Attack defense
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
As an important network security feature, attack defense detects attacks by inspecting arriving packets and takes prevention actions.
An attack defense policy contains a set of attack detection and prevention action configuration. Prevention actions include logging, packet dropping, blacklisting, and client verification. The device supports the following attack defense policies:
Scanning attack defense policy.
Flood attack defense policy.
Single-attack defense policy.
Apply an attack defense policy to a security zone to inspect packet received in the security zone.
Scanning attack detection and prevention
Scanning is a preintrusion activity used to prepare for intrusion into a network. The scanning allows the attacker to find a way into the target network and to disguise the attacker's identity.
Attackers use scanning tools to probe a network, find vulnerable hosts, and discover services that are running on the hosts. Attackers can use the information to launch attacks.
The device can detect and prevent the IP sweep (address scanning) and port scanning attacks. If an attacker performs port scanning from multiple hosts to the target host, distributed port scan attacks occur.
Apply a scanning attack defense policy to the security zone that is connected to the external network. Scanning attack detection inspects the incoming packet rate of connections to the target system. If a source initiates connections at a rate equal to or exceeding the pre-defined threshold, the device can take the following actions:
Output logs.
Drop subsequent packets from the IP address of the attacker.
Add the attacker's IP address to the IP blacklist.
You can specify a detection sensitivity level for a scanning attack defense policy. The threshold values and detection periods are fixed for detection sensitivity levels high, medium, and low. To customize the threshold and the detection period, set the detection level to User-defined.
If the prevention action is adding attacker's IP address to the IP blacklist, you must enable the blacklist feature on the security zone to which the scanning attack defense policy is applied.
Flood attack detection and prevention
An attacker launches a flood attack by sending a large number of forged requests to the victim in a short period of time. The victim is too busy responding to these forged requests to provide services for legal users, and a DoS attack occurs.
Apply a flood attack defense policy to the security zone that is connected to the external network to protect internal servers. Flood attack detection monitors the rate at which connections are initiated to the internal servers. With flood attack detection enabled, the device is in attack detection state. When the packet receiving rate from an IP address or packet sending rate to an IP address reaches or exceeds the source or destination IP-based threshold, the device enters prevention state and takes the specified actions. When the rate is below the silence threshold (three-fourths of the threshold), the device returns to the attack detection state.
You can configure flood attack detection and prevention for a specific IP address. For non-specific IP addresses, the device uses the global attack prevention settings.
An appropriate threshold can effectively prevent attacks. The system provides the threshold learning feature to automatically learn the global threshold. This feature allows the device to learn the global threshold based on the traffic flows in the network as follows:
Monitors the packet sending rate in the network.
Calculates the global threshold based on the peak rate learned within the threshold learning duration.
The threshold learning feature includes the following modes:
One-time learning—The device performs threshold learning only once.
Periodic learning—The device performs threshold learning at intervals. The most recent learned threshold always takes effect.
The threshold learning learns the threshold of all types of flood attacks. You can enable auto application of the learned threshold.
If the network traffic statistics is not known yet, use the default settings of the flood attack prevention parameters first, and then adjust the threshold based on the threshold learning result.
Single-packet attack detection and prevention
Single-packet attacks are also known as malformed packet attacks. An attacker typically launches single-packet attacks by using the following methods:
An attacker sends defective packets to a device, which causes the device to malfunction or crash.
An attacker sends normal packets to a device, which interrupts connections or probes network topologies.
An attacker sends a large number of forged packets to a target device, which consumes network bandwidth and causes denial of service (DoS).
Apply the single-packet attack defense policy to the security zone that is connected to the external network. Single-packet attack detection inspects incoming packets based on the packet signature. If an attack packet is detected, the device can take the following actions:
Output logs.
Drop attack packets.
The device supports detecting both well-known single-packet attacks and attack packets with user-defined signatures.
Attack detection exemption
The attack defense policy uses the ACL to identify exempted packets. The policy does not check the packets permitted by the ACL. You can configure the ACL to identify packets from trusted servers. The exemption feature reduces the false alarm rate and improves packet processing efficiency.
If an ACL is used for attack detection exemption, only the following match criteria in the ACL permit rules take effect:
Source IP address.
Destination IP address.
Source port.
Destination port.
Protocol.
VRF.
Non-first fragments.
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Restrictions and guidelines
If a device has multiple service cards, the threshold value in a flood attack policy is card specific. The global threshold of the device is the product of multiplying the threshold value by the service card quantity.
Adjust the threshold according to the application scenarios. If the number of packets sent to a protected server is normally large, set a large threshold. A small threshold might affect the server services. For a network that is unstable or susceptible to attacks, set a small threshold.
If the specified ACL does not exist or does not contain a rule, attack detection exemption does not take effect.
If an ACL is used for attack detection exemption, only the following match criteria in the ACL permit rules take effect:
Source IP address.
Destination IP address.
Source port.
Destination port.
Protocol.
VRF.
Non-first fragments.
The threshold learning feature learns the thresholds of the following attacks only on the default ports:
DNS flood attacks.
DNS response flood attacks.
SIP flood attacks.
HTTP flood attacks.
HTTP slow attacks.
HTTPS flood attacks.
Once you set the source IP-based threshold to 0 for a flood attack type, the device does not apply the source IP-based learning result to this attack type even if learning result automatic application is enabled. You cannot manually apply the source IP-based learning result to this attack type, neither. The same restriction applies when you set the destination IP-based threshold to 0.
