Application audit
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
| This feature parses personal information from user packets and must be used for legitimate purposes. |
Based on application recognition (APR), application audit audits and records Internet access behaviors of users by identifying behaviors and behavior contents of applications.
Basic concepts
Application behaviors
Applications and programs are characterized by different behaviors. For example, IM applications are characterized by login and message sending. FTP is characterized by file upload and file download.
Behavior contents
A behavior content is the content of a behavior. For example, the content of a login behavior is the account information. The content of an FTP file upload behavior is the file name. You can match behavior contents by using a string or a number.
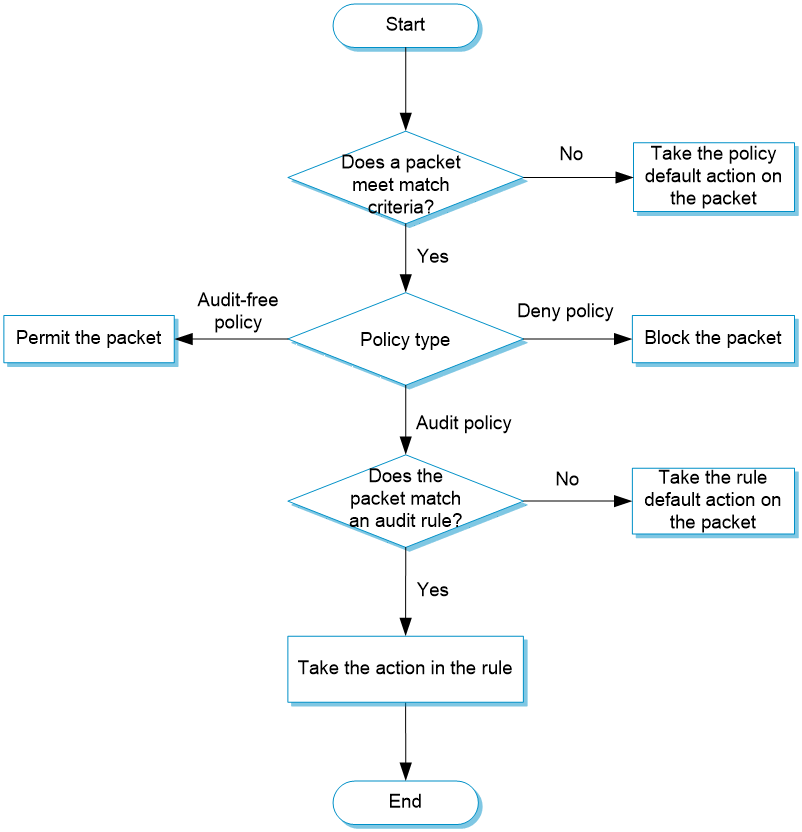
Application audit process
Figure-1 Application audit process
Application audit policy
Different audit policies process matching packets differently.
Policy types
Application audit policies have the following types:
Audit policy —Audits packets that meet match criteria in the policy.Audit-free policy —Does not audit packets that meet match criteria in the policy.Deny policy —Drops packets that meet match criteria in the policy.
Policy matching
Multiple application audit policies can exist on a device. The device compares a packet with policies in their configuration order. When a match is found, the match process ends. If no match is found, the device applies the default action to the packet.
You can view the configuration order of policies on the
Match criteria
Multiple match criteria can be configured in an application audit policy. A policy is matched if all match criteria in the policy are matched.
The following match criteria are available:
Source and destination security zones.
Source and destination IP addresses.
Users/user groups.
Applications/application groups.
Services.
Time ranges.
One match criterion can contain multiple match values. For example, you can configure multiple address object groups for a source IP address match criterion. A match criterion is matched if any of its match values is matched.
Audit rule
Audit rules can be configured for an audit policy to perform more granular control on user behaviors and to generate audit logs.
The following rule match modes are available:
in-order —The device compares packets with audit rules in ascending order of rule ID. When a packet matches a rule, the device stops the match process and performs the action defined in the rule.all —The device compares packets with audit rules in ascending order of rule ID.If a packet matches a rule with the permit action, all subsequent rules continue to be matched.
The device takes the action with higher priority on matching packets. The deny action has higher priority than the permit action.
If a packet matches a rule with the deny action, the device stops the match process and performs the deny action.
The device processes packets as follows based on the match result:
If a packet matches all items in an audit rule, the action in the audit rule is taken on the packet.
If a packet matches only the specified application or application category in an audit rule, the packet is allowed to pass through.
If a packet does not match the specified application or application category in an audit rule, the default action for audit rules is taken on the packet.
Email protection can be configured in a rule. The device detects incoming emails, counts emails based on recipients, and protects recipients from attacks. Specifically, you can configure the following functions:
Limit email sending —Prevents users from sending emails to users of a different domain. For example, the user at [email protected] cannot receive emails from the user at [email protected].Prevent e mail bomb ing —Protects recipients from being overwhelmed by large numbers of emails from the same sender during a short period of time.
