ARP
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
ARP
ARP resolves IP addresses into MAC addresses on Ethernet networks.
An ARP table stores dynamic ARP entries and static ARP entries.
Dynamic ARP entries
ARP automatically creates and updates dynamic entries. A dynamic ARP entry is removed when its aging timer expires or the output interface goes down. In addition, a dynamic ARP entry can be overwritten by a static ARP entry.
Dynamic ARP entries can be converted into static ARP entries, which cannot be converted into dynamic ARP entries again.
To prevent an interface from holding too many ARP entries, you can set the maximum number of dynamic ARP entries that the interface can learn.
Static ARP entries
A static ARP entry is manually configured and maintained. It does not age out and cannot be overwritten by any dynamic ARP entry.
Static ARP entries protect communication between devices because attack packets cannot modify the IP-to-MAC mapping in a static ARP entry.
To communicate with a host by using a fixed IP-to-MAC mapping, configure a short static ARP entry on the device. To communicate with a host by using a fixed IP-to-MAC mapping through an interface in a VLAN, configure a long static ARP entry on the device.
IP-MAC binding entries
The device prevents user spoofing attacks by using an IP-MAC binding table to filter out illegitimate packets with forged source IP addresses or MAC addresses.
IP-MAC binding entries can be created manually or generated in bulk.
Manual creation —You can manually create IP-MAC binding entries one by one. This method is applicable only to networks that do not contain many hosts.Bulk generation —You can configure the device to generate IPv4-MAC binding entries in bulk based on ARP entries on an interface. This method is applicable only to networks that contain many hosts.
Configure IP-MAC binding entries on the device to improve communication security. Upon receiving a packet, the device compares the source IP address and source MAC address in the packet with the IP-MAC binding entries.
If the source IP address and source MAC address match the same entry, the device determines that the packet is from a legal user and permits the packet to pass through.
In the following situations, the device determines that the packet is a forged packet and drops the packet:
Only the source IP address or source MAC address matches a binding entry.
The source IP address and source MAC address match two different binding entries.
If the source IP address and the source MAC address match no binding entry, the device processes the packet based on the default action.
ARP p rotection
ARP protection checks for illegitimate users in a VLAN on interfaces based on the sender IP address and sender MAC address in ARP packets.
When the device acts as a DHCP server, the device forwards ARP packets without inspecting the sender IP address and MAC address in the packets.
In other scenarios, the device forwards an ARP packet only if it finds a matching long static ARP entry for that packet. If no match is found, the device determines that the packet is illegitimate and discards it.
A long static ARP entry contains more information than IP and MAC addresses for forwarding, such as VLAN and output interface information. Support for long static ARP entries depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Configure ARP
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Assign IP addresses to interfaces on the
Network >Interface Configuration >Interfaces page.Configure routes on the
Network >Routing page. Make sure the routes are available.Create security zones on the
Network >Security Zones page.Add interfaces to security zones. You can add interfaces to a security zone on the
Security Zones page or select a security zone for an interface on theInterfaces page.Configure security policies to permit the target traffic on the
Policies >Security Policies page.
Configure IP-MAC binding entries
To have the IP-MAC binding entries take effect, enable the IP-MAC binding feature on the specified interface. After you enable this feature on an interface, the device uses IP-MAC binding entries to match the source IP address and source MAC address in incoming packets.
To configure IP-MAC binding entries:
Click the
Network tab.In the navigation pane, select
ARP .In the
IP-MAC binding settings area, configure parameters as shown in Table-1.Figure-1 Configuring IP-MAC binding
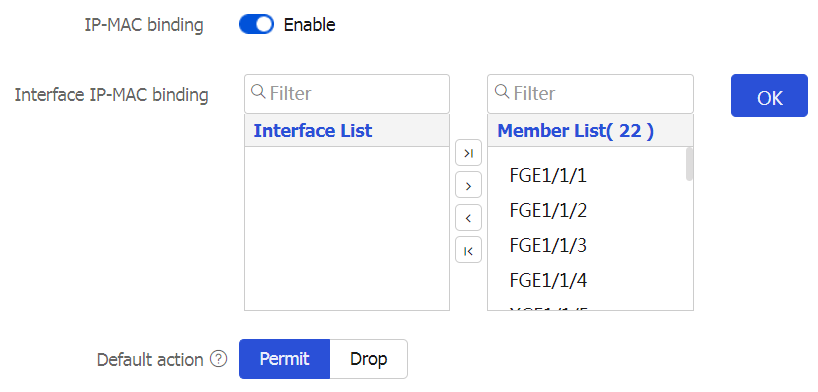
Table-1 IP-MAC binding configuration items
Item
Description
IP-MAC binding
Select whether to enable the IP-MAC binding feature.