Configure attack defense and prevention
Configure attack defense as shown in Figure-1.
Figure-1 Attack defense configuration procedure
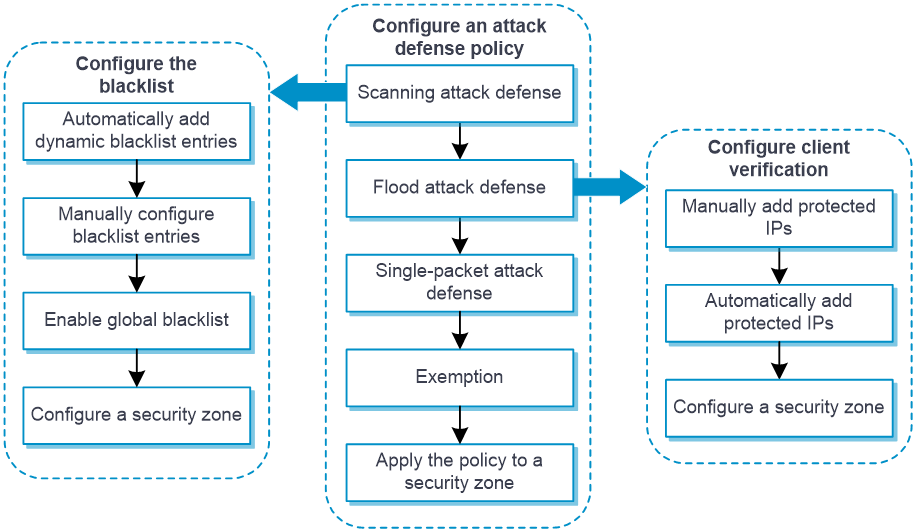
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Assign IP addresses to interfaces on the Network > Interface Configuration > Interfaces page.
Configure routes on the Network > Routing page. Make sure the routes are available.
Create security zones on the Network > Security Zones page.
Add interfaces to security zones. You can add interfaces to a security zone on the Security Zones page or select a security zone for an interface on the Interfaces page.
Configure security policies to permit the target traffic on the Policies > Security Policies page.
Create an attack defense policy
Before you configure attack defense and prevention, create an attack defense policy. Specify the attack detection criteria and prevention actions in the policy based on the network security requirements.
Procedure
Click the Objects tab.
In the navigation pane, select App Security > Attack Defense Policies.
Click Create. On the page that opens, click a tab and configure the detection conditions and actions to be taken for an attack based on actual network security requirements. Different types of attack defense features are non-sequenced. You can configure one or several of them as required. For more information about configuring attack defense features, see "Configure a scanning attack defense policy," "Configure a flood attack defense policy," "Configure a single-packet attack defense policy," and "Configure attack detection exemption."
Figure-2 Creating an attack defense policy
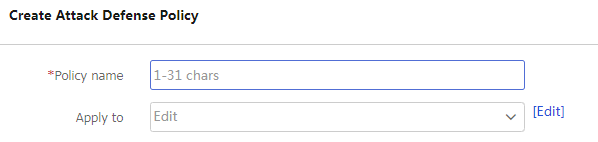
Table-1 Configuration items for an attack defense policy
Item
Description
Policy name
Enter the name of an attack defense policy. Valid characters include letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-).
Apply to
Select a security zone to which the attack defense policy is applied. A security zone can have only one attack defense policy applied. An attack defense policy can be applied to multiple security zones.
The list includes the default security zone and security zones that have been configured on the Network > Security Zones page.
Configure a scanning attack defense policy
Create an attack defense policy and configure basic parameters. For more information, see "Create an attack defense policy."
Click the Scanning Attack Defense tab and configure the policy as described in Table-2.
Figure-3 Configure a scanning attack defense policy
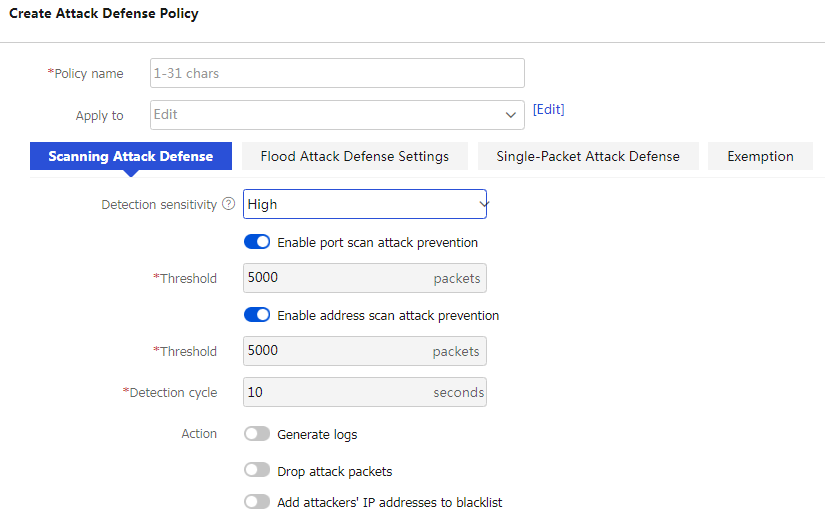
Table-2 Configuration items for a scanning attack defense policy
Item
Description
Detection sensitivity
Scanning attack detection level:
Close—Disables the scanning attack defense.
