic system and all member devices in the system. There is no need to physically connect to each member device to configure and manage them individually.
![]() Simplified service: IRF are also run as a single device. For example, the routing protocol will be calculated as a single device. With the application of the cross-device link aggregation technology, it can replace the original generation tree protocol, which saves the interaction of a large number of protocol packets between devices, simplifies network operation, and shortens the convergence time when the network is turbulent.
Simplified service: IRF are also run as a single device. For example, the routing protocol will be calculated as a single device. With the application of the cross-device link aggregation technology, it can replace the original generation tree protocol, which saves the interaction of a large number of protocol packets between devices, simplifies network operation, and shortens the convergence time when the network is turbulent.
![]() Elastic expansion: can realize elastic expansion according to user needs and ensure user investment. And new devices can be "hot-swapped" when they join or leave the IRF architecture, without affecting the normal operation of other devices.
Elastic expansion: can realize elastic expansion according to user needs and ensure user investment. And new devices can be "hot-swapped" when they join or leave the IRF architecture, without affecting the normal operation of other devices.
![]() High reliability: high reliability IRF is reflected in three aspects: link, equipment and protocol. The physical ports between member devices support the aggregation function, and the physical connection between the IRF system and the upper and lower-layer devices also supports the aggregation function, which improves the reliability of the link through multi-link backup; the IRF system consists of multiple member devices. Once the master device fails, the system will quickly and automatically elect a new master to ensure uninterrupted services through the system, thus realizing device-level 1: N backup; the IRF system will have a real-time protocol hot backup function responsible for the configuration information of the protocol. Backup to all other member devices to achieve 1: N protocol reliability.
High reliability: high reliability IRF is reflected in three aspects: link, equipment and protocol. The physical ports between member devices support the aggregation function, and the physical connection between the IRF system and the upper and lower-layer devices also supports the aggregation function, which improves the reliability of the link through multi-link backup; the IRF system consists of multiple member devices. Once the master device fails, the system will quickly and automatically elect a new master to ensure uninterrupted services through the system, thus realizing device-level 1: N backup; the IRF system will have a real-time protocol hot backup function responsible for the configuration information of the protocol. Backup to all other member devices to achieve 1: N protocol reliability.
![]() High performance: For high-end switches, the increase in performance and port density is limited by the hardware structure. The performance and port density of an IRF system is the sum of the performance and port numbers of all devices inside the IRF. Therefore, the IRF technology can easily expand the switching capability of the device and the density of user ports several times, thereby greatly improving the performance of the device.
High performance: For high-end switches, the increase in performance and port density is limited by the hardware structure. The performance and port density of an IRF system is the sum of the performance and port numbers of all devices inside the IRF. Therefore, the IRF technology can easily expand the switching capability of the device and the density of user ports several times, thereby greatly improving the performance of the device.
Complete Security Control Strategy
H3C S5590-EI series switches support the EAD ( terminal access control ) function, and cooperate with the background system to integrate terminal security measures such as terminal antivirus and patch repair with network security measures such as network access control and access authority control into a linked security The system, through the inspection, isolation, repair, management and monitoring of network access terminals, makes the entire network change from passive defense to active defense, from single-point defense to comprehensive defense, and from decentralized management to centralized policy management. , worms and other emerging security threats overall defense capabilities.
H3C S5590-EI series switches support centralized MAC address authentication, 802.1x authentication, support dynamic or static binding of user identification elements such as user account, IP, MAC, VLAN, and port, and implement user policies (VLAN, QoS, ACL) dynamic distribution; support with H3C's iMC system for real-time management of online users, timely diagnosis and disintegration of illegal network behavior.
H3C S5590-EI series switches provide enhanced ACL control logic, support large-capacity ingress and egress port ACLs, and support VLAN-based ACL delivery, which simplifies the user configuration process and avoids waste of ACL resources. In addition, H3C S5590-EI series switches will also support unicast reverse path finding technology (uRPF). The route between the interface and the source address specified in the packet is to verify its authenticity. If it does not exist, the packet is deleted, so that we can effectively prevent the source address spoofing that is increasingly flooding in the network.
MACsec Hardware Encryption
MACsec (Media Access Control Security, MAC security) defines the method of data security communication based on IEEE 802 local area network. MACsec can provide users with secure MAC layer data transmission and reception services, including user data encryption, data frame integrity check and data source authenticity verification.
MACsec is usually used in conjunction with the 802.1X authentication framework. After the 802.1X authentication process is successful, it identifies the message sent by the authenticated device and uses the MKA (MACsec Key Agreement, MACsec Key Agreement) protocol to negotiate the generated key pair Authenticated user data is encrypted and integrity checked to prevent the port from processing packets from unauthenticated devices or tampered with unauthenticated devices.
