- Table of Contents
-
- 05-Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-ARP configuration
- 02-IP addressing configuration
- 03-DHCP configuration
- 04-DNS configuration
- 05-IP forwarding basics configuration
- 06-Adjacency table configuration
- 07-IP performance optimization configuration
- 08-UDP helper configuration
- 09-IPv6 basics configuration
- 10-DHCPv6 configuration
- 11-IPv6 fast forwarding configuration
- 12-Fast forwarding configuration
- 13-Tunnel configuration
- 14-GRE configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 11-IPv6 fast forwarding configuration | 77.51 KB |
Contents
Configuring IPv6 fast forwarding·
Displaying and maintaining IPv6 fast forwarding
IPv6 fast forwarding configuration example
The device operates in IRF or standalone (the default) mode. For information about IRF mode, see IRF Configuration Guide.
Overview
Fast forwarding reduces route lookup time and improves packet forwarding efficiency by using a high-speed cache and data-flow-based technology. It uses a six-tuple (source IPv6 address, destination IPv6 address, source port number, destination port number, protocol number, and VPN instance name) to identify a data flow. After the first packet of a flow is forwarded through the routing table, fast forwarding creates an entry for the flow and uses the entry to forward subsequent packets of the flow.
Configuration procedure
To configure IPv6 fast forwarding:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable IPv6 fast forwarding. |
ipv6 fast-forwarding |
By default, IPv6 fast forwarding is enabled. |
|
3. Set the aging time of IPv6 fast forwarding entries. |
ipv6 fast-forwarding aging-time aging-time |
By default, the aging time of IPv6 fast forwarding entries is 30 seconds. |
Displaying and maintaining IPv6 fast forwarding
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display IPv6 fast forwarding table information (in standalone mode). |
display ipv6 fast-forwarding cache [ ipv6-address ] [ slot slot-number ] |
|
Display IPv6 fast forwarding table information (in IRF mode). |
display ipv6 fast-forwarding cache [ ipv6-address ] [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] |
|
Display the aging time of the IPv6 fast forwarding entry. |
display ipv6 fast-forwarding aging-time |
|
Clear IPv6 fast forwarding table information (in standalone mode). |
reset ipv6 fast-forwarding cache [ slot slot-number ] |
|
Clear IPv6 fast forwarding table information (in IRF mode). |
reset ipv6 fast-forwarding cache [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] |
IPv6 fast forwarding configuration example
By default, Ethernet, VLAN, and aggregate interfaces are down. To configure such an interface, bring the interface up by executing the undo shutdown command.
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 1, enable IPv6 fast forwarding on Switch B.
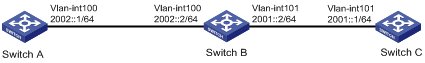
Configuration procedure
1. Configure Switch A:
# Configure the IPv6 address of interface VLAN-interface 100.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] interface Vlan-interface100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 address 2002::1 64
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Configure a static route.
[SwitchA] ipv6 route-static 2001:: 64 2002::2
2. Configure Switch C:
# Configure the IPv6 address of VLAN-interface 101.
<SwitchC> system-view
[SwitchC] interface Vlan-interface101
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface101] ipv6 address 2001::1 64
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface101] quit
# Configure a static route.
[SwitchC] ipv6 route-static 2002:: 64 2001::2
3. Configure Switch B:
# Enable IPv6 fast forwarding.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ipv6 fast-forwarding
# Configure the IPv6 address of VLAN-interface 100.
[SwitchB] interface Vlan-interface100
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 address 2002::2 64
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Configure the IPv6 address of VLAN-interface 101.
[SwitchB] interface Vlan-interface101
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface101] ipv6 address 2001::2 64
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface101] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display the IPv6 fast forwarding table on Switch B.
[SwitchB] display ipv6 fast-forwarding cache
The output shows that no IPv6 fast forwarding entry exists.
# Ping the IPv6 address of VLAN-interface 101 of Switch C from Switch A. Reply packets can be received.
[SwitchA] ping ipv6 2001::1
PING 2001::1 : 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 2001::1
bytes=56 Sequence=1 hop limit=64 time = 69 ms
Reply from 2001::1
bytes=56 Sequence=2 hop limit=64 time = 1 ms
Reply from 2001::1
bytes=56 Sequence=3 hop limit=64 time = 1 ms
Reply from 2001::1
bytes=56 Sequence=4 hop limit=64 time = 1 ms
Reply from 2001::1
bytes=56 Sequence=5 hop limit=64 time = 1 ms
--- 2001::1 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 1/14/69 ms
# Display the IPv6 fast forwarding table on Switch B.
[SwitchB] display ipv6 fast-forwarding cache
Total number of IPv6 fast-forwarding items: 2
Src IP: 2002::1 Src port: 129
Dst IP: 2001::1 Dst port: 0
Protocol: 58
VPN instance: N/A
Input interface: Vlan-interface100
Output interface: Vlan-interface101
Src IP: 2001::1 Src port: 128
Dst IP: 2002::1 Dst port: 0
Protocol: 58
VPN instance: N/A
Input interface: Vlan-interface101
Output interface: Vlan-interface100
The output shows that IPv6 fast forwarding entries have been created.