Low—Specifies the low level. This level provides basic scanning attack detection and has a low false alarm rate, but many scanning attacks cannot be detected.
Medium—Specifies the medium level. Compared with the high and low levels, this level has medium false alarm rate and attack detection accuracy.
High—Specifies the high level. This level can detect most of the scanning attacks, but has a high false alarm rate. Some packets from active hosts might be considered as attack packets.
User-defined—Specifies the user-defined level. You can set a threshold for scanning attack prevention.
Configure the following parameters as needed:
Enable port scan attack prevention—This feature is enabled when Detection sensitivity is set to Low, Medium, or High. You can determine whether to enable this feature when Detection sensitivity is set to User-defined.
Threshold (packets)—Threshold that triggers port scanning attack prevention. The value is 100000 for the low detection sensitivity level, 40000 for the medium detection sensitivity level, and 5000 for the high detection sensitivity level. You can specify a threshold when Detection sensitivity is set to User-defined. This parameter is not displayed when Detection sensitivity is disabled.
Enable address scan attack prevention—This feature is enabled when Detection sensitivity is set to Low, Medium, or High. You can determine whether to enable this feature when Detection sensitivity is set to User-defined.
Threshold (packets)—Threshold that triggers address scanning attack prevention. The value is 100000 for the low detection sensitivity level, 40000 for the medium detection sensitivity level, and 5000 for the high detection sensitivity level. You can specify a threshold when Detection sensitivity is set to User-defined. This parameter is not displayed when Detection sensitivity is disabled.
Detection period—Scanning attack detection cycle. The detection period is 10 seconds when Detection sensitivity is set to Low, Medium, or High. You can specify a detection cycle when Detection sensitivity is set to User-defined. This parameter is not displayed when Detection sensitivity is disabled.
Actions
Prevention actions against scanning attacks.
Generate logs.
Drop attack packets.
Add attackers' IP addresses to blacklist.
Age out after n minutes—Aging time for the dynamically added blacklist entries. This parameter is available only when Add attackers' IP addresses to blacklist is selected.
Prevention actions are not available when Detection sensitivity is disabled.
Click Apply. The newly created scanning attack defense policy will be displayed on the Attack Defense Policies page.
Configure a flood attack defense policy
Create an attack defense policy and configure basic parameters. For more information, see "Create an attack defense policy."
Click the Flood Attack Defense Settings tab. To configure global parameters for the attack defense policy, see Table-3. To configure IP-specific flood attack defense, see Table-5.
Figure-4 Configuring a flood attack defense policy
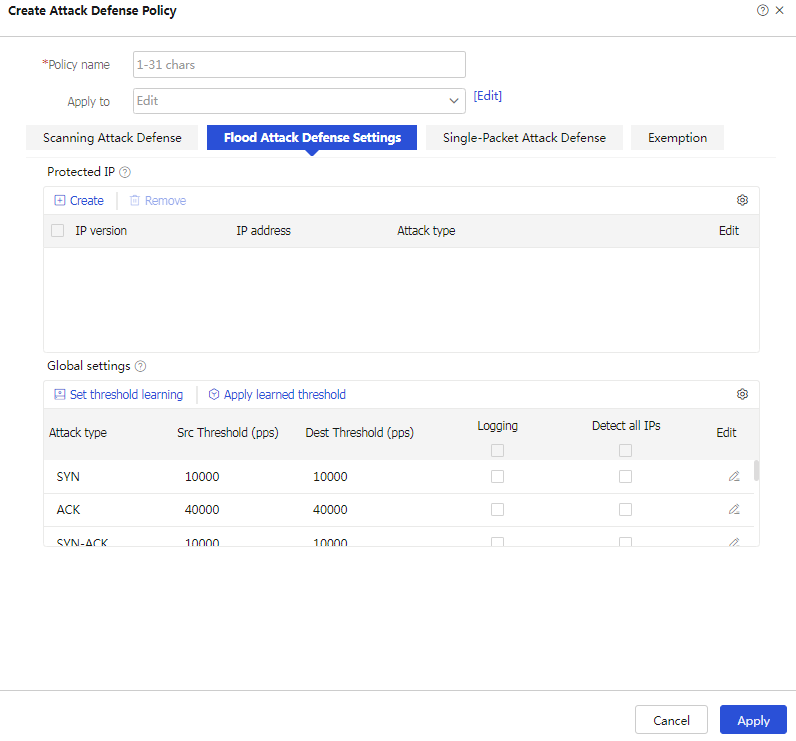
Figure-5 Editing global settings for the flood attack defense policy
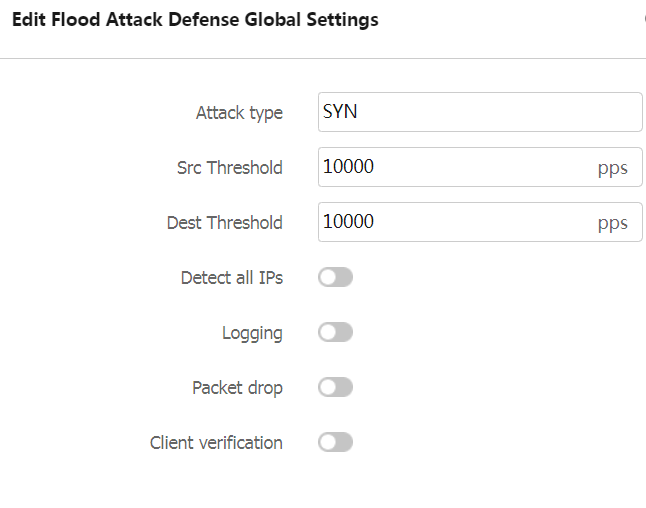
Table-3 Configuration items for flood attack defense global settings
Item
Description
Attack type
Flood attack types:
ACK—Specifies the ACK flood attack type. An ACK packet is a TCP packet only with the ACK flag set. Upon receiving an ACK packet from a client, the server must search half-open connections for a match. An ACK flood attacker sends a large number of ACK packets to the server. This causes the server to be busy searching for half-open connections, and the server is unable to process packets for normal services.
