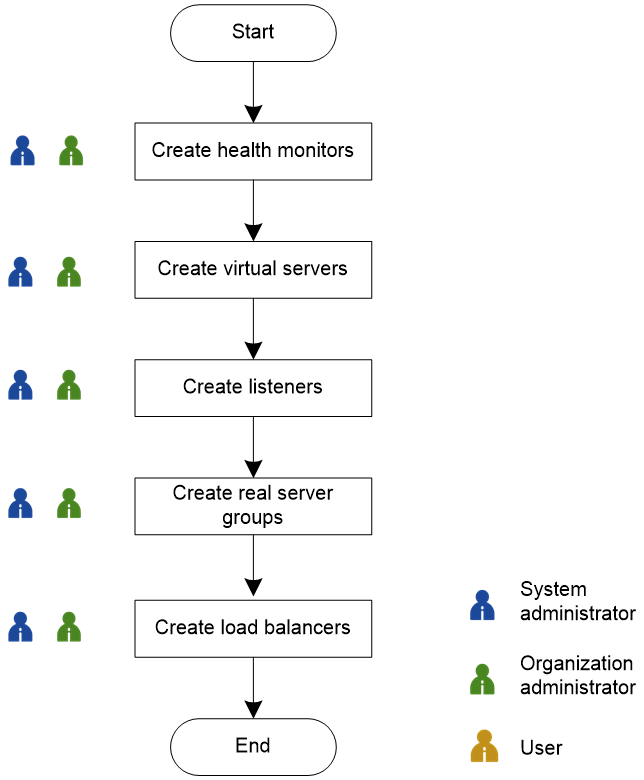
Manage service chain load balancers
Create a service chain LB instance
Perform this task to create an LB instance in a service chain. An LB instance can be a load balancer, virtual server, listener, real server group, or health monitor.
Prerequisites
Before you create a virtual server, first create the VPC, VPN of the VPC, and cloud hosts.
To access a load balancer in the public network, you must create and assign an elastic IP address to the load balancer.
Workflow
|
Task |
Description |
|
Create health monitors |
Health monitors are used for detecting the operating status of real servers. Multiple monitor methods are supported. |
|
Create virtual servers |
Virtual servers are virtual carriers of user services. A virtual server can be used by multiple listeners. Service requests (with different protocols and port numbers) matching different listeners can be processed by one virtual server. |
|
Create listeners |
Listeners listen to service requests received by the LB device. When a request matches the protocol, port number, and virtual server IP address configured for a listener, the LB device distributes the request to the associated virtual server. |
|
Create real server groups |
Multiple real servers with the same or similar functions can form a real server group. You can specify the common attributes for real server group members, such as LB method, health monitor method, and session persistence method. |
|
Create load balancers |
In this procedure, you can associate load balancers with listeners. |
Procedure
On the top navigation bar, click Cloud Services, and then select Load Balancing from the Network menu.
Click the Service Chain LB tab.
Perform the following tasks as needed:
To create a load balancer, select Load Balancer.
To create a virtual server, select Virtual Servers.
To create a listener, select Listener.
To create a real server group, select Real Server Groups.
To create a health monitor, select Health Monitors.
Click Create.
Configure the relevant parameters.
|
Operation |
Parameter |
Description |
|
Create a load balancer |
Resource |
Specify the resource where the load balancer resides. |
|
Listener |
Select listeners from the available
listener list, and then click If no available listeners exit, click Create to create a listener. |
|
|
Create a virtual server |
IP Version |
Select an IP version. Options are IPv4 and IPv6. |
|
Subnet |
Specify the subnet or VPN to which the virtual server belongs. |
|
|
Server IP |
Specify the virtual service IP address, which must belong to the specified subnet or VPN. |
|
|
Floating IP |
Optional. Specify an elastic IP address. To access the external network, you can configure this parameter. |
|
|
Create a listener |
IP Version |
Select an IP version. Options are IPv4 and IPv6. |
|
Virtual Servers |
Select one or more existing virtual servers. When a request matches the protocol, port number, and virtual server IP address configured for a listener, the LB device distributes the request to the associated virtual server. If no available virtual servers exist, click Add Virtual Server to add a virtual server. |
|
|
Protocol |
Select a protocol. Options are: · HTTP—An application layer protocol that supports cookie-based session persistence. This protocol is used for applications that recognize data contents, such as web applications and mobile games. · TCP—A protocol that supports source address-based session persistence. This protocol applies to scenarios that require high data accuracy, such as file transmission, email sending, and email receiving. · HTTPS—A protocol that encrypts and transmits data. |
|
|
SSL Key |
Specify the SSL key file. This field is required when the protocol is HTTPS. For more information about this parameter, see Creating a certificate. |
|
|
SSL Certificate |
Specify the SSL certificate file. This field is required when the protocol is HTTPS. For more information about this parameter, see Creating a certificate. |
|
|
Port Number |
Specify the monitored port by its number. |
|
|
Connection Limit |
Specify the maximum number of connections. The default setting 0 means not limited. |
|
|
Idle Timeout (Seconds) |
Specify the idle timeout time for TCP connections. If a client does not send a TCP packet to the server before the time expires, the TCP session ages. For F5 LB devices, you must configure this parameter. |
|
|
User Source Network Address Translation |
Specify whether to allow the virtual server to translate the source IP addresses of packets. |
|
|
X-Forwarded-For |
Specify whether to allow the virtual server to insert real source IP addresses of packets to the HTTP extended fields. |
|
|
State |
Specify whether to enable the listener. |
|
|
Default Real Server Farm |
Specify the monitored real server group. If no available real server groups exist, click Create Real Server Group to create a real server group. To edit a real server group, click Edit in the Actions column for it. |
|
|
Create a real server group |
