- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-Text | 2.65 MB |
Examining the installation site
Installing the switch in a 19-inch rack
Rack-mounting by using front mounting brackets (S5150X-16S-EI and S5150X-16ST-EI)
Rack-mounting by using front and rear mounting brackets (S5150-24S-PWR-EI)
Mounting the switch on a workbench
Grounding the switch with a grounding strip
Grounding the switch with a grounding conductor buried in the earth ground
Installing/removing a power module
Installing a PSR150-A1/PSR150-D1/PSR75-12A power module
Removing a PSR150 power module
Installing a PSR360-56A/PSR720-56A/PSR1110-56A power module
Removing a PSR360-56A/PSR720-56A/PSR1110-56A power module
Connecting the AC power cord for the fixed AC power module
Connecting a DC power cord for the fixed DC power module
Connecting the power cord for a PSR150-A1 or PSR75-12A power module
Connecting the DC power cord for a PSR150-D1 power module
Connecting the power cord for a PSR360-56A, PSR720-56A, or PSR1110-56A power module
Accessing the switch for the first time
Setting up the configuration environment
Connecting the serial console cable
Connecting the mini USB console cable
Planning IRF fabric size and the installation site
Identifying the master switch and planning IRF member IDs
Planning IRF topology and connections
Identifying physical IRF ports on the member switches
Configuring basic IRF settings
Connecting the physical IRF ports
Verifying the IRF fabric setup
Maintenance and troubleshooting
Hot swappable power module failure
Configuration terminal display problems
Appendix A Chassis views and technical specifications
Appendix B FRUs and compatibility matrixes
Power modules and compatibility matrixes
1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet port
2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port
1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED
2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED
Preparing for installation
H3C S5150-EI Switch Series includes the following models:
· S5150X-16S-EI
· S5150X-16ST-EI
· S5150-24S-PWR-EI
Safety recommendations
To avoid any equipment damage or bodily injury caused by improper use, read the following safety recommendations before installation. Note that the recommendations do not cover every possible hazardous condition.
· Before cleaning the switch, remove all power cords from the switch. Do not clean the switch with wet cloth or liquid.
· Do not place the switch near water or in a damp environment. Prevent water or moisture from entering the switch chassis.
· Do not place the switch on an unstable case or desk. The switch might be severely damaged in case of a fall.
· Ensure good ventilation of the equipment room and keep the air inlet and outlet vents of the switch free of obstruction.
· Connect the yellow-green protection grounding cable before power-on.
· Make sure the operating voltage is in the required range.
· To avoid electrical shocks, do not open the chassis while the switch is operating.
· To avoid damage caused by improper operation, do not open the chassis even if the switch is powered off.
· When replacing power modules, wear an ESD wrist strap to avoid damaging the units.
Examining the installation site
The S5150-EI switches must be used indoors. You can mount your switch in a rack or on a workbench, but make sure:
· Adequate clearance is reserved at the air inlet and outlet vents for ventilation.
· The rack or workbench has a good ventilation system.
· Identify the hot aisle and cold aisle at the installation site, and make sure ambient air flows into the switch from the cold aisle and exhausts to the hot aisle.
· Identify the airflow designs of neighboring devices, and prevent hot air flowing out of the neighboring device from entering the device.
· The rack is sturdy enough to support the switch and its accessories.
· The rack or workbench is reliably grounded.
To ensure correct operation and long service life of your switch, install it in an environment that meets the requirements described in the following subsections.
Temperature/humidity
Maintain temperature and humidity in the equipment room as described in "Appendix A Chassis views and technical specifications."
· Lasting high relative humidity can cause poor insulation, electricity leakage, mechanical property change of materials, and metal corrosion.
· Lasting low relative humidity can cause washer contraction and ESD and bring problems including loose captive screws and circuit failure.
· High temperature can accelerate the aging of insulation materials and significantly lower the reliability and lifespan of the switch.
For the temperature and humidity requirements of different switch models, see "Technical specifications."
Cleanliness
Dust buildup on the chassis might result in electrostatic adsorption, which causes poor contact of metal components and contact points, especially when indoor relative humidity is low. In the worst case, electrostatic adsorption can cause communication failure.
Table 1 Dust concentration limit in the equipment room
|
Substance |
Concentration limit (particles/m³) |
|
Dust |
≤ 3 x 104 (no visible dust on the tabletop over three days) |
|
NOTE: Dust diameter ≥ 5 μm |
|
The equipment room must also meet strict limits on salts, acids, and sulfides to eliminate corrosion and premature aging of components, as shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Harmful gas limits in the equipment room
|
Gas |
Maximum concentration (mg/m3) |
|
SO2 |
0.2 |
|
H2S |
0.006 |
|
NH3 |
0.05 |
|
Cl2 |
0.01 |
EMI
All electromagnetic interference (EMI) sources, from outside or inside of the switch and application system, adversely affect the switch in the following ways:
· A conduction pattern of capacitance coupling.
· Inductance coupling.
· Electromagnetic wave radiation.
· Common impedance (including the grounding system) coupling.
To prevent EMI, perform the following tasks:
· If AC power is used, use a single-phase three-wire power receptacle with protection earth (PE) to filter interference from the power grid.
· Keep the switch far away from radio transmitting stations, radar stations, and high-frequency devices.
· Use electromagnetic shielding, for example, shielded interface cables, when necessary.
Laser safety
|
|
WARNING! The switch is Class 1 laser device. Do not stare into any fiber port when the switch has power. The laser light emitted from the optical fiber might hurt your eyes. |
Installation tools
No installation tools are provided with the switch. Prepare the following tools yourself:
· Flat-blade screwdriver
· Phillips screwdriver
· ESD wrist strap
Installing the switch
|
|
CAUTION: Keep the tamper-proof seal on a mounting screw on the chassis cover intact, and if you want to open the chassis, contact H3C for permission. Otherwise, H3C shall not be liable for any consequence. |
Figure 1 Hardware installation flow
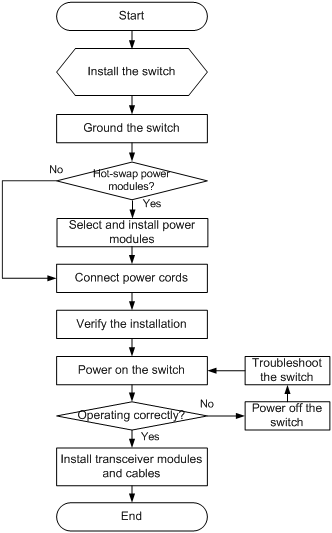
Installing the switch in a 19-inch rack
Installation methods
Table 3 Installation methods for the S5150-EI switches
|
Model |
Installation methods |
Installation requirements |
Installation procedure |
|
S5150X-16S-EI S5150X-16ST-EI |
Using front mounting brackets |
Install the front mounting brackets at the port side or power module side. |
See "Rack-mounting by using front mounting brackets (S5150X-16S-EI and S5150X-16ST-EI)." |
|
S5150-24S-PWR-EI |
Using front and rear mounting brackets |
· Install the front mounting brackets at the port side or power module side. · Install the rear mounting brackets according to the rack depth. ¡ If the rack depth is in the range of 429 to 595 mm (16.89 to 23.43 in), orient the bracket with the wide flange inside the rack. ¡ If the rack depth is in the range of 274 to 440 mm (10.79 to 17.32 in) and the distance from the rear rack posts to the inner surface of the cabinet door is longer than 153 mm (6.02 in), orient the bracket with the wide flange outside the rack. |
See "Rack-mounting by using front and rear mounting brackets (S5150-24S-PWR-EI)." |
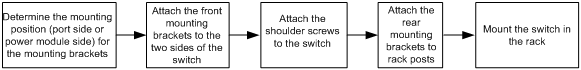
Figure 2 Procedure for rack-mounting by using front mounting brackets

Figure 3 Procedure for rack-mounting by using front and rear mounting brackets
|
|
NOTE: If a rack shelf is available, you can put the switch on the rack shelf, slide the switch to an appropriate location, and attach the switch to the rack by using the mounting brackets. |
Mounting brackets
Table 4 Mounting brackets for the S5150-EI switches
|
Mounting bracket |
S5150X-16S-EI |
S5150-24S-PWR-EI |
|
Front mounting brackets and M4 screws (Figure 4) |
Provided |
Provided |
|
Rear mounting brackets and shoulder screws (Figure 5) |
N/A |
Provided |
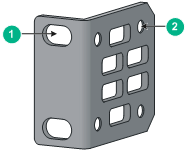
Figure 4 Front mounting bracket
|
(1) Hole for attaching the bracket to a rack |
(2) Hole for attaching the bracket to the switch chassis |
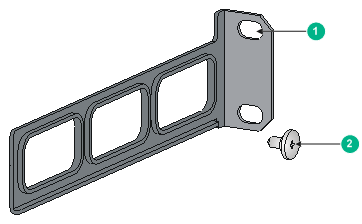
Figure 5 Rear mounting bracket and shoulder screw
|
(1) Hole for attaching the bracket to a rack |
(2) Shoulder screw |
Rack-mounting by using front mounting brackets (S5150X-16S-EI and S5150X-16ST-EI)
You can install the front mounting brackets at the power module-side or port-side mounting position as needed.
This task requires two people.
To install the switch in a 19-inch rack by using the front mounting brackets:
1. Identify the mounting positions.
2. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
3. Attach the front mounting brackets to the chassis:
a. Unpack the front mounting brackets and the M4 screws (supplied with the switch) for attaching the brackets to the switch chassis.
b. Align the round holes in the wide flange of one front mounting bracket with the screw holes in the chassis.
c. Use M4 screws to attach the mounting bracket to the chassis.
d. Repeat the proceeding two steps to attach the other mounting bracket to the chassis.
