User management
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
Local users
Users
A local user is a set of user attributes stored in the local user database on the device for network access. A local user is uniquely identified by its username.
To implement local authentication, authorization, and accounting, create local users and configure user attributes on the device.
User groups
User groups simplify local user configuration and management. A user group contains a group of local users and has a set of local user attributes. You can configure local user attributes for a user group to implement centralized user attributes management for the local users in the group. Local user attributes that are manageable by using user groups are authorization attributes.
Each new created local user belongs to the system defined user group named
Password control
To enhance password security for users, you can configure the password control feature.
You can define the minimum length of user passwords. The system rejects any password that is shorter than the configured minimum length. By default, the minimum password length is 10 characters.
A password can be a combination of characters from the following types:
Uppercase letters A to Z.
Lowercase letters a to z.
Digits 0 to 9.
Special characters. See Table-1.
Character name
Symbol
Character name
Symbol
Ampersand sign
&
Apostrophe
'
Asterisk
*
At sign
@
Back quote
`
Back slash
\
Blank space
N/A
Caret
^
Colon
:
Comma
,
Dollar sign
$
Dot
.
Equal sign
=
Exclamation point
!
Left angle bracket
<
Left brace
{
Left bracket
[
Left parenthesis
(
Minus sign
-
Percent sign
%
Plus sign
+
Pound sign
#
Quotation marks
"
Right angle bracket
>
Right brace
}
Right bracket
]
Right parenthesis
)
Semi-colon
;
Slash
/
Tilde
~
Underscore
_
Vertical bar
|
Depending on the system's security requirements, you can set the minimum number of character types a password must contain and the minimum number of characters for each type, as shown in Table-2.
Table-2 Password composition check
Password combination level
Minimum number of character types
Minimum number of characters for each type
Level 1
One
One
Level 2
Two
One
Level 3
Three
One
Level 4
Four
One
When a user sets or changes a password, the system examines whether the password meets the combination requirement. If the password does not meet the requirement, the operation fails.
By default, the minimum number of character types is one and the minimum number of characters for each type is one.
Password complexity check
The strength of a password increases as its complexity grows. A less complicated password is more likely to be cracked. For example, a password that contains the username or repeated characters is more likely to be cracked than those do not. To increase system security, configure a password complexity checking policy to make sure the user-configured passwords are complex enough against most password attacks.
You can apply the following password complexity requirements:
A password cannot contain the username or the username spelled backwards. For example, if the username is
abc , the password cannot beabc982 or2cba .
For this feature to take effect on a local user, you must enable it both in the user-specific password control settings and in the global password control settings.
A password cannot contain more than two consecutive identical characters. For example, password
a111 is not allowed.
For this feature to take effect on a local user, you can enable it in the user-specific password control settings or in the global password control settings.
Password history
This feature allows the system to store passwords that a user has used. When a user changes the password, the system compares the new password with the current password and those stored in the password history records. The new password must be different from the current one and those stored in the history records by a minimum of four characters. If the new password does not meet this requirement, the system displays an error message and rejects the password change operation.
You can set the maximum number of history password records for the system to maintain for each user. When the number of history password records exceeds the setting, the most recent record overwrites the earliest one.
Password updating
This feature allows you to set the minimum interval at which users can change their passwords. A user can only change the password once within the specified interval.
The minimum interval does not apply to the following situations:
A user is prompted to change the password at the first login.
The password expiration time expires.
User login control
You can set the idle time for local user accounts globally. For the idle time to take effect on a local user account, a user must have used that local user account to successfully log in to the device. After the idle time takes effect on a local user account, if no user has logged in successfully by using that user account within the idle time, the account will be locked. To restore the login permission of the account, access the local user page and clear the user idle lock state for the account.
Identity users
The user identification feature can be used with other security features to perform user-based network access control and network privilege management.
The user identification feature has the following benefits:
Facilitates security policy deployment on a per-user basis.
Implements network access behaviors auditing on users by providing user-based network attack/access traffic statistics.
Enables the device to use fixed usernames instead of dynamic IP addresses to implement policy control.
Identity users
Identity users are used to record identification information of network access users from different sources. The identification information includes the username, user group name, and identity domain name of the users. The user identification module uniformly manages identity users from different sources.
