SNMP
Introduction
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is used for a management station to access and operate the devices on a network, regardless of their vendors, physical characteristics, and interconnect technologies.
SNMP enables network administrators to read and set the variables on managed devices for state monitoring, troubleshooting, statistics collection, and other management purposes.
SNMP framework
The SNMP framework contains the following elements:
SNMP manager —Works on an NMS to monitor and manage the SNMP-capable devices in the network.SNMP agent —Works on a managed device to receive and handle requests from the NMS, and sends notifications to the NMS when events, such as an interface state change, occur.Management Information Base (MIB) —Specifies the variables (for example, interface status and CPU usage) maintained by the SNMP agent for the SNMP manager to read and set.
SNMP versions
The device supports SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3. For an NMS and an SNMP agent to establish an SNMP connection, they must use the same SNMP version.
SNMPv1 —Uses community names for authentication. To access an SNMP agent, an NMS must use the same community name as set on the SNMP agent. If the community name used by the NMS differs from the community name set on the agent, the NMS cannot establish an SNMP session to access the agent or receive traps from the agent.SNMPv2c —Uses community names for authentication. SNMPv2c is compatible with SNMPv1, but supports more operation types, data types, and error codes.SNMPv3 —Uses a user-based security model (USM) to secure SNMP communication. You can configure authentication and privacy mechanisms to authenticate and encrypt SNMP packets for integrity, authenticity, and confidentiality.
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Configure SNMP
Analysis
Configure a security policy as shown in the following figure:
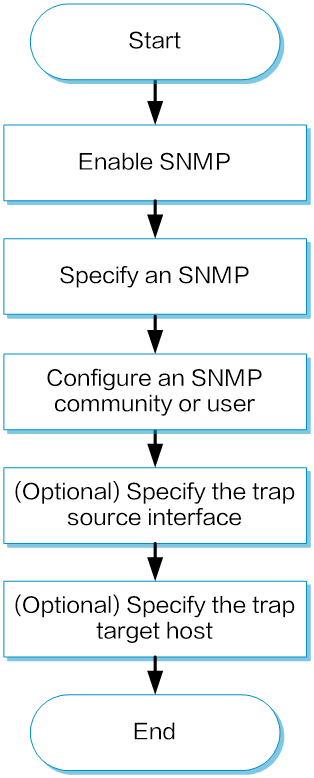
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Assign IP addresses to interfaces on the
Network >Interface Configuration >Interfaces page.Configure routes on the
Network >Routing page. Make sure the routes are available.Create security zones on the
Network >Security Zones page.Add interfaces to security zones. You can add interfaces to a security zone on the
Security Zones page or select a security zone for an interface on theInterfaces page.Configure security policies to permit the target traffic on the
Policies >Security Policies page.
Configure SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c settings
SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c are configured in the same way.
Click the
System tab.In the navigation pane, select
Maintenance >SNMP .Enable SNMP.
Figure-1 Enabling SNMP
Select one or multiple SNMP versions and set the common settings for the versions as described in the following table.
Figure-2 Configuring global settings
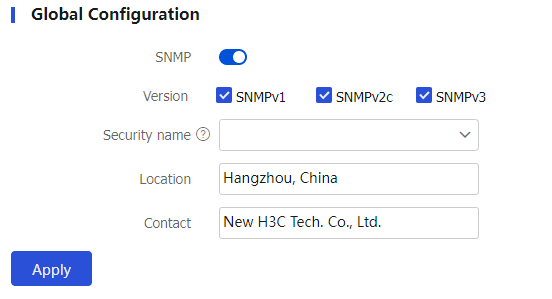
Table-1 Configuration items for SNMP versions and their common settings
Item
Description
Version
Specify SNMP versions. Options are:
SNMPv1
SNMPv2c
SNMPv3
The device can receive packets of an SNMP version only after you specify that SNMP version. For an NMS and device to communicate, they must use the same SNMP version. If settings of multiple SNMP versions take effect, the device and NMS will negotiate for an SNMP version to communicate.
The community name and data carried in SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c packets are in plaintext form, which has security risks. As a best practice, uses SNMPv3.
