MAC authentication
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
MAC authentication controls network access by authenticating source MAC addresses on an interface. The feature does not require client software, and users do not have to enter a username and password for network access. The device initiates a MAC authentication process when it detects an unknown source MAC address on a MAC authentication-enabled interface. If the MAC address passes authentication, the user can access authorized network resources. If the authentication fails, the device marks the MAC address as a silent MAC address, drops the packet, and starts a quiet timer. The device drops all subsequent packets from the MAC address within the quiet time. The quiet mechanism avoids repeated authentication during a short time.
Authorization VLAN
The authorization VLAN controls the access of a MAC authentication user to authorized network resources. The device supports authorization VLANs assigned locally.
Interface MAC authentication operating mode
MAC authentication can operate in the following modes on an interface:
Single-VLAN mode —In single-VLAN mode, the interface reauthenticates an online user when traffic received from that user contains a VLAN tag different from the VLAN in which the user was authenticated. The authentication process differs depending on the authorization VLAN assignment status:If no authorization VLAN has been assigned to the online user, the device first logs off the user and then reauthenticates the user in the new VLAN.
If the online user has been assigned an authorization VLAN, the user will not be logged off.
Multi-VLAN mode —In multi-VLAN mode, the interface forwards traffic from a user in different VLANs without reauthentication if the user has been authenticated and come online in any VLAN on the interface. Free of reauthentication, traffic from an online user can be sent in different VLANs without delay or service interruption.
Guest VLAN
The MAC authentication guest VLAN on an interface accommodates users that have failed MAC authentication for any reason other than server unreachable. For example, the VLAN accommodates users for which invalid passwords are entered.
You can deploy a limited set of network resources in the MAC authentication guest VLAN. For example, a software server for downloading software and system patches.
An interface of hybrid link type is always assigned to a MAC authentication guest VLAN as an untagged member. After the assignment, do not reconfigure the interface as a tagged member in the VLAN.
The device reauthenticates users in the MAC authentication guest VLAN at a specific interval. Table-1 shows the way that the network access device handles guest VLANs for MAC authentication users.
Authentication status | VLAN manipulation |
A user in the MAC authentication guest VLAN passes MAC authentication. | The device remaps the MAC address of the user to the authorization VLAN assigned by the authentication server. If no authorization VLAN is configured for the user, the device remaps the MAC address of the user to the PVID of the interface. |
A user in the MAC authentication guest VLAN fails MAC authentication. | The user is still in the MAC authentication guest VLAN. |
Critical VLAN
The MAC authentication critical VLAN on an interface accommodates users that have failed MAC authentication because no RADIUS authentication servers are reachable. Users in a MAC authentication critical VLAN can access only network resources in the critical VLAN.
The critical VLAN feature takes effect when MAC authentication is performed only through RADIUS servers. If a MAC authentication user fails local authentication after RADIUS authentication, the user is not assigned to the critical VLAN.
Table-2 shows the way that the network access device handles critical VLANs for MAC authentication users.
Authentication status | VLAN manipulation |
A user fails MAC authentication because all the RADIUS servers are unreachable. | The device maps the MAC address of the user to the MAC authentication critical VLAN. The user is still in the MAC authentication critical VLAN if the user fails MAC reauthentication because all the RADIUS servers are unreachable. If no MAC authentication critical VLAN is configured, the device maps the MAC address of the user to the PVID of the interface. |
A user in the MAC authentication critical VLAN fails MAC authentication for any reason other than server unreachable. | If a guest VLAN has been configured, the device maps the MAC address of the user to the guest VLAN. If no guest VLAN is configured, the device maps the MAC address of the user to the PVID of the interface. |
A user in the MAC authentication critical VLAN passes MAC authentication. | The device remaps the MAC address of the user to the authorization VLAN assigned by the authentication server. If no authorization VLAN is configured for the user, the device remaps the MAC address of the user to the PVID of the access interface. |
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Restrictions and guidelines
General restrictions and guidelines
For configuration of MAC authentication on interfaces, only interfaces operating at Layer 2 support MAC authentication.
To use MAC authentication on an interface, you must enable the feature both globally and on the interface.
Restrictions and guidelines: Guest VLAN
Before you configure the MAC authentication guest VLAN on an interface, complete the following tasks:
Create the VLAN to be specified as the MAC authentication guest VLAN.
Configure the link type of the interface as hybrid, and configure the VLAN as an untagged member on the interface.
Enable MAC-based VLAN on the interface.
When you configure the MAC authentication guest VLAN on an interface, follow the guidelines in Table-3.