Figure 6 Attaching the front mounting bracket to the port side (S5150X-16ST-EI)
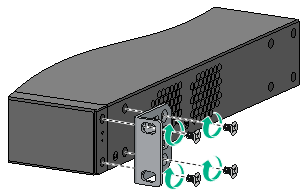
Figure 7 Attaching the front mounting bracket to the power module side (S5150X-16ST-EI)
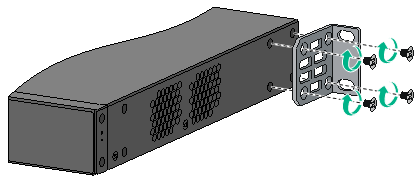
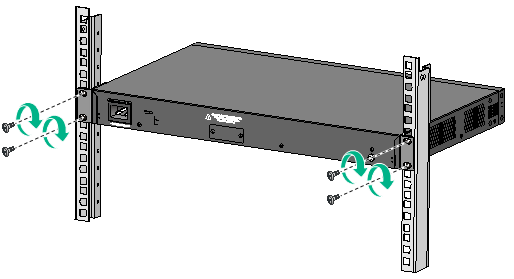
4. Mount the chassis in the rack:
a. Install cage nuts (user-supplied) in the mounting holes in the front rack posts. Make sure the corresponding cage nuts on the left and right front rack posts are at the same height.
b. One person holds the switch chassis and aligns the installation holes on the mounting brackets with the cage nuts on the rack posts.
c. The other person uses M6 screws (user supplied) to attach the mounting brackets to the rack.
Figure 8 Mounting the switch in the rack (front mounting brackets at the port side)
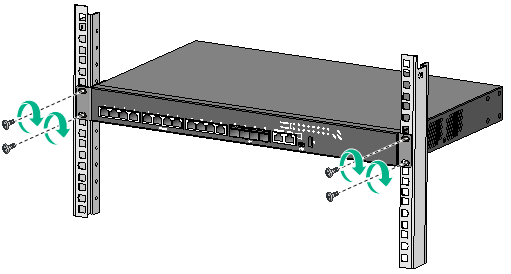
Figure 9 Mounting the switch in the rack (front mounting brackets at the power module side)
Rack-mounting by using front and rear mounting brackets (S5150-24S-PWR-EI)
You can install the front mounting brackets at the port-side or power-side mounting position as needed. The following takes port-side mounting as an example. The power-side mounting is similar.
This task requires two people.
To install the switch in a 19-inch rack by using the front and rear mounting brackets:
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Attach the front mounting brackets and shoulder screws to the chassis:
a. Unpack the front mounting brackets and the M4 screws for attaching the brackets to the switch chassis.
b. Align the round holes in the wide flange of one front mounting bracket with the screw holes in the port-side mounting position on one side of the chassis (see Figure 10).
c. Use M4 screws (supplied with the switch) to attach the mounting bracket to the chassis.
d. Repeat the proceeding two steps to attach the other mounting bracket to the chassis.
e. Unpack the shoulder screws.
f. Install the shoulder screws. Attach the shoulder screw to one of the two installation positions as red-marked in Figure 10.
Figure 10 Attaching the front mounting brackets and shoulder screws to the chassis (S5150-24S-PWR-EI)
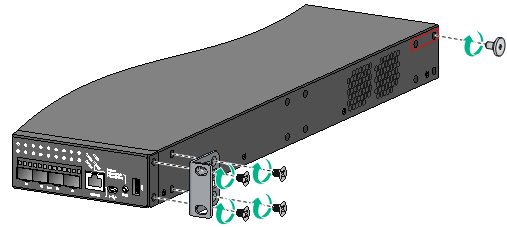
3. Attach the rear mounting brackets to the rack:
a. Determine to orient the rear mounting brackets with the wide flange inside or outside the rack.
b. Install cage nuts (user-supplied) in the mounting holes in the rear rack posts. Make sure the corresponding cage nuts on the left and right rear rack posts are at the same height.
c. Attach the rear mounting brackets to the rear posts with M6 screws (user supplied), as shown in Figure 11.
Do not fully fasten the M6 screws before mounting the switch in the rack.
Figure 11 Attaching the rear mounting brackets to a rack with the wide flange inside the rack
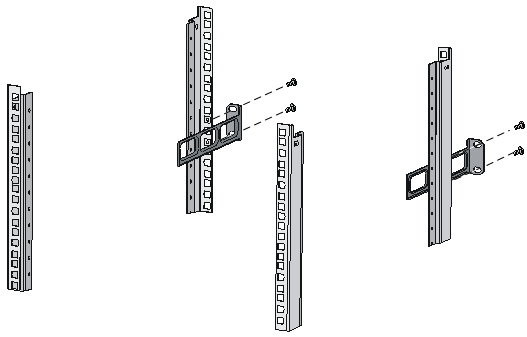
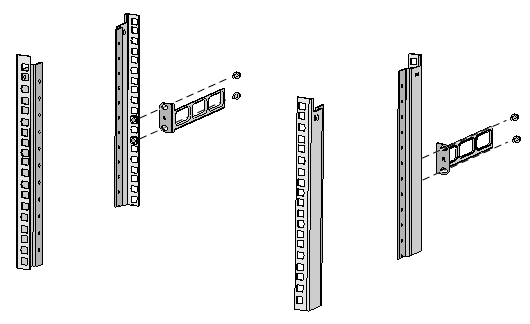
Figure 12 Attaching the rear mounting brackets to a rack with the wide flange outside the rack
4. Mount the switch chassis in the rack:
a. Install cage nuts (user-supplied) in the mounting holes in the front rack posts. Make sure the corresponding cage nuts on the front and rear rack posts are at the same height.
b. One person supports the chassis bottom with one hand, holds the front part of the chassis with the other hand, and pushes the chassis into the rack gently.
Make sure the shoulder screws closely contact with the upper edges of the rear mounting brackets, as shown in Figure 13.
c. The other person uses M6 screws (user-supplied) to attach the front mounting brackets to the front rack posts. Make sure the switch is installed securely in the rack.
Figure 13 Mounting the switch in the rack (with the wide flange of the mounting brackets inside the rack)
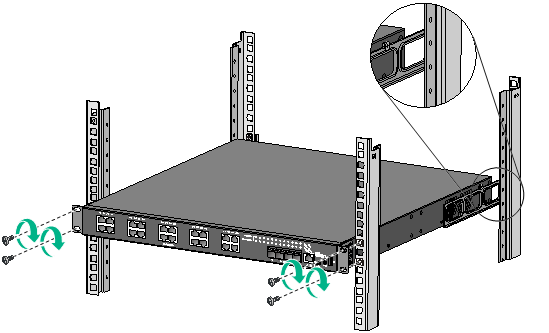
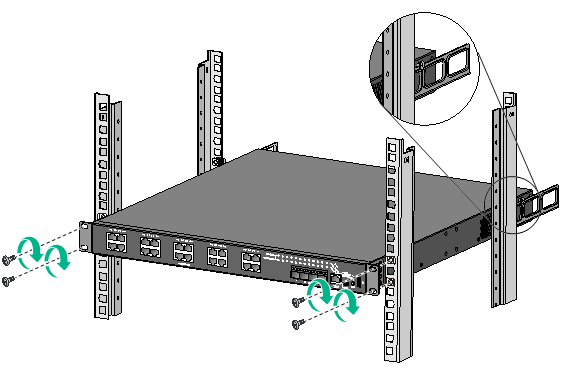
Mounting the switch on a workbench
|
|
IMPORTANT: · Ensure good ventilation and 10 cm (3.9 in) of clearance around the chassis for heat dissipation. · Avoid placing heavy objects on the switch. |
To mount the switch on a workbench:
1. Verify that the workbench is sturdy and reliably grounded.
2. Place the switch with bottom up, and clean the round holes in the chassis bottom with dry cloth.
3. Attach the rubber feet to the four round holes in the chassis bottom.
4. Place the switch with upside up on the workbench.
Grounding the switch
|
|
WARNING! Correctly connecting the switch grounding cable is crucial to lightning protection and EMI protection. |
The power input end of the switch has a noise filter, whose central ground is directly connected to the chassis to form the chassis ground (commonly known as PGND). You must securely connect this chassis ground to the earth so the faradism and leakage electricity can be safely released to the earth to minimize EMI susceptibility of the switch.
You can ground the switch in one of the following ways, depending on the grounding conditions available at the installation site:
· Grounding the switch with a grounding strip
· Grounding the switch with a grounding conductor buried in the earth ground
|
|
NOTE: The power and grounding terminals in this section are for illustration only. |
Grounding the switch with a grounding strip
|
|
WARNING! Connect the grounding cable to the grounding system in the equipment room. Do not connect it to a fire main or lightning rod. |
If a grounding strip is available at the installation site, connect the grounding cable to the grounding strip.
Connecting the grounding cable to the chassis
1. Remove the grounding screw from the rear panel of the switch chassis.
2. Use the grounding screw to attach the ring terminal of the grounding cable to the grounding screw hole.
Figure 15 Connecting the grounding cable to the chassis
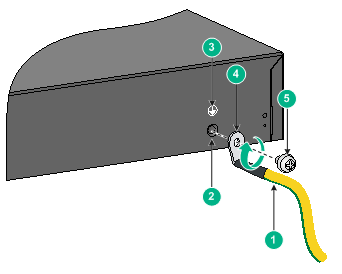
|
(1) Grounding cable |
(2) Grounding hole |
|
(3) Grounding sign |
(4) Ring terminal |
|
(5) Grounding screw |
|
3. Verify that the grounding cable has been securely connected to the rear grounding point.
Connecting the grounding cable to a grounding strip (S5150-24S-PWR-EI)
1. Remove the hex nut of a grounding post on the grounding strip.
2. Cut the grounding cable to a length required for connecting to the grounding strip.
3. Attach a ring terminal to the grounding cable:
a. Use a wire stripper to strip 5 mm (0.20 in) of insulation off the end of the grounding cable.
b. Slide the heat-shrink tubing onto the cable and insert the bare metal part into the end of the ring terminal.
c. Use a crimper to secure the metal part of the cable to the ring terminal.
d. Slide the heat-shrink tubing down the cable until the tube covers the joint.
e. Use a heat gun to shrink the tubing around the cable.
Figure 16 Attaching a ring terminal to the grounding cable

4. Connect the ring terminal to the grounding post of the grounding strip, and fasten it with the removed hex nut.
Figure 17 Connecting the grounding cable to a grounding strip
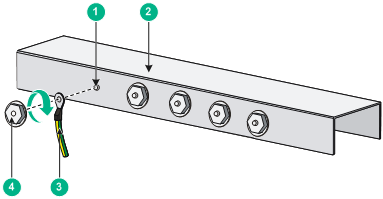
|
(1) Grounding post |
(2) Grounding strip |
|
(3) Grounding cable |
(4) Hex nut |
Connecting the grounding cable to a grounding strip (S5150X-16S-EI and S5150X-16ST-EI)
1. Cut the grounding cable to a length required for connecting to the grounding strip.
2. Use a wire stripper to strip 20 mm (0.79 in) of insulation off the end of the grounding cable. Then use needle-nose pliers to bend the bare metal part to the shape as shown in Figure 18. Make sure the bended part can securely attached to the grounding post on the grounding strip.