DNS—Specifies the DNS flood attack type. The DNS server processes and replies all DNS queries that it receives. A DNS flood attacker sends a large number of forged DNS queries. This attack consumes the bandwidth and resources of the DNS server, which prevents the server from processing and replying legal DNS queries.
DNS reply—Specifies the DNS reply flood attack type. The DNS client processes all incoming DNS replies. A DNS reply flood attacker sends excessive forged DNS replies. This attack consumes the bandwidth and resources of the DNS client, and prevents the client from processing legitimate DNS replies.
FIN—Specifies the FIN flood attack type. FIN packets are used to shut down TCP connections. A FIN flood attacker sends a large number of forged FIN packets to a server. The victim might shut down correct connections, or be unable to provide services because it is busy searching for matching connections.
HTTP—Specifies the HTTP flood attack type. Upon receiving an HTTP GET or POST request, the HTTP server performs complex operations, including character string searching, database traversal, data reassembly, and format switching. These operations consume a large amount of system resources. An HTTP flood attacker sends a large number of HTTP GET or POST requests that exceed the processing capacity of the HTTP server, which causes the server to crash.
HTTP slow—Specifies the HTTP slow flood attack type. When an attacker holds a large number of HTTP concurrent connections to the HTTP server, the system resources of the server are occupied by these connections. As a result, the server cannot process normal services.
HTTPS—Specifies the HTTPS flood attack type. Upon receiving an HTTPS request, the HTTPS server performs complex operations. These operations consume a large amount of system resources. An HTTPS flood attacker sends a large number of HTTPS requests that exceed the processing capacity of the HTTPS server, which causes the server to crash.
ICMP—Specifies the ICMP flood attack type. An ICMP flood attacker sends ICMP request packets, such as ping packets, to a host at a fast rate. Because the target host is busy replying to these requests, it is unable to provide services.
ICMPv6—Specifies the ICMPv6 flood attack type. An ICMPv6 flood attacker sends ICMPv6 request packets, such as ping packets, to a host at a fast rate. Because the target host is busy replying to these requests, it is unable to provide services.
RST—Specifies the RST flood attack type. RST packets are used to abort TCP connections when TCP connection errors occur. An RST flood attacker sends a large number of forged RST packets to a server. The victim might shut down correct connections, or be unable to provide services because it is busy searching for matching connections.
SIP—Specifies the SIP flood attack type. After receiving a SIP INVITE packet from a SIP client, the server must allocate resources to establish and trace the session with the SIP client. A SIP flood attacker sends a large number of fake INVITE request packets at a rate exceeding the processing capacity of the SIP server, which causes the server to crash.
SYN—Specifies the SYN flood attack type. A SYN flood attacker exploits the TCP three-way handshake characteristics and makes the victim unresponsive to legal users. An attacker sends a large number of SYN packets with forged source addresses to a server. This causes the server to open a large number of half-open connections and respond to the requests. However, the server will never receive the expected ACK packets. The server is unable to accept new incoming connection requests because all of its resources are bound to half-open connections.
SYN-ACK—Specifies the SYN-ACK flood attack type. Upon receiving a SYN-ACK packet, the server must search for the matching SYN packet it has sent. A SYN-ACK flood attacker sends a large number of SYN-ACK packets to the server. This causes the server to be busy searching for SYN packets, and the server is unable to process packets for normal services.
UDP—Specifies the UDP flood attack type. A UDP flood attacker sends UDP packets to a host at a fast rate. These packets consume a large amount of the target host's bandwidth, so the host cannot provide other services.
Src Threshold (pps)
Enter a global source IP-based threshold that triggers flood attack prevention. The default is 40000 for ARP flood attack and 10000 for other types of flood attacks.
With global flood attack detection configured, the device is in attack detection state. When the receiving rate of the packets originated from an IP address reaches or exceeds the threshold, the device enters prevention state and takes the specified actions.
If you set this parameter to 0, the system does not perform source IP-based flood attack detection.
Dest Threshold (pps)
Enter a global destination IP address-based threshold that triggers flood attack prevention. The default is 40000 for ARP flood attack and 10000 for other types of flood attacks.
With global flood attack detection configured, the device is in attack detection state. When the sending rate of packets to an IP address reaches or exceeds the threshold, the device enters prevention state and takes the specified actions.
The global destination IP-based threshold applies to global flood attack detection. Adjust the threshold according to the application scenarios. If the number of packets sent to a protected server is normally large, set a large threshold. A small threshold might affect the server services. For a network that is unstable or susceptible to attacks, set a small threshold.
If you set this parameter to 0, the system does not perform destination IP-based flood attack detection.
Logging
Enable logging for flood attack events. Log messages are sent to the log system.
Detect All IPs
Enable global flood attack detection.