Table-3 Relationships of the MAC authentication guest VLAN with other security features
Feature | Relationship description |
Quiet feature of MAC authentication | The MAC authentication guest VLAN feature has higher priority. When a user fails MAC authentication, the user can access the resources in the guest VLAN. The user's MAC address is not marked as a silent MAC address. |
Super VLAN | You cannot specify a VLAN as both a super VLAN and a MAC authentication guest VLAN. |
Port security intrusion protection | The guest VLAN feature has higher priority than the block MAC action, but lower priority than the shutdown action of the port security intrusion protection feature. |
Restrictions and guidelines: Critical VLAN
Before you configure the MAC authentication critical VLAN on an interface, complete the following tasks:
Create the VLAN to be specified as the MAC authentication critical VLAN.
Configure the link type of the interface as hybrid, and configure the VLAN as an untagged member on the interface.
Enable MAC-based VLAN on the interface.
When you configure the MAC authentication critical VLAN on an interface, follow the guidelines in Table-4.
Table-4 Relationships of the MAC authentication critical VLAN with other security features
Feature | Relationship description |
Quiet feature of MAC authentication | The MAC authentication critical VLAN feature has higher priority. When a user fails MAC authentication because no RADIUS authentication server is reachable, the user can access the resources in the critical VLAN. The user's MAC address is not marked as a silent MAC address. |
Port security intrusion protection | The critical VLAN feature has higher priority than the block MAC action but lower priority than the shutdown action of the port security intrusion protection feature. |
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Add interfaces to security zones. You can add interfaces to a security zone on the
Security Zones page or select a security zone for an interface on theInterfaces page.Configure security policies to permit the target traffic on the
Policies >Security Policies page.
Configure MAC authentication
To have the device perform MAC authentication on the access users connected to an interface, make sure MAC authentication is enabled both globally and on that interface.
Click the
Network tab.In the navigation pane, select
Security Access >MAC Access >MAC Authentication .Select
Enable to enable global MAC authentication.Figure-1 Enabling global MAC authentication

Select
Enable interface-specific MAC authentication to enable MAC authentication for the target interface.Figure-2 Enabling interface-specific MAC authentication
Click
Edit for the target interface to enter theEdit MAC Authentication page.Figure-3 Editing MAC authentication settings on an interface
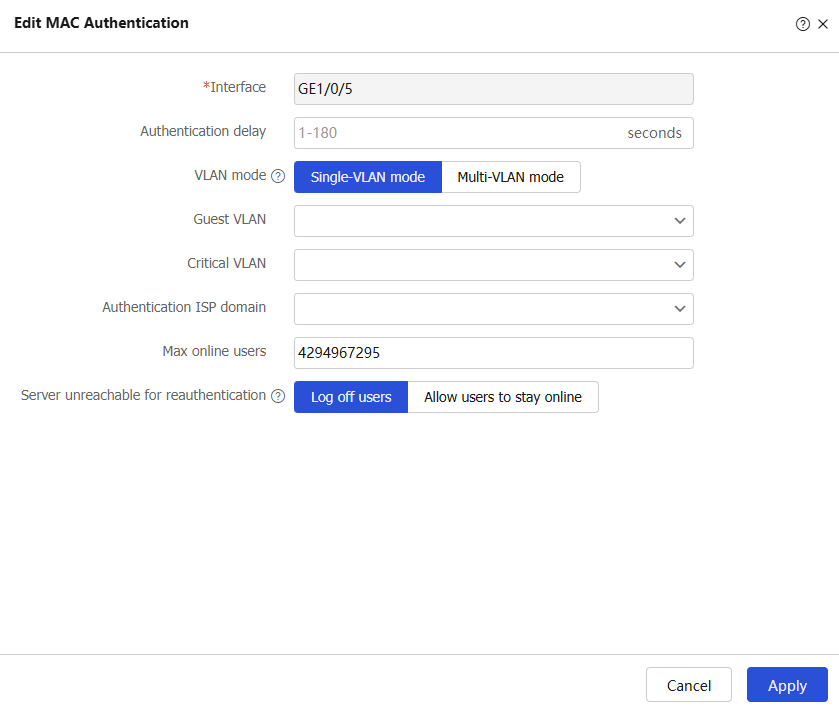
Configure the MAC authentication parameters.
Table-5 MAC authentication configuration items
Item
Description
Authentication delay
Set the MAC authentication delay time.
If you do not set a delay time, MAC authentication delay is disabled.
VLAN mode
Select a VLAN mode for the interface, which can be single-VLAN mode or multi-VLAN mode.
Guest VLAN
Specify a guest VLAN to accommodate users that have failed MAC authentication.
Critical VLAN
Specify a critical VLAN to accommodate users that have failed MAC authentication because of server unreachable.
Authentication ISP domain
Specify an authentication ISP domain for users that access the interface.
Max online users
Set the maximum number of concurrent MAC authentication users allowed to access the interface.
Server unreachable for reauthentication
Select whether to log off users or allow users to stay online if no server is reachable for reauthentication of the users.
Click
OK .