APR
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
The application recognition (APR) feature recognizes application protocols of packets for application-based services received on or sent out of ports and collects quantity and transmit rate statistics.
APR uses the following methods to recognize an application protocol:
Port-based application recognition (PBAR).
Network-based application recognition (NBAR).
Application protocols in this help are application protocols that can be recognized by APR. Applications are predefined or user-defined.
PBAR
PBAR maps a port to an application protocol and recognizes packets of the application protocol according to the port-protocol mapping.
PBAR supports the following port-protocol mappings:
Predefined—An application protocol uses the port defined by the system.
User-defined—An application protocol uses the port defined by the user.
PBAR offers the following mappings to maintain and apply user-defined port configuration:
General port mapping—Maps a user-defined port to an application protocol. All packets destined for that port are regarded as packets of the application protocol. For example, if port 2121 is mapped to FTP, all packets destined for that port are regarded as FTP packets.
Host-port mapping—Maps a user-defined port to an application protocol for packets to or from some specific hosts. For example, you can establish a host-port mapping so that all packets destined for the network segment 10.110.0.0/16 on port 2121 are regarded as FTP packets. To define the range of the hosts, you can specify the ACL, the host IP address range, or the subnet.
NBAR
NBAR uses predefined or user-defined NBAR rules to match packet contents to recognize the application protocols of matching packets. Predefined NBAR rules are automatically generated from the APR signature library.
In the current software version, only predefined NBAR rules are supported, and they are not configurable.
Application group
You can add application protocols that have similar signatures or restrictions to an application group. APR recognizes packets of the application protocols by matching the packet contents with the signatures or restrictions. If a packet is recognized as the packet of an application protocol in the application group, the packet is considered to be a packet of the application group.
An application group can contain multiple predefined and user-defined applications.
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Licensing requirements
To use NBAR, you must purchase and install the required license. After the license expires, NBAR can still use the existing signature library but cannot update the signature library. For more information about licensing, see the license management help.
Restrictions and guidelines
Before using the APR feature, update the APR signature library to the latest version.
Configure APR
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Assign IP addresses to interfaces on the Network > Interface Configuration > Interfaces page.
Configure routes on the Network > Routing page. Make sure the routes are available.
Create security zones on the Network > Security Zones page.
Add interfaces to security zones. You can add interfaces to a security zone on the Security Zones page or select a security zone for an interface on the Interfaces page.
Configure security policies to permit the target traffic on the Policies > Security Policies page.
Configure an application
You can create and modify user-defined applications for PBAR on the Applications page.
Port mapping categories
The following port mapping categories are available for PBAR:
General port mapping—Maps a user-defined port to an application protocol. All packets destined for that port are regarded as packets of the application protocol. For example, if port 2121 is mapped to FTP, all packets destined for that port are regarded as FTP packets.
ACL-based host-port mapping—Maps a port to an application protocol for the packets matching the specified ACL.
Subnet-based host-port mapping—Maps a port to an application protocol for the packets sent to the specified subnet. If multiple subnet-based mappings are applied to packets and these subnets overlap, PBAR matches the packets destined for the overlapped segment with the port mapping of the subnet that has the smallest range.
IP address-based host-port mapping—Maps a port to an application protocol for the packets destined for the specified IP addresses.
Create a port mapping
Click the Objects tab.
Select APP Security > App Recognition > Applications.
Click the Objects tab.
Select APP Security > App Recognition > Applications.
Enter a name for the application, and select risk types. The device calculates a risk level based on the specified risk types.
Enter an application name, and click Create in the Port mappings area.
Create a port mapping for the application.
Figure-1 Creating an application
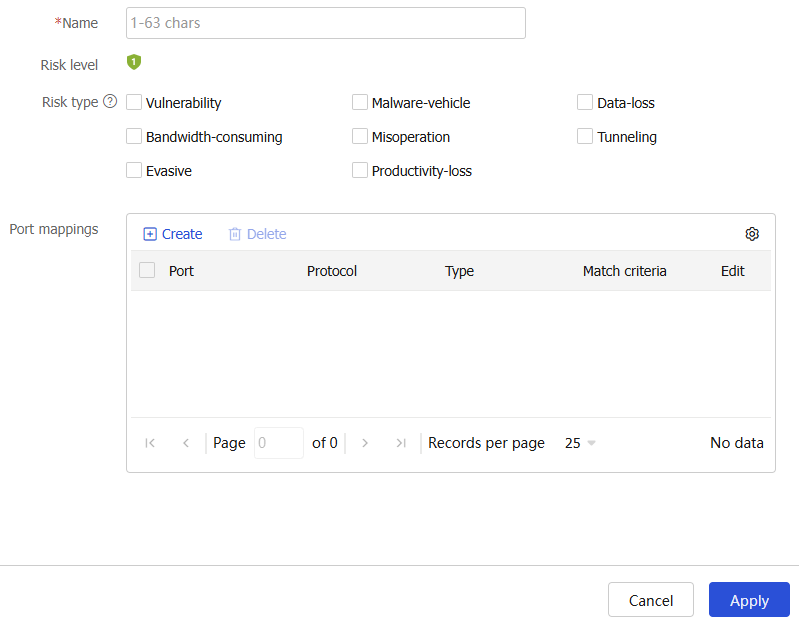
Figure-2 Creating a port mapping