Client verification
Enable client verification. The device automatically adds the victim IP addresses to the protected IP list, and provides proxy services for protected IP addresses.
Packet drop
Use packet dropping as the prevention action. The device drops subsequent attack packets destined for the victim IP addresses.
Target ports
A comma-separated list of up to 32 port number items, for example, 1-10,80. Each item specifies a port by its port number or a range of ports in the form of start-port-number to end-port-number. The end-port-number cannot be smaller than the start-port-number. The port number is in the range of 1 to 65535.
The device performs flood attack detection only on packets destined for the target ports.
The target port setting applies to global flood attack detection and IP address-specific flood attack detection with no port specified. If IP address-specific flood attack detection is configured with specific ports, the device detects flood attacks on these ports for the specified IP address.
This parameter is available only for DNS, DNS reply, HTTP, HTTP slow, HTTPS, and SIP flood attack types.
Concurrent connections
Enter a threshold for allowed concurrent HTTP connections. The default is 5000.
HTTP slow attack detection is triggered when the number of HTTP concurrent connections reaches the threshold.
This parameter is available only for the HTTP slow attack type.
Content-Length
Enter a threshold for the length of the Content-Length filed in the HTTP packet header. The default is 10000.
This parameter is available only for the HTTP slow attack type.
Payload length
Enter a threshold for the HTTP packet payload. The default is 50.
An HTTP packet is an abnormal packet if its Content-Length field value is greater than the specified threshold and its payload is shorter than the specified length.
This parameter is available only for the HTTP slow attack type.
Abnormal packets
Enter a threshold for abnormal packets. The default is 10.
This parameter is available only for the HTTP slow flood attack type.
Detection cycle
Set an attack detection period, in seconds.
The device takes prevention actions when the number of received abnormal packets exceeds the threshold within the detection period.
This parameter is available only for the HTTP slow flood attack type.
Blacklist
Select whether to use blacklisting as an attack prevention action.
If the blacklist feature is enabled in the security zone to which the attack defense policy applies, the device drops packets from the blacklisted IP addresses.
This parameter is available only for the HTTP slow flood attack type.
Blacklist aging time
Set an aging time of dynamic blacklist entries, in seconds. The default is 10.
This parameter is available only when blacklisting is used as a prevention action for the HTTP slow flood attack.
Set threshold learning
Configure threshold learning parameters as shown in Table-4.
Before configuring the threshold learning feature on the Edit page, you must complete the configuration of the attack defense policy first.
Apply learned threshold
Use the learned thresholds as the thresholds for flood attack prevention.
This setting takes effect only on attack types that are enabled with Detect All IPs and have the threshold learning result.
To configure threshold learning, click Set threshold learning in the Global settings area on the Flood Attack Defense Settings tab. Before you configure threshold learning on the edit page, you must complete the configuration of the attack defense policy.
Figure-6 Configuring threshold learning
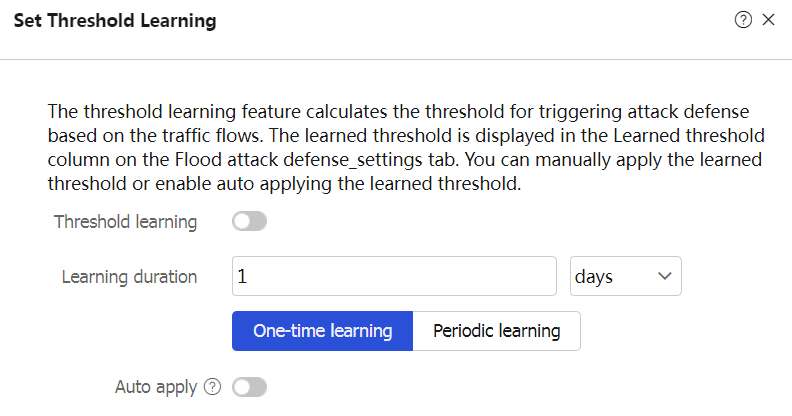
Table-4 Configuration items for threshold learning
Item
Description
Threshold learning
As a best practice, enable threshold learning to provide a reference for threshold setting.
Learning duration
Duration of threshold learning. The system calculates the thresholds for different attacks based on the peak rate learned within the threshold learning duration.
Learning mode
The following modes are available:
One-time learning—The device performs threshold learning only once.
Periodic learning—The device performs threshold learning at intervals.
Auto apply
Automatically apply the most recent thresholds that the device has learned.
This parameter takes effect only on attack types that are enabled with Detect All IPs and have the threshold learning result.
Tolerance
Threshold learning tolerance value that increases the learned threshold to a larger value before threshold application. This mechanism enables the threshold learning feature to promptly respond to traffic fluctuation.
To add protected IP addresses against flood attacks, click Create in the Protected IP area on the Flood Attack Defense Settings tab.