H3C S 5590-EI series switches support upgraded MACsec encryption technology and use 256-bit encryption algorithm to further improve data security; All ports of the device provide 256-bit MACsec encryption to ensure data security.
Precision Time Protocol (PTP)
H3C S5590-EI series switches support the 1588V2 function to meet the high-precision time synchronization requirements between network devices. Compared with GPS time synchronization with the same precision, it improves security and lowers deployment costs.
Intelligent Network Quality Analyzer (iNQA)
H3C S5590-EI series switches support iNQA. iNQA provides the following benefits:
![]() True measurement results—iNQA measures the service packets directly to calculate packet loss results, thus reflecting the real network quality.
True measurement results—iNQA measures the service packets directly to calculate packet loss results, thus reflecting the real network quality.
![]() Wide application range—Applicable to Layer 2 network and Layer 3 IP network. iNQA supports the network-level and direct link measurement flexibly.
Wide application range—Applicable to Layer 2 network and Layer 3 IP network. iNQA supports the network-level and direct link measurement flexibly.
![]() Fast fault location—iNQA obtains the packet loss time, packet loss location, and number of lost packets in real time.
Fast fault location—iNQA obtains the packet loss time, packet loss location, and number of lost packets in real time.
![]() Applicable to different applications—You can apply iNQA to multiple scenarios, such as point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, and multipoint-to-multipoint.
Applicable to different applications—You can apply iNQA to multiple scenarios, such as point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, and multipoint-to-multipoint.
Multichassis Link Aggregation Group (M-LAG) (Original DRNI)
H3C S5590-EI series switches support M-LAG, which enables links of multiple switches to aggregate into one to implement device-level link backup. M-LAG is applicable to servers dual-homed to a pair of access devices for node redundancy.
![]() Streamlined topology: M-LAG simplifies the network topology and spanning tree configuration by virtualizing two physical devices into one logical device.
Streamlined topology: M-LAG simplifies the network topology and spanning tree configuration by virtualizing two physical devices into one logical device.
![]() Independent upgrading: The DR member devices can be upgraded independently one by one to minimize the impact on traffic forwarding.
Independent upgrading: The DR member devices can be upgraded independently one by one to minimize the impact on traffic forwarding.
![]() High availability: The DR system uses a keepalive link to detect multi-active collision to ensure that only one member device forwards traffic after a DR system splits.
High availability: The DR system uses a keepalive link to detect multi-active collision to ensure that only one member device forwards traffic after a DR system splits.
Visualization Ability
H3C S5590-EI series switches support Telemetry technology, which can send the switch's real-time resource information and alarm information to the O&M platform through the gRPC protocol.
The platform can realize network quality backtracking, troubleshooting, risk early warning, architecture optimization and other functions to accurately guarantee user experience by analyzing real-time data.
Al-driven PoE
![]() Fast PoE: Typically, PIs does not deliver power to PDs the moment the PSE is powered on but wait until the PSE completes startup. Fast PoE enables PIs to deliver power to PDs within few seconds after power is supplied to the PSE.
Fast PoE: Typically, PIs does not deliver power to PDs the moment the PSE is powered on but wait until the PSE completes startup. Fast PoE enables PIs to deliver power to PDs within few seconds after power is supplied to the PSE.
![]() Perpetual PoE: Perpetual PoE continuously monitors the PD states and ensures continued power supply to PDs even when the PSE device is hot rebooting.
Perpetual PoE: Perpetual PoE continuously monitors the PD states and ensures continued power supply to PDs even when the PSE device is hot rebooting.
![]() AI-driven PoE: Innovatively integrating AI technologies into PoE switches, H3C AI-driven PoE enables completely automated, intelligently managed, healed, and optimized PoE, bringing convenient and outstanding PoE experience to users.
AI-driven PoE: Innovatively integrating AI technologies into PoE switches, H3C AI-driven PoE enables completely automated, intelligently managed, healed, and optimized PoE, bringing convenient and outstanding PoE experience to users.
