Packet capture
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
The packet capture feature captures incoming and outgoing packets, generates packet capture records, and saves the records to a .cap file. The file can reside on the device or a remote file server. You can use a packet analyzer such as Wireshark to view the file for traffic analysis.
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Restrictions and guidelines
Only one packet capture process can run on the device.
You can configure packet capture parameters only when packet capture is not started.
Start packet capture only when necessary. Packet capture affects device performance.
If packet capture saves .cap files on the device, back up the .cap files on the device as required after you finish packet capture. Starting packet capture again deletes the existing .cap files.
Packet capture is not supported on non-default contexts that use their own respective interfaces. For more information about contexts, see "Contexts."
To capture packets of non-default contexts that share interfaces, you must start packet capture on the default context.
Before starting packet capture for a context, you must configure flow mirroring at the CLI to mirror the packets to the main security engine of the security engine group to which the context belongs. For more information about flow mirroring, see flow mirroring configuration in Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Perform packet capture
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Assign IP addresses to interfaces on the Network > Interface Configuration > Interfaces page.
Configure routes on the Network > Routing page. Make sure the routes are available.
Create security zones on the Network > Security Zones page.
Add interfaces to security zones. You can add interfaces to a security zone on the Security Zones page or select a security zone for an interface on the Interfaces page.
Configure security policies to permit the target traffic on the Policies > Security Policies page.
Start packet capture
By capturing network packets, you can quickly identify the causes of network failures, analyze performance bottlenecks, and monitor and audit traffic to ensure network security.
Select System > Diagnosis Center > Packet Capture.
Click Start packet capture.
Figure-1 Configuring packet capture filters
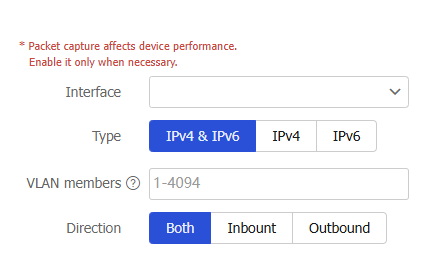
Configure filters as shown in Table-1.
Table-1 Configuration items for setting filters
Item
Description
Interface
Specify the interface on which packets are to be captured.
Type
Specify the type of packets to capture:
IPv4 & IPv6—Capture all packets.
IPv4—Capture packets that match the specified IPv4 advanced ACL.
IPv6—Capture packets that match the specified IPv6 advanced ACL.
ACL
Specify an advanced ACL to match the packets of interest.
VLAN members
Capture packets in the specified VLANs.
Direction
Specify the direction of packets to be captured. Options:
Both—Capture packets received and sent by the device.
Inbound—Capture packets received by the device.
Outbound—Capture packets sent by the device.
Click Start.
On the Packet Capture page, the Packet Capture Status field displays Started.
To stop packet capture, click Stop packet capture.
Figure-2 Stopping packet capture

The Packet Capture Status field displays Stopped. The bottom pane displays information about generated .cap files.
Configure packet capture settings
The system first saves packet capture records to memory. After the maximum number of packet capture records for a file is reached, the system saves the records to a file and clears the records in memory. The file can be saved locally or saved to an FTP or TFTP server.
Select System > Diagnosis Center > Packet Capture.
Click Set packet capture parameters.
Figure-3 Configuring packet capture parameters
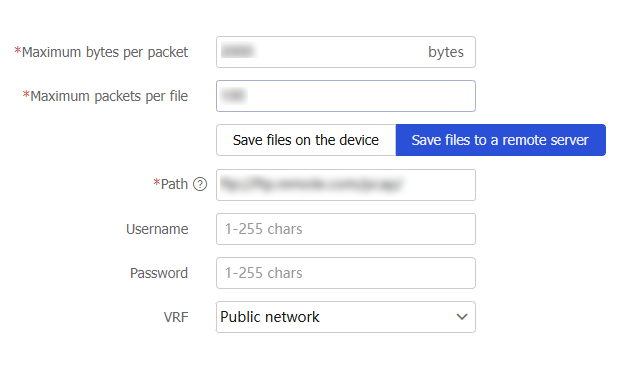
Configure packet capture parameters as shown in Table-2:
Table-2 Packet capture configuration items
Item
Description
Maximum bytes per packet
Specify the maximum number of bytes for a capture record.
If a packet is longer than the value of this item, the system truncates the packet.
Maximum packets per file
Specify the maximum number of packet capture records for a .cap file.
The system first saves packet capture records to memory. After the maximum number of packet capture records for a file is reached, the system saves the records to a file and clears the records in memory.
A greater value for this item requires more memory space. If the available memory space is limited, decrease the value.
Save files on the device
Save the .cap files on the device.
If you select this option, you can set the Maximum storage space item to specify the maximum storage space for .cap files. After the maximum storage space is reached, the system stops capturing packets.
Save files to a remote server
Save the .cap files to an FTP or TFTP server. To save .cap files to an FTP server, you must configure the username and password for accessing the FTP server.
VRF
VRF to which the FTP or TFTP server belongs.
Click OK.