Figure-7 Adding protected IP addresses against flood attacks
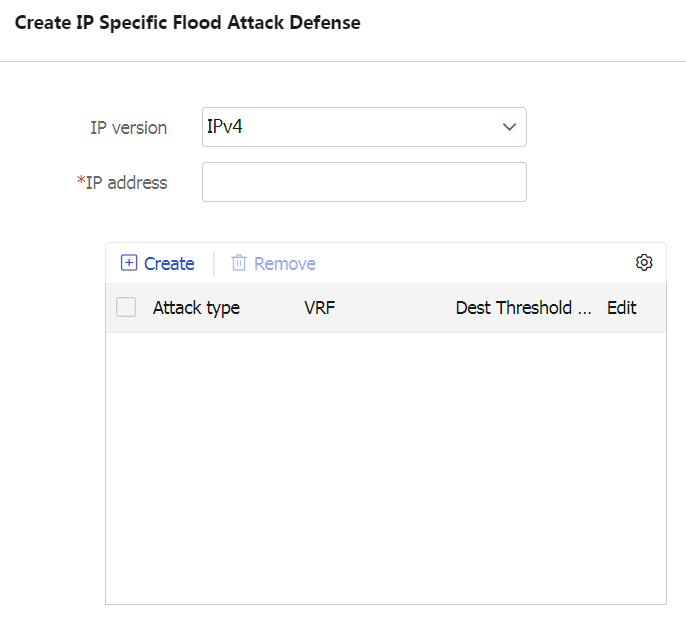
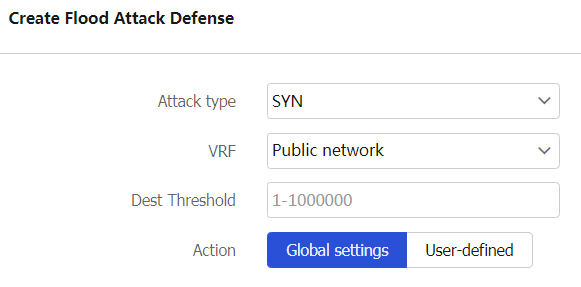
Table-5 Configuration items for IP-specific flood attack defense
Item
Description
IP version
Select an IP version, IPv4 or IPv6.
IP address
Enter an IP address to be protected.
The protected IPv4 address cannot be 255.255.255.255 or 0.0.0.0.
The protected IPv6 address cannot be a multicast address or ::.
Attack type
For more information, see Table-3.
VRF
VRF to which the protected IP address belongs. You can select an existing VRF or create a new one. The newly created VRF will be displayed on the Network > Interface Configuration > VRF page.
Dest Threshold (pps)
Set the destination IP-based threshold that triggers flood attack prevention. The default is 40000 for ARP flood attack and 10000 for other types of flood attacks.
Threshold
Set thresholds for HTTP slow attack defense. The following methods are available:
Global settings—Select this option to use the global threshold settings in the Global settings area.
User-defined—Select this option and specify thresholds. The default threshold settings are as follows:
The number of concurrent connections is 5000.
The value of the Content-Length field is 10000.
The payload length is 50.
The number of abnormal packets is 10.
This parameter is available only for the HTTP slow flood attack type.
Target ports
Specify ports to be protected. The device detects packets that are destined for the specified ports. The following methods are available:
Global settings—Select this option to use the global settings. By default, the global settings protect well-known ports specific to protocols. For example, the HTTP flood attack prevention protects port 80.
User-defined—Select this option to specify a port or a comma-separated list of port number items, for example, 1-10,80. Each item specifies a port by its port number or a range of ports in the form of start-port-number to end-port-number. The end-port-number cannot be smaller than the start-port-number.
This parameter is available only for DNS, DNS reply, HTTP, HTTP slow, HTTPS, and SIP flood attack types.
Detection cycle
Set an attack detection period. The following methods are available:
Global settings—Select this option to use the global detection period set in the Global settings area.
User-defined—Select this option and set a detection period. If no detection period is specified, the global detection period applies.
This parameter is available only for the HTTP slow attack type.
Action
Specify prevention actions against the flood attack. The following methods are available:
Global settings——Select this option to use the global prevention actions in the Global settings area.
User-defined——Select this option and specify prevention actions.
Logging—Use logging as the prevention action. Flood attack events are logged and log messages are sent to the log system.
Packet drop—Use packet dropping as the prevention action. The device drops subsequent attack packets destined for the victim IP addresses.
Client verification—Use client verification as the prevention action. The device automatically adds the victim IP addresses to the protected IP list, and provides proxy services for protected IP addresses.
Blacklist
Select whether to use blacklisting as an attack prevention action. The device automatically blacklists the packet source IP address when an attack is detected.
If the blacklist feature is enabled in a security zone, the device drops packets from the blacklisted IP address.
This parameter is available only for the HTTP slow attack type.
Aging time
Set an aging time of the dynamic blacklist entry, in seconds. The default is 10.
This parameter is available only when the blacklisting action is selected for the HTTP slow flood attack.
Click Apply. The newly created flood attack defense policy will be displayed on the Attack Defense Policies page.
Configure a single-packet attack defense policy
Create an attack defense policy and configure basic parameters. For more information, see "Create an attack defense policy."
Click the Single-Packet Attack Defense tab and configure the policy as described in Table-6.