The device supports the following methods to create identity users:
Learning from the local user database —The user identification module learns local user information from the local user database and saves the user information as identity users.Importing from a .cs v file —The network administrator imports user information from a .csv file to the device and the device automatically creates identity users based on the imported information.Importing from third-party servers —The device initiates user information requests to third-party servers, imports network access user information, and then creates identity users based on the imported information. This method enables the network administrator to manage identity users when user information is on the third-party servers. Supported third-party servers include LDAP servers and IMC RESTful servers.
Identity users will be deleted due to one of the following reasons:
The network administrator deletes identity users manually.
The user identification module automatically deletes identity users after the corresponding network access users are deleted from the local user database.
Identity groups
Identity users can be added to different groups for batch configuration and hierarchical user management. The groups are called identity groups. The user identification module uniformly manages identity groups from different sources.
The device supports the following methods to create identity groups:
Learning from the local user database —When a local user group is created, the device instructs the user identification module to create an identity group with the same group name.Importing from a .csv file —The device imports identity user account information from a .csv file and then automatically creates identity groups based on the imported information.Importing from third-party server s —The device can import identity user account information from an IMC RESTful server or LDAP servers and then create identity groups based on the group information in the accounts. The device can also directly obtain user group information from LDAP servers and then creates identity groups.
An identity group is activated when it is used by an application module, and all services based on the identity group will take effect. When the application module stops using the identity group, the identity group is inactive.
Identity groups will be deleted due to one of the following reasons:
The network administrator deletes identity groups.
The user identification module automatically deletes an identity group if the corresponding local user group is deleted from the local user database.
Identity user management
All identity users are organized in a tree structure. An identity user can belong to one or multiple identity groups. An identity group can belong to one or multiple higher-layer identity groups. The tree structure facilitates user location and query. As shown in Figure-1, the device uniquely identifies a managed object by the combination of identity domain and username or the combination of identity domain and identity group.
Figure-1 Identity user management architecture
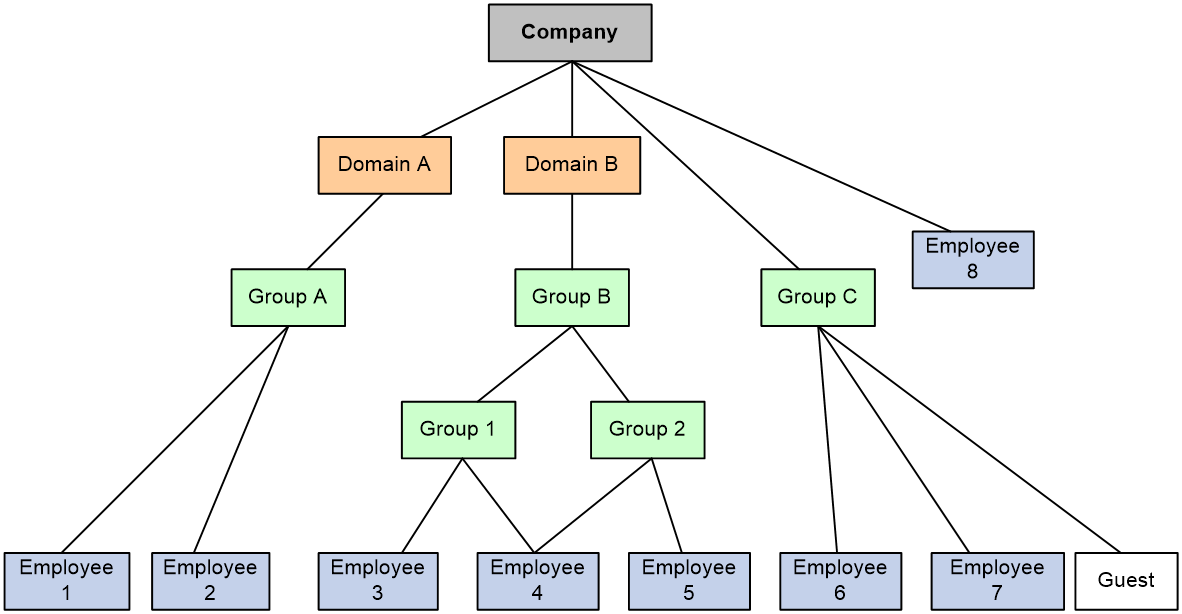
Identity-based user access control
The following shows the process for identity-based user access control:
Identity authentication. A network access user passes identity authentication and comes online.
