- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-IPsec Troubleshooting Guide | 76.62 KB |
Troubleshooting IP tunnels and IPsec VPNs
IPsec issues
Failures in triggering IKE negotiations (using an IPsec profile)
Symptom
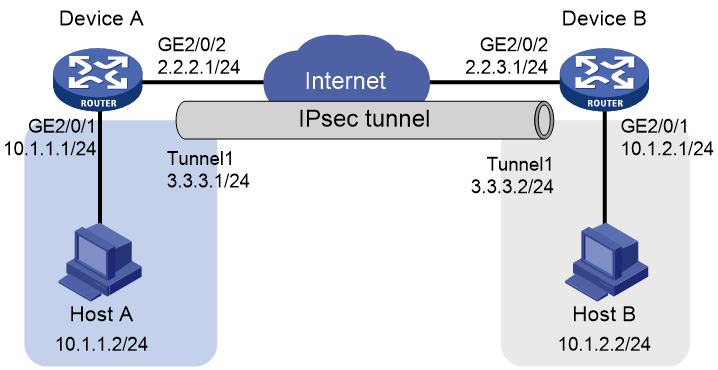
As shown in Figure 1, an IKE-based IPsec tunnel needs to be established between Device A and Device B to protect the private network traffic between Host A and Host B. The encapsulation mode for the IPsec tunnel is the tunnel mode. After completing the configuration on Device A and Device B, traffic fails to be forwarded between Host A and Host B.
After you execute the display ike sa command on Device A, no information is displayed, which indicates that the phase-1 IKE negotiation was unsuccessful. RD is displayed in the Flag field after you execute the display ike sa command and no information is displayed after you execute the display ipsec sa command. This indicates that the phase-2 IKE negotiation was also unsuccessful.
<DeviceA> display ike sa
Flags:
RD--READY RL--REPLACED FD-FADING RK-REKEY
ID Profile Remote Flag Remote-Type Remote-ID
--------------------------------------------------------------------
<DeviceA> display ipsec sa
<DeviceA>
When you execute the display ike statistics command on Device A to view IKE statistics, no noticeable error is found.
<DeviceA> display ike statistics
IKE statistics:
No matching proposal: 0
Invalid ID information: 0
Unavailable certificate: 0
Unsupported DOI: 0
Unsupported situation: 0
Invalid proposal syntax: 0
Invalid SPI: 0
Invalid protocol ID: 0
Invalid certificate: 0
Authentication failure: 0
…
After you execute the display ipsec statistics command on Device A to view IPsec statistics, no noticeable error is found.
<DeviceA> display ipsec statistics
IPsec packet statistics:
Received/sent packets: 0/0
Received/sent bytes: 0/0
Received/sent packet rate: 0/0 packets/sec
Received/sent byte rate: 0/0 bytes/sec
Dropped packets (received/sent): 0/0
Dropped packets statistics
No available SA: 0
Wrong SA: 0
Invalid length: 0
Authentication failure: 0
Encapsulation failure: 0
Decapsulation failure: 0
Replayed packets: 0
ACL check failure: 0
MTU check failure: 0
Loopback limit exceeded: 0
Crypto speed limit exceeded: 0
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The route between IPsec gateways is unreachable.
· The IPsec profile configuration is incorrect.
· The configurations of the IKE profiles and IKE proposals are incorrect.