Figure-8 Configuring a single-packet attack defense policy
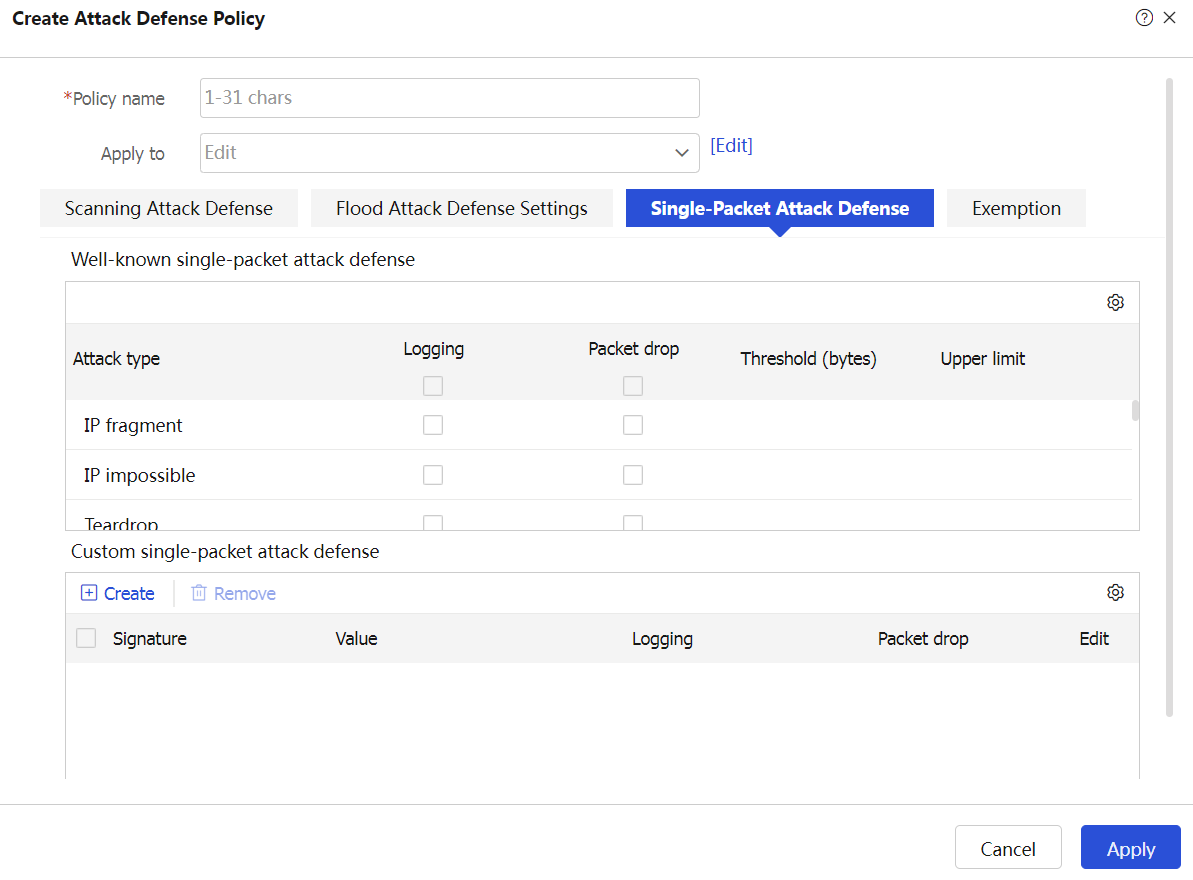
Table-6 Configuration items for well-known single packet attack defense
Item
Description
Attack type
Specify a well-known single packet attack type:
IP fragment—An attacker sends the victim an IP datagram with an offset smaller than 5, which causes the victim to malfunction or crash.
IP impossible—An attacker sends IP packets whose source IP address is the same as the destination IP address, which causes the victim to malfunction.
Teardrop—An attacker sends a stream of overlapping fragments. The victim will crash when it tries to reassemble the overlapping fragments.
Tiny fragment—An attacker makes the fragment size small enough to force Layer 4 header fields into the second fragment. These fragments can pass the packet filtering because they do not hit any match.
IP option abnormal—An attacker sends IP datagrams in which the IP options are abnormal. This attack intends to probe the network topology. The target system will break down if it is incapable of processing error packets.
Smurf—An attacker broadcasts an ICMP echo request to target networks. These requests contain the victim's IP address as the source IP address. Every receiver on the target networks will send an ICMP echo reply to the victim. The victim will be flooded with replies, and will be unable to provide services. Network congestion might occur.
Traceroute—An attacker uses traceroute tools to probe the topology of the victim network.
Ping of death—An attacker sends the victim an ICMP echo request larger than 65535 bytes that violates the IP protocol. When the victim reassembles the packet, a buffer overflow can occur, which causes a system crash.
Large ICMP—An attacker sends large ICMP packets to crash the victim. Large ICMP packets can cause memory allocation error and crash the protocol stack.
Large ICMPv6—An attacker sends large ICMPv6 packets to crash the victim. Large ICMPv6 packets can cause memory allocation error and crash the protocol stack.
TCP invalid flags—An attacker sends packets with invalid TCP flags to the target host, which can cause the target system to crash.
TCP null flag—An attacker sends TCP packet with no flags to the target host, which can cause the target system to crash.
TCP all flags—An attacker sends TCP packet with all flags set to the target host, which can cause the target system to crash.
TCP SYN-FIN—An attacker sends TCP packet with both SYN and FIN flags set to the target host, which can cause the target system to crash.
TCP FIN only flag—An attacker sends TCP packet with only the FIN flag set to the target host, which can cause the target system to crash.
TCP Land—An attacker sends the target a large number of TCP SYN packets with the source and destination IP addresses same as the IP of the target. The half connection resources on the target will run out and the target cannot operate correctly.
WinNuke—An attacker sends Out-Of-Band (OOB) data to the TCP port 139 (NetBIOS) on the victim that runs Windows system. The malicious packets contain an illegal Urgent Pointer, which causes the victim's operating system to crash.
