- Table of Contents
-
- 09-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA configuration
- 02-Password control configuration
- 03-Keychain configuration
- 04-Public key management
- 05-PKI configuration
- 06-IPsec configuration
- 07-SSH configuration
- 08-SSL configuration
- 09-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 10-IP source guard configuration
- 11-ARP attack protection configuration
- 12-ND attack defense configuration
- 13-uRPF configuration
- 14-Crypto engine configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 13-uRPF configuration | 110.65 KB |
Contents
Restrictions and guidelines: uRPF configuration
Display and maintenance commands for uRPF
Example: Configuring uRPF for interfaces
Configuring uRPF
About uRPF
Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (uRPF) protects a network against source address spoofing attacks, such as DoS and DDoS attacks.
uRPF application scenario
Attackers send packets with a forged source address to access a system that uses IPv4-based authentication, in the name of authorized users or even the administrator. Even if the attackers or other hosts cannot receive any response packets, the attacks are still disruptive to the attacked target.
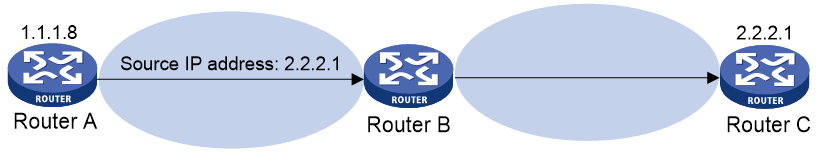
Figure 1 Source address spoofing attack
As shown in Figure 1, an attacker on Router A sends the server (Router B) requests with a forged source IP address 2.2.2.1 at a high rate. Router B sends response packets to IP address 2.2.2.1 (Router C). Consequently, both Router B and Router C are attacked. If the administrator disconnects Router C by mistake, the network service is interrupted.
Attackers can also send packets with different forged source addresses or attack multiple servers simultaneously to block connections or even break down the network.
uRPF can prevent these source address spoofing attacks. It checks whether an interface that receives a packet is the output interface of the FIB entry that matches the source address of the packet. If not, uRPF considers it a spoofing attack and discards the packet.
uRPF check modes
uRPF supports strict and loose modes.
Strict uRPF check
To pass strict uRPF check, the source address of a packet and the receiving interface must match the destination address and output interface of a FIB entry. In some scenarios (for example, asymmetrical routing), strict uRPF might discard valid packets.
Strict uRPF is often deployed between a PE and a CE.
Loose uRPF check
To pass loose uRPF check, the source address of a packet must match the destination address of a FIB entry. Loose uRPF can avoid discarding valid packets, but might let go attack packets.
Loose uRPF is often deployed between ISPs, especially in asymmetrical routing.
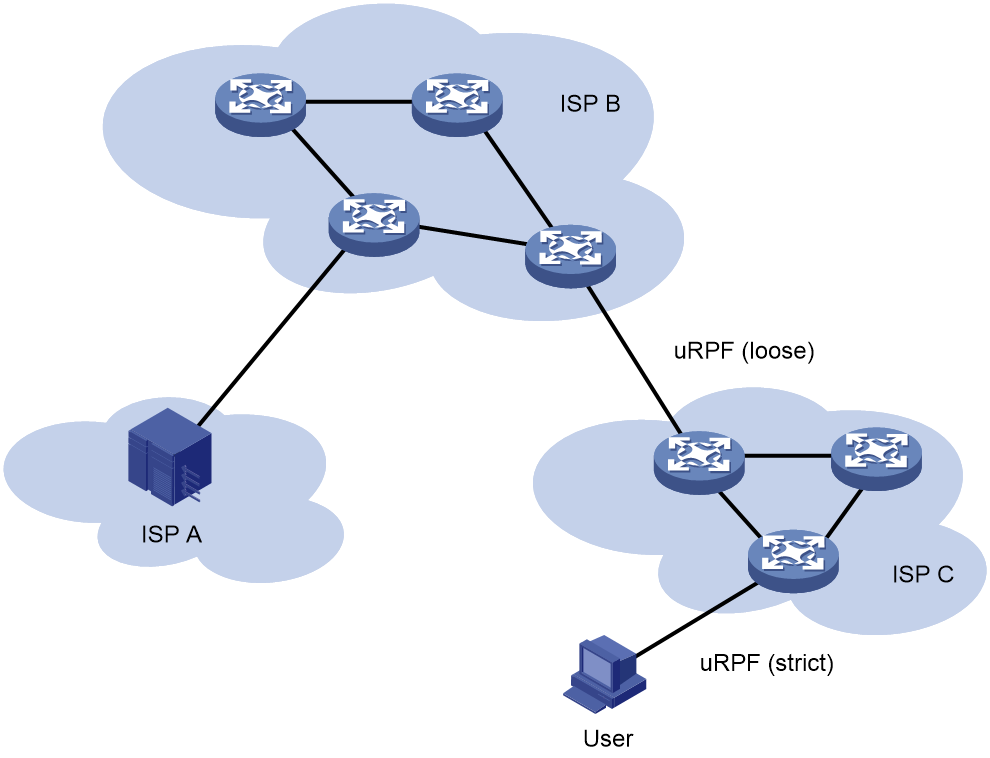
Network application
As shown in Figure 2, strict uRPF check is configured between an ISP network and a customer network. Loose uRPF check is configured between ISPs.
For special packets or users, you can configure ACLs.
Restrictions and guidelines: uRPF configuration
If you configure uRPF globally and on an interface, the interface preferentially uses the interface-specific settings.
Do not use strict uRPF if ECMP routing is available in the network. Service packets that travel along ECMP routes cannot pass the strict uRPF check and will be dropped.
Enabling uRPF globally
Restrictions and guidelines
Global uRPF takes effect on all interfaces of the device.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable uRPF globally.
ip urpf { loose | strict }
By default, uRPF is disabled.
Enabling uRPF on an interface
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable uRPF.
ip urpf { loose | strict }
By default, uRPF is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for uRPF
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display uRPF configuration. |
display ip urpf [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ slot slot-number ] |
uRPF configuration examples
Example: Configuring uRPF for interfaces
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, perform the following tasks:
· Configure strict uRPF check on HundredGigE 1/0/1 of Router B and permit packets from network 10.1.1.0/24.
· Configure strict uRPF check on HundredGigE 1/0/1 of Router A and allow using the default route for uRPF check.
Procedure
|
IMPORTANT: By default, interfaces on the device are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface. |
1. Configure Router B:
# Configure ACL 2010 to permit traffic from network 10.1.1.0/24.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] acl basic 2010
[RouterB-acl-ipv4-basic-2010] rule permit source 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterB-acl-ipv4-basic-2010] quit
# Specify an IP address for HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[RouterB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[RouterB-HundredGigE1/0/1] ip address 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
# Configure strict uRPF check on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[RouterB-HundredGigE1/0/1] ip urpf strict acl 2010
2. Configure Router A:
# Specify an IP address for HundredGigE 1/0/1.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
# Configure strict uRPF check on HundredGigE 1/0/1 and allow using the default route for uRPF check.
[RouterA-HundredGigE1/0/1] ip urpf strict allow-default-route