Interface IP-MAC binding
Enable the IP-MAC binding feature on specified interfaces. After you enable IP-MAC binding on an interface, the device uses IP-MAC binding entries to match the source IP address and source MAC address in incoming packets.
Filter interfaces in
Interface List .Click the
Add icon to add selected interfaces toMember List .Click the
Add All icon to add all interfaces inInterface List toMember List .
Click
OK .
Default action
Default action for packets that do not match any IP-MAC binding entries:
Permit —Forwards packets.D rop —Drops packets.
In the
IP-MAC binding list area, clickCreate to manually configure an IP-MAC binding entry.Figure-2 Creating an IP-MAC binding entry
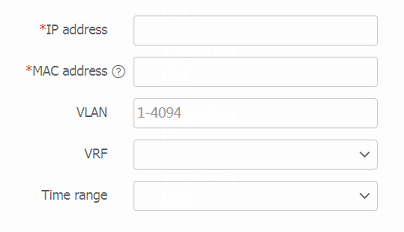
Table-2 IP-MAC binding entry configuration items
Item
Description
IP address
IP address in the IP-MAC binding entry.
MAC address
MAC address in the IP-MAC binding entry.
VRF
Name of the VPN instance to which the IP-MAC binding entry belongs.
VLAN
VLAN to which the IP-MAC binding entry belongs.
Time range
Time range during which the IP-MAC binding entry takes effect.
State
State of the IP-MAC binding entry:
Active.
Inactive.
Inactive time range.
Nonexistent VRF.
Inactive VRF and time range.
Click
OK . The newly-created IP-MAC binding entry is displayed in the IP-MAC binding list.Figure-3 IP-MAC binding entry

Configure ARP entries
Click the
Network tab.In the navigation pane, select
ARP .In the
ARP list area, clickCreate to manually create an ARP entry.Figure-4 Creating an ARP entry
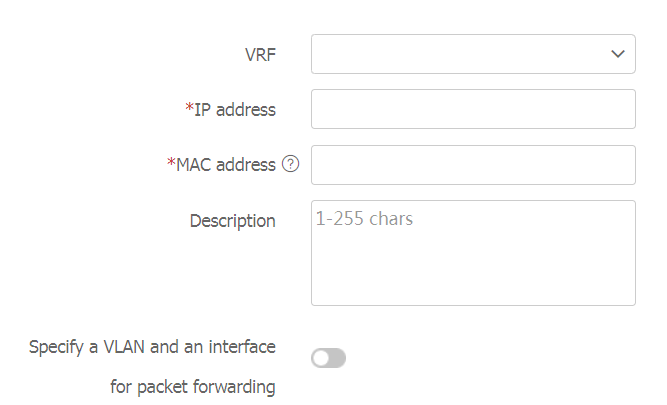
Table-3 ARP entry configuration items
Item
Description
VRF
Name of the VPN instance to which the ARP entry belongs.
IP address
IP address in the ARP entry.
MAC address
