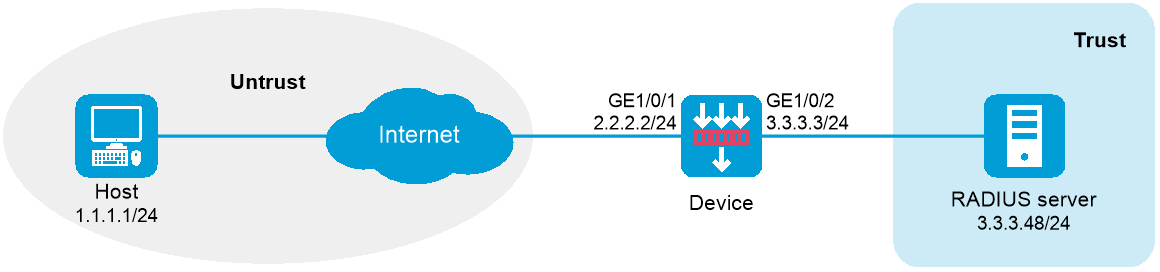
As shown in Figure 1, configure an IPsec tunnel to protect the traffic between the host and the device.
Set up IPsec SAs through IKE negotiations.
Configure the host and the device to use preshared key for authentication in the phase-1 IKE negotiation.
Configure the device to use RADIUS to perform remote extended authentication on the host.
This configuration example was created and verified on F9900 of the F5000-AI120 device.
Make sure the host, device, and server can reach each other.
Configure a local user account on the device to provide identity authentication for the host. In this example, the account uses username test and password 123456TESTplat&!.
1. Assign IP addresses to interfaces.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[Device] interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
2. Configure settings for routing.
This example configures a static route, and the next hop in the route is 2.2.2.3.
[Device] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 24 2.2.2.3
3. Add interfaces to security zones.
[Device] security-zone name untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
[Device] security-zone name trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
4. Configure security policy rules to permit the traffic between the Untrust and Local security zones, so the host can access the device:
# Configure a rule named ipseclocalout1 to allow the device to send packets to the host.
[Device] security-policy ip
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name ipseclocalout1
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-ipseclocalout1] source-zone local
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-ipseclocalout1] destination-zone untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-ipseclocalout1] source-ip-host 2.2.2.2
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-ipseclocalout1] destination-ip-host 1.1.1.1
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-ipseclocalout1] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-ipseclocalout1] quit
# Configure a rule named ipseclocalin1 to allow the device to receive the packets sent from the host.
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name ipseclocalin1
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-ipseclocalin1] source-zone untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-ipseclocalin1] destination-zone local
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-ipseclocalin1] source-ip-host 1.1.1.1
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-ipseclocalin1] destination-ip-host 2.2.2.2
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-ipseclocalin1] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-ipseclocalin1] quit
# Configure a rule named ipseclocalout2 to allow the device to send packets to the RADIUS server.
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name ipseclocalout2
[Device-security-policy-ip-3-ipseclocalout2] source-zone local
[Device-security-policy-ip-3-ipseclocalout2] destination-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-3-ipseclocalout2] source-ip-host 3.3.3.3
[Device-security-policy-ip-3-ipseclocalout2] destination-ip-host 3.3.3.48
[Device-security-policy-ip-3-ipseclocalout2] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-3-ipseclocalout2] quit
# Configure a rule named ipseclocalin2 to allow the device to receive the packets sent from the RADIUS server.
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name ipseclocalin2
[Device-security-policy-ip-4-ipseclocalin2] source-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-4-ipseclocalin2] destination-zone local
[Device-security-policy-ip-4-ipseclocalin2] source-ip-host 3.3.3.48
[Device-security-policy-ip-4-ipseclocalin2] destination-ip-host 3.3.3.3
[Device-security-policy-ip-4-ipseclocalin2] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-4-ipseclocalin2] quit
[Device-security-policy-ip] quit
5. Configure a RADIUS scheme:
# Create a RADIUS scheme named ike-scheme.
[Device] radius scheme ike-scheme
# Specify the IP address and service port of the primary RADIUS authentication server.
[Device-radius-ike-scheme] primary authentication 3.3.3.48 1645
# Set the shared key for secure RADIUS authentication communication.
[Device-radius-ike-scheme] key authentication simple abc
# Configure the device to send the username without the ISP domain name to the RADIUS server. (The configuration varies with the RADIUS server's requirements for username.)
[Device-radius-ike-scheme] user-name-format without-domain
[Device-radius-ike-scheme] quit
6. Configure an ISP domain:
# Create an ISP domain named ike and specify the RADIUS scheme used for authenticating the IKE users.
[Device] domain ike
[Device-isp-ike] authentication ike radius-scheme ike-scheme
[Device-isp-ike] quit
7. Configure an IPv4 advanced ACL to identify the packets to be protected.
[Device] acl advanced 3101
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3101] rule permit ip source 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 destination 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
[Device-acl-ipv4-adv-3101] quit
8. Configure an IPsec transform set to specify the packet encapsulation mode, security protocols, and algorithms.
The IPsec transform set settings at both sides of the IPsec tunnel must be the same.