3. Attach the bended part of the grounding cable to the grounding post and use the hex nut to fasten the bended part to the post.
Figure 18 Connecting the grounding cable to the grounding strip
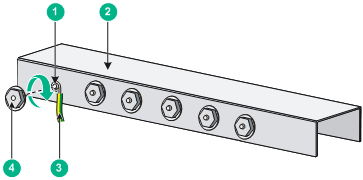
|
(1) Grounding post |
(2) Grounding strip |
|
(3) Grounding cable |
(4) Hex nut |
Grounding the switch with a grounding conductor buried in the earth ground
If the installation site has no grounding strips, but earth ground is available, hammer a 0.5 m (1.64 ft) or longer angle iron or steel tube into the earth ground to serve as a grounding conductor.
The dimensions of the angle iron must be a minimum of 50 × 50 × 5 mm (1.97 × 1.97 × 0.20 in). The steel tube must be zinc-coated and its wall thickness must be a minimum of 3.5 mm (0.14 in).
Weld the yellow-green grounding cable to the angel iron or steel tube and treat the joint for corrosion protection.
Figure 19 Grounding the switch by burying the grounding conductor into the earth ground
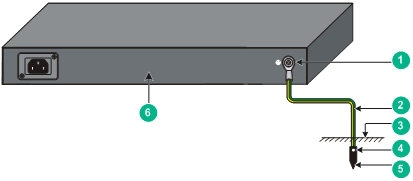
|
(1) Grounding screw |
(2) Grounding cable |
(3) Earth |
|
(4) Joint |
(5) Grounding conductor |
(6) Chassis rear panel |
Installing/removing a power module
|
|
WARNING! In power redundancy mode, you can replace a power module without powering off the switch but you must strictly follow the installation and procedures in Figure 20 and Figure 21 to avoid any bodily injury or damage to the switch. |
|
|
CAUTION: Provide a circuit breaker for each power module. |
Figure 20 Installation procedure
![]()
![]()
Installing a PSR150-A1/PSR150-D1/PSR75-12A power module
|
|
CAUTION: To prevent damage to the power module or the connectors on the backplane, insert the power module gently. If you encounter a hard resistance when inserting the power module, pull out the power module and insert it again. |
For the PSR150-A1, PSR150-D1, and PSR75-12A power modules, the installation and removal procedures are the same. The following takes the PSR150-A1 power module as an example.
To install a power module:
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Remove the filler panel from the target power module slot as follows:
a. Remove the screws on the filler panel.
b. Use a flathead screwdriver to remove the filler panel.
Figure 22 Removing the filler panel
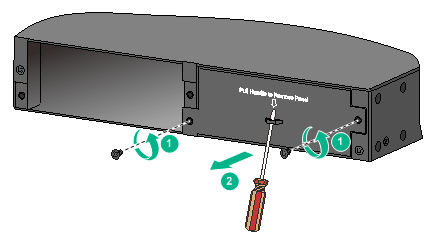
3. Unpack the power module and verify that the power module model is correct.
4. Correctly orient the power module with the power module slot (use the letters on the power module faceplate for orientation), grasp the handle of the power module with one hand and support its bottom with the other, and slide the power module slowly along the guide rails into the slot (see callout 1 in Figure 23).
5. Fasten the captive screws on the power module with a Phillips screwdriver to secure the power module in the chassis (see callout 2 in Figure 23). If the captive screw cannot be tightly fastened, verify the installation of the power module.
6. Install the filler panel over the empty power module slot to prevent dust and ensure good ventilation if you install only one power module.
Figure 23 Installing a PSR150-A1 power module
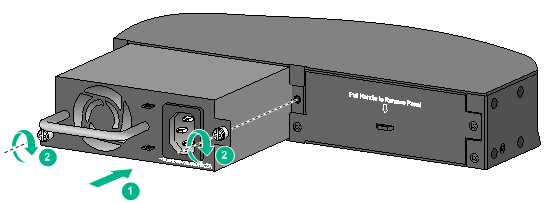
Removing a PSR150 power module
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Disconnect the power cord.
3. Loosen the captive screws of the power module with a Phillips screwdriver until they are completely disengaged.
4. Grasp the handle of the power module with one hand and pull it out a little, support the bottom with the other hand, and pull the power module slowly along the guide rails out of the slot.
Put away the removed power module in an antistatic bag or the power module package bag for future use.
5. Install the filler panel to prevent dust and ensure good ventilation if no power module is installed in the slot.
Installing a PSR360-56A/PSR720-56A/PSR1110-56A power module
|
|
CAUTION: To prevent damage to the power module or the connectors on the backplane, insert the power module gently. If you encounter a hard resistance when inserting the power module, pull out the power module and insert it again. |
For the PSR360-56A, PSR720-56A and PSR1110-56A power modules, the installation and removal procedures are the same. The following takes the PSR720-56A power module as an example.
To install a power module:
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Remove the filler panel, if any, from the target power module slot.
Put your forefinger into the hole in the front panel and pull out the filler panel gently.
Figure 24 Removing the filler panel
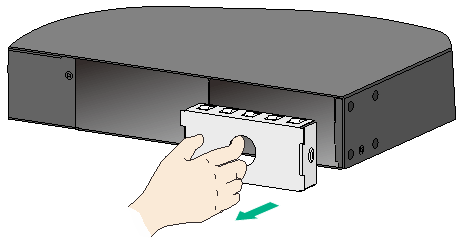
3. Unpack the power module and verify that the power module model is correct.
Put away the packaging box and packaging bag of the power module for future use.
4. Correctly orient the power module with the power module slot (use the letters on the power module faceplate for orientation), grasp the handle of the power module with one hand and support its bottom with the other, and slide the power module slowly along the guide rails into the slot until you hear that the latch of the power module clicks into the slot.
When you insert the power module into the slot, you can do that through slight inertia so that the terminals of the power module can have a good contact with the backplane.
The PSR1110-56A power module adds 64 mm (2.52 in) to the depth of the switch, as shown in Figure 26.
5. Install the filler panel over the empty power module slot to prevent dust and ensure good ventilation if you install only one power module.
Figure 25 Installing a power module
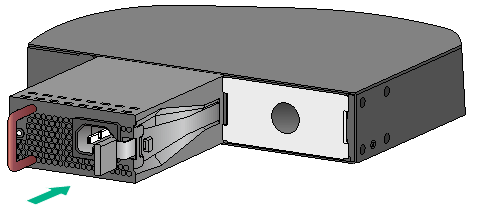
Figure 26 PSR1110-56A installed in the chassis
Removing a PSR360-56A/PSR720-56A/PSR1110-56A power module
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Disconnect the power cord.
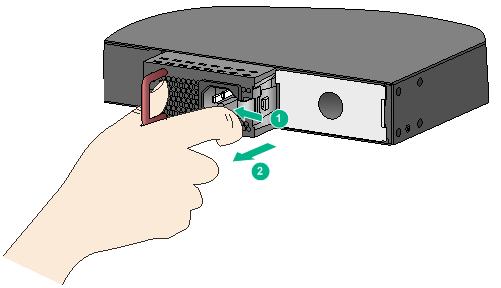
3. Press the latch towards the handle, and pull the power module along the guide rails until it is part-way out.
4. Grasp the handle of the power module with one hand, support the bottom with the other hand, and pull the power module slowly along the guide rails out of the slot.
Put away the removed power module in an antistatic bag or the power module package bag for future use.
5. Install the filler panel to prevent dust and ensure good ventilation if no power module is installed in the slot.
Figure 27 Removing the power module
Connecting the power cord
|
|
CAUTION: · The AC power cord for the PSR150-A1 and PSR75-12A uses C13 connector, while the AC power cord for the PSR360-56A/PSR720-56A/PSR1110-56A uses high-temperature C15 connector. Do not mix them. · Provide a circuit breaker for each power cord. · Before connecting a power cord, make sure the circuit breaker on the power cord is turned off. |
Table 5 Power cord connection procedures at a glance
|
Switch |
Power mode |
Connection procedure reference |
|
S5150X-16S-EI |
AC power source or 240 VDC high-voltage power source (PSR150-A1 or PSR75-12A power module) |
Connecting the power cord for a PSR150-A1 or PSR75-12A power module |
|
–48 VDC power source in the equipment room or an RPS800-A or RPS1600-A (PSR150-D1 power module) |
||
|
S5150X-16ST-EI |
AC power source |
|
|
+12 VDC RPS power source (RPS800-A) |
||
|
S5150-24S-PWR-EI |
AC power source (PSR360-56A, PSR720-56A, or PSR1110-56A power module) |
Connecting the power cord for a PSR360-56A, PSR720-56A, or PSR1110-56A power module |
Connecting the AC power cord for the fixed AC power module
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Attach the hooks of the bail latch into the holes on the two sides of the AC-input power receptacle, and pull the bail latch upwards (see Figure 28).
3. Connect the female connector of the AC power cord to the AC-input power receptacle on the switch (see callout 1 in Figure 29).
4. Pull the bail latch down to secure the connector to the power receptacle (see callout 2 in Figure 29).
5. Connect the other end of the power cord to an AC power source.
Figure 28 Connecting the AC power cord for the fixed AC power module (1)
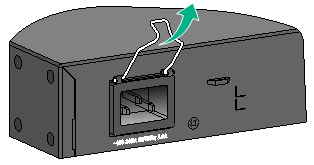
Figure 29 Connecting the AC power cord for the fixed AC power module (2)
Connecting a DC power cord for the fixed DC power module
|
|
CAUTION: · The DC-input power receptacle on the switch requires a DC power cord with a JD5-A connector. · To connect to an H3C recommended RPS, use a power cord compatible with the RPS. |
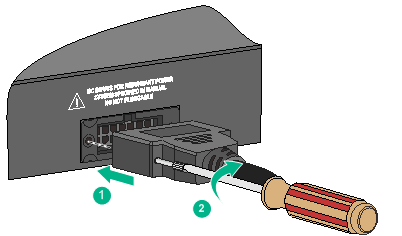
To connect a DC power cord for the fixed DC power module:
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Remove the cover from the DC receptacle as shown in Figure 30. Install the cover if you are not to connect a power cord to the receptacle.
