BGP
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an exterior gateway protocol (EGP). It is called internal BGP (IBGP) when it runs within an AS and called external BGP (EBGP) when it runs between ASs. As shown in Figure-1, EBGP runs between Router A and Router B, and IBGP runs between Router B and Router C. An AS refers to a group of routers that use the same routing policy and work under the same administration.
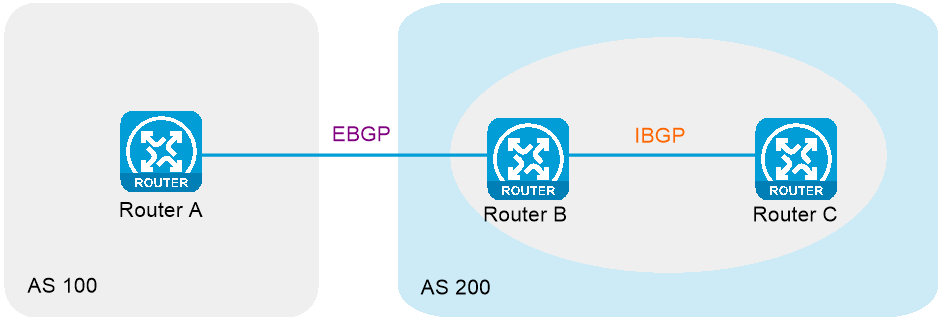
The current version in use is BGP-4. It is widely used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
Basic concepts
BGP speaker and BGP peer
A router running BGP is a BGP speaker. A BGP speaker establishes peer relationships with other BGP speakers to exchange routing information over TCP connections.
BGP peers include the following types:
IBGP peers —Reside in the same AS as the local router.EBGP peers —Reside in different ASs from the local router.
If you create a BGP peer without selecting an address family for it, the BGP peer remains in idle state. It does not attempt to establish peer relationships through Open messages.
MP-BGP
BGP-4 can only advertise IPv4 unicast routing information.
Multiprotocol Extensions for BGP-4 (MP-BGP) can advertise routing information for the following address families:
IPv6 unicast address family.
IPv4 multicast address family and IPv6 multicast address family.
PIM uses static and dynamic unicast routes to perform RPF check before creating multicast routing entries. When the multicast and unicast topologies are different, you can use MP-BGP to advertise the routes for RPF check. MP-BGP stores the routes in the BGP multicast routing table.
IPv4 MDT address family.
MP-BGP advertises MDT information including the PE address and default group so that multicast VPN can create a default MDT that uses the PE as the root on the public network. For more information about multicast VPN, see
IP Multicast Configuration Guide .
Controlling BGP route generation
BGP routes can be generated in the following ways:
Inject a local network. Perform this task to inject a network in the local routing table to the BGP routing table, so BGP can advertise the network to BGP peers. The ORIGIN attribute of BGP routes advertised in this way is IGP. You can also use a routing policy to control route advertisement.

The specified network must be available and active in the local IP routing table.
Redistribute IGP routes: Perform this task to configure route redistribution from an IGP to BGP.
By default, BGP does not redistribute default IGP routes. You can configure BGP to redistribute default IGP routes into the BGP routing table.

The ORIGIN attribute of BGP routes redistributed from IGPs is INCOMPLETE.
Only active routes can be redistributed.
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Restrictions and guidelines
Before you perform operations on the
BGP Network andBGP Route Redistribution tabs, select address families on BGP Address Family tab first. If you do not follow this sequence, the system displays an error message.For a device with BGP configuration, if you clear the
Enable BGP option underBGP status and then clickApply , the BGP process will be disabled, and the BGP configuration will be lost.
Configure BGP
Analysis
Configure BGP as shown in Figure-2.
Figure-2 BGP configuration procedure
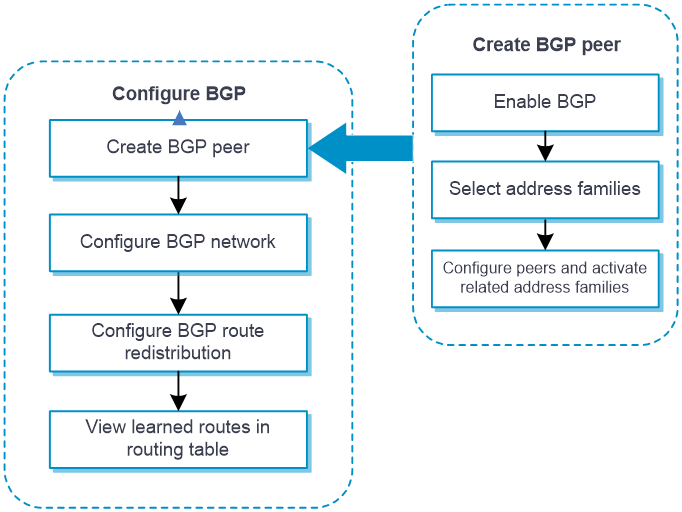
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Assign IP addresses to interfaces on the
Network >Interface Configuration >Interfaces page.Create security zones on the
Network >Security Zones page.Add interfaces to security zones. You can add interfaces to a security zone on the
Security Zones page or select a security zone for an interface on theInterfaces page.Configure security policies to permit the target traffic on the
Policies >Security Policies page.