User identification. The device obtains the username and IP address of the online user, and associates the information with the local identity user account and the local identity group. Then, the username-IP mapping for the network access user is created. The administrator can also add static username-IP mappings to permit network access without identity authentication.
Identity-based access control. The device identifies the source IP address of the traffic destined for the network, and resolves the IP address to the username and user group based on the mapping. The device performs network access control for the user or user group based on other security feature settings such as blacklist and object policy.
Online users
Online users are online network access users (including portal, PPP, and IPoE users) that are managed by the user identification module. The device records the username, identity domain name, IP address, and MAC address of online users.
Online users include dynamic online users and static online users.
Dynamic creation.
Online network access users that access the network through the device —After a user passes local or remote authentication and comes online, the user identification module searches the user's username and domain name in local identity users. If a matching entry is found, the device creates an online user entry for the user.Online network access users obtained from third-party server s —After the device obtains information about an online user from a third-party server, the user identification module searches the user's username and domain name in local identity users. If a matching entry is found, the device creates an online user entry for the user. The device can obtain information about all online users of third-party servers (including online users on the other devices) for unified management and monitoring. Supported third-party servers include IMC RESTful server.
Static configuration.
The network administrator manually creates online users. Each static identity user contains the mapping between the username and the IP addresses of the user. After a static identity user is created, the user identification module searches the user's username and domain name in local identity users. If a matching entry is found, the device creates a static online user entry for the static identity user. Static online users can access the network without identity authentication but their access to the network is controlled by security features. The network administrator can configure static identity users when only few people need to temporarily access the network.
Application modules can impose security policies on online users. When online user entries are deleted, the user identification module will instruct the application modules to stop processing services for the users.
Online users will be deleted due to one of the following reasons:
The network administrator deletes online users manually.
The access modules instruct the user identification module to delete online users after the associated network access users go offline.
All dynamic online users are deleted after the device restarts up.
All dynamic online users are deleted after the user identification feature is disabled.
The third-party servers instruct the device to delete online users after associated users go offline.
User import policies
A user import policy is used to import identity users, online users, or identity groups from a RESTful server or LDAP servers.
The user import policy supports the following import methods:
Automatic import —The device first imports all identity users and online users from the servers specified in the policy and then automatically imports identity users from the servers periodically.Manual import —The device initiates connection requests to the servers specified in the policy and then imports all identity users and online users from the servers.
Email server
An email server is used for the random password generation feature.
The system can generate random passwords for network access users on the Web interface and use emails to send the random passwords to the users. After that, the users can use the random passwords to log in to the device.
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Restrictions and guidelines
Restrictions and guidelines for users
A non-password-protected local user passes authentication if the user provides the correct username and passes attribute checks. To enhance security, configure a password for each local user.
For portal users, only the authorization ACL and idle timeout attributes take effect.
For SSL VPN users, only the SSL VPN resource group attribute takes effect.
Deletion of identity users does not delete the corresponding network access users from the local user database.
Restrictions and guidelines for user import policy configuration
When you import users from a .CSV template, make sure the file is a standard .CSV file and do not modify the annotation headers of the template. A violation might cause data loss.
To use the IMC RESTful server, make sure the server is installed with the SSM component and runs on IMC PLAT 7.0 (E0201) or its patch version.
After the device establishes a connection with the RESTful server, the RESTful server sends real-time user login and logout information for the device to update online users.
Restrictions and guidelines for email server configuration
Before you configure the email address of the receiver, you must configure the email server.
Restrictions and guidelines for password control
The settings on the
The
After password control is enabled, the password set for a local user must have a minimum of four different characters.
For password control settings configured for a user to take effect, you must enable password control. To enable password control, click
Configure user management
Configure local users
You can create local users manually or import local users in bulk.
