MAC
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
An Ethernet device uses a MAC address table to forward frames. A MAC address entry includes a destination MAC address, an outgoing interface, and a VLAN ID. When the device receives a frame, it uses the destination MAC address of the frame to look for a match in the MAC address table.
The device forwards the frame out of the outgoing interface in the matching entry if a match is found.
The device floods the frame in the VLAN of the frame if no match is found.
Types of MAC address entries
A MAC address table can contain the following types of entries:
Dynamic entries —A dynamic entry can be manually configured or dynamically learned to forward frames with a specific destination MAC address out of the associated interface. A dynamic entry can age out. A manually configured dynamic entry has the same priority as a dynamically learned one.Static entries —A static entry is manually added to forward frames with a specific destination MAC address out of the associated interface, and it never ages out. A static entry has higher priority than a dynamically learned one.Blackhole entries —A blackhole entry is manually configured and never ages out. A blackhole entry is configured for filtering out frames with a specific source or destination MAC address. For example, to block all frames destined for or sourced from a user, you can configure the MAC address of the user as a blackhole MAC address entry.
Aging timer for dynamic MAC address entries
For security and efficient use of table space, the MAC address table uses an aging timer for dynamic entries learned on all interfaces. If a dynamic MAC address entry is not updated before the aging timer expires, the device deletes the entry. This aging mechanism ensures that the MAC address table can promptly update to accommodate latest network topology changes.
A stable network requires a longer aging interval, and an unstable network requires a shorter aging interval.
An aging interval that is too long might cause the MAC address table to retain outdated entries. As a result, the MAC address table resources might be exhausted, and the MAC address table might fail to update its entries to accommodate the latest network changes.
An interval that is too short might result in removal of valid entries, which would cause unnecessary floods and possibly affect the device performance.
To reduce floods on a stable network, set a long aging timer or disable the timer to prevent dynamic entries from unnecessarily aging out. Reducing floods improves the network performance. Reducing flooding also improves the security because it reduces the chances for a data frame to reach unintended destinations.
MAC address learning
MAC address learning is enabled by default. To prevent the MAC address table from being saturated when the device is experiencing attacks, disable MAC address learning. For example, you can disable MAC address learning to prevent the device from being attacked by a large amount of frames with different source MAC addresses.
When global MAC address learning is enabled, you can disable MAC address learning on a single interface.
You can also configure the MAC learning limit on an interface to limit the MAC address table size. A large MAC address table will degrade forwarding performance. When the limit is reached, the interface stops learning any MAC addresses. You can also configure whether to forward frames whose source MAC address is not in the MAC address table.
VLAN ID check
This feature enables the device to check the VLAN ID of each packet that matches a session entry during Layer 2 forwarding.
With VLAN ID check enabled, the device permits a packet only if its VLAN ID is the same as the VLAN ID in the matching session entry.
With VLAN ID check disabled, the device permits a packet if it matches a session entry.
On a hot backup system, you must disable VLAN ID check if the traffic incoming interfaces on the primary and secondary devices belong to different VLANs. If you enable VLAN ID check, traffic cannot match session entries correctly after a primary/secondary device switchover occurs or when asymmetric-path traffic exists.
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure MAC address entries, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
The manually configured static and blackhole MAC address entries cannot survive a reboot if you do not save the configuration.
The manually configured dynamic MAC address entries are lost upon reboot whether or not you save the configuration.
Configure MAC address entries
A MAC address entry records the interface and VLAN to a MAC address belongs. Supported MAC address entry types include
Click the
Network tab.In the navigation pane, select
Links >MAC > MAC Address Entries .Click
Create .Figure-1 Creating a MAC address entry
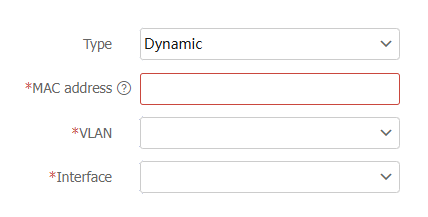
Configure parameters for the MAC address entry.
Table-1 MAC address entry configuration items
Item
Description
Type
Select the type of the MAC address entry. Options include:
Dynamic .Static .Blackhole .
MAC address
Specify a MAC address in the format of H-H-H. You cannot specify a multicast MAC address, an all-zero MAC address, or an all-F MAC address.
VLAN
Specify the VLAN ID.
Interface
Click
OK .(Optional.) Select
Advanced Settings , and then enable or disableVLAN ID Check .Figure-2 Advanced settings