URL filtering
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
URL filtering controls access to the Web resources by filtering the URLs that the users visit.
URL
A URL is a reference to a resource that specifies the location of the resource on a network and a mechanism for retrieving it. The syntax of a URL is protocol://hostname[:port]/path/[;parameters][?query]#fragment. Figure-1 shows an example URL.
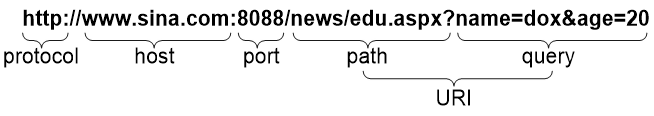
Table-1 describes the fields in a URL.
Table-1 URL field descriptions
Field | Description |
protocol | Transmission protocol, such as HTTP. |
host | Domain name or IP address of the server where the indicated resource is located. |
[:port] | Optional field that identifies the port number of the transmission protocol. If this field is omitted, the default port number of the protocol is used. |
/path/ | String that identifies the directory or file where the indicated resource is stored. The path is a sequence of segments separated by zero or multiple forward slashes. |
[parameters] | Optional field that contains special parameters. |
[?query] | Optional field that contains parameters to be passed to the software for querying dynamic webpages. Each parameter is a <key>=<value> pair. Different parameters are separated by an ampersand (&). |
URI | Uniform resource identifier that identifies a resource on a network. |
URL filtering rule
A URL filtering rule matches URLs based on the content in the URI or hostname field.
URL filtering provides the following types of URL filtering rules:
Predefined URL filtering rules —Signature-based URL filtering rules. The device automatically generates them based on the local URL filtering signatures. In most cases, the predefined rules are sufficient for URL filtering.User-defined URL filtering rules —Regular expression- or text-based URL filtering rules that are manfully configured. You can configure the hostname or URI field in a URL filtering rule. If you configure both the hostname and URI fields, a packet matches the URL filtering rule only when the packet matches both the hostname and URI fields.
A URL filtering rule supports the following URL matching methods:
T ext -based matching —Matches the hostname and URI fields of a URL against text patterns.When performing text-based matching for the hostname field of a URL, the device first determines if the text pattern contains the asterisk (*) wildcard character at the beginning or end.
If the text pattern does not contain the asterisk (*) wildcard character at the beginning or end, the hostname matching succeeds if the hostname of the URL matches the text pattern.
If the text pattern contains the asterisk (*) wildcard character at the beginning, the hostname matching succeeds if the hostname of the URL matches or ends with the text pattern without the wildcard character.
If the text pattern contains the asterisk (*) wildcard character at the end, the hostname matching succeeds if the hostname of the URL matches or starts with the text pattern without the wildcard character.
If the text pattern contains the asterisk (*) wildcard character at both the beginning and the end, the hostname matching succeeds if the hostname of the URL matches or includes the text pattern without the wildcard characters.
Text-based matching for the URI field works in the same way that text-based matching for the hostname field works.
Regular expression-based matching —Matches the hostname and URI fields of a URL against regular expressions. For example, if you set the regular expression for hostname matching tosina.*cn , URLs that carry thenews.sina.com.cn hostname will be matched.
URL category
URL filtering provides the URL categorization feature to facilitate filtering rule management.
You can classify multiple URL filtering rules to a URL category and specify an action for the category. If a matching rule is in multiple URL categories, the system takes the action for the category with the highest severity level. A greater value indicates a higher severity level.
URL filtering supports the following types of URL categories:
Predefined URL categories.
The predefined URL categories contain the predefined URL filtering rules. Each predefined URL category has a unique severity level in the range of 1 to 999, and a category name that begins
Pre -. Predefined URL categories cannot be modified.User-defined URL categories.
You can manually create URL categories and configure filtering rules for them. The severity level of a user-defined URL category is in the range of 1000 to 65535. You can edit the filtering rules and change the severity level for a user-defined URL category.
URL filtering profile
A URL filtering profile can contain multiple URL categories, and each category has an action defined for packets that match a filtering rule in the category. You can also specify the default action for packets that do not match any filtering rules in the profile.