Hardware Specifications
S5590-24UXM4YC-EI | S5590-48UXM4YC-EI | |
Port Switching Capacity | 792Gbps | 984Gbps |
Packet Forwarding Capacity | 440Mpps | 583Mpps |
Switching Capacity | 2.4Tbps | 2.4Tbps |
Dimensions (W×D×H) (unit: mm ) | 440×400×44 | 440×400×44 |
Weight | ≤6.8kg | ≤7kg |
Console port | 1 | |
Flash/SDRAM | 8G/2G | |
Packet Buffer | 4.5M | |
Ethernet port for management | 10/100/1000Base-T electrical port: 1 | |
USB port | 1 | |
10/100/1000BASE-T port (PoE++) | 16 | 32 |
10M/100M/1G/2.5G/5G/10G Base-T Ports (PoE++) | 8 | 16 |
1G/10G/25GBase-X SFP28 | 4 | 4 |
Expansion card slot | 1 | |
PoE | PoE++ support | |
Expansion board | 2-port 10G SFP+ interface card 4-port 10G SFP+ interface card 4-port 25GE SFP28 interface card 2-port 40GE QSFP+ interface card | 2-port 10G SFP+ interface card 4-port 10G SFP+ interface card 4-port 25GE SFP28 interface card 2-port 40GE QSFP+ interface card |
Input voltage | AC: Rated voltage range: 100 to 240V AC: 50/60Hz | |
Power Supply slots | 2(Hot swappable) | |
Machine leakage current | Meet UL60950-1/EN60950-1/IEC60950-1 /GB4943 standard | |
Working temperature | -5 ºC to 45 ºC | |
Relative humidity of working environment (non-condensing) | 5 % to 95 % | |
Software Specifications
Feature | S5590-EI Series Switches |
Ethernet Configuration | Cross-device link aggregation Static aggregation Dynamic aggregation AutoMDIX LRM (Long Reach Multimode) (LSWM4SP8PM can support LRM transceiver) Speed Auto/Manual Duplex Auto/Full/Half |
Port Characteristics | Support IEEE802.3x flow control (full duplex) Supports storm suppression based on port rate percentage Supports PPS-based storm suppression Support bps-based storm suppression |
MAC address table | Support black hole MAC address Supports setting the maximum number of port MAC addresses to learn |
VLAN | Access/Trunk/Hybrid VLAN Port-based VLAN support MAC-based VLAN IP subnet-based VLAN Protocol-based VLAN IEEE 802.1P(CoS priority) Super VLAN Private VLAN Voice VLAN Support QinQ, flexible QinQ Support VLAN Mapping Support Private VLAN Support Voice VLAN QinQ (802.1Q-in-802.1Q) VLAN mapping Static/Dynamic/Blackhole/Multiport unicast MAC MAC automatic learning and aging Port-based/VLAN-based MAC learning limit MAC filter Port isolation VLAN ID range 0 to 4095(Total 4096) Access/Trunk/Hybrid VLAN Port-based VLAN MAC-based VLAN IP subnet-based VLAN Protocol-based VLAN IEEE 802.1P(CoS priority) Super VLAN Private VLAN Voice VLAN QinQ (802.1Q-in-802.1Q) Vlan mapping Static/Dynamic/Blackhole/Multiport unicast MAC MAC automatic learning and aging Port-based/VLAN-based MAC learning limit MAC filter Port isolation IEEE 802.3x flow control (full duplex) Storm suppression based on port rate percentage PPS -based storm suppression bps -based storm suppression LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) and LLDP-MED (Link Layer Discovery Protocol Media Endpoint Discovery) Broadcast/multicast/unknown unicast storm constrain Jumbo frame Store-and-forward (Default) |
Layer 2 Ring Network Protocol | Loop detection (VLAN and VXLAN network) MVRP (Multiple VLAN Registration Protocol) GVRP (Generic VLAN Registration Protocol) PVST (Per-VLAN Spanning Tree) (compatible with PVST+/RPVST+) Support STP/RSTP/MSTP Support SmartLink Support RRPP Support ERPS (G.8032) Ethernet ring network protection switching BPDU/root/loop/TC-BPDU/PVST BPDU/disputeloopback guard BPDU filter Role/TC-BPDU transmission restriction Support port single-pass detection, Edge Port |
IRF2 Intelligent Resilience Architecture | Support IRF2 Intelligent Resilience Architecture (fast convergence within 50ms) Support distributed device management, distributed link aggregation, distributed elastic routing Supports stacking via standard Ethernet interfaces, etc. Supports local stacking and remote stacking |
IP Services | Static/Dynamic/Gratuitous/proxy ARP ARP snooping/fast-reply/direct route advertisement/ping ARP attack detection ARP source suppression Ping, Tracert DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) DHCP Server/relay agent/client/snooping DHCP Option 43, Option 82, and Option 184, DNS (Domain Name System) DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) mDNS(Multicast Domain Name System) IRDP (ICMP Router Discovery Protocol) UDP helper ND (Neighbor Discovery) ND snooping/proxy/direct route advertisement/ping DHCPv6 Server/relay agent/client/snooping/guard GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) HTTP redirect GRE tunneling VXLAN tunneling and VXLAN-DCI tunneling IPv4/IPv6 over IPv4 tunneling, and IPv4/IPv6 over IPv6 tunneling IPv4/IPv6 Fast Forwarding |