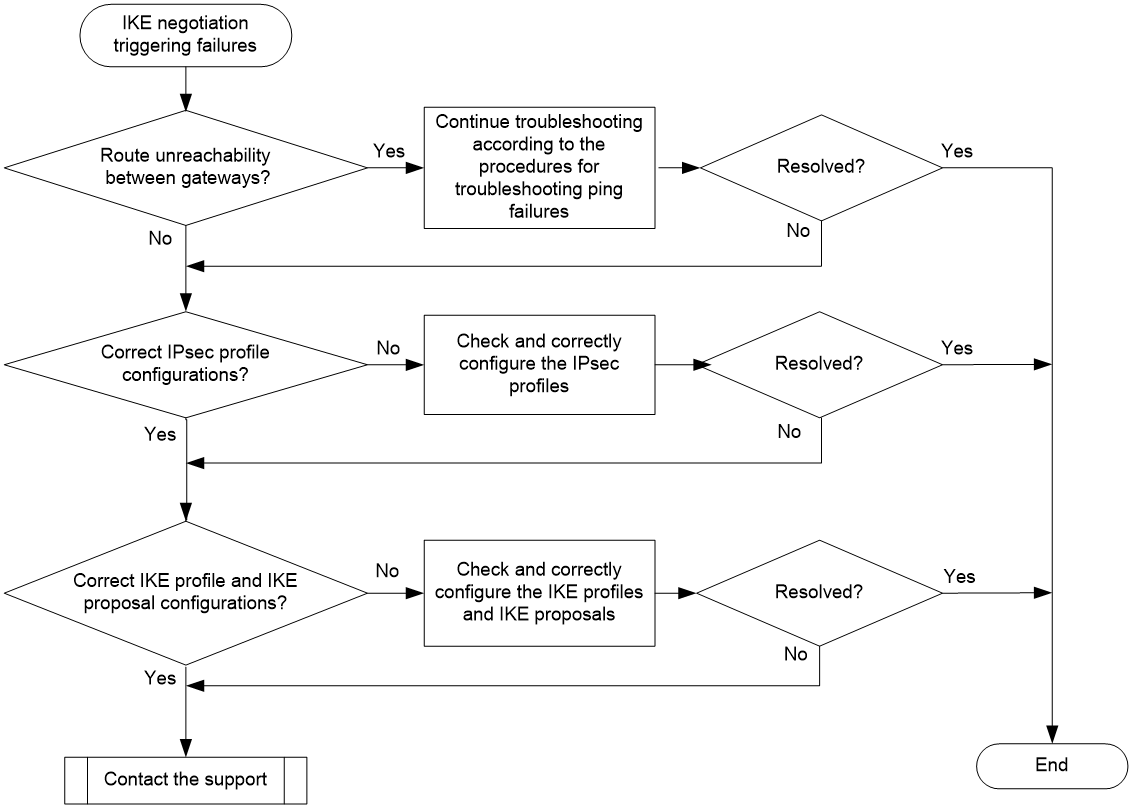
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 2 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Solution
1. Check whether the IPsec gateways can ping each other:
Use the ping command to check the network connectivity.
a. If the ping is unsuccessful, continue troubleshooting according to the procedures for troubleshooting ping failures in Troubleshooting Layer 3—IP Services. Make sure Host A and Host B can ping their respective IPsec gateways, and the IPsec gateways can ping each other.
b. If the issue persists, go to step 2.
2. Check whether the IPsec profile configurations are correct:
a. Execute the display ipsec profile command to check whether the configurations on the local IPsec gateway Device A and the peer IPsec gateway Device B are complete. Verify that both transform set and IKE profile have been configured on each device. Make sure security proposals with the same encryption algorithm, authentication algorithm, and PFS are configured on the devices.
For example, the output on Device A is as follows:
[DeviceA] display ipsec profile
-------------------------------------------
IPsec profile: myprofile
Mode: isakmp
-------------------------------------------
Transform set: tran1
IKE profile: profile
SA duration(time based): 3600 seconds
SA duration(traffic based): 1843200 kilobytes
SA soft-duration buffer(time based): 1000 seconds
SA soft-duration buffer(traffic based): 43200 kilobytes
SA idle time: 100 seconds
[DeviceA] display ipsec transform-set
IPsec transform set: tran1
State: complete
Encapsulation mode: tunnel
ESN: Enabled
PFS:
Transform: AH-ESP
AH protocol:
Integrity: SHA1
ESP protocol:
Integrity: SHA1
Encryption: AES-CBC-128
The output on Device B is as follows:
[DeviceB] display ipsec profile
-------------------------------------------
IPsec profile: myprofile
Mode: isakmp
-------------------------------------------
Transform set: tran1
IKE profile: profile
SA duration(time based): 3600 seconds
SA duration(traffic based): 1843200 kilobytes
SA soft-duration buffer(time based): 1000 seconds
SA soft-duration buffer(traffic based): 43200 kilobytes
SA idle time: 100 seconds
[DeviceB] display ipsec transform-set
IPsec transform set: tran1
State: complete
Encapsulation mode: tunnel
ESN: Enabled
PFS:
Transform: AH-ESP
AH protocol:
Integrity: SHA1
ESP protocol:
Integrity: SHA1
Encryption: AES-CBC-128
b. If the issue persists, go to step 3.