To use SNMP notifications in an IPv6 environment, specify SNMPv2c or SNMPv3.
Trap source interface
Select an interface as the source interface of traps. The system will use the primary IP address of that interface as the source IP of traps. The NMS will use that IP address to identify the agent. Even if the agent sends traps from multiple interfaces, the NMS can use that IP address to filter all traps from the agent.
If the specified interface is configured with a valid IP address, the device will use that IP as the source IP of traps. This configuration does not take effect if the specified interface is not configured with a valid IP address, and will take effect automatically after the interface is configured with a valid IP.
Location
Enter physical location of the device.
For the device to be easily identified and managed, configure this parameter to record the physical location of the device on the device.
Contact
Enter contact information of the device.
This information helps the maintenance personnel to contact the device vendor in time when the device fails.
Click
Apply for the SNMP versions and their common settings to take effect.Select SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c.
Figure-3 Configuring SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c settings
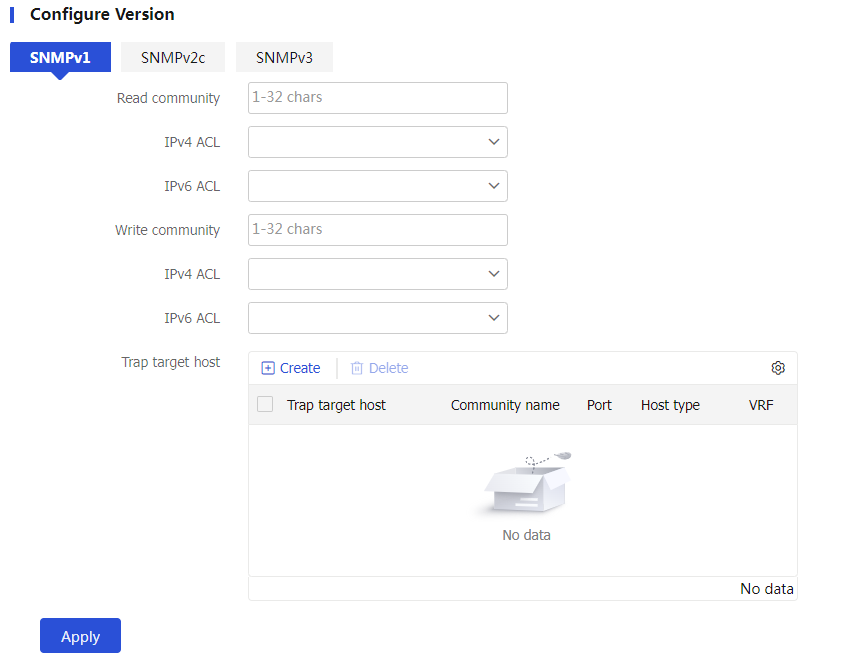
Table-2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c configuration items
Item
Description
Read community
SNMP read community name, case sensitive. Using this community name, the NMS has only read access to the MIB objects on the agent.
You can also specify escape characters (a backslash \ followed by characters) as the read community name.
Write community
SNMP read-write community name, case sensitive. Using this community name, the NMS has read and write access to the MIB objects on the agent.
You can also specify escape characters (a backslash \ followed by characters) as the read-write community name.
Trap target host
Create the trap target host. You can configure multiple trap target hosts as required for the device to send traps to multiple NMSs.
Host type . Options are:IPv4 or IPv6 address : Specify a target host by its IPv4 or IPv6 addressIPv4 host : Specify a target host by its host name. The device will use the IPv4 address of the host to send traps to the target host.IPv6 host : Specify a target host by its host name. The device will use the IPv6 address of the host to send traps to the target host.
Trap target host : IP address or host name of the target host. If you specify an IPv6 address, it cannot be a link local address. If you specify a host name, the host name is case insensitive and can contain only letters, digits, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and dots (.).Community name : SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c community name, which will be used as the authentication parameter for the trap target host.Port : Port number uses for the target host to receive the traps.
Click
Apply for the SNMP settings to take effect.