Create a local user
Click the
Objects tab.In the navigation pane, select
User >User Management >Local Users .Click the
Users tab and then clickCreate . TheCreate User page opens.Figure-2 Users tab
Create a local user.
Figure-3 Creating a local user
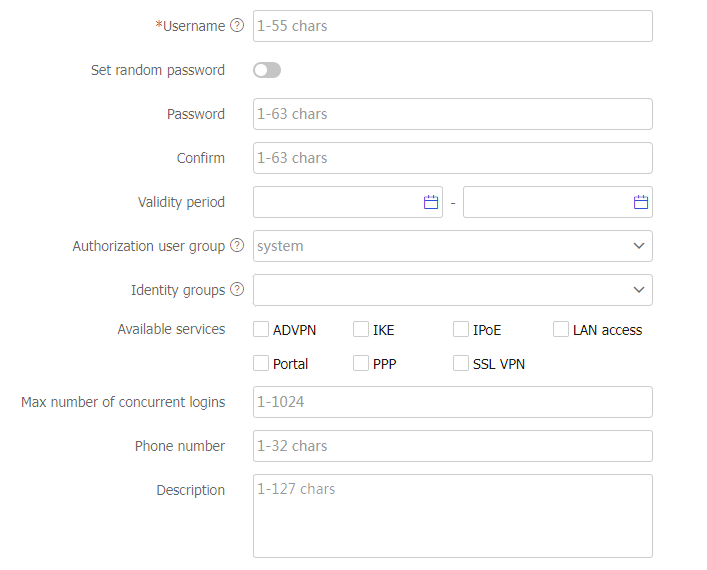
Table-3 Local user configuration items
Item
Description
Username
Enter the name of a network access user.
The user accesses the network resources through the device.
To implement local authentication, you must configure local users on the device
Set random password
Select to generate a random password for the user.
Receiver email
Enter the email address of the receiver to receive the random password.
Before you configure this field, please enter the Email Server page to configure the email server.
Password
Enter the password of the user.
Confirm
Enter the password of the user again,
Validity period
Set the validity period of the user.
Expired user accounts cannot be used for authentication.
If both the start time and end time are specified, the end time must be later than the start time.
If only the start time is specified, the user is valid since the specified time.
If only the end time is specified, the user is valid until the specified time.
Authorization user group
Select an authorization user group.
Each local user belongs to a user group and has all attributes of the group. The attributes include the password control attributes and authorization attributes.
Identity group
Select an identity group.
The user identification module controls the network access of a local user based on the identity group to which the user belongs.
Available services
Select services that the user can use.
Local authentication checks the service types of a local user. If none of the service types is available, the user cannot pass authentication.
Max number of concurrent logins
Enter the maximum number of users that can concurrently access the device by using the same username.
When the number of logins using a username reaches the limit, no more local users can access the device by using the username.
Phone number
Enter the phone number of the user.
Description
Enter the descriptive information of the user.
(Optional.) Configure authorization attributes.
Figure-4 Authorization attributes
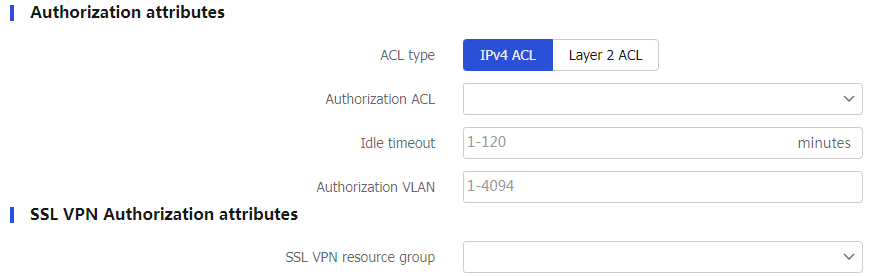
Table-4 Authorization attribute configuration items
Item
Description
ACL type
IPv4 ACL : You can create rules to match packets by source IP address, destination IP address, or protocol type.Layer 2 ACL : You can create rules to match packets by Layer 2 information, including source MAC address, destination MAC address, data link layer protocol, and encapsulation type.Authorization ACL
Select an authorization ACL.
The device restricts authenticated users to access only the network resources permitted by the ACL.