URL filtering whitelist/blacklist rule
The device supports using URL-based whitelist and blacklist rules to filter HTTP packets. If the URL in an HTTP packet matches a blacklist rule, the packet is dropped. If the URL matches a whitelist rule, the packet is permitted to pass through. You can configure the hostname or URI field in a URL filtering rule. If you configure both the hostname and URI fields, a packet matches the URL filtering rule only when the packet matches both the hostname and URI fields.
URL filtering cloud query
You can enable cloud query in a URL filtering profile to improve URL filtering accuracy for HTTP traffic.
With cloud query enabled, the device will send URLs that do not match any local URL filtering rules to the cloud server for further query. The device determines the action to apply according to the query result returned from the cloud server.
If a matching rule is found for the URL, the action specified for the URL category to which the rule belongs apply. If the rule belongs to multiple URL categories, the action specified for the category with the highest severity level apply.
If no matching rule is found, the device executes the default action of the URL filtering profile on the packet. If the default action is not configured, the device permits the packet to pass through.
Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) is a security protocol designed to protect datagram protocols. It is suitable for low-delay scenarios such as real-time communication (VoIP, video conferencing), IoT devices (wireless sensor networks), and streaming services.
HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is a protocol for transmitting hypertext data via a secure communication channel. It is suitable for scenarios requiring secure data transfer, such as online banking, social media platforms, email services, and Web applications that require user authentication and data encryption.
URL filtering action
You can specify URL filtering actions for URL categories and specify the default action for a URL filtering profile.
The device supports the following URL filtering actions:
Blacklist —Drops matching packets and adds the sources of the packets to the IP blacklist. If the IP blacklist feature is enabled, packets from the blacklisted sources will be blocked for the blacklist period. If the IP blacklist feature is not enabled, packets from the blacklisted sources are not blocked.For more information about the IP blacklist feature, see the attack defense online help.
To configure the blacklist period for the blacklist action, go to
Object >APP Security >Security Actions >Block .Permit —Permits matching packets to pass.Redirect —Redirects matching packets to a webpage.Reset —Closes the TCP connections for matching packets by sending TCP reset messages.L ogging —Logs matching packets. This action takes effect only after the logging function is enabled in the URL filtering profile.
URL filtering mechanism
URL filtering takes effect after you apply a URL filtering profile to a security policy rule.
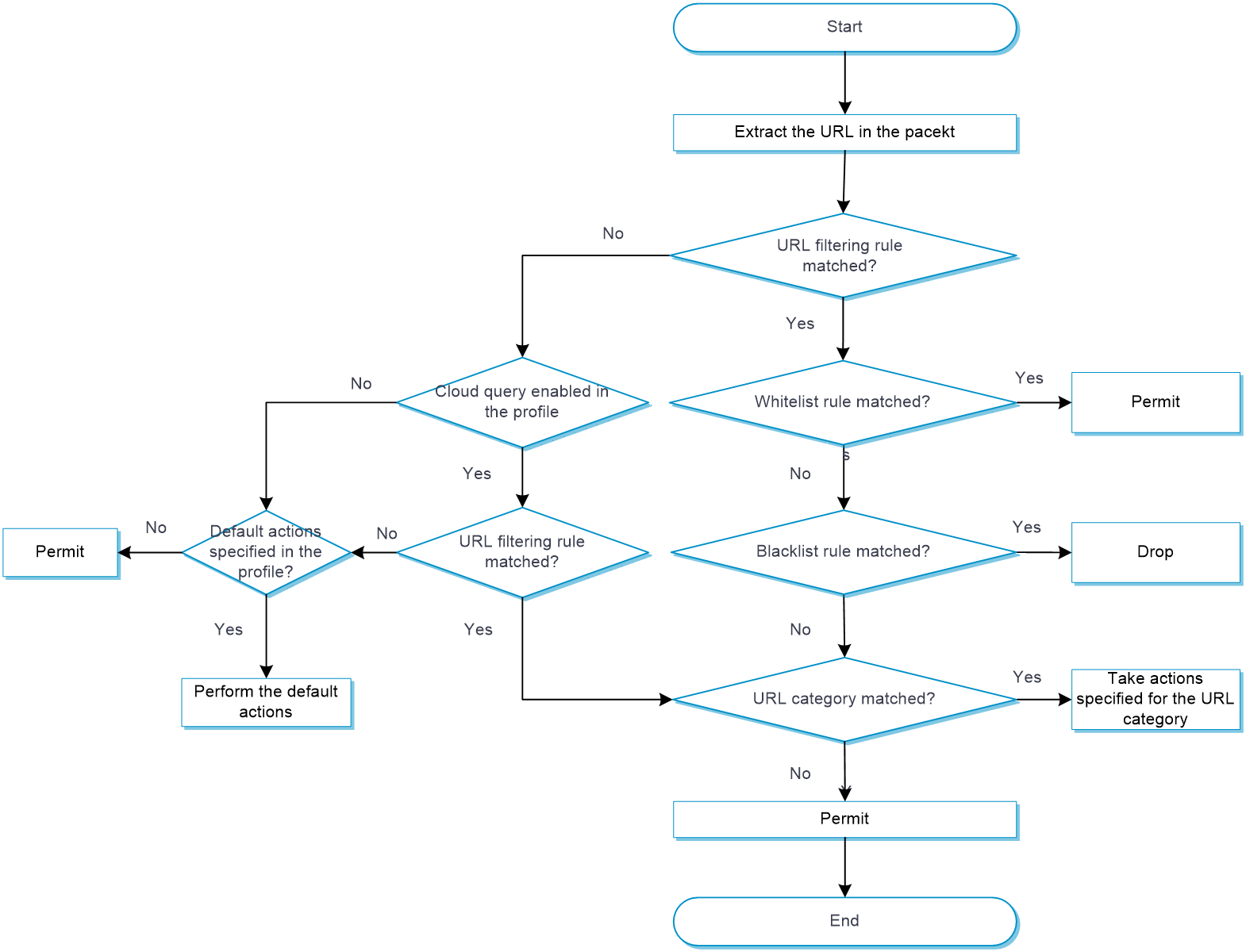
As shown in Figure-2, upon receiving an HTTP packet, the device performs the following operations:
The device compares the packet with the security policies.
If the packet matches a security policy that is associated with a URL filtering profile, the device extracts the URL from the packet.