UDP Bomb—An attacker sends a malformed UDP packet. The length value in the IP header is larger than the IP header length plus the length value in the UDP header. When the target system processes the packet, a buffer overflow can occur, which causes a system crash.
UDP snork—An attacker sends a UDP packet with destination port 135 (the Microsoft location service) and source port 135, 7, or 19. This attack causes an NT system to exhaust its CPU.
UDP fraggle—An attacker sends a large number of packets with source UDP port 7 and destination UDP port 19 (UDP chargen port) to a network. These packets use the victim's IP address as the source IP address. Replies will flood the victim, resulting in DoS.
IPv6 ext header abnormal—An attacker sends IPv6 packets with disordered or repeated IPv6 extension headers to the target.
IPv6 ext header exceed—An attacker sends IPv6 packets with IPv6 extension headers exceeding the upper limit to the target.
In abnormal IPv6 extension header and IPv6 extension header exceeded attack detection, the device examines the ESP header and headers before it. Headers after the ESP header are not examined.
Logging
Enable logging for the single-packet attack events. Log messages are sent to the log system.
Packet drop
Use packet dropping as the prevention action. The device drops subsequent attack packets destined for the victim IP addresses.
Threshold (bytes)
Maximum length of safe ICMP or ICMPv6 packets, in bytes.
28 to 65534 for ICMP packets.
48 to 65534 for ICMPv6 packets.
To create a single-packet attack defense policy to detect packets with user-defined signatures, click Create in the Custom single-packet attack defense area.
Figure-9 Creating a single-packet attack defense policy with user-defined packet signatures
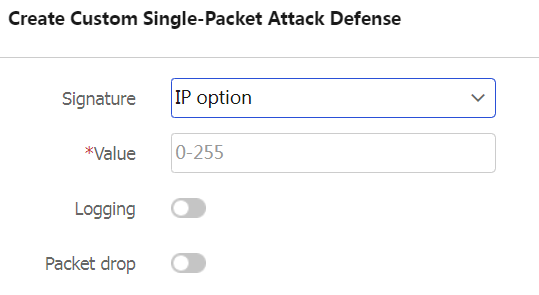
Table-7 Configuration items for a single-packet attack defense policy with user-defined packet signatures
Item
Description
Signature
Packet signatures:
IP option—Specifies attack packets with a specific IP option.
ICMP—Specifies ICMP attack packets.
ICMPv6—Specifies ICMPv6 attack packets
IPv6 extension header—Specifies attack packets with IPv6 extension headers.
Value
Signature value in the range of 0 to 255. This value indicates the IP option code, or the type value in ICMP packets, ICMPv6 packets, or IPv6 extension headers.
Logging
Enable logging for the single-packet attack events. Log messages are sent to the log system.
Packet drop
Use packet dropping as the prevention action. The device drops subsequent attack packets destined for the victim IP addresses.
Click Apply. The newly created single-packet attack defense policy will be displayed on the Attack Defense Policies page.
Configure attack detection exemption
Create an attack defense policy and configure basic parameters. For more information, see "Create an attack defense policy."
Click the Exemption tab and configure the parameters as described in Table-8.
Figure-10 Configuring attack detection exemption
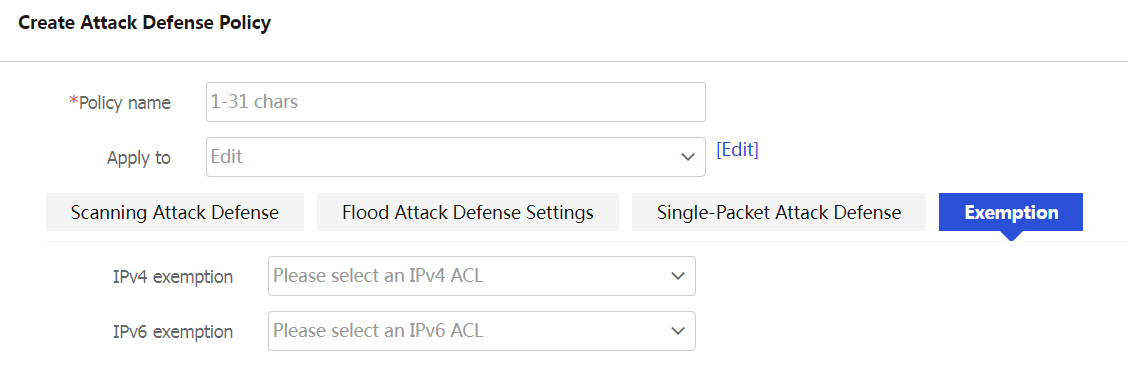
Table-8 Attack detection exemption configuration items
Item
Description
IPv4 exemption
IPv4 ACL for attack detection exemption. You can select an existing IPv4 ACL or create a new IPv4 ACL. The created ACL will be displayed on the Objects > ACLs > IPv4 ACLs page.
If the specified ACL does not exist or does not contain a rule, attack detection exemption does not take effect.
IPv6 exemption
IPv6 ACL for attack detection exemption. You can select an existing IPv6 ACL or create a new IPv6 ACL. The created ACL will be displayed on the Objects > ACLs > IPv6 ACLs page.
If the specified ACL does not exist or does not contain a rule, attack detection exemption does not take effect.
Click Apply. The attack detection exemption configuration will be displayed on the Attack Defense Policies page.