You can select an existing ACL or create a new ACL. To view the newly created ACL, visit
Objects >ACL and access the IPv4 or IPv6 page.Idle timeout
Enter the idle cut timeout period.
The device logs out a user if the user's total traffic in the idle timeout period at the specified direction is less than the specified minimum traffic.
Authorization VLAN
Enter a VLAN ID.
The device restricts authenticated users to access only the network resources in the VLAN.
SSL VPN resource group
Enter an SSL VPN resource group.
The device restricts authenticated users to access only the network resources specified in the SSL VPN resource group.
(Optional.) Configure binding attributes.
Figure-5 Binding attributes
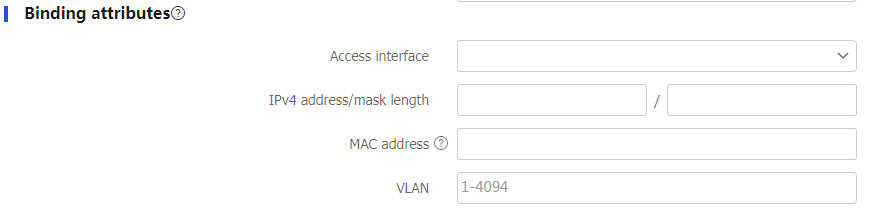
Table-5 Binding attribute configuration items
Item
Description
Access interface
Select an access interface.
If the actual access interface of the user is not the same as the binding interface, the user fails authentication.
IPv4 address/mask length
Enter an IPv4 address and its mask length.
If the IP address/mask length of the user is not the same as the binding IPv4 address/mask length, the user fails authentication.
MAC address
Enter a MAC address.
If the MAC address of the user is not the same as the binding MAC address, the user fails authentication.
VLAN
Enter a VLAN ID.
If the user belongs to a VLAN different from the binding VLAN, the user fails authentication.
(Optional.) Configure password settings.
Figure-6 Password settings
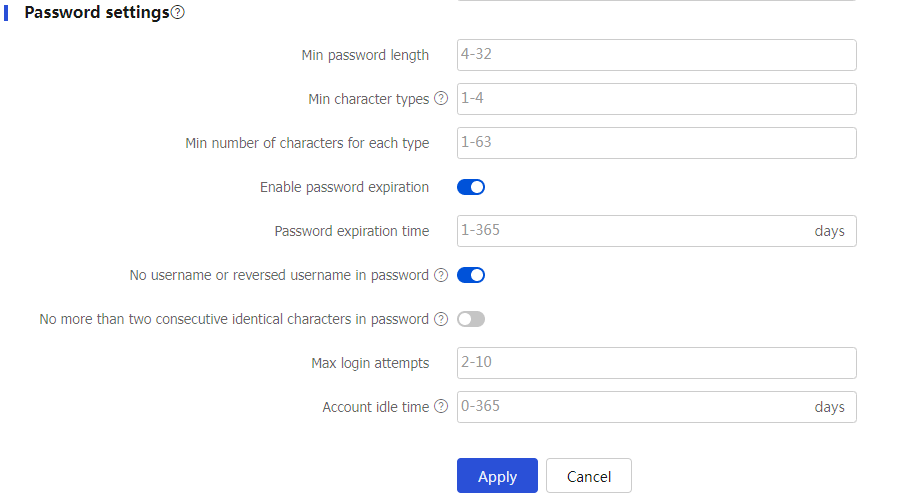
Table-6 Password setting configuration items
Item
Description
Min password length
Enter the minimum password length.
If the password that a user enters is shorter than this value, the system rejects the password setting.
Min character types
Enter the minimum number of character types in a password.
If the number of character types in the password that a user enters is less than this value, the system rejects the password setting.
Min number of characters for each type
Enter the minimum number of characters for each type in a password.
If the number of characters for each type in the password that a user enters is less than this value, the system rejects the password setting.
Enable password expiration
Select this item to restrict the password validity period.
Password expiration time
Set the password expiration time. A user needs to change its password to a new password when its password expires.
No username or reversed username in password
Select this item to reject a password that has the username or the reverse of the username.