3. Correctly orient the DC power cord connector with the power receptacle on the power module, and insert the connector into the power receptacle. See callout 1 in Figure 31.
If you cannot insert the connector into the receptacle, re-orient the connector rather than use excessive force to push it in.
4. Fasten the screws on the connector with a flat-blade screwdriver to secure the connector in the power receptacle. See callout 2 in Figure 31.
5. Connect the other end of the power cord to an RPS.
Figure 30 Removing the cover from the DC receptacle
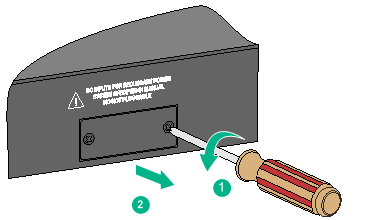
Figure 31 Connecting a DC power cord for the fixed DC power module
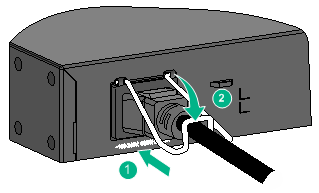
Connecting the power cord for a PSR150-A1 or PSR75-12A power module
The power cord connection procedure is the same for the PSR150-A1 and PSR75-12A. This procedure uses the PSR150-A1 as an example.
To connect the power cord for a PSR150-A1 power module:
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Attach the hooks of the bail latch (supplied with the power module) into the two holes next to the power receptacle on the power module, and pull the bail latch leftwards (see Figure 32).
3. Connect the female connector of the power cord supplied with the power module to the power receptacle (see callout 1 in Figure 33).
4. Pull the bail latch rightwards to secure the connector to the power receptacle (see callout 2 in Figure 33).
5. Connect the other end of the power cord to an AC power source or a 240V high-voltage DC power source.
Figure 32 Connecting the power cord for a PSR150-A1 power module (1)
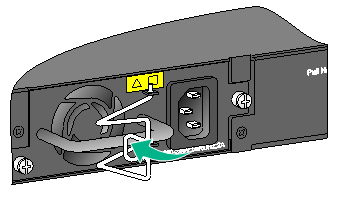
Figure 33 Connecting the power cord for a PSR150-A1 power module (2)
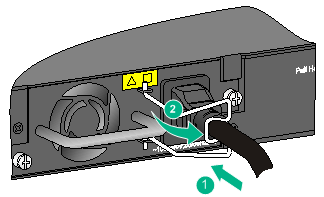
Connecting the DC power cord for a PSR150-D1 power module
|
|
WARNING! · To use a –48 VDC power source for power supply, purchase an H3C recommended DC power cord yourself. · To use an RPS for power supply, purchase a power cord compatible with the RPS yourself. · To connect a DC power cord to a –48 VDC power source, identify the positive (+) and negative (-) marks on the two wires of the power cord to avoid connection mistakes. |
To connect the DC power cord for a PSR150-D1 power module
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Unpack the DC power cord, correctly orient the connector of the power cord and align it with the power receptacle on the power module, and insert the connector into the power receptacle (see callout 1 in Figure 34).
The power receptacle is foolproof. If you cannot insert the connector into the receptacle, re-orient the connector rather than use excessive force to push it in.
3. Fasten the screws on the connector with a flat-blade screwdriver to secure the connector to the power receptacle (see callout 2 in Figure 34).
4. Connect the other end of the power cord to a –48 VDC power source or an RPS.
Figure 34 Connecting the DC power cord for a PSR150-D1 power module
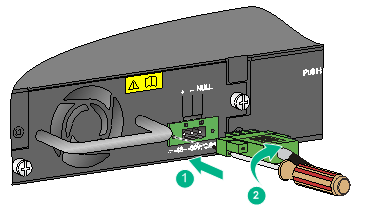
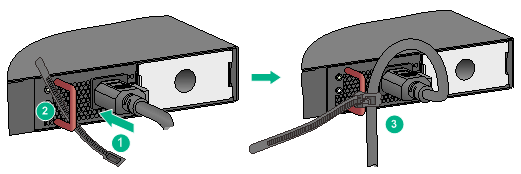
Connecting the power cord for a PSR360-56A, PSR720-56A, or PSR1110-56A power module
The following takes the PSR720-56A as an example. The connection procedure for the PSR360-56A and PSR1110-56A is similar.
To connect the power cord for a PSR720-56A power module:
1. Wear an ESD wrist strap and make sure it makes good skin contact and is reliably grounded.
2. Plug the female connector end of the power cord into the power-input socket of the power module (see callout 1 in Figure 35).
3. Use a cable tie to secure the power cord to the handle of the power module (see callout 2 and callout 3 in Figure 35).
4. Connect the other end of the power cord to an AC power source.
Figure 35 Connecting the power cord for a PSR720-56A power module
Verifying the installation
After you complete the installation, verify the following information:
· There is enough space for heat dissipation around the switch, and the rack or workbench is stable.
· The grounding cable is securely connected.
· The correct power source is used.
· The power cords are correctly connected.
· All the interface cables are cabled indoors. If any cable is routed outdoors, verify that the socket strip with lightning protection and lightning arresters for network ports have been correctly connected.
Accessing the switch for the first time
Setting up the configuration environment
You can access the switch through the serial console port or the Mini USB console port. If you connect both ports, you can access the switch only through the Mini USB console port.
No serial console cable or Mini USB console cable is provided with the switch. You can prepare the cable yourself or purchase one from H3C.
Figure 36 Connecting the console port to a PC
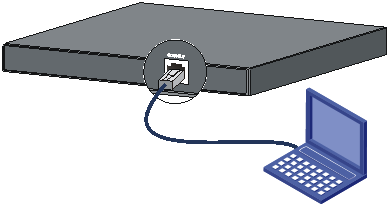
Connecting the serial console cable
A serial console cable is an 8-core shielded cable, with a crimped RJ-45 connector at one end for connecting to the serial console port of the switch, and a DB-9 female connector at the other end for connecting to the serial port on the console terminal.
Figure 37 Serial console cable
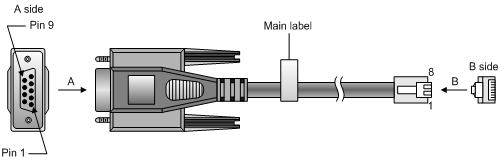
Table 6 Serial console port signaling and pinout
|
RJ-45 |
Signal |
DB-9 |
Signal |
|
1 |
RTS |
8 |
CTS |
|
2 |
DTR |
6 |
DSR |
|
3 |
TXD |
2 |
RXD |
|
4 |
SG |
5 |
SG |
|
5 |
SG |
5 |
SG |
|
6 |
RXD |
3 |
TXD |
|
7 |
DSR |
4 |
DTR |
|
8 |
CTS |
7 |
RTS |
To connect a configuration terminal (for example, a PC) to the switch:
1. Plug the DB-9 female connector of the serial console cable to the serial port of the PC.
2. Connect the RJ-45 connector to the serial console port of the switch.
|
|
NOTE: · Identify the mark on the serial console port and make sure you are connecting to the correct port. · The serial ports on PCs do not support hot swapping. To connect a PC to an operating switch, first connect the PC end. To disconnect a PC from an operating switch, first disconnect the switch end. |
Connecting the mini USB console cable
A mini USB console cable has a mini USB-Type B connector at one end to connect to the mini USB console port of the switch, and a standard USB Type A connector at the other end to connect to the USB port on the PC.
To connect to the PC through the mini USB console cable:
1. Connect the standard USB Type A connector to the USB port of the PC.
2. Connect the mini USB Type B connector to the mini USB console port of the switch.
3. Click the following link, or copy it to the address bar on the browser to log in to download page of the USB console driver, and download the driver.
4. Select a driver program according to the operating system you use:
¡ XR21V1410_XR21B1411_Windows_Ver1840_x86_Installer.EXE—32-bit operating system.
¡ XR21V1410_XR21B1411_Windows_Ver1840_x64_Installer.EXE—64-bit operating system.
5. Click Next on the installation wizard.
Figure 38 Device Driver Installation Wizard
6. Click Continue Anyway if the following dialog box appears.
Figure 39 Software Installation
7. Click Finish.
Figure 40 Completing the device driver installation wizard
Setting terminal parameters
To configure and manage the switch through the console port, you must run a terminal emulator program, TeraTermPro or PuTTY, on your PC. You can use the emulator program to connect a network device, a Telnet site, or an SSH site. For more information about the terminal emulator programs, see the user guides for these programs.
The following are the required terminal settings:
· Bits per second—9,600.
· Data bits—8.
· Parity—None.
· Stop bits—1.
· Flow control—None.
Powering on the switch
Before powering on the switch, verify that the following conditions are met:
· The power cord is correctly connected.
· The input power voltage meets the requirement of the switch.
· The console cable is correctly connected.
· The PC has started, and its serial port settings are consistent with the console port settings on the switch.
Power on the switch. During the startup process, you can access Boot ROM menus to perform tasks such as software upgrade and file management. The Boot ROM interface and menu options differ with software versions. For more information about Boot ROM menu options, see the software-matching release notes for the device.
After the startup completes, you can access the CLI to configure the switch.
For more information about the configuration commands and CLI, see H3C S5150-EI Switch Series Configuration Guides and H3C S5150-EI Switch Series Command References.
Setting up an IRF fabric
You can use H3C IRF technology to connect and virtualize S5150-EI switches into a large virtual switch called an "IRF fabric" for flattened network topology, and high availability, scalability, and manageability.
IRF fabric setup flowchart
Figure 41 IRF fabric setup flowchart
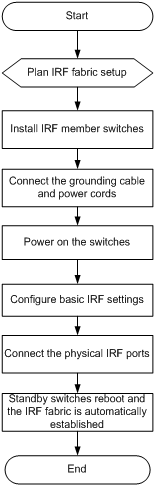
To set up an IRF fabric:
|
Step |
Description |
|
1. Plan IRF fabric setup |
Plan the installation site and IRF fabric setup parameters: · Planning IRF fabric size and the installation site · Identifying the master switch and planning IRF member IDs · Planning IRF topology and connections |
|
2. Install IRF member switches |
See "Installing the switch in a 19-inch rack" or "Mounting the switch on a workbench." |
|
3. Connect ground wires and power cords |
See "Grounding the switch" and "Connecting the power cord." |
|
4. Power on the switches |
N/A |
|
5. Configure basic IRF settings |
See H3C S5150-EI Switch Series IRF Configuration Guide. |
|
6. Connect the physical IRF ports |
Connect physical IRF ports on switches. Use SFP+ transceiver modules and fibers over a long distance, or use SFP+ network cables or twisted pair cables over a short distance. All switches except the master switch automatically reboot, and the IRF fabric is established. |
Planning IRF fabric setup
This section describes issues that an IRF fabric setup plan must cover.