The device compares the extracted URL with the whitelist and blacklist rules in the URL filtering profile.
If the URL matches a whitelist rule, the packet is permitted to pass through.
If the URL matches a blacklist rule, the packet is dropped.
If the URL does not match any whitelist or blacklist rule in the profile, the device performs step 3.
The device compares the extracted URL with the URL filtering rules in the URL filtering profile.
If the URL matches a URL filtering rule that belongs to a user-defined URL category, the devices takes the action specified for the URL category.
If the URL filtering rule belongs to multiple user-defined URL categories, the action specified for the URL category with the highest severity level apply.
If URL reputation is enabled, the device determines whether the matching URL filtering rule belongs to an attack category in the URL reputation signature library. If yes, the device takes the action specified for the attack category on the packet.
If the URL matches a URL filtering rule that belongs to a predefined URL category, the devices takes the action specified for the URL category.
If the URL filtering rule belongs to multiple predefined URL categories, the action specified for the URL category with the highest severity level apply.
If the URL does not match any rule in the policy, and cloud query is disabled in the profile, the default action specified for the policy applies. If the default action is not configured, the device permits the packet to pass through.
If the URL does not match any rule in the policy, and cloud query is enabled in the policy, the device performs step 4.
The device forwards the URL to the cloud server for further query.
If a matching rule is found for the URL, the device determines the action to take on the packet as described in step 3.
If no matching rule is found, the device executes the default action of the policy on the packet. If the default action is not configured, the device permits the packet to pass through.
Figure-2 URL filtering mechanism
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Licensing requirements
To use URL filtering, you must purchase and install the required license. If the license expires, the existing URL filtering signature library is still available but you cannot upgrade the library on the device or perform a URL filtering cloud query task. For more information about licensing, see the license management online help.
Restrictions and guidelines
Restrictions and guidelines: Configuration submission
Clicking
Submit to submit configuration causes transient DPI service interruption. DPI-based services might also be interrupted. For example, security policies cannot control access to applications.After you submit the configuration, the system prompts
Configuration succeeded . However, the configuration might not have been activated completely. The device cannot recognize packets as expected before the activation completes.
Restrictions and guidelines: Text-based URL filtering rule configuration
Follow these guidelines when you use the asterisk character (*) in the text pattern for hostname or URI matching:
For hostname matching, the asterisk (*) can appear only at the beginning or end of the text pattern as a wildcard character to match zero or more characters.