IP routing | Support static routing Support RIPv1/v2, RIPng Support OSPFv1/v2, OSPFv3 Support BGP4, BGP4+ for IPv6 Support IS-IS, IS-IS V6 Support equal-cost routing, policy routing Support VRRP/VRRPv3 Support O SPF multi-process, MD5 encryption authentication, S TUB/NSSA area Support route COST setting, support inter-area route filtering |
IPv6 | Support IPv4/IPv6 dual stack protocol Support ND (Neighbor Discovery) Support PMTU Support IPv6-Ping, IPv6-Tracert, IPv6-Telnet, IPv6-TFTP, IPv6 - ICMP, IPv6 -DNS, IPv6-FTP, IPv6-NTP Support manual tunnel, automatic tunnel IPv4 support over IPv6 tunnel Support 6to4 tunnel Support ISATAP tunnel Support GRE tunnel |
Multicast | PIM-DM, PIM-SM, PIM-SSM, and Any-RP PIM snooping IGMPv1/IGMPv2/IGMPv3 IGMP proxying IGMP Snooping IGMP snooping proxying IGMP Filter and IGMP Fast leave IPv6 PIM-DM, PIM-SM, PIM-SSM, and Any-RP IPv6 PIM snooping MLDv1/MLDV2 MLD proxying MLD Snooping MLD snooping proxying Multicast routing and forwarding Multicast VLAN MVPN (Multicast VPN) Multicast policy and Multicast QoS Support MSDP, MSDP for IPv6 Support MBGP, MBGP for Ipv6 |
Mirror | Stream mirroring supported Support N:4 port mirroring Supports local and remote port mirroring Support ERS PAN |
ACL\QoS | Support L2 (Layer 2) ~ L4 (Layer 4) packet filtering function, provide based on source MAC address, destination MAC address, source IP (IPv4/IPv6) address, destination IP (IPv4/IPv6) address, TCP/UDP port number, Traffic Classification for VLANs Support Time Range ACL Supports bidirectional ACL policies in inbound and outbound directions Supports issuing ACLs based on VLANs Supports limiting the rate at which the port receives packets and the rate at which it sends packets Support message redirection Diff-Serv QoS Eight queues each interface 802.1p, TOS, DSCP, and EXP priority mapping 802.1p and DSCP priority re-marking of packets Support CAR (Committed Access Rate) function Support flexible queue scheduling algorithm, can be set based on port and queue at the same time, support SP, WFQ, SP+WFQ three modes Traffic shaping Time ranges Traffic classification based on source MAC, destination MAC, source IP, destination IP, port, protocol, and VLAN Congestion avoidance, Tail-Drop, RED (Random Early Detection) and WRED (Weighted Random Early Detection) |
MPLS | Static LSP (label switched path) LDP (Label Distribution Protocol) IPv6 LDP Tunnel policies VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) Support MPLS MCE MPLS support L3VPN MPLS support L2VPN MPLS support SR MPLS Ping/Tracert MCE (Multi-VPN Instance Customer Edge) IPv6 MCE MPLS OAM |
VxLAN | Support VxLAN Layer 2 and Layer 3 gateways Support VxLAN routing Centralized VXLAN gateway Distributed VXLAN gateway VXLAN M-LAG VXLAN-DCI OVSDB (Open vSwitch Database) VXLAN VTEP MP-BGP EVPN control plane EVPN VXLAN EVPN M-LAG |
Safety features | Support RBAC (Role-based access control) Support user hierarchical management and password protection Support 802.1X authentication / centralized MAC address authentication Support Portal authentication Support Guest VLAN Support AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) Support RADIUS authentication Support HW TACACS+ certification Support MAC authentication Support Web authentication Support Triple authentication Support Guest VLAN SSH1.x and SSH2.0(Secure Shell) SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) HTTPs Support port isolation Support port security Support EAD Support SAVI and SAVA to ensure the security of IPv6 environment Support DHCP Snooping to prevent spoofed DHCP server Support dynamic ARP inspection to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks and ARP denial of service Support BPDU guard, Root guard Support uRPF (Unicast Reverse Path Detection) to prevent IP source address spoofing and prevent viruses and attacks