Planning IRF fabric size and the installation site
Choose switch models and identify the number of required IRF member switches, depending on the user density and upstream bandwidth requirements. The switching capacity of an IRF fabric equals the total switching capacities of all member switches.
Plan the installation site depending on your network solution, as follows:
· Place all IRF member switches in one rack for centralized high-density access.
· Distribute the IRF member switches in different racks to implement the ToR access solution for a data center.
|
|
NOTE: For the maximum IRF member devices supported by the S5150-EI, see the release notes that come with the switch. |
Identifying the master switch and planning IRF member IDs
Determine which switch you want to use as the master for managing all member switches in the IRF fabric.
An IRF fabric has only one master switch. You configure and manage all member switches in the IRF fabric at the CLI of the master switch. IRF member switches automatically elect a master.
You can affect the election result by assigning a high member priority to the intended master switch. For more information about master election, see H3C S5150-EI Switch Series IRF Configuration Guide.
Prepare an IRF member ID assignment scheme. An IRF fabric uses member IDs to uniquely identify and manage its members, and you must assign each IRF member switch a unique member ID.
Planning IRF topology and connections
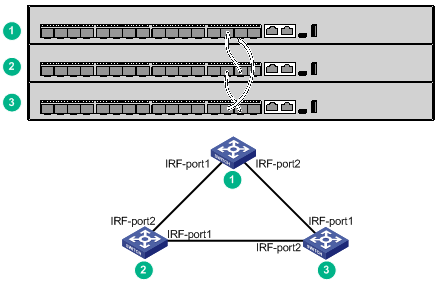
You can create an IRF fabric in daisy chain topology or more reliable ring topology. In ring topology, the failure of one IRF link does not cause the IRF fabric to split as in daisy chain topology. Instead, the IRF fabric changes to a daisy chain topology without interrupting network services.
You connect the IRF member switches through IRF ports, the logical interfaces for the connections between IRF member switches. Each IRF member switch has two IRF ports: IRF-port 1 and IRF-port 2. To use an IRF port, you must bind a minimum of one physical port to it.
When connecting two neighboring IRF member switches, you must connect the physical ports of IRF-port 1 on one switch to the physical ports of IRF-port 2 on the other switch.
The S5150-EI switches can provide 10-GE IRF connections through 1/10GBASE-T Ethernet ports/SFP+ ports, and you can bind several 1/10GBASE-T Ethernet ports/SFP+ ports to an IRF port for increased bandwidth and availability.
Figure 42 and Figure 43 show the topologies of an IRF fabric made up of three S5150X-16S-EI switches. The IRF port connections in the two figures are for illustration only, and more connection methods are available.
Figure 42 IRF fabric in daisy chain topology
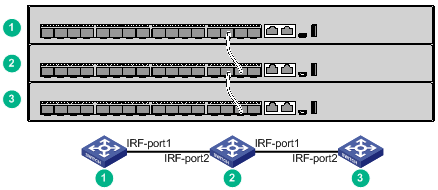
Figure 43 IRF fabric in ring topology
Identifying physical IRF ports on the member switches
Identify the physical IRF ports on the member switches according to your topology and connection scheme.
Table 7 shows the physical ports that can be used for IRF connection and the port use restrictions.
Table 7 Physical IRF port requirements
|
Chassis |
Candidate physical IRF ports |
Requirements |
|
S5150X-16S-EI |
16 fixed SFP+ ports on the front panel |
All physical ports to be bound to an IRF port must be the same type. |
|
S5150X-16ST-EI |
4 fixed SFP+ ports and 12 fixed 1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet ports on the front panel |
|
|
S5150-24S-PWR-EI |
4 fixed SFP+ ports on the front panel |
Planning the cabling scheme
Use twisted pair cables, SFP+ network cables, or SFP+ transceiver modules and fibers to connect the IRF member switches. If the IRF member switches are far away from one another, choose SFP+ transceiver modules with optical fibers. If the IRF member switches are all in one equipment room, choose twisted pair cables or SFP+ network cables. For more information about SFP+ network cables and SFP+ transceiver modules, see "Appendix C Ports and LEDs."
The following subsections describe several recommended IRF connection schemes, and all these schemes use a ring topology.
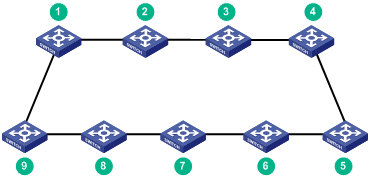
Connecting the IRF member switches in one rack
Use SFP+ network cables to connect the IRF member switches (9 switches in this example) in a rack as shown in Figure 44. The switches in the ring topology (see Figure 45) are in the same order as connected in the rack.
Figure 44 Connecting the switches in one rack

Connecting the IRF member switches in a ToR solution
You can install IRF member switches in different racks side by side to deploy a top of rack (ToR) solution.
Figure 46 shows an example for connecting 9 top of rack IRF member switches by using SFP+ transceiver modules and optical fibers. The topology is the same as Figure 45.
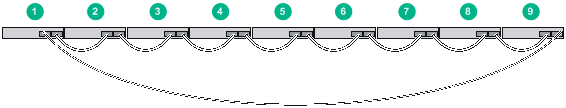
Configuring basic IRF settings
After you install the IRF member switches, power on the switches, and log in to each IRF member switch (see H3C S5150-EI Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide) to configure their member IDs, member priorities, and IRF port bindings.
Follow these guidelines when you configure the switches:
· Assign the master switch higher member priority than any other switch.
· When connecting two neighboring IRF member switches, you must connect the physical ports of IRF-port 1 on one switch to the physical ports of IRF-port 2 on the other switch.
· Execute the display irf configuration command to verify the basic IRF settings.
For more information about configuring basic IRF settings, see H3C S5150-EI Switch Series IRF Configuration Guide.
Connecting the physical IRF ports
Use twisted pair cables, SFP+ network cables, or SFP+ transceiver modules and fibers to connect the IRF member switches as planned.
Wear an ESD wrist strap when you connect SFP+ network cables or SFP+ transceiver modules and fibers. For how to connect them, see H3C SFP/SFP+/XFP Transceiver Modules and Network Cables Installation Guide.
Verifying the IRF fabric setup
To verify the basic functionality of the IRF fabric after you finish configuring basic IRF settings and connecting IRF ports:
1. Log in to the IRF fabric through the console port of any member switch.
2. Create a Layer 3 interface, assign it an IP address, and make sure the IRF fabric and the remote network management station can reach each other.
3. Use Telnet, web, or SNMP to access the IRF fabric from the network management station. (See H3C S5150-EI Switch Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide.)
4. Verify that you can manage all member switches as if they were one node.
5. Display the running status of the IRF fabric by using the commands in Table 8.
Table 8 Displaying and maintaining IRF configuration and running status
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display information about the IRF fabric. |
display irf |
|
Display all members’ IRF configurations that take effect at a reboot. |
display irf configuration |
|
Display IRF fabric topology information. |
display irf topology |
|
|
NOTE: To avoid IP address collision and network problems, configure a minimum of one multi-active detection (MAD) mechanism to detect the presence of multiple identical IRF fabrics and handle collisions. For more information about MAD detection, see H3C S5150-EI Switch Series IRF Configuration Guide. |
Maintenance and troubleshooting
Power module failure
Fixed power module failure
The S5150X-16ST-EI switch uses fixed power modules, and supports three power input modes: AC input, RPS DC input, and concurrent AC and RPS DC inputs.
Look at the system status LED and the RPS status LED of the switch to identify power system failure.
Table 9 Description for the power failure indication LEDs
|
LED |
Mark |
Status |
Description |
|
System status LED |
SYS |
Off |
The switch is powered off. |
|
RPS status LED |
RPS |
Steady green |
The AC input is normal, and the RPS is in position or operating correctly. |
|
Steady yellow |
RPS power input is normal, but AC input has failed or AC input is not connected. |
||
|
Off |
No RPS is connected. |
AC input
· Symptom
The system status LED is off.
· Solution
To resolve the issue:
a. Verify that the AC power cord is securely connected to the switch, and the AC-input power receptacle on the switch and the connected AC power source are in good condition.
b. Verify that the external AC power system is operating correctly.
c. Verify that the operating temperature of the switch is in an acceptable range, and the power module has good ventilation. Over-temperature can cause the power module to stop working and enter protection state.
d. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.
RPS DC input
· Symptom
The system status LED or RPS status LED is off.
· Solution
To resolve the issue:
a. Verify that the switch is securely connected to the RPS.
b. Verify that the RPS is operating correctly.
c. Verify that the operating temperature of the switch is in an acceptable range, and the power module has good ventilation. Over-temperature can cause the power module to stop working and enter protection state.
d. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.
Concurrent RPS and AC inputs
· Symptom 1
The system status LED is off.
· Solution
To resolve the issue:
a. Verify that the AC power cord is securely connected to the switch, and the AC-input power receptacle on the switch and the connected AC power source are in good condition.
b. Verify that the external AC power system is operating correctly.
c. Verify that the switch is securely connected to the RPS.
d. Verify that the RPS is operating correctly.
e. Verify that the operating temperature of the switch is in an acceptable range, and the power module has good ventilation. Over-temperature can cause the power module to stop working and enter protection state.
f. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.
· Symptom 2
The system status LED is on but the RPS status LED is steady yellow.
· Solution
To resolve the issue:
a. Verify that the AC power cord is securely connected to the switch, and the AC-input power receptacle on the switch and the connected AC power source are in good condition.
b. Verify that the external AC power system is operating correctly.
c. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.
· Symptom 3
The system status LED is on but the RPS status LED is off.
· Solution
To resolve the issue:
a. Verify that the switch is securely connected to the RPS.
b. Verify that the RPS is operating correctly.
c. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.
Hot swappable power module failure
This section applies to the S5150X-16S-EI and S5150-24S-PWR-EI switches.