MAC address in the ARP entry.
Description
Description for the ARP entry.
Specify a VLAN and an interface for packet forwarding
Select this option to enable packet forwarding on a specified interface in a VLAN.
Support for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
VLAN
Specify a VLAN for packet forwarding. This parameter appears only when you select
Specify a VLAN and an interface for packet forwarding .Interface
Specify an interface for packet forwarding. This parameter appears only when you select
Specify a VLAN and an interface for packet forwarding .Click
OK . The newly created ARP entry is displayed in the ARP list and itsType field displaysStatic .Figure-5 ARP list

To switch a dynamic ARP entry to a static one, select the dynamic ARP entry, and then click
Freeze . After switchover, the static ARP entry cannot be restored to a dynamic one.Figure-6 Switching a dynamic ARP entry to a static one
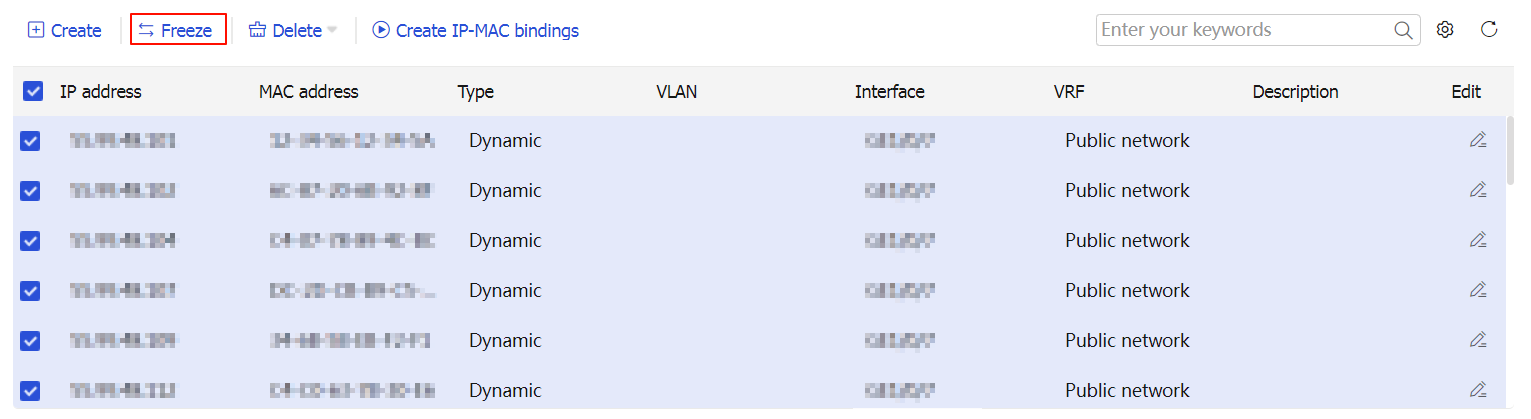
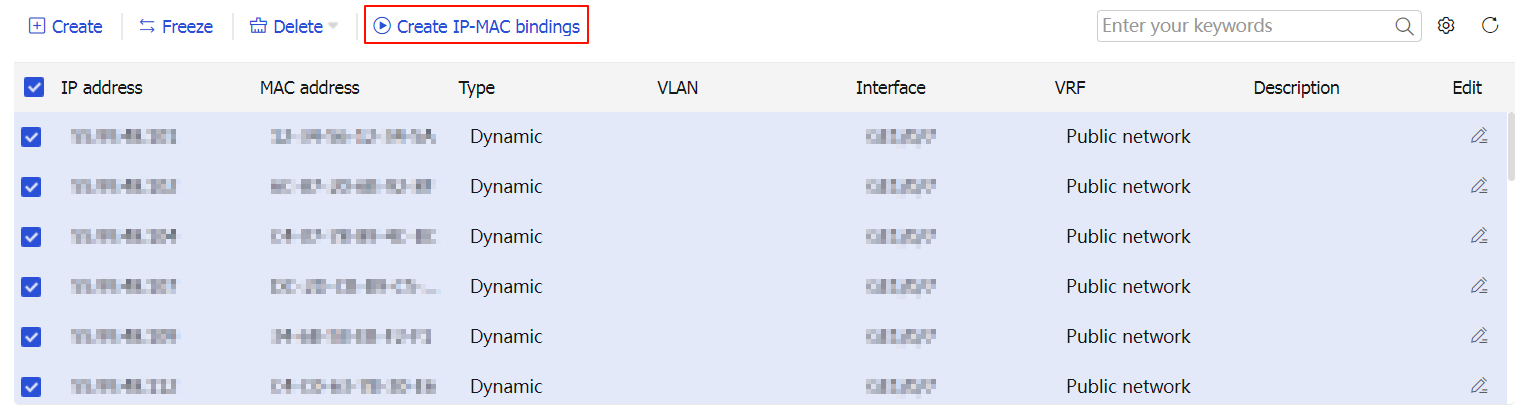
To create IP-MAC binding entries based on ARP entries, select the ARP entries, and then click
Create IP-MAC bindings . The generated IP-MAC binding entries are displayed in the IP-MAC binding list.Figure-7 IP-MAC binding
Configure ARP protection
Click the
Network tab.In the navigation pane, select
ARP .In the
ARP protection area, identify the enabling status of ARP protection for the VLANs on the device.Figure-8 ARP protection
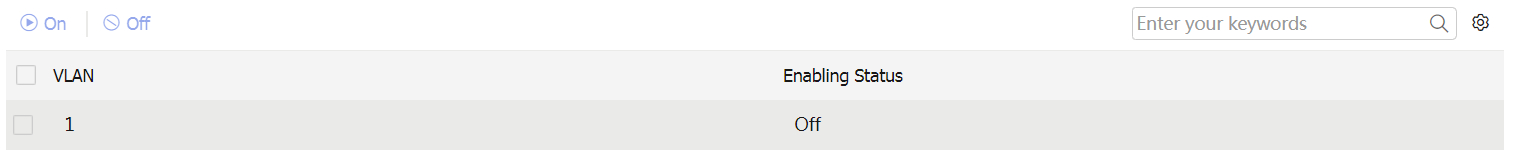
Table-4 ARP protection items
Item
Description
VLAN
VLAN ID.
ARP protection status
ARP protection enabling status:
Enabled.
Disabled.
Select the target VLANs, and then click
Enable orDisable to enable or disable ARP protection for the selected VLANs, respectively.