[Device] ipsec transform-set tran1
[Device-ipsec-transform-set-tran1] encapsulation-mode transport
[Device-ipsec-transform-set-tran1] protocol esp
[Device-ipsec-transform-set-tran1] esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
[Device-ipsec-transform-set-tran1] esp authentication-algorithm sha1
[Device-ipsec-transform-set-tran1] quit
9. Configure an IKE keychain to specify the key information used for IKE communication:
The preshared key used by both sides of the communication must be the same.
[Device] ike keychain keychain1
[Device-ike-keychain-keychain1] pre-shared-key address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 key simple 123456TESTplat&!
[Device-ike-keychain-keychain1] quit
10. Configure an IKE profile to specify the security parameters used for setting up IKE SAs.
[Device] ike profile profile1
[Device-ike-profile-profile1] keychain keychain1
[Device-ike-profile-profile1] local-identity address 2.2.2.2
[Device-ike-profile-profile1] match remote identity address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
[Device-ike-profile-profile1] client-authentication xauth
[Device-ike-profile-profile1] quit
11. Configure an IPsec policy to establish an IPsec tunnel to protect the specified data.
[Device] ipsec policy map1 10 isakmp
[Device-ipsec-policy-isakmp-map1-10] remote-address 1.1.1.1
[Device-ipsec-policy-isakmp-map1-10] security acl 3101
[Device-ipsec-policy-isakmp-map1-10] transform-set tran1
[Device-ipsec-policy-isakmp-map1-10] ike-profile profile1
[Device-ipsec-policy-isakmp-map1-10] quit
12. Apply the IPsec policy to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ipsec apply policy map1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
Perform the following tasks on the host and make sure the configuration matches that on the device:
Specify the IP address of the remote security gateway.
Set the preshared key used for IKE negotiation.
Configure the username and password for IKE extended authentication.
Specify the security protocol, encryption algorithm, and authentication algorithm.
Configure IKE negotiation parameters.
Configure the local ID and remote ID.
(Details not shown.)
# Initiate a connection from the host (1.1.1.1) to the device (2.2.2.2) to trigger IKE negotiation. (Details not shown.)
# On the device, verify that an IKE SA to the peer 1.1.1.1 is established and that extended authentication is enabled for remote users.
[Device] display ike sa verbose remote-address 1.1.1.1
-----------------------------------------------
Connection ID: 18
Outside VPN:
Inside VPN:
Profile: profile1
Transmitting entity: Initiator
Initiator cookie: 1bcf453f0a217259
Responder cookie: 5e32a74dfa66a0a4
-----------------------------------------------
Local IP/port: 2.2.2.2/500
Local ID type: IPV4_ADDR
Local ID: 2.2.2.2
Remote IP/port: 1.1.1.1/500
Remote ID type: IPV4_ADDR
Remote ID: 1.1.1.1
Authentication-method: PRE-SHARED-KEY
Authentication-algorithm: SHA1
Encryption-algorithm: DES-CBC
Life duration(sec): 86400
Remaining key duration(sec): 84565
Exchange-mode: Aggressive
Diffie-Hellman group: Group 1
NAT traversal: Detected
Extend authentication: Enabled
Assigned IP address:
Vendor ID index: 0xa1d
Vendor ID sequence number: 0x0
# On the host, enter the correct username and password for extended authentication. After the authentication succeeds, the IPsec tunnel will be established. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that IPsec SAs have been established on the device.
[Device] display ipsec sa
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
ipsec apply policy map1
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
#
security-zone name Trust
import interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
#
security-zone name Untrust
import interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
#
ip route-static 1.1.1.0 24 2.2.2.3
#
acl advanced 3101
rule 0 permit ip source 2.2.2.2 0 destination 1.1.1.1 0
#
radius scheme ike-scheme
primary authentication 3.3.3.48 1645
key authentication simple abc
user-name-format without-domain
#
domain ike
authentication ike radius-scheme ike-scheme
#
ipsec transform-set tran1
encapsulation-mode transport
protocol esp
esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
esp authentication-algorithm sha1
#
ipsec policy map1 10 isakmp
transform-set tran1
security acl 3101
remote-address 1.1.1.1
ike-profile profile1
#
ike profile profile1
keychain keychain1
local-identity address 2.2.2.2
match remote identity address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
client-authentication xauth
#
ike keychain keychain1
pre-shared-key address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 key simple 123456TESTplat&!
#
security-policy ip
rule 0 name ipseclocalout1
action pass
source-zone local
destination-zone untrust
source-ip-host 2.2.2.2
destination-ip-host 1.1.1.1
rule 1 name ipseclocalin1
action pass
source-zone untrust
destination-zone local
source-ip-host 1.1.1.1
destination-ip-host 2.2.2.2
rule 2 name ipseclocalout2
action pass
source-zone local
destination-zone trust
source-ip-host 3.3.3.3
destination-ip-host 3.3.3.48
rule 3 name ipseclocalin2
action pass
source-zone trust
destination-zone local
source-ip-host 3.3.3.48
destination-ip-host 3.3.3.3
#