For the S5150X-16S-EI, examine the PWR1 or PWR2 LED of the switch to identify power module failure.
For the S5150-24S-PWR-EI, examine the PWR1 or PWR2 LED of the switch and the LEDs on the power module to identify power module failure.
· For more information about the PWR1 and PWR2 LEDs on the front panel of the switch, see Table 22.
· For more information about the LEDs on a power module, see H3C PSR360-56A Power Module User Manual, H3C PSR720-56A Power Module User Manual, and H3C PSR1110-56A Power Module User Manual.
Power module failure
· Symptom
The power module status LEDs are not steady green.
· Solution
To resolve the issue:
a. Verify that the switch power cord is correctly connected.
b. Verify that the power source meets the requirement.
c. Verify that the operating temperature of the switch is in an acceptable range and the power module has good ventilation.
d. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.
To replace a hot swappable power module, see "Installing/removing a power module."
Fan failure
The S5150-EI series switches use fixed fans. If a fan failure occurs, contact H3C Support and do not attempt to fix the problem yourself.
Configuration terminal display problems
If the configuration environment setup is correct, the configuration terminal displays booting information when the switch is powered on. If the setup is incorrect, the configuration terminal displays nothing or garbled text.
No display
Symptom
The PC displays nothing when the switch is powered on.
Solution
To resolve the issue:
1. Verify that the power module is supplying power to the switch.
2. Verify that the console cable is correctly connected.
3. Verify that the console cable does not have any problems and the PC settings are correct.
4. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.
Garbled display
Symptom
The display on the PC is garbled.
Solution
To resolve the issue:
1. Verify that the following settings are configured for the terminal:
¡ Baud rate—9,600.
¡ Data bits—8.
¡ Parity—None.
¡ Stop bits—1.
¡ Flow control—None.
2. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.
Appendix A Chassis views and technical specifications
Chassis views
S5150X-16S-EI
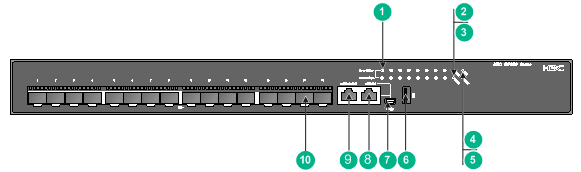
Figure 47 S5150X-16S-EI front panel
|
(1) SFP+ port LED |
(2) Power module 1 status LED (PWR1) |
|
(3) Power module 2 status LED (PWR2) |
(4) System status LED (SYS) |
|
(5) Management Ethernet port status LED (MGMT) |
(6) USB port |
|
(7) Mini USB console port |
(8) Serial console port |
|
(9) Management Ethernet port |
(10) SFP+ port |
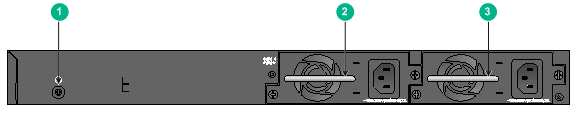
Figure 48 S5150X-16S-EI rear panel
|
(1) Grounding screw |
(2) Power module slot 1 |
|
(3) Power module slot 2 |
|
|
|
NOTE: The S5150X-16S-EI switch comes with power module slot 1 empty and power module slot 2 installed with a filler panel. You can install one or two power modules for the switch as required. In this figure, two PSR150-A AC power modules are installed in the power module slots. |
S5150X-16ST-EI
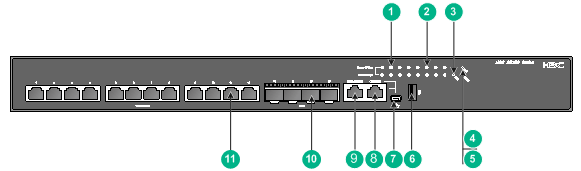
Figure 49 S5150X-16ST-EI front panel
|
(1) 1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED |
(2) SFP+ port LED |
|
(3) RPS status LED (RPS) |
(4) System status LED (SYS) |
|
(5) Management Ethernet port status LED (MGMT) |
(6) USB port |
|
(7) Mini USB console port |
(8) Serial console port |
|
(9) Management Ethernet port |
(10) SFP+ port |
|
(11) 1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet port |
|
Figure 50 S5150X-16ST-EI rear panel
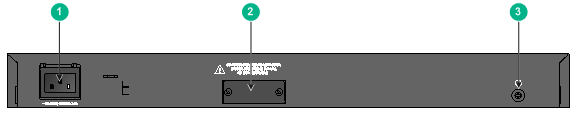
|
(1) AC-input power receptacle |
(2) DC-input power receptacle |
|
(3) Grounding screw |
|
S5150-24S-PWR-EI
Figure 51 S5150-24S-PWR-EI front panel
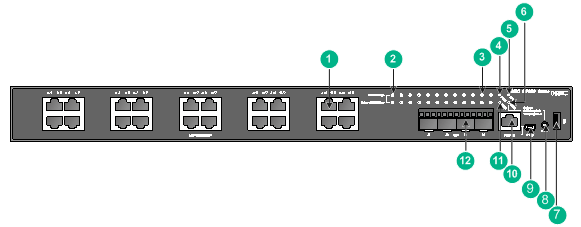
|
(1) 2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port |
(2) 2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED |
|
(3) SFP+ port LED |
(4) Power module 1 status LED (PWR1) |
|
(5) System status LED (SYS) |
(6) Port mode LED (MODE) |
|
(7) USB port |
(8) Port LED mode switching button |
|
(9) Mini USB console port |
(10) Serial console port |
|
(11) Power module 2 status LED (PWR2) |
(12) SFP+ port |
Figure 52 S5150-24S-PWR-EI rear panel
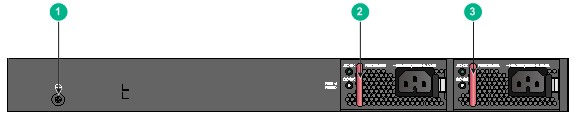
|
(1) Grounding screw |
(2) Power module slot 1 |
|
(3) Power module slot 2 |
|
|
|
NOTE: The S5150-24S-PWR-EI switch comes with power module slot 1 empty and power module slot 2 installed with a filler panel. You can install one or two power modules for the switch as required. In this figure, two PSR720-56A AC power modules are installed in the power module slots. |
Technical specifications
Table 10 Technical specifications for non-PoE switch models
|
Item |
S5150X-16S-EI |
S5150X-16ST-EI |
|
Dimensions (H × W × D) |
43.6 × 440 × 360 mm (1.72 × 17.32 × 14.17 in) |
43.6 × 440 × 260 mm (1.72 × 17.32 × 10.24 in) |
|
Weight |
≤ 6.5 kg (14.33 lb) |
≤ 5 kg (11.02 lb) |
|
Console ports |
· 1 × mini USB console port · 1 × serial console port Only the mini USB console port is available when you connect both ports. |
|
|
USB ports |
1 |
|
|
Management Ethernet ports |
1 |
|
|
SFP+ ports |
16 |
4 |
|
1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet ports |
N/A |
12 |
|
Power module slots |
2 |
N/A |
|
Input voltage |
PSR75-12A power module: · AC input ¡ Rated voltage range: 100 VAC to 240 VAC @ 50 Hz or 60 Hz ¡ Max voltage range: 90 VAC to 290 VAC @ 47 Hz to 63 Hz · High-voltage DC input ¡ Rated voltage range: 240 VDC ¡ Max voltage range: 180 VDC to 320 VDC PSR150-A1 power module: · AC input ¡ Rated voltage range: 100 VAC to 240 VAC @ 50 Hz or 60 Hz ¡ Max voltage range: 90 VAC to 264 VAC @ 47 Hz to 63 Hz · High-voltage DC input ¡ Rated voltage range: 240 VDC ¡ Max voltage range: 180 VDC to 320 VDC PSR150-D1 power module: You can use a –48 VDC power source in the equipment room or an H3C RPS (RPS800-A or RPS1600-A). · Rated voltage range: –48 VDC to –60 VDC · Max voltage range: –36 VDC to –72 VDC |
· AC-input ¡ Rated voltage range: 100 VAC to 240 VAC @ 50 Hz or 60 Hz ¡ Max voltage range: 90 VAC to 264 VAC @ 47 Hz to 63 Hz · +12 VDC-input (use an H3C RPS800-A RPS as the DC power source) ¡ Rated voltage range: 11 VDC to 12 VDC ¡ Max voltage range: 10.8 VDC to 13.2 VDC |
|
Power consumption (static) |
· 1 × PSR75-12A: 15 W · 2 × PSR75-12A: 18 W · 1 × PSR150-A1: 22 W · 2 × PSR150-A1: 26 W · 1 × PSR150-D1: 22 W · 2 × PSR150-D1: 29 W |
· AC: 26 W · DC: 22 W |
|
Power consumption (full configuration) |
· 1 × PSR75-12A: 38 W · 2 × PSR75-12A: 40 W · 1 × PSR150-A1: 46 W · 2 × PSR150-A1: 60 W · 1 × PSR150-D1: 50 W · 2 × PSR150-D1: 54 W |
· AC: 75 W · DC: 68 W |
|
Chassis leakage current compliance |
UL60950-1, EN60950-1, IEC60950-1, GB4943.1 |
|
|
Melting current of power module fuse |
· PSR75-12A: 3.15 A, 250 V · PSR150-A1: 3.15 A, 250 V · PSR150-D1: 8 A, 250 V |
· AC-input: 5 A, 250 V · DC-input: 8 A, 250 V |
|
Operating temperature |
0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F) |
|
|
Relative humidity |
5% to 95%, noncondensing |
|
|
Cooling system |
Built-in fans that provide left-to-right airflow through the chassis |
|
|
Fire resistance compliance |
UL60950-1, EN60950-1, IEC60950-1, GB4943.1 |
|
Table 11 Technical specifications for PoE switch models
|
Item |
S5150-24S-PWR-EI |
|
Dimensions (H × W × D) |
43.6 × 440 × 460 mm (1.72 × 17.32 × 18.11 in) |
|
Weight |
≤ 6.5 kg (14.33 lb) |
|
Console ports |
· 1 × mini USB console port · 1 × serial console port Only the mini USB console port is available when you connect both ports. |
|
USB ports |
1 |
|
SFP+ ports |
4 |
|
2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet ports |
20 |
|
Power module slots |
2, on the rear panel |
|
Input voltage |
· PSR360-56A/PSR720-56A AC-input ¡ Rated voltage range: 100 VAC to 240 VAC @ 50 Hz or 60 Hz ¡ Max voltage range: 90 VAC to 264 VAC @ 47 Hz to 63 Hz · PSR1110-56A AC-input ¡ Rated voltage range: 115 VAC to 240 VAC @ 50 Hz or 60 Hz ¡ Max voltage range: 102.5 VAC to 264 VAC @ 47 Hz to 63 Hz |
|
PoE power capacity |
Depends on the power module configurations. For more information, see the following table. |
|
Power consumption (static) |
· Single power module: 51 W · Dual power modules: 112 W |
|
Power consumption (full configuration) |
841 W (including PoE power consumption) |
|
Chassis leakage current compliance |
UL60950-1, EN60950-1, IEC60950-1, GB4943.1 |
|
Melting current of power module fuse |
· PSR360-56A: 6.3 A, 250 V · PSR720-56A/PSR1110-56A: 15 A, 250 V |
|
Operating temperature |
0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F) |
|
Relative humidity |
5% to 95%, noncondensing |
|
Cooling system |
Built-in fans that provide left-to-right airflow through the chassis |
|
Fire resistance compliance |
UL60950-1, EN60950-1, IEC60950-1, GB4943.1 |
Table 12 S5150-24S-PWR-EI switch PoE power capacity
|
Power module configuration |
Total PoE power capacity |
Max PoE power capacity per port |
|
Two PSR1110-56A |
720 W |
· Ports 1 to 4: 60 W · Ports 5 to 20: 30 W |
|
One PSR1110-56A and one PSR720-56A |
720 W |
|
|
One PSR1110-56A and one PSR360-56A |
720 W |
|
|
Two PSR720-56A |
720 W |
|
|
One PSR1110-56A |
720 W |
|
|
One PSR720-56A and one PSR360-56A |
720 W |
|
|
One PSR720-56A |
570 W |
|
|
Two PSR360-56A |
570 W |
|
|
One PSR360-56A |
210 W |
Appendix B FRUs and compatibility matrixes
Power modules and compatibility matrixes
The S5150X-16S-EI and S5150-24S-PWR-EI switches support hot swapping of power modules. The following table describes power modules available for the switch.