3. Check whether the IPsec profiles are correctly configured on the tunnel interfaces.
a. Execute the interface tunnel command on the IPsec gateway Device A to enter tunnel interface Tunnel 1. Execute the display this command to check whether the local and peer addresses and the IPsec profile are configured correctly on the tunnel interface.
[DeviceA] interface tunnel 1
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] display this
#
interface Tunnel1 mode ipsec
ip address 3.3.3.1 255.255.255.0
source 2.2.2.1
destination 2.2.3.1
tunnel protection ipsec profile myprofile
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] quit
If configuration errors exist, modify the configuration as follows:
[DeviceA] interface tunnel 1 mode ipsec
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] ip address 3.3.3.1 255.255.255.0
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] source 2.2.2.1
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] destination 2.2.3.1
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] tunnel protection ipsec profile myprofile
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] quit
b. Execute the interface tunnel command on the IPsec gateway Device B to enter tunnel interface Tunnel 1. Execute the display this command to check whether the local and peer addresses and the IPsec profile are configured correctly on the tunnel interface.
[DeviceB] interface tunnel 1
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] display this
#
interface Tunnel1 mode ipsec
ip address 3.3.3.2 255.255.255.0
source 2.2.3.1
destination 2.2.2.1
tunnel protection ipsec profile myprofile
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] quit
If configuration errors exist, modify the configuration as follows:
[DeviceB] interface tunnel 1 mode ipsec
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] ip address 3.3.3.2 255.255.255.0
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] source 2.2.3.1
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] destination 2.2.2.1
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] tunnel protection ipsec profile myprofile
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] quit
c. If the issue persists, go to step 4.
4. Check whether the IKE profile and IKE proposal configurations are correct.
a. Check the IKE profile configuration on each device. Verify that the local and peer IPsec gateway addresses are configured correctly. If preshared key authentication is used, the preshared keys configured (using the pre-shared-key command) on the local and peer ends must be the same. If RSA signature or digital envelope authentication is used, make sure the digital certificate is within the validity period (displayed in the Validity field of the output for the display pki certificate domain command).
For example, the IKE profile configuration on Device A is as follows:
[DeviceA] ike keychain keychain1
[DeviceA-ike-keychain-keychain1] pre-shared-key address 2.2.3.1 255.255.255.0 key simple 123456TESTplat&!
[DeviceA-ike-keychain-keychain1] quit
[DeviceA] ike profile profile
[DeviceA-ike-profile-profile] keychain keychain1
[DeviceA-ike-profile-profile] local-identity address 2.2.2.1
[DeviceA-ike-profile-profile] match remote identity address 2.2.3.1 255.255.255.0
[DeviceA-ike-profile-profile] quit
The IKE profile configuration on Device B is as follows:
[DeviceB] ike keychain keychain1
[DeviceB-ike-keychain-keychain1] pre-shared-key address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.0 key simple 123456TESTplat&!
[DeviceB-ike-keychain-keychain1] quit
[DeviceB] ike profile profile
[DeviceB-ike-profile-profile] keychain keychain1
[DeviceB-ike-profile-profile] local-identity address 2.2.3.1
[DeviceB-ike-profile-profile] match remote identity address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.0
[DeviceB-ike-profile-profile] quit
b. Execute the display ike proposal command on IPsec gateways Device A and Device B respectively to view the IKE proposal configurations. Verify that the IKE proposal configurations are consistent.
[DeviceA] display ike proposal
Priority Authentication Authentication Encryption Diffie-Hellman Duration
method algorithm algorithm group (seconds)
-----------------------------------------------------------------
default PRE-SHARED-KEY SHA1 DES-CBC Group 1 86400
[DeviceB] display ike proposal
Priority Authentication Authentication Encryption Diffie-Hellman Duration
method algorithm algorithm group (seconds)
-----------------------------------------------------------------
default PRE-SHARED-KEY SHA1 DES-CBC Group 1 86400
c. If the issue persists, go to step 5.
5. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
¡ Collected information related to establishment of the IPsec tunnel after you execute the debugging commands as follows.
<DeviceA> terminal debugging
The current terminal is enabled to display debugging logs.
<DeviceA> terminal monitor
The current terminal is enabled to display logs.
<DeviceA> debugging ike all
<DeviceA> debugging ipsec all