For URI matching, the asterisk (*) can appear at the beginning or end of the text pattern as a wildcard character to match zero or more characters, or appear in the middle as a non-wildcard character.
Restrictions and guidelines: Regular expression-based URL filtering rule configuration
The regular expression pattern can contain a maximum of four branches. For example,
'abc(c|d|e|\x3D)' is valid, and'abc(c|onreset|onselect|onchange|style\x3D)' is invalid.Nested braces are not allowed. For example,
'ab((abcs*?))' is invalid.A branch cannot be specified after another branch. For example,
'ab(a|b)(c|d)^\\r\\n]+?' is invalid.A minimum of four non-wildcard characters must exist before an asterisk (
* ) or question mark (?). For example,'abc*' is invalid and'abcd*DoS\x2d\d{5}\x20\x2bxi\\r\\nJOIN' is valid.
Restrictions and guidelines: Whitelist
If a packet matches a whitelist rule, the
URL Category column in the URL filtering log list displaysWhitelist .If the referer header of an HTTP request matches the URL filtering whitelist, the
URL C ategory column in the URL filtering log list displaysReferer Whitelist .With whitelist mode enabled, if a packet fails to match any whitelist rules, the
URL C ategory column in the URL filtering log list displaysBlacklist .If whitelist mode is enabled, the device supports outputting URL filtering logs only as fast logs instead of system logs. For more information about URL filtering logs, see the basic log settings online help.
Restrictions and guidelines: URL filtering cloud query
Support for URL filtering cloud query depends on the device model.
Configure URL filtering
Analysis
Configure URL filtering as shown in Figure-3.
Figure-3 URL filtering configuration procedure