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Licensing requirements
Application auditing is based on application recognition (APR). To use application auditing, you must purchase and install the required license. After the license expires, the application auditing feature is available through the existing APR signature library, but you cannot update the APR signature library. For more information about licensing, see the license management help.
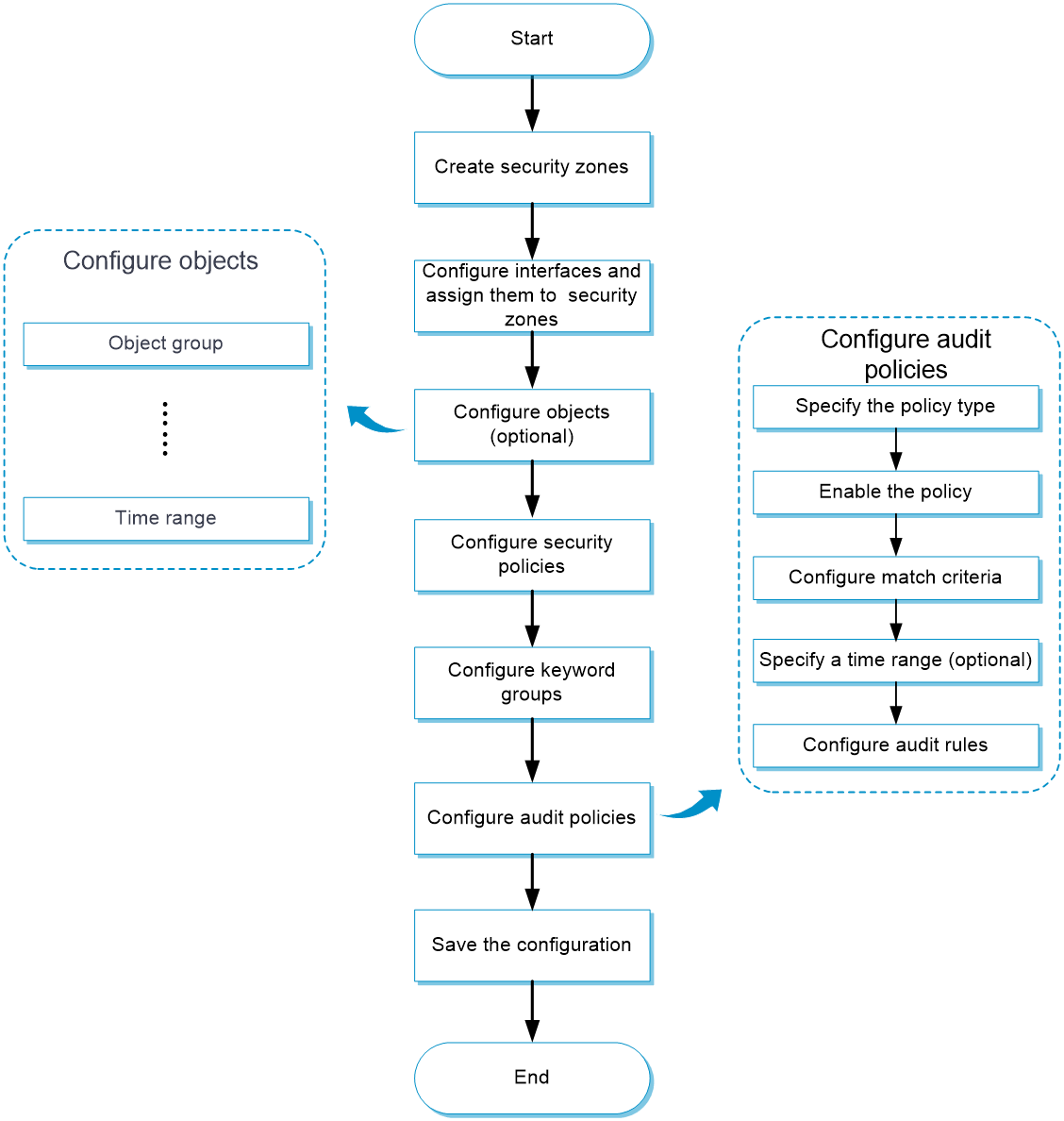
Configure application audit
Figure-2 shows the configuration procedure for application audit.
Figure-2 Application audit configuration procedure
Before configuring application audit, configure security policies to allow traffic to flow through the device. For information about configuring security policies, see "Security Policy Help."
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Assign IP addresses to interfaces on the
Network >Interface Configuration >Interfaces page.Configure routes on the
Network >Routing page. Make sure the routes are available.Create security zones on the
Network >Security Zones page.Add interfaces to security zones. You can add interfaces to a security zone on the
Security Zones page or select a security zone for an interface on theInterfaces page.Configure security policies to permit the target traffic on the
Policies >Security Policies page.
Purchase and install the APR license.
Upgrade the APR signature library to the most recent version on the official website.
Configure an application audit policy
Select
Policies >A pplication A udit .Click
Create in theA pplication A udit page.Create an application audit policy.