|
Power modules |
S5150X-16S-EI |
S5150-24S-PWR-EI |
|
PSR150-A1 |
Supported |
N/A |
|
PSR150-D1 |
Supported |
N/A |
|
PSR75-12A |
Supported |
N/A |
|
PSR360-56A |
N/A |
Supported |
|
PSR720-56A |
N/A |
Supported |
|
PSR1110-56A |
N/A |
Supported |
You can install one power module, or two power modules for redundancy on the S5150X-16S-EI switch. The switch supports mix of an AC power module and a DC power module.
You can install one power module, or two power modules for redundancy on the S5150-24S-PWR-EI switch. The PoE capabilities of these switches vary by power module configuration. For more information, see Table 12.
Hot swappable power modules
|
Power module |
Item |
Specifications |
Reference |
|
|
PSR150-A1 |
AC input |
Rated input voltage |
100 VAC to 240 VAC @ 50 Hz or 60 Hz |
H3C PSR150-A & PSR150-D Series Power Modules User Manual |
|
Max input voltage |
90 VAC to 264 VAC @ 47 Hz to 63 Hz |
|||
|
High-voltage DC input |
Rated input voltage |
240 VDC |
||
|
Max input voltage |
180 VDC to 320 VDC |
|||
|
Max output power |
150 W |
|||
|
PSR150-D1 |
Rated input voltage |
–48 VDC to –60 VDC |
||
|
Max input voltage |
–36 VDC to –72 VDC |
|||
|
Max output power |
150 W |
|||
|
PSR75-12A |
AC input |
Rated input voltage |
100 VAC to 240 VAC @ 50 Hz or 60 Hz |
H3C PSR75-12A Power Module User Manual |
|
Max input voltage |
90 VAC to 290 VAC @ 47 Hz to 63 Hz |
|||
|
High-voltage DC input |
Rated input voltage |
240 VDC |
||
|
Max input voltage |
180 VDC to 320 VDC |
|||
|
Max output power |
75 W |
|||
|
PSR360-56A |
Rated input voltage range |
100 VAC to 240 VAC @ 50 Hz or 60 Hz |
H3C PSR360-56A Power Module User Manual |
|
|
Max input voltage range |
90 VAC to 264 VAC @ 47 Hz to 63 Hz |
|||
|
Max output power |
360 W |
|||
|
PSR720-56A |
Rated input voltage range |
100 VAC to 240 VAC @ 50 Hz or 60 Hz |
H3C PSR720-56A Power Module User Manual |
|
|
Max input voltage range |
90 VAC to 264 VAC @ 47 Hz to 63 Hz |
|||
|
Max output power |
720 W |
|||
|
PSR1110-56A |
Rated input voltage range |
115 VAC to 240 VAC @ 50 Hz or 60 Hz |
H3C PSR1110-56A Power Module User Manual |
|
|
Max input voltage range |
102.5 VAC to 264 VAC @ 47 Hz to 63 Hz |
|||
|
Max output power |
1110 W |
|||
|
|
NOTE: The PSR1110-56A power module (including its handle) adds 64 mm (2.52 in) to the depth of the switch. |
Appendix C Ports and LEDs
Ports
Console port
The switch has two console ports: a serial console port and a mini USB console port.
Table 13 Console port specifications
|
Item |
Serial console port |
Mini USB console port |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
Mini USB-Type B |
|
Compliant standard |
EIA/TIA-232 |
USB 2.0 |
|
Transmission baud rate |
9600 bps (default) to 115200 bps |
|
|
Services |
· Provides connection to an ASCII terminal. · Provides connection to the serial port of a local PC running terminal emulation program. |
Provides connection to the USB port of a local PC running terminal emulation program. |
Management Ethernet port
All S5150-EI switches except for the S5150-24S-PWR-EI provide a management Ethernet port on the front panel. You can connect the management Ethernet port to a PC or management station for loading and debugging software or remote management.
Table 14 Management Ethernet port specifications
|
Item |
Specification |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
|
Port transmission rate |
10/100 Mbps, half/full duplex 1000 Mbps, full duplex MDI/MDI-X auto-sensing |
|
Transmission medium and max transmission distance |
100 m (328.08 ft) over category-5 twisted pair cable |
|
Standards |
IEEE 802.3i, 802.3u, 802.3ab |
|
Functions and services |
Switch software and Boot ROM upgrade, network management |
USB port
The switch has one OHC-compliant USB2.0 port on the front panel that can upload and download data at a rate up to 480 Mbps. You can use this USB port to access the file system on the flash of the switch, for example, to upload or download application and configuration files.
|
|
NOTE: USB devices from different vendors vary in compatibilities and drivers. H3C does not guarantee the correct operation of USB devices from all vendors on the switch. If a USB device fails to operate on the switch, replace it with one from another vendor. |
1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet port
The S5150X-16ST-EI switch provides 1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet ports.
Table 15 1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet port specifications
|
Item |
Specification |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
|
Interface attributes |
1/10 Gbps, full duplex, MDI/MDI-X auto-sensing |
|
Max transmission distance |
· Category-6 UTP—55 m (180.45 ft) · Category-6 STP—100 m (328.08 ft) · Category-6A and above twisted pair—100 m (328.08 ft) |
|
Transmission medium |
Category-6 (or above) twisted pair cable |
|
Standards |
IEEE 802.3ab, 802.3an |
2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port
The S5150-24S-PWR-EI switch provides 2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet ports.
Table 16 2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port specifications
|
Item |
Specification |
|
Connector type |
RJ-45 |
|
Interface attributes |
100 Mbps, full duplex 1/2.5 Gbps, full duplex MDI/MDI-X auto-sensing |
|
Max transmission distance |
· Category-5 UTP—100 m (328.08 ft). As a best practice, configure the switch to operate in full duplex mode at 100/1000 Mbps. · Category-6 UTP—55 m (180.45 ft) · Category-6 STP—100 m (328.08 ft) · Category-6A and above twisted pair—100 m (328.08 ft) |
|
Transmission medium |
Category-5 (or above) twisted pair cable |
|
Standards |
IEEE 802.3ab, 802.3ae, 802.3at, 802.3az, 802.3z |
SFP+ port
The S5150X-16S-EI switch provides 16 fixed SFP+ ports on the front panel, and other switch models provide 4 fixed SFP+ ports on the front panel. To connect the peer SFP+ ports over a long distance, use SFP/SFP+ transceiver modules and fibers. To connect the peer SFP+ ports over a short distance, use SFP/SFP+ cables. You can install the 1000 Mbps SFP transceiver modules and cables in Table 17, 10 Gbps SFP+ transceiver modules in Table 18, or 10 Gbps SFP+ network cables in Table 19 in the SFP+ ports.