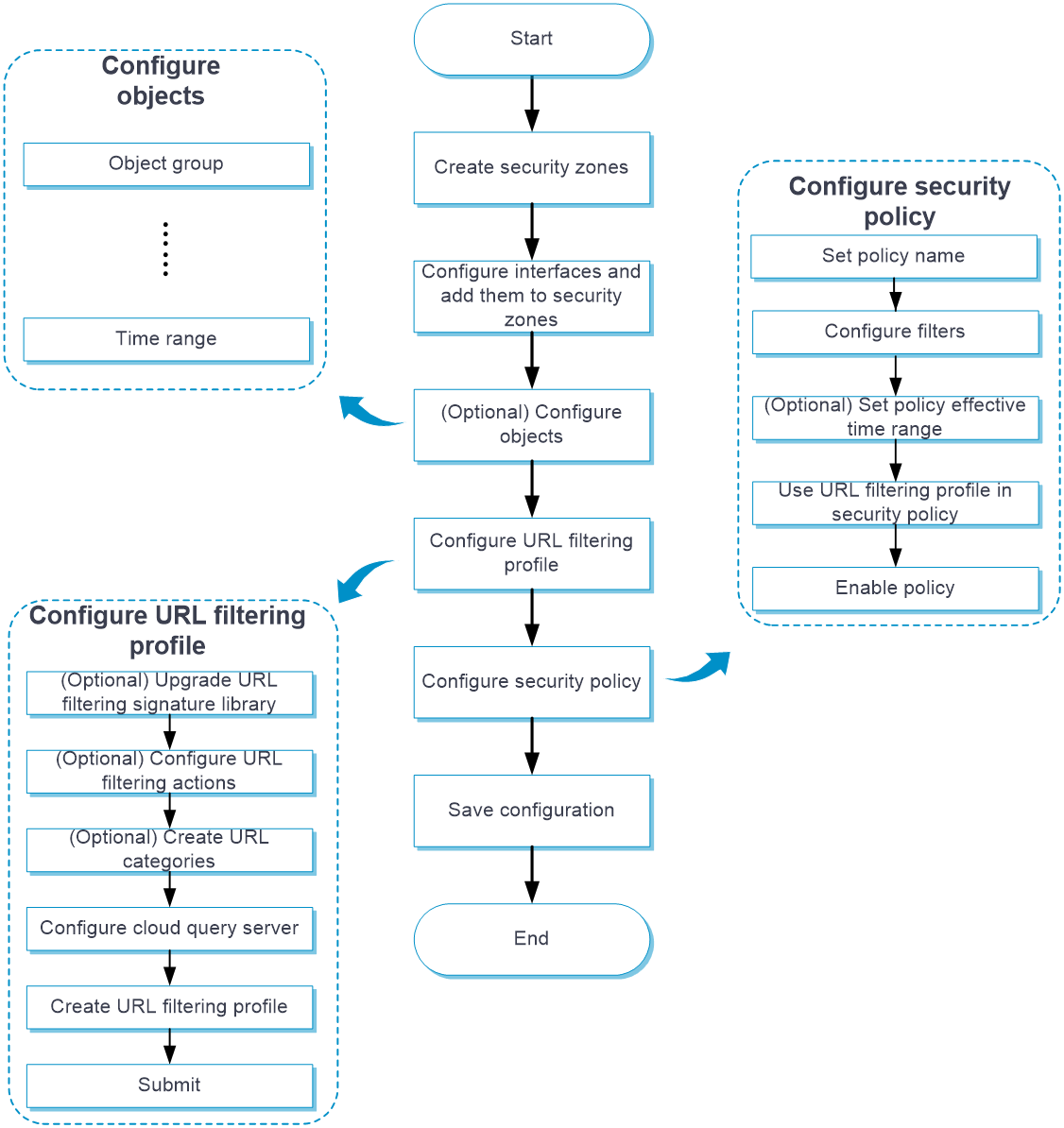
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Assign IP addresses to interfaces on the
Network >Interface Configuration >Interfaces page.Configure routes on the
Network >Routing page. Make sure the routes are available.Create security zones on the
Network >Security Zones page.Add interfaces to security zones. You can add interfaces to a security zone on the
Security Zones page or select a security zone for an interface on theInterfaces page.Configure security policies to permit the target traffic on the
Policies >Security Policies page.
Quickly configure URL filtering
You can configure the following settings in a URL filtering profile:
Enable cloud query.
Specify the default action for packets that do not match any URL filtering rule.
Configure whitelist and blacklist rules. The whitelist rules take precedence over the blacklist rules.
Specify actions for URL categories.
A URL filtering profile contains all URL categories on the device. You can specify the actions for individual URL categories in the URL filtering profile. If an HTTP packet matches a URL filtering rule in a URL category, the action specified for the category applies to the packet. If the matching rule is in multiple URL categories, the action specified for the category with the highest severity level is taken.
Procedure
Click the
Object tab.In the navigation pane, select
APP Security >URL Filtering >URL Categories .Click
Create .Create a URL filtering profile.
Figure-4 Configuring a URL filtering profile
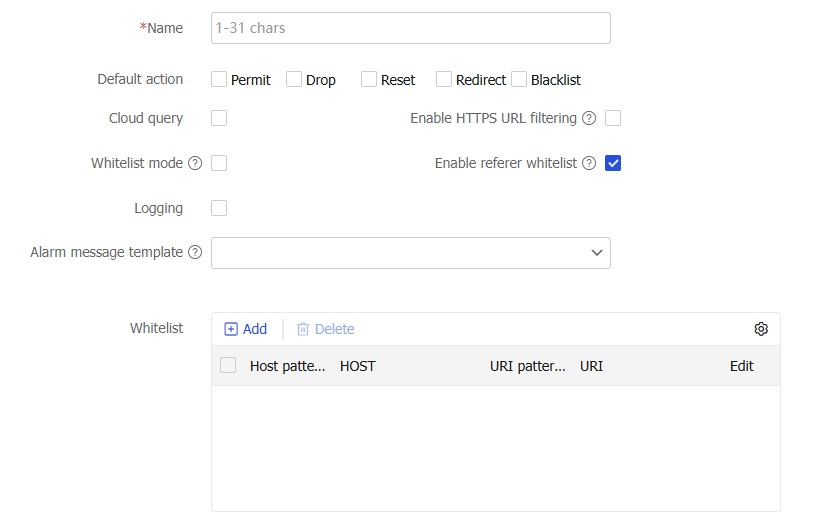
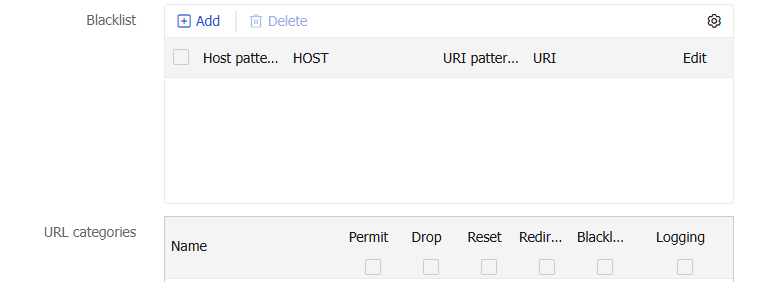

Table-2 URL filtering profile configuration items
Item
Description
Name
Enter a name for the URL filtering profile.