Figure-3 Creating an application audit policy

Figure-4 Configuring the parameters of an application audit policy
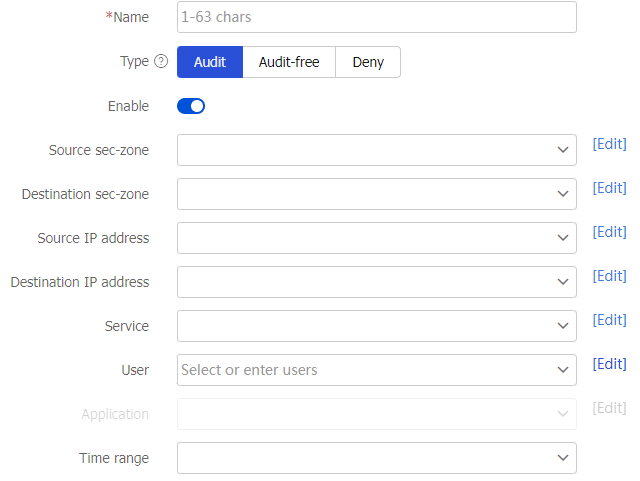
Table-1 Application audit policy configuration items
Item
Description
Name
Enter a name for the application audit policy.
Type
Select the application audit policy type: Audit, Audit-free, and Deny.
Enable
Enable the policy to make it take effect.
Source security zone
Specify a source security zone as a match criterion.
Destination security zone
Specify a destination security zone as a match criterion.
Source IP address
Specify a source IP address object group as a match criterion.
Destination IP address
Specify a destination IP address object group as a match criterion.
Service
Specify a service object group as a match criterion.
User
Specify a user as a match criterion.
Application
Specify an application or application group as a match criterion.
Time range
Specify a time range during which the policy is in effect.
On the audit policy creation page, click
Create in theAudit rule area to configure an audit rule to perform refined auditing on the behaviors and behavior contents of applications. This item can be configured only for an Audit-type policy.Figure-5 Creating an audit rule
Figure-6 Confguring the parameters of an audit rule
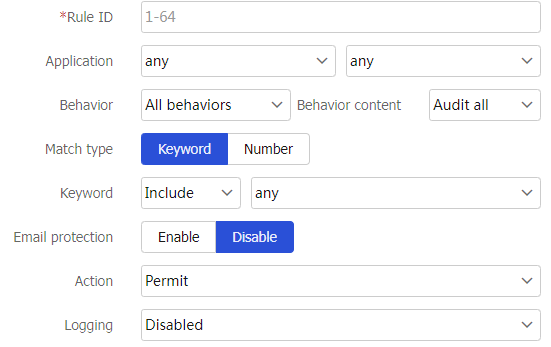
Table-2 Audit rule configuration items
Item
Description
Rule ID
Enter a rule ID.
Application
Select the applications to be audited.
Behavior
Select the behaviors to be audited.
Behavior content
Select the behavior contents to be audited.
Match type
Specify the behavior content type:
Keyword .Number .
Keyword
Operator used when behavior contents are matched:
For keyword-type behavior contents:
Include ,Exclude ,Equal ,Unequal .For number-type behavior contents:
Equal ,Unequal ,Greater ,Less ,Greater-equal ,Less-equal .
Email protection
Select
Enable to configure theL i mit email sending andPrevent email bombing functions.Limit email sending
Select
Enable to prevent users from sending emails to users of a different domain.Prevent email bombing
Configure this function to protect recipients from being overwhelmed by large numbers of emails from the same sender during a short period of time.
Detection time —The specified maximum number of emails can be received from the same user during this time.Email count —The maximum number of emails that can be received from the same user during the detection time.
Action
Select an action to take on packets matching audit rules:
Permit orDeny .Logging
Select
Enabled orDisabled to enable or disable generation of logs.Click
OK . The new audit rule is created successfully.Click
OK . The new application audit policy appears in theA udit P olicy page.Figure-7 Application audit policy created successfully

Configure a keyword group
Select
Policies >A pplication A udit >A udit Polic ies .Click
Keyword Group .Figure-8 Clicking
Keyword Group 
Click
Create to create a keyword group.Figure-9 Creating a keyword group
Figure-10 Configuring the parameters of a keyword group
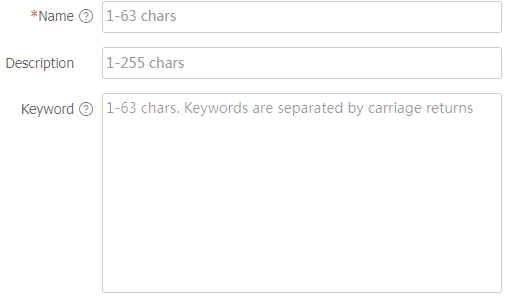
Table-3 Keyword group configuration items
Item
Description
Name
Enter a name for the keyword group.
Description
Enter a description for the keyword group, which helps the administrator identify the keyword group.
Keyword
Enter keywords to be audited. Keywords are separated by carriage returns.
Click
OK . The new keyword group appears in theKeyword Group page.Figure-11 Keyword group created successfully