No more than two consecutive identical characters in password
Select this item to reject a password that has more than two identical consecutive characters.
Max login attempts
Set the maximum number of consecutive login attempts. When a user fails the maximum number of consecutive attempts, login attempt limit limits the user and user account according to the specified action.
Account handling for login failure
Specify the action to take if the number of login failures of a user reaches the maximum number of login attempts. Options:
Lock permanently.
Lock temporarily.
Not lock.
Account lock time
Set the period during which login is denied. After the specified period of time, a user can use the user account to log in to the device.
Account idle time
Set the idle time for the local user account. For the idle time to take effect on the local user account, a user must have used the local user account to successfully log in to the device. After the idle time takes effect on the local user account, if no user has logged in successfully by using the user account within the idle time, the account will be locked. To restore the login permission of the account, access the local user page and clear the user idle lock state for the account.
Click
OK . The user is displayed on theUsers page.
Import local users in bulk
Click the
Objects tab.In the navigation pane, select
User >User Management >Local Users .Click the
Users tab and then clickImport . TheImport Users page opens.Figure-7 Users tab
Import local users.
Figure-8 Importing local users
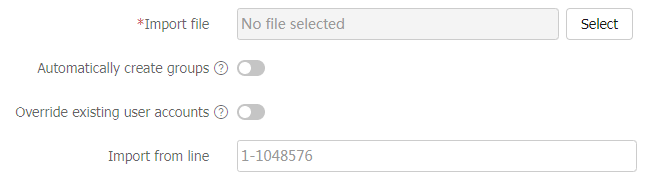
Table-7 Configuration items for importing local users
Item
Description
Import file
Specify a .CSV file for the device to import local users.
Make sure the .CSV file is a standard .csv file and do not modify the annotation headers of the template. A violation might cause data loss.
Automatically create groups
Select this item to enable the device to automatically create an identity group for a user if the identity group to which the user belongs does not exist on the device.
If you do not select this item, the device does not create nonexistent user groups and it assigns the user to the system-defined user group
system .Overriding existing user accounts
Select this item to enable the device to override an existing identity user account that has the same name as an identity user account to be imported.
If you do not select this item, the device retains the existing identity user account.
Import from line
Enter the number of the line at which the account import begins.
If you do not specify the line number, the device imports identity user account information from the first line.
Click
OK . The imported local users are displayed on theUsers page.
Configure password control
Click the
Objects tab.In the navigation pane, select
User >User Management >Local Users .Click the
Users tab and then clickPassword control . TheUser Password Control page opens.Figure-9 Users tab
Configure the password control settings.
Figure-10 Password control settings
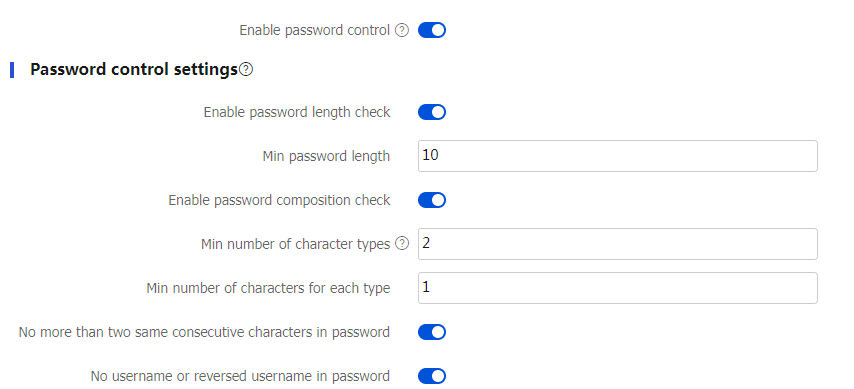
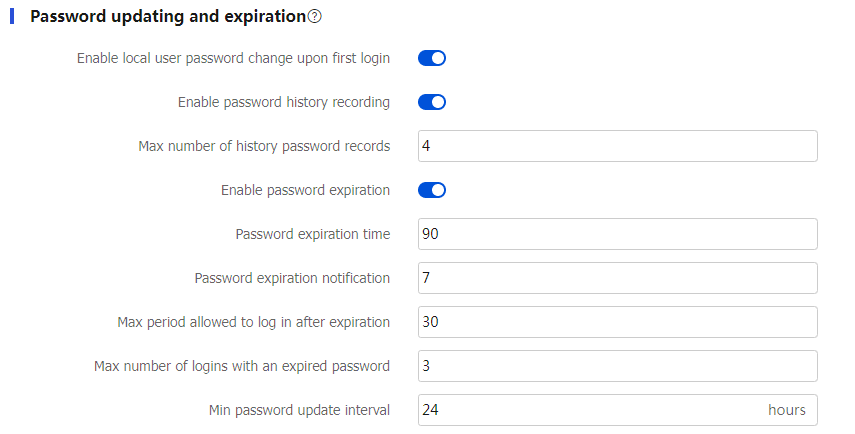
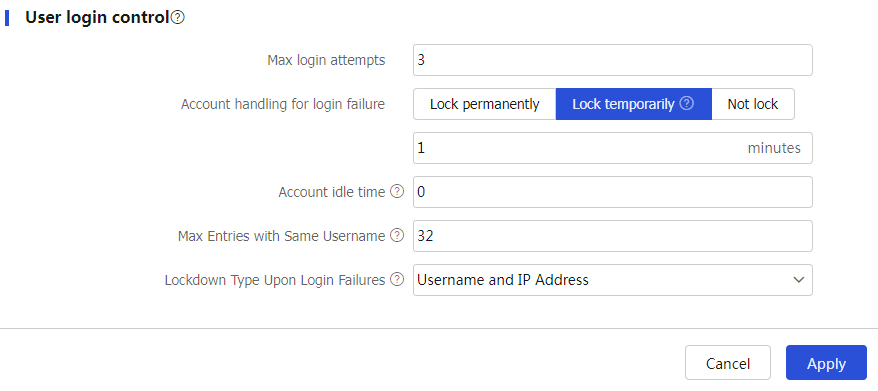
Table-8 Password control configuration items
Item
Description
Enable password control
Select this item to enable password control.