LB Mode |
Select an LB mode. Options are ROUND_ROBIN, LEAST_CONNECTIONS, RANDOM, and SOURCE_IP. For more information about this parameter, see "Create a listener." |
|
Session Persistence |
Select a session persistence method. Options are APP_COOKIE, HTTP_COOKIE, and SOURCE_IP. For more information about this parameter, see "Create a listener." |
|
|
Cookie Name |
Specify the cookie name. This field is required when the session persistence method is APP_COOKIE. Make sure the cookie name matches that configured for the application on the back-end real server. |
|
|
Health Monitors |
Select health monitors from the available
health monitor list, and then click If no available health monitors exit, click Create to create a health monitor. |
|
|
Create a health monitor |
Monitor Method |
Specify the health monitor protocol. Options are PING, TCP, HTTP, and HTTPS. |
|
Delay (Seconds) |
Specify the probe interval. |
|
|
Timeout (Seconds) |
Specify the timeout time for the health monitor. If a health check is not completed before the timer expires, the check is considered timed out. |
|
|
Max Probes |
Specify the maximum number of consecutive probe failures. If this number is reached, the real server is excluded from load balancing services. |
|
|
Monitor Port |
Specify the port used by the listener to monitor back-end real servers. This field is required when the monitor method is TCP. |
|
|
HTTP |
Specify the HTTP method. In the current software version, only the GET option is available. This field is required when the monitor method is HTTP or HTTPS. |
|
|
URL |
Specify the URL for the health monitor to access the real server. You can configure this parameter when the monitor method is HTTP or HTTPS. |
|
|
Expected Status Codes |
Specify the expected status codes received upon access to the real server resources based on the specified URL. The status codes contain information about server status. You can configure this parameter when the monitor method is HTTP or HTTPS. |
|
|
Expected Response |
Specify the expected response content. If the response packet contains the expected response content, the member is valid. If the response packet does not contain the expected response content, the member is invalid. You can configure this parameter when the monitor method is HTTP or HTTPS. |
|
|
Response Packet Offset (Bytes) |
Specify the offset of the expected content in the response packets. If this parameter is 0, LB device performs content matching from the first byte of the response packets. If no match is found, the next byte is looked up. If this parameter is not 0, LB device performs content matching from the first byte after the offset. If no match is found, the LB device performs content matching from the first byte of the response packets. If no match is found again, the second byte is looked up. You can configure this parameter when the monitor method is HTTP or HTTPS. |
Click OK.
Edit a service chain LB instance
Perform this task to edit an LB instance in a service chain.
Restrictions and guidelines
When you edit a load balancer, you can edit its associated health monitors.
When you edit a virtual server, you can specify its floating IP address.
When you edit a listener, you can edit its connection limit, idle timeout time, as well as the enabling status for SNAT, XFF, and listener.
When you edit a real server group, you can edit its name, LB mode, session persistence method, and associated health monitors. You can also add or delete real servers for the real server group.
When you edit a health monitor, you can edit its probe delay, timeout time, maximum probes, HTTP method, URL, expected status codes, expected response content, and response packet offset.
Procedure
On the top navigation bar, click Cloud Services, and then select Load Balancing from the Network menu.
Click the Service Chain LB tab.
Perform the following tasks as needed:
To edit a load balancer, select Load Balancer.
To edit a virtual server, select Virtual Servers.
To edit a listener, select Listener.
To edit a real server group, select Real Server Groups.
To edit a health monitor, select Health Monitors.
Click Edit in the Actions column for the target entry.
Edit the relevant parameters as needed as described in "Parameters."
Click OK.
Delete service chain LB instances
Perform this task to delete LB instances in a service chain.
|
You can delete only service chain LB instances that are not being used. |
Procedure
On the top navigation bar, click Cloud Services, and then select Load Balancing from the Network menu.
Click the Service Chain LB tab.
Perform the following tasks as needed:
To delete load balancers, select Load Balancer.
To delete virtual servers, select Virtual Servers.
To delete listeners, select Listener.
To delete real server groups, select Real Server Groups.
To delete health monitors, select Health Monitors.
To delete one entry, click Delete in the Actions column for it. To delete multiple entries, select them and then click Delete.