Table 17 1000 Mbps SFP transceiver modules and cables available for the SFP+ ports
|
Module and cable description |
Central wavelength (nm) |
Connector |
Cable/fiber diameter (µm) |
Multimode fiber modal bandwidth (MHz × km) |
Max transmission distance |
|
SFP copper transceiver module |
|||||
|
SFP-GE-T |
N/A |
RJ-45 |
Twisted-pair cable |
N/A |
100 m (328.08 ft) |
|
SFP-GE-T-D |
N/A |
RJ-45 |
Twisted-pair cable |
N/A |
100 m (328.08 ft) |
|
SFP fiber transceiver module |
|||||
|
SFP-GE-SX-MM850-A |
850 |
LC |
Multi-mode, 50/125 |
500 |
550 m (1804.46 ft) |
|
400 |
500 m (1640.42 ft) |
||||
|
Multi-mode, 62.5/125 |
200 |
275 m (902.23 ft) |
|||
|
160 |
220 m (721.78 ft) |
||||
|
SFP-GE-SX-MM850-D |
850 |
LC |
Multi-mode, 50/125 |
500 |
550 m (1804.46 ft) |
|
400 |
500 m (1640.42 ft) |
||||
|
Multi-mode, 62.5/125 |
200 |
275 m (902.23 ft) |
|||
|
160 |
220 m (721.78 ft) |
||||
|
SFP-GE-LX-SM1310-A |
1310 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
10 km (6.21 miles) |
|
Multi-mode, 50/125 |
500 or 400 |
550 m (1804.46 ft) |
|||
|
Multi-mode, 62.5/125 |
500 |
550 m (1804.46 ft) |
|||
|
SFP-GE-LX-SM1310-D |
1310 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
10 km (6.21 miles) |
|
SFP-GE-LH40-SM1310 |
1310 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
40 km (24.86 miles) |
|
SFP-GE-LH40-SM1310-D |
1310 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
40 km (24.86 miles) |
|
SFP-GE-LH40-SM1550 |
1550 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
40 km (24.86 miles) |
|
SFP-GE-LH70-SM1550 |
1550 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
70 km (43.50 miles) |
|
SFP-GE-LH80-SM1550 |
1550 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
80 km (49.71 miles) |
|
SFP-GE-LH80-SM1550-D |
1550 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
80 km (49.71 miles) |
|
SFP-GE-LH100-SM1550 |
1550 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
100 km (62.14 miles) |
|
SFP-GE-LX-SM1310-BIDI |
· TX: 1310 · RX: 1490 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
10 km (6.21 miles) |
|
SFP-GE-LX-SM1490-BIDI |
· TX: 1490 · RX: 1310 |
||||
|
SFP cable |
|||||
|
SFP-STACK-Kit |
N/A |
1.5 m (4.92 ft) |
|||
Table 18 10 Gbps SFP+ transceiver modules available for the SFP+ ports
|
Module description |
Central
wavelength |
Connector |
Fiber
diameter |
Multimode
fiber modal bandwidth |
Max transmission distance |
|
SFP-XG-SX-MM850-A |
850 |
LC |
Multi-mode, 50/125 |
2000 |
300 m (984.25 ft) |
|
500 |
82 m (269.03 ft) |
||||
|
400 |
66 m (216.54 ft) |
||||
|
Multi-mode, 62.5/125 |
200 |
33 m (108.27 ft) |
|||
|
160 |
26 m (85.30 ft) |
||||
|
SFP-XG-SX-MM850-D |
850 |
LC |
Multi-mode, 50/125 |
2000 |
300 m (984.25 ft) |
|
500 |
82 m (269.03 ft) |
||||
|
400 |
66 m (216.54 ft) |
||||
|
Multi-mode, 62.5/125 |
200 |
33 m (108.27 ft) |
|||
|
160 |
26 m (85.30 ft) |
||||
|
SFP-XG-SX-MM850-E |
850 |
LC |
Multi-mode, 50/125 |
2000 |
300 m (984.25 ft) |
|
500 |
82 m (269.03 ft) |
||||
|
400 |
66 m (216.54 ft) |
||||
|
Multi-mode, 62.5/125 |
200 |
33 m (108.27 ft) |
|||
|
160 |
26 m (85.30 ft) |
||||
|
SFP-XG-LX-SM1310 |
1310 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
10 km (6.21 miles) |
|
SFP-XG-LX-SM1310-D |
1310 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
10 km (6.21 miles) |
|
SFP-XG-LX-SM1310-E |
1310 |
LC |
Single-mode, 9/125 |
N/A |
10 km (6.21 miles) |
Table 19 SFP+ network cables available for the SFP+ ports
|
Cable description |
Cable length |
|
LSWM1STK |
0.65 m (2.13 ft) |
|
LSWM2STK |
1.2 m (3.94 ft) |
|
LSWM3STK |
3 m (9.84 ft) |
|
LSTM1STK |
5 m (16.40 ft) |
Figure 53 SFP+ network cable

|
(1) Connector |
(2) Pull latch |
|
|
NOTE: · As a best practice, use only H3C SFP/SFP+ transceiver modules and SFP+ network cables for the SFP+ ports. · The SFP/SFP+ transceiver modules and SFP+ network cables available for the switch are subject to change over time. For the most up-to-date list of SFP/SFP+ transceiver modules and SFP+ network cables, consult your H3C sales representative or technical support engineer. · For the specifications for the H3C SFP/SFP+ transceiver modules and SFP+ network cables, see H3C Transceiver Modules User Guide. |
LEDs
Table 20 S5150-EI switch LEDs at a glance
|
LED |
Switch |
Remarks |
|
System status LED |
All switch models |
See Table 21. |
|
Power module status LED |
S5150X-16S-EI S5150-24S-PWR-EI |
See Table 22. |
|
RPS status LED |
S5150X-16ST-EI |
See Table 23. |
|
Port mode LED |
S5150-24S-PWR-EI |
See Table 24. |
|
Management Ethernet port LED |
S5150X-16S-EI S5150X-16ST-EI |
See Table 25. |
|
1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED |
S5150X-16S-EI |
See Table 26. |
|
2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED |
S5150-24S-PWR-EI |
See Table 27. |
|
SFP+ port LED |
All switch models |
See Table 28. |
System status LED
The system status LED shows the operating state of the switch.
Table 21 System status LED description
|
LED mark |
Status |
Description |
|
SYS |
Steady green |
The switch is operating correctly. |
|
Flashing green (1 Hz) |
The switch is performing power-on self test (POST). |
|
|
Steady red |
The switch has failed the POST or is faulty. |
|
|
Flashing yellow (1 Hz) |
Some ports have failed to pass POST or are faulty. |
|
|
Off |
The switch is powered off. |
Power module status LED
The S5150X-16S-EI and S5150-24S-PWR-EI switches provide two power module slots at the rear. For each power module, these switches provide a power module status LED on the front panel. For more information about power modules, see the related power modules user manual.
Table 22 Power module status LED description
|
LED mark |
Status |
Description |
|
PWR1 |
Steady green |
A power module is installed in power module slot 1, and the power module is outputting power correctly. |
|
Steady yellow |
A power module is installed in power module slot 1, but the power module has failed or no power is input to the power module. |
|
|
Off |
No power module is installed in power module slot 1. |
|
|
PWR2 |
Steady green |
A power module is installed in power module slot 2, and the power module is outputting power correctly. |
|
Steady yellow |
A power module is installed in power module slot 2, but the power module has failed or no power is input to the power module. |
|
|
Off |
No power module is installed in power module slot 2. |
RPS status LED
The S5150X-16ST-EI switch supports RPS input. The RPS status LED shows the status of the RPS input.
Table 23 RPS status LED description
|
LED mark |
Status |
Description |
|
RPS |
Steady green |
Both the RPS DC input and the AC input are normal. |
|
Steady yellow |
The RPS DC input is normal, but the AC input is disconnected or has failed. |
|
|
Off |
The RPS DC input is abnormal or no RPS is connected. |
Port mode LED
To show more information about the switch through the port status LEDs, the S5150-24S-PWR-EI switch provides a port mode LED. The port mode LED indicates the type of information that the network port LEDs are showing.
Table 24 Port mode LED description
|
LED mark |
Status |
Description |
|
Mode |
Steady green |
The port status LEDs are showing port rates. |
|
Flashing green |
The port status LEDs are showing the status of PoE power supply on the ports. |
|
|
Flashing yellow |
The port status LEDs indicate the IRF member ID of the switch. For example, if the LEDs for ports 1 to 5 are steady green and the other LEDs are off, the IRF member ID of the switch is 5. |
Management Ethernet port LEDs
The S5150X-16S-EI and S5150X-16ST-EI switches provide a management Ethernet port LED to indicate the operating state of the management Ethernet port.
Table 25 Management Ethernet port LED description
|
Management Ethernet port LED (MGMT) status |
Description |
|
Steady green |
A link is present on the port and the port is operating at 1000 Mbps. |
|
Flashing green |
The port is sending or receiving data at 1000 Mbps. |
|
Steady yellow |
A link is present on the port and the port is operating at 10/100 Mbps. |
|
Flashing yellow |
The port is sending or receiving data at 100 or 10 Mbps. |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED
Table 26 1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED description
|
1/10GBASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED status |
Description |
|
Steady green |
A link is present on the port and the port is operating at 10 Gbps. |
|
Flashing green |
The port is sending or receiving data at 10 Gbps. |
|
Steady yellow |
A link is present on the port and the port is operating at 1 Gbps. |
|
Flashing yellow |
The port is sending or receiving data at 1 Gbps. |
|
Flashing yellow (3 Hz) |
The port has failed POST. |
|
Off |
· No link is present on the port. · The port is operating in PoE mode (for PoE switches only.) |
2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED
The S5150-24S-PWR-EI switch provides a status LED for each 2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port. The status LED and the port mode LED work in conjunction to indicate the operating status of the 2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port.
Table 27 2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED description
|
Port mode LED (Mode) status |
2.5G/1000/100BASE-T autosensing Ethernet port LED status |
Description |
|
Steady green (rate mode) |
Steady green |
A link is present on the port and the port is operating at 2.5 Gbps. |
|
Flashing green |
The port is sending or receiving data at 2.5 Gbps. |
|
|
Steady yellow |
A link is present on the port and the port is operating at 100/1000 Mbps. |
|
|
Flashing yellow |
The port is sending or receiving data at 100/1000 Mbps. |
|
|
Flashing yellow (1 Hz) |
The port has failed POST. |
|
|
Off |
No link is present on the port. |
|
|
Flashing green (PoE mode) |
Steady green |
PoE power supply is normal. |
|
Flashing green (1 Hz) |
The device attached to the port requires power higher than the maximum or currently available PoE output power on the port. |
|
|
Steady yellow |
The port is experiencing a PoE failure. |
|
|
Flashing yellow (3 Hz) |
The port has failed POST. |
|
|
Off |
The port is not supplying power through PoE. |
|
|
Flashing yellow (IRF mode) |
Steady green |
The port status LEDs on the switch indicate the IRF member IDs of the switch. For example, if the LED for port 5 is steady green and the other port LEDs are off, the IRF member ID of the switch is 5. |
SFP+ port LED
Table 28 SFP+ port LED description
|
SFP+ port LED status |
Description |
|
Steady green |
A link is present on the port and the port is operating at 10 Gbps. |
|
Flashing green |
The port is sending or receiving data at 10 Gbps. |
|
Steady yellow |
A link is present on the port and the port is operating at 1 Gbps. |
|
Flashing yellow |
The port is sending or receiving data at 1 Gbps. |
|
Flashing yellow (3 Hz) |
The port has failed POST. |
|
Off |
· No link is present on the port. · The port mode LED operates in PoE mode or IRF mode (for PoE switches only.) |