Configure SNMPv3 settings
Set the common settings for the versions as described in Table-1.
Click
Apply for the SNMP settings to take effect.Select SNMPv3 and configure the settings as required.
Figure-4 Configuring SNMPv3 settings
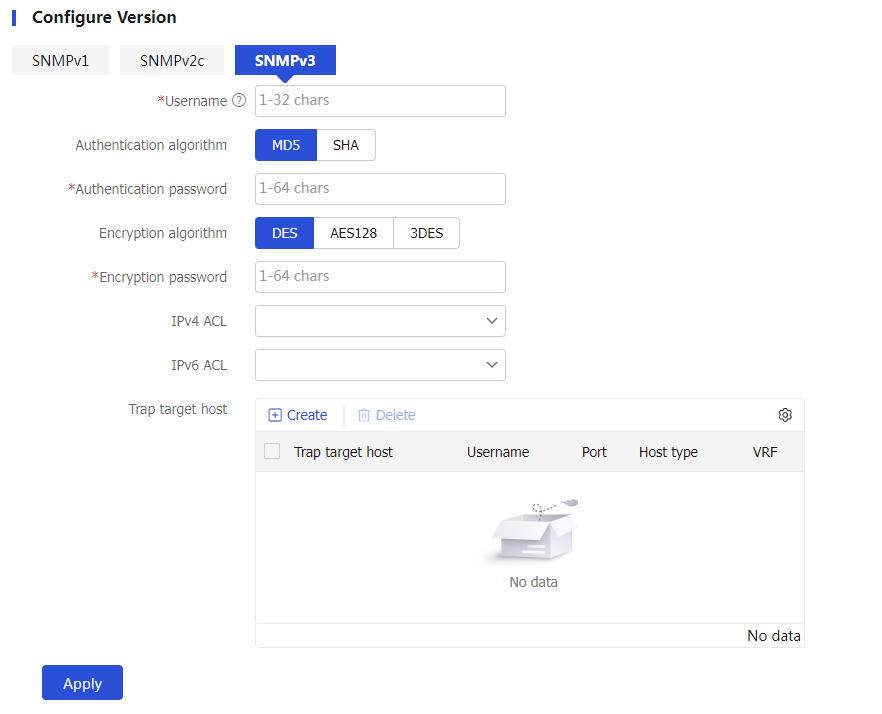
Table-3 SNMPv3 configuration items
Item
Description
Username
SNMPv3 username, case sensitive.
If the username changes, you must reconfigure the authentication and encryption passwords.
Authentication algorithm
Select an SNMPv3 authentication algorithm. Options are:
MD5 : HMAC-MD5 algorithm.SHA : HMAC-SHA1 algorithm.
Authentication password
Set an authentication password, which is case sensitive.
For the device and NMS to establish an SNMP connection, the device and NMS must use the same authentication password.
Encryption algorithm
Select an SNMPv3 encryption algorithm. Options are:
DES : Data Encryption Standard algorithm that uses a 56-bit key.AES128 : Advanced Encryption Standard algorithm that uses a 128-bit key.3DES : Triple Data Encryption Standard algorithm that uses a 168-bit key.
Encryption password
Set an encryption password, which is case sensitive.
For the device and NMS to establish an SNMP connection, the device and NMS must use the same encryption password.
Trap target host
Create the trap target host. You can configure multiple trap target hosts as required for the device to send traps to multiple NMSs.
Host type . Options are:IPv4 or IPv6 address : Specify a target host by its IPv4 or IPv6 addressIPv4 host : Specify a target host by its host name. The device will use the IPv4 address of the host to send traps to the target host.IPv6 host : Specify a target host by its host name. The device will use the IPv6 address of the host to send traps to the target host.
Trap target host : IP address or host name of the target host. If you specify an IPv6 address, it cannot be a link local address. If you specify a host name, the host name is case insensitive and can contain only letters, digits, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and dots (.).Username : SNMPv3 username, which will be used as the authentication parameter for the trap target host.Port : Port number uses for the target host to receive the traps.
Click
Apply for the SNMP settings to take effect.