Support IP/Port/MAC binding function Control Plane Protection (CoPP), Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIPS) Attack detection and prevention TCP attack prevention IPSG (IP source guard) IPv6 RA Guard ARP attack protection ND attack protection MFF (MAC-forced forwarding) SAVI (Source Address Validation Improvement) FIPS (Federal Information Processing Standards) MACsec (Media Access Control Security) All ports AES256 MACsec (Include the ports in expansion card) Microsegmentation Hierarchical user management and password protection Basic and advanced ACLs for packet filtering Support OSPF, RIPv2 message plaintext and MD5 ciphertext authentication Support PKI (Public Key Infrastructure, public key infrastructure) |
Network Management | NQA (Network quality analyzer) iNQA (Intelligent Network Quality Analyzer) eMDI (Enhanced Media Delivery Index) Performance management through gRPC or NETCONF NTP (Network Time Protocol) Support hot patch function, online patch upgrade Support XModem /FTP/TFTP loading and upgrading Support command line interface (CLI), Telnet, Console port for configuration Support netcool network management platform Support SNMPv1/v2/v3, RMON (Remote Monitoring) BFD support for VRRP/IS-IS/BGP/RIP/OSPF/Static Routing Support iMC intelligent management center Support Syslog, system log, hierarchical alarm, debug information output NTP support Support power alarm function, fan, temperature alarm Support Ping, Tracert Support VCT (Virtual Cable Test) cable detection function Support DLDP (Device Link Detection Protocol) unidirectional link detection protocol Port mirroring SPAN (Switch Port Analyzer)/RSPAN (Remote SPAN) Flow mirroring N:4 port mirroring local and remote port mirroring sFlow Information center NETCONF/YANG (XML-based network management protocol) Support Python script management operation and maintenance Support Loopback-detection port loopback detection Support NetStream function, traffic analysis sampling ratio 1:1 Supportbuilt-inWebGUI Support secure boot |
OpenFlow | OpenFlow 1.3 Multiple controllers (EQUAL, master/slave) Multiple tables flow Group table |
Energy Saving | Port automatic power down function Port timing down function (Schedule job) Support EEE (802.3az) energy saving standard |
Performance Specification
Entries | S5590-EI Series Switches |
MAC address entries | max 320K |
VLAN table | 4K |
VLAN interface | 4093 |
IPv4 routing entries | max 80K |
IPv4 ARP entries | 65015 |
IPv4 ACL entries | IN: 3.25K EG: 0.75K |
IPv4 multicast L2 entries | 8K |
IPv4 multicast L3 entries | 4K |
IPv6 unicast routing entries | 32K |
QOS forward queues | 8 |
IPv6 ACL entries | Ingress: 1.625K Egress: 0.375 |
IPv6 ND entries | 32K |
IPv6 multicast L2 entries | 8K |
IPv6 multicast L3 entries | 4K |
Jumbo frame length | 13312 |
Max Stacking Members | 9 |
Max Stacking Bandwidth | 400Gbps |
PoE Power Capacity
Power supply 2 | S5590-24UXM4YC-EI | S5590-48UXM4YC-EI | |||
Total PoE power capacity | PoE Ports Quantity | Total PoE power capacity | PoE Ports Quantity | ||
PSR600-54A-B | / | 450W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 450W | 15.4W (802.3af): 29 |
30W (802.3at): 15 | 30W (802.3at): 15 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 7 | 60W (802.3bt): 7 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 5 | 90W (802.3bt): 5 | ||||
PSR920-54A-B | / | 770W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 770W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 25 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 12 | 60W (802.3bt): 12 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 8 | 90W (802.3bt): 8 | ||||
PSR1600-54A-B (Input Voltage: 90V AC~176V AC) | / | 770W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 770W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 25 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 12 | 60W (802.3bt): 12 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 8 | 90W (802.3bt): 8 | ||||
PSR1600-54A-B (Input Voltage:176V AC~290V AC or 180V DC~320V DC) | / | 1450W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 1450W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 48 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 24 | 60W (802.3bt): 24 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 16 | 90W (802.3bt): 16 | ||||