Default action
Select the default action to take on packets that do not match any URL filtering rules. Options are
Permit ,Drop ,Reset ,Redirect , andBlacklist .Cloud query
Select the box to enable cloud query.
Logging
Select the box to enable logging for packets matching URL filtering rules.
Before you select this item, configure the default action first.
Alarm message template
Select an alarm template. This template enables the device to send an alarm message to a client when the URL requested by the client is blocked by URL filtering.
For more information about the template configuration, see security actions.
Enable HTTPS URL filtering
Select the box to enable URL filtering on undecrypted HTTPS traffic.
If the SSL decryption action is selected in any enabled proxy policy, this feature does not take effect. For more information about SSL decryption, see proxy policies.
Enable referer whitelist
Select the box to allow an HTTP request to pass if its referer header matches the URL filtering whitelist.
Whitelist mode
Select the box to allow users to access the websites in the URL filtering whitelist only.
Whitelist
Add whitelist rules to the URL filtering profile as needed.
To add a whitelist rule to the URL filtering profile:
In the
Whitelist area, clickAdd .The
Add Whitelist Rule window opens.From the
Match pattern list, select the match pattern type for the host name field. Options areText andRegular expression .Enter the match pattern for the host name field.
From the
Match pattern list, select the match pattern type for theURI field. Options areText ,Regular expression , and–NONE— .Enter the match pattern for the URI
–NONE— option is selected for the match pattern of the URI field.
Blacklist
Add blacklist rules to the URL filtering profile as needed.
URL categories
In the
URL categories area, select the actions for individual URL categories. Supported actions arePermit ,Drop ,Reset ,Redirect ,Blacklist , andLogging .Before you select the logging action for a URL category, select an action among the
Permit ,Drop ,Reset ,Redirect , andBlacklist actions first.Enable URL reputation
Select the box to enable URL reputation to block access to malicious URLs. With this feature enabled, the device will compare the URL extracted from a packet with the URLs in the URL reputation signature library. If a match is found, the URL is considered a malicious URL and the actions specified for the attack category where the matching URL belongs will be taken. If no match is found, the device permits the packet to pass through.
Action configuration
Configure the actions for individual attack categories in the URL reputation signature library.
Click
OK .The URL filtering profile is displayed on the
URL Filtering Profiles page.Use the URL filtering profile in a security policy.
For more information about security policies, see security policies.
Figure-5 Using the URL filtering profile in a security policy

To have the configuration activated, click
Submit .This operation can cause temporary DPI service outage. As a best practice, perform the operation after all DPI service configurations are complete.
Configure a URL category
Perform this task to create a user-defined URL category and configure filtering rules to meet specific URL filtering requirements.
Procedure
Click the
Object tab.In the navigation pane, select
APP Security >URL Filtering >URL Categories .Click
Create .Create a URL category.
Figure-6 Creating a URL category
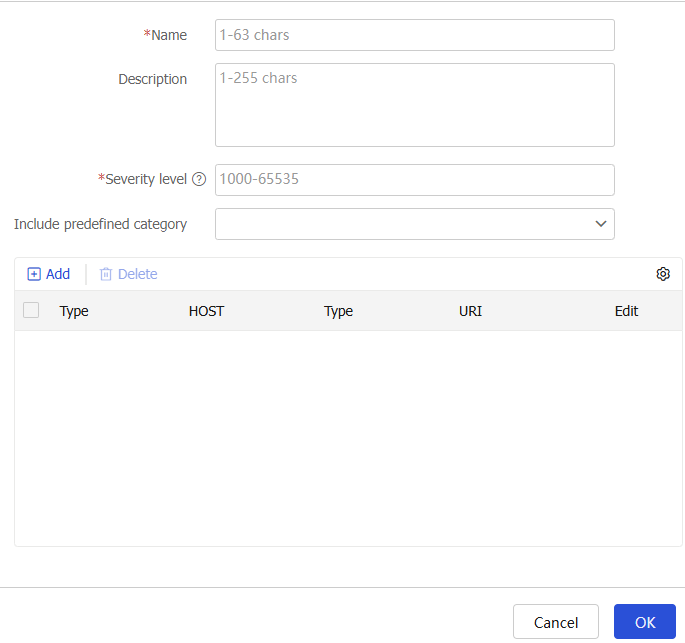
Table-3 URL category configuration items
Item
Description
Name
Enter a name for the URL category. The category name cannot start with
Pre - .Description
Enter a description for the URL category.