Table-1 Port mapping configuration items
Item
Description
Port number
Enter the number of a port to which the application is mapped.
Protocol
Select a transport layer protocol. Possible values include All, DCCP, SCTP, TCP, UDP, and UDP-Lite.
If All is selected, packets that meet the following conditions are recognized as the specified application protocol's packets:
Packets are encapsulated by any transport layer protocol.
Packets have the specified port.
Type
Select a match type from the following values:
All, representing general port mapping.
IPv4 address-based host-port mapping.
IPv6 address-based host-port mapping.
IPv4 subnet-based host-port mapping.
IPv6 subnet-based host-port mapping.
IPv4 ACL-based host-port mapping.
IPv6 ACL-based host-port mapping.
Match criteria
Enter an IP address range if IP address-based host-port mapping was selected earlier.
Enter an IP subnet if subnet-based host-port mapping was selected earlier.
Enter an ACL if ACL-based host-port mapping was selected earlier.
Select a VRF instance.
Click OK.
You can create multiple port mappings for an application. PBAR selects a port mapping to recognize the application protocol of a packet in the following order:
IP address-based port mapping.
Subnet-based port mapping.
ACL-based host-port mapping.
General port mapping.
Click OK on the Create Application page.
On the Applications page, select Show user-defined applications only to verify the configuration.
Figure-3 Show user-defined applications only

Edit a predefined application
Select a predefined application, and click Edit on the right side.
Figure-4 Editing a predefined application
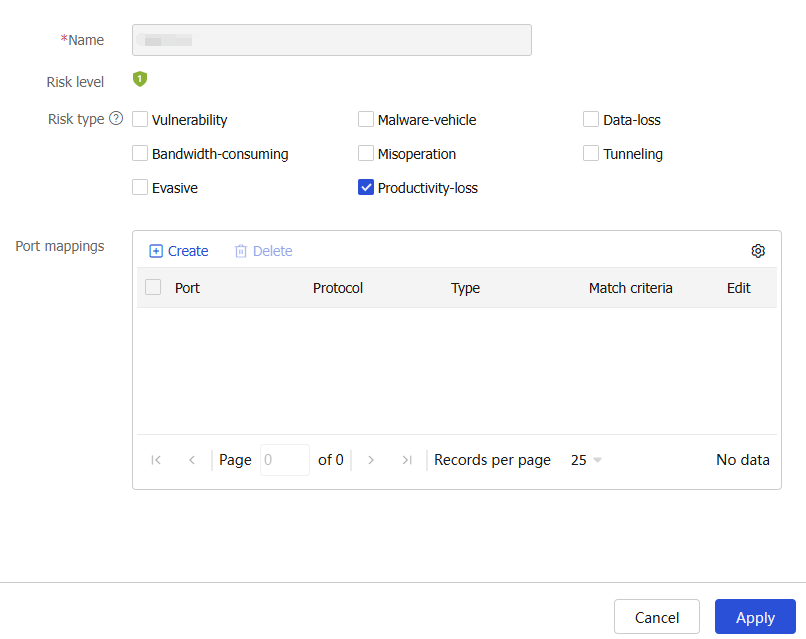
Follow the step described in "Configure an application" to add port mappings for the application.
Figure-5 Adding a port mapping

After editing, the newly added port-mappings take effect immediately. A packet that matches a newly added port-mapping can be recognized as the packet of the application.
Configure an application group
You can add applications that have similar characteristics or limitations to an application group.
Procedure
Click the Objects tab.
Select APP Security > App Recognition > Application Groups.
Click Create.
Create an application group.
Figure-6 Creating an application group
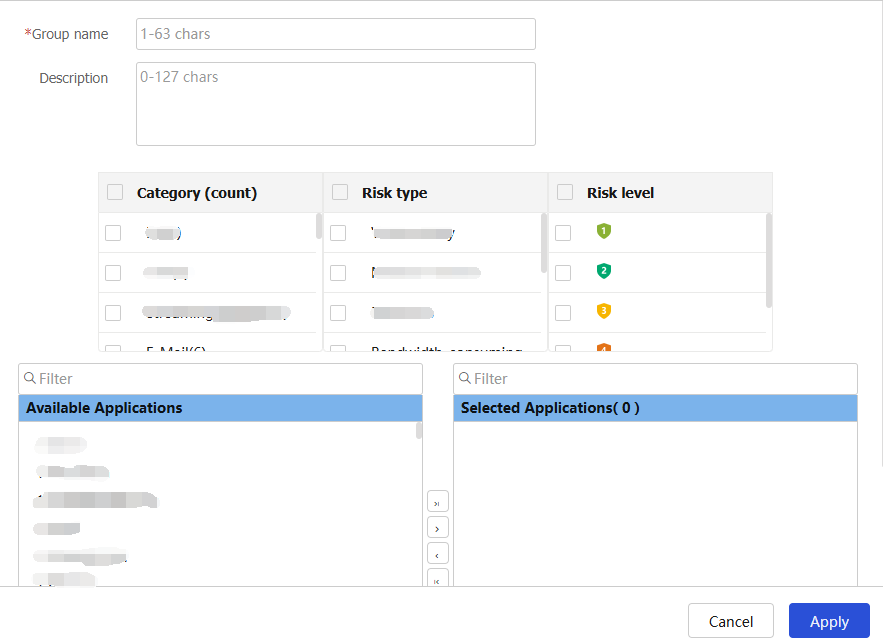
Table-2 Application group configuration items
Item
Description
Group
Enter a name for the application group.
Description
Enter a description for identification and management purposes.
Category
Select categories to filter desired applications.
Risk type
Select risk types to filter desired applications.
Risk level
Select risk levels to filter desired applications.
Filter
Move applications from the Available Applications list to the Selected Applications list.
Click OK.
Verify the configuration on the Application Groups page.