PSR600-54A-B | PSR600-54A-B | 1020W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 1020W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 34 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 17 | 60W (802.3bt): 17 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 11 | 90W (802.3bt): 11 | ||||
PSR600-54A-B | PSR920-54A-B | 1020W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 1020W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 34 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 17 | 60W (802.3bt): 17 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 11 | 90W (802.3bt): 11 | ||||
PSR600-54A-B | PSR1600-54A-B (Input Voltage: 90V AC~176V AC) | 1020W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 1020W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 34 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 17 | 60W (802.3bt): 17 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 11 | 90W (802.3bt): 11 | ||||
PSR600-54A-B | PSR1600-54A-B (Input Voltage:176V AC~290V AC or 180V DC~320V DC) | 1020W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 1020W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 34 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 17 | 60W (802.3bt): 17 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 11 | 90W (802.3bt): 11 | ||||
PSR920-54A-B | PSR920-54A-B | 1600W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 1600W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 48 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 24 | 60W (802.3bt): 26 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 17 | 90W (802.3bt): 17 | ||||
PSR920-54A-B | PSR1600-54A-B (Input Voltage: 90V AC~176V AC) | 1260W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 1260W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 42 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 21 | 60W (802.3bt): 21 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 14 | 90W (802.3bt): 14 | ||||
PSR920-54A-B | PSR1600-54A-B (Input Voltage:176V AC~290V AC or 180V DC~320V DC) | 1600W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 1600W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 48 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 24 | 60W (802.3bt): 26 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 17 | 90W (802.3bt): 17 | ||||
PSR1600-54A-B (Input Voltage: 90V AC~176V AC) | PSR1600-54A-B (Input Voltage: 90V AC~176V AC) | 1600W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 1600W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 48 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 24 | 60W (802.3bt): 26 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 17 | 90W (802.3bt): 17 | ||||
PSR1600-54A-B (Input Voltage: 90V AC~176V AC) | PSR1600-54A-B (Input Voltage:176V AC~290V AC or 180V DC~320V DC) | 1600W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 1600W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 48 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 24 | 60W (802.3bt): 26 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 17 | 90W (802.3bt): 17 | ||||
PSR1600-54A-B (Input Voltage:176V AC~290V AC or 180V DC~320V DC) | PSR1600-54A-B (Input Voltage:176V AC~290V AC or 180V DC~320V DC) | 2850W | 15.4W (802.3af): 24 | 2850W | 15.4W (802.3af): 48 |
30W (802.3at): 24 | 30W (802.3at): 48 | ||||
60W (802.3bt): 24 | 60W (802.3bt): 47 | ||||
90W (802.3bt): 24 | 90W (802.3bt): 31 | ||||
Standards And Protocols Compliance
Organization | Standards And Protocols |
IEEE | IEEE 802.1D (STP) IEEE 802.1p (CoS) IEEE 802.1Q (VLANs) IEEE 802.1s (MSTP) IEEE 802.1w (RSTP) IEEE 802.1X (Security) IEEE 802.3ad (LACP) IEEE 802.3u (Fast Ethernet 100BASE-T/100BASE-TX) IEEE 802.3ab (1000BASE-T) IEEE 802.3x (Flow Control) IEEE 802.3z (1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-LX) |
RFC | RFC1771 (BGPv4) RFC1772 (Application of the BGP) RFC1965 (BGPv4 autonomous system confederations) RFC1997 (Communities attribute) RFC2385 (Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) MD5 authentication for BGP) RFC2439 (Route flap dampening) RFC2796 (Route reflection) RFC1657 (Definitions of Managed Objects for BGPv4) |