Severity level
Assign a unique severity level in the range of 1000 to 65535 to the URL category. The larger the value, the higher the severity level.
Include predefined category
Select a predefined URL category to add all its rules to the URL category.
Add URL filtering rules to the URL category:
Click
Add .From the
Match pattern list, select the match pattern type for the host name field. Options areText andRegular expression .Enter the match pattern for the host name field.
From the
Match pattern list, select the match pattern type for the URI field. Options areText ,Regular expression , and–NONE— .Enter the match pattern for the URI
–NONE— Click
OK .Repeat the preceding steps to add more URL filtering rules.
Figure-7 Adding a URL filtering rule
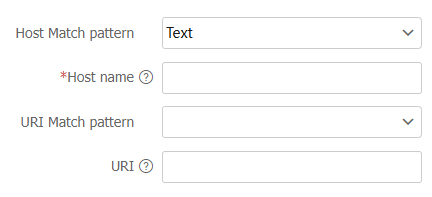
Click
OK .The URL category is displayed on the
URL Categories page.
Configure the cloud query server
Enabling URL filtering cloud query in a URL filtering profile allows the device to more accurately identify HTTP packets and control the packets more precisely.
URL filtering rules learned from the cloud server are cached in the device's URL filtering cache for message matching. You can adjust the upper limit of URL filtering cache records and the minimum retaining time for rules as needed.
To configure the cloud query server for URL filtering:
Click the
Object tab.In the navigation pane, select
APP Security >URL Filtering >URL Categories .Click
Configure next to theCloud server connection status field.Configure the cloud query server.
Figure-8 Configuring the cloud query server
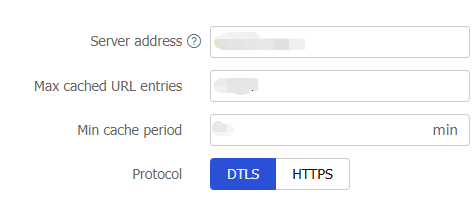
Table-4 Cloud query server configuration items
Item
Description
Server address
Enter the IP address or hostname of the cloud query server. Only the cloud query server of our company is supported.
Max cached URL entries
Specify the maximum number of URL entries that can be cached.
The device creates a URL cache entry for each unique URL submitted to the cloud query server for cloud query. The cloud query result will be stored in the cache entry.
Min cache period
Specify the minimum cache period for a URL cache entry in minutes.
Setting the minimum cache period for URL cache entries ensures that the entries will not be deleted during the specified period of time.
When the URL filtering cache is full, the system identifies the cache period of the oldest URL cache entry to determine whether to overwrite it:
If the cache period of the entry is equal to or less than the minimum cache period, the system does not delete the entry. The new entry is not cached.
If the cache period of the entry is greater than the minimum cache period, the system overwrites the entry with the new entry.
However, if the configured maximum number of cached URL entries is less than that of the currently cached entries, the system will delete the oldest cache entries even if their cache periods are equal to or less than the minimum cache period.
Protocol
Protocol for the cloud server, including:
DTLS —Suitable for low-delay scenarios such as real-time communication (VoIP, video conferencing), IoT devices (wireless sensor networks), and streaming services.HTTPS —Suitable for scenarios requiring secure data transfer, such as online banking, social media platforms, email services, and Web applications that require user authentication and data encryption.
Configure Proxy Server
Configure the proxy server's address, port, and the username and password for logging in to the proxy server. This field is available only when the cloud server protocol is HTTPS.
Click
OK .