Configure BGP
BGP is a distance vector routing protocol that implements inter-AS route reachability and optimal route selection. It is an exterior gateway protocol and is widely used between ISPs.
Enable BGP
Navigate to the
Network >Routing >BGP page.Select
Enable BGP , and then configure other BGP settings as needed.Figure-3 BGP configuration
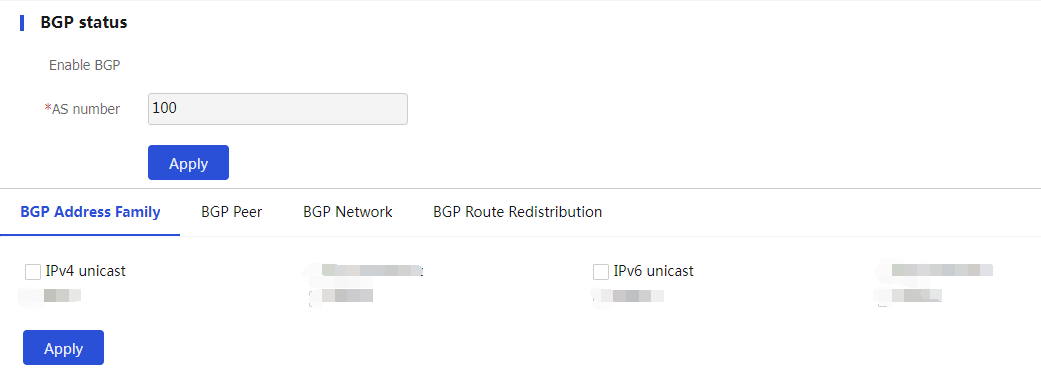
Table-1 BGP state configuration items
Item
Description
Enable BGP
Select whether to enable BGP.
AS Number
Specify an AS number for AS identification.
Specify BGP address families as needed. You can then perform address family-specific configuration.
Create a BGP peer
Navigate to the
Network >Routing >BGP page.Click the
BGP Peer tab, and then clickCreate .Configure the BGP peer settings as needed.
Figure-4 Creating a BGP peer
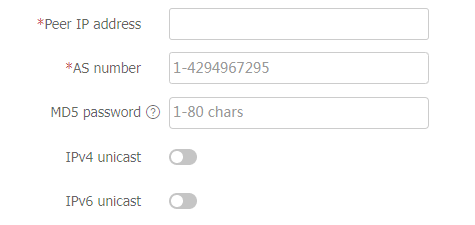
Table-2 BGP peer configuration items
Item
Description
Peer IP Address
Specify the IPv4 address of the peer.
AS Number
Specify the AS number of the peer.
If the AS number of the peer is the same as that of the local router, the peer is an IBGP peer.
If the AS number of the peer is different from that of the local router, the peer is an EBGP peer.
MD5 Authentication
Configure MD5 authentication settings to enhance BGP data security.
Click
OK . TheBGP Peer page will display the peer if it is created successfully.
Create a BGP network
Navigate to the
Network >Routing >BGP page.Click the
BGP Network tab, and then clickCreate .Configure BGP network settings as needed.
Figure-5 Creating a BGP network
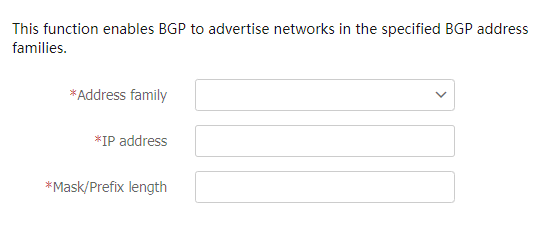
Table-3 BGP network configuration items
Click
OK . TheBGP Network page will display the network if it is created successfully.
Create a BGP route redistribution rule
Navigate to the
Network >Routing >BGP page.Click the
BGP Route Redistribution tab, and then clickCreate .Configure the following BGP route redistribution settings as needed:
Figure-6 Creating a BGP route redistribution rule
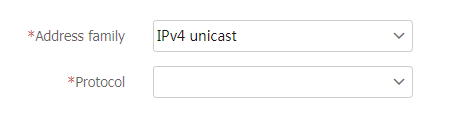
Table-4 BGP route redistribution configuration items
Item
Description
Address Family
Specify a BGP address family view.
Protocol
Specify an IGP as needed.
BGP can then redistribute routes from the specified IGP to the BGP routing table and advertise these routes to peers.
Process ID
Specify an IGP process by its ID.
If the protocol is IS-IS, IPv6 IS-IS, OSPF, OSPFv3, RIP, or RIPng, and you do not specify a process, BGP redistributes routes from process 1.