RFC2328 (OSPF v2) RFC1587 (OSPF NSSA) RFC2370 (OSPF opaque link-state advertisement (LSA) option) RFC1850 (OSPF v2 Management Information Base (MIB), traps) | |
ISO10589 (IS-IS) RFC1195 (IS-IS) RFC2973 (IS-IS mesh groups) | |
RFC1058 (RIP v1) RFC1723 (RIP v2) RFC2453 (RIP v2) RFC2083 (PNG (Portable Network Graphics) Specification Version) | |
RFC791 (IP) RFC792 (ICMP) RFC793 (TCP) RFC768 (UDP) RFC826 (ARP) RFC783 (TFTP) RFC854 (Telnet) RFC894 (IP Over Ethernet) RFC950 (Internet Standard Subnetting Procedure) RFC959 (FTP) RFC1141 (Incremental updating of the Internet checksum) RFC1122 (Requirements for Internet Hosts -Communication Layers) RFC1256 (ICMP Router Discovery Messages) RFC1393 (Trace route Using an IP Option) RFC 1812 (IPv4) RFC 2338 (VRRP) RFC 2787 (Definitions of Managed Objects for VRRP) RFC 2474 (Diffserv) RFC 2131 (DHCP) RFC 2132 (DHCP and BOOTP Extension) RFC2280 (Routing Policy Specification Language (RPSL)) RFC1305 (NTPv3) RFC1157 (SNMP) RFC857 (Telnet Echo Option) RFC858 (Telnet Suppress Go Ahead Option) RFC1093 (NSFNET routing architecture) RFC 2138 (Radius Authentication) RFC 2139 (Radius Accounting) RFC1492 (TACACS) RFC 1518, 1519 (CIDR) RFC 2622 (Routing policy) RFC 2338 (VRRP) | |
RFC 1112 (Host extensions for IP multicasting) RFC 2236 (Internet Group Management Protocol, Version 2) RFC 2715 (Interoperability Rules for Multicast Routing Protocols) RFC 2362 (PIM-SM) Draft (PIM-DM: draft-ietf-idmr-pim-dm-06) RFC 2283 (Multi-protocol Extensions for BGPv4) | |
RFC 2267 (Network Ingress Filtering) RFC2474 (Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers) RFC2475 (Architecture for Differentiated Service) RFC3168 (The Addition of Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) to IP) | |
RFC2702 (Requirements for Traffic Engineering Over MPLS) RFC3031 (Multi-protocol Label Switching Architecture) RFC3032 (MPLS Label Stack Encoding) RFC3033 (The Assignment of the Information Field and Protocol Identifier in the Q.2941 Generic Identifier and Q.2957 User-to-user Signaling for the Internet Protocol) RFC3036 (LDP Specification) RFC3037 (LDP Applicability) | |
RFC2547 (BGP/MPLS VPN) RFC2764 (A Framework for IP Based Virtual Private Networks) RFC2796 (BGP Route Reflection - An Alternative to Full Mesh IBGP) RFC2842 (Capabilities Advertisement with BGPv4) RFC2858 (Multi-protocol Extensions for BGPv4) RFC2917 (A Core MPLS IP VPN Architecture) RFC2918 (Route Refresh Capability for BGPv4) RFC3107 (Carrying Label Information in BGPv4) | |
Draft (Draft-martini-l2circuit-trans-mpls-08.txt) Draft (Draft-martini-l2circuit-encap-mpls-04.txt) Draft (Draft-kompella-ppvpn-l2vpn-01.txt) | |
RFC2080 (RIPng for IPv6) RFC1981 (Path MTU Discovery for IP version 6) RFC2460 (Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6) Specification) RFC2461 (Neighbor Discovery for IP Version 6 (IPv6)) RFC2462 (IPv6 Stateless Address Auto configuration) RFC2463 (Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMPv6) for the Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) Specification) RFC2545 (BGP support IPv6) RFC2740 (OSPF for IPv6) RFC3513 (Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) Addressing Architecture) RFC3596 (DNS Extensions to Support IP Version 6) Draft (Draft-ietf-isis-ipv6-04.txt) | |
RFC 1493 (Bridge MIB) RFC 2674 (VLAN MIB Extension) RFC 1573 (Private IF MIB) RFC 1213 (MIB II) RFC 1724 (RIP Version 2 MIB Extension) RFC 1850 (OSPF Version 2 MIB Extension) RFC 2787 (VRRP MIB) RFC 2618 (RADIUS Authentication Client MIB) RFC 2620 (RADIUS Accounting Client MIB) RFC 1155 (Structure and Mgmt Information (SMIv1)) RFC 1157 (SNMPv1/v2c) RFC 1213, 1573 (MIB II) RFC 1901-1907 (SNMPv2c, SMIv2 and Revised MIB-II) RFC 2271 (FrameWork) RFC 2578-2580 (SMIv2) RFC 2819 (RMON) RFC 2668 (IEEE 802.3 MAU MIB) RFC 2665 (Pause control) RFC 2233 (Interfaces MIB) RFC2452 (MIB for TCP6) RFC2454 (MIB for UDP6) RFC2466 (MIB for ICMP6) | |
EMC | FCC Part 15 (CFR 47) Class A EN 55022 Class A ICES -003 Class A CISPR 22 Class A VCCI Class A AS/NZS 3548 Class A EN 55024 EN 61000-3-2 EN 61000-3-3 EN 61000-4-2 EN 61000-4-3 EN 61000-4-4 EN 61000-4-5 EN 61000-4-6 EN 61000-4-11 CISPR 24 Class A ETSI EN 300 386 V1.3.2:2003 IEC 61000-3-2 IEC 61000-3-3 |