Enable password length check
Select this item to enable password length check.
Min password length
Enter the minimum password length.
If the password that a user enters is shorter than this value, the system rejects the password setting.
Enable password composition check
Select this item to enable password composition check.
Min number of character types
Enter the minimum number of character types in a password.
If the number of character types in the password that a user enters is less than this value, the system rejects the password setting.
Min number of characters for each type
Enter the minimum number of characters for each type in a password.
If the number of characters for each type in the password that a user enters is less than this value, the system rejects the password setting.
No more than two same consecutive characters in password
Select this item to reject a password that has more than two identical consecutive characters.
No username or reversed username in password
Select this item to reject a password that has the username or the reverse of the username.
Enable local user password change upon first login
Specify whether to enable local user password change upon first login.
If you enable this feature, the system requires a user to change the password upon first successful login.
Enable password history recording
Select this item to enable password history recording.
Max number of history password records
Enter the maximum number of history password records.
When the number of history password records exceeds this value, the most recent record overwrites the earliest one.
Enable password expiration
Globally enable password expiration to restrict the password validity period.
Password expiration time
Globally set the password expiration time. A user needs to change its password to a new password when its password expires.
Password expiration notification
Set the number of days before a user's password expires during which the user is notified of the pending password expiration.
Max period allowed to log in after expiration
Set the maximum number of days during which a user can log in using an expired password.
Max number of logins with an expired password
Set the maximum number of times a user can log in after the password expires.
Min password update interval
Enter the minimum password update interval.
A user can only change the password once within the specified interval.
Max login attempts
Set the maximum number of consecutive login attempts. When a user fails the maximum number of consecutive attempts, login attempt limit limits the user and user account according to the specified action.
Account handling for login failure
Specify the action to take if the number of login failures of a user reaches the maximum number of login attempts. Options:
Lock permanently.
Lock temporarily.
Not lock.
Account idle time
Set the idle time for local user accounts globally. For the idle time to take effect on a local user account, a user must have used that local user account to successfully log in to the device. After the idle time takes effect on a local user account, if no user has logged in successfully by using that user account within the idle time, the account will be locked. To restore the login permission of the account, access the local user page and clear