Safety | EN 60950:2000 EN 60825-1:1993+A1:1997 and EN 60825-2:2000 UL 60950 3rd Edition CSA C22.2 No. 60950 3rd Edition IEC 60950: 1999 AS/NZS 3260 |
Product ID | Product Description |
H3C S5590-24UXM4YC-EI L3 Ethernet Switch with 16*10/100/1000Base-T Ports(PoE++), 8*1G/2.5G/5G/10G Base-T Ports(PoE++), 4*10G/25GBase-X SFP28 Ports, and 1 Slot, Without Power Supplies | |
LS-5590-48UXM4YC-EI-GL | H3C S5590-48UXM4YC-EI L3 Ethernet Switch with 32*10/100/1000Base-T Ports(PoE++), 16*1G/2.5G/5G/10G Base-T Ports(PoE++), 4*10G/25GBase-X SFP28 Ports, and 1 Slot, Without Power Supplies |
Fan | |
LSPM1FANSB-SN | H3C Fan Module (Fan Panel Side Exhaust Airflow) |
Power supply | |
PSR600-54A-B | H3C, PSR600-54A-B,600W/56V PoE Power Supply |
PSR920-54A-B | H3C, PSR920-54A-B,920W/56V PoE Power Supply |
PSR1600-54A-B | H3C, PSR1600-54A-B,1600W/56V PoE Power Supply |
Modules | |
LSWM2SP2PB | 2-Port 10G SFP Plus Ethernet Optical Interface Module |
LSW2SP2PM | 2-Port 10G SFP Plus Interface Card with MACSec |
LSWM2ZSP2P | 2-Port 25G SFP28 Ethernet Optical Interface Module |
LSWM2QP2P | 2-Port 40G QSFP Plus Interface Card |
Transceivers | |
SFP-XG-SX-MM850-A | SFP+ Module(850nm,300m,LC) |
SFP-XG-SX-MM850-D | SFP+ Module(850nm,300m,LC) |
SFP-XG-SX-MM850-E | SFP+ Module(850nm,300m,LC) |
SFP-XG-LX-SM1270-BIDI | 10G SFP+ BIDI Optical Transceiver Module (TX1270nm/RX1330nm,10km,LC) |
SFP-XG-LX-SM1310 | SFP+ Module(1310nm,10km,LC) |
SFP-XG-LX-SM1310-D | SFP+ Module(1310nm,10km,LC) |
SFP-XG-LX-SM1310-E | SFP+ Module(1310nm,10km,LC) |
SFP-XG-LX-SM1330-BIDI | 10G SFP+ BIDI Optical Transceiver Module (TX1330nm/RX1270nm,10km,LC) |
SFP-XG-LH40-SM1270-BIDI | 10G SFP+ BIDI Optical Transceiver Module (TX1270nm/RX1330nm,40km,LC) |
SFP-XG-LH40-SM1330-BIDI | 10G SFP+ BIDI Optical Transceiver Module (TX1330nm/RX1270nm,40km,LC) |
SFP-XG-LH40-SM1550 | SFP+ Module(1550nm,40km,LC) |
SFP-XG-LH80-SM1490-BIDI | 10G SFP+ BIDI Optical Transceiver Module (TX1490nm/RX1550nm,80km,LC) |
SFP-XG-LH80-SM1550 | SFP+ Module(1550nm,80km,LC) |
SFP-XG-LH80-SM1550-BIDI | 10G SFP+ BIDI Optical Transceiver Module (TX1550nm/RX1490nm,80km,LC) |
SFP-XG-LH80-SM1550-D | SFP+ Module(1550nm,80km,LC) |
SFP-XG-CPRI-IR-SM1310 | SFP+ 10G CPRI Optical Transceiver Module(-40°C to 85°C,1310nm,1.4km,LC) |
SFP-XG-CPRI-LR-SM1310 | SFP+ 10G CPRI Optical Transceiver Module(-40°C to 85°C,1310nm,10km,LC) |
SFP-25G-LR-SM1310 | 25G SFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (1310nm,10km,LR,SM,LC) |
SFP-25G-SR-MM850 | 25G SFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,100m,SR,MM,LC) |
SFP-25G-CSR-MM850 | 25G SFP28 Optical Transceiver Module (850nm,300m OM3,CSR,MM,LC) |
Cables | |
CAB-CON-1.8m | Single Cable,Console Serial Port Cable,1.8m,D9F,28UL20276(4P)(P296U),MPH-8P8C |
LSWM1STK | SFP+ Cable 0.65m |
LSWM2STK | SFP+ Cable 1.2m |
LSWM3STK | SFP+ Cable 3m |
LSTM1STK | SFP+ Cable 5m |
SFP-XG-D-AOC-10M | SFP+ to SFP+ 10m Active Optical Cable |
SFP-XG-D-AOC-20M | SFP+ to SFP+ 20m Active Optical Cable |
SFP-XG-D-AOC-7M | SFP+ to SFP+ 7m Active Optical Cable |
SFP-25G-D-AOC-10M | 25G SFP28 to 25G SFP28 10m Active Optical Cable |
SFP-25G-D-AOC-20M | 25G SFP28 to 25G SFP28 20m Active Optical Cable |
SFP-25G-D-AOC-3M | 25G SFP28 to 25G SFP28 3m Active Optical Cable |
SFP-25G-D-AOC-5M | 25G SFP28 to 25G SFP28 5m Active Optical Cable |
SFP-25G-D-AOC-7M | 25G SFP28 to 25G SFP28 7m Active Optical Cable |
SFP-25G-D-CAB-1M | 25G SFP28 to 25G SFP28 1m Passive Cable |
SFP-25G-D-CAB-3M | 25G SFP28 to 25G SFP28 3m Passive Cable |
SFP-25G-D-CAB-5M | 25G SFP28 to 25G SFP28 5m Passive Cable |
Resource Center
- Cloud & AI
- InterConnect
- Intelligent Computing
- Intelligent Storage
- Security
- SMB Products
- Intelligent Terminal Products
- Product Support Services
- Technical Service Solutions
Product Support Services
Technical Service Solutions
- Resource Center
- Policy
- Online Help
- Technical Blogs
Resource Center
Policy
Online Help
- Become A Partner
- Partner Policy & Program
- Global Learning
- Partner Sales Resources
- Partner Business Management
- Service Business
Global Learning
- Profile
- News & Events
- Online Exhibition Center
- Contact Us

 Products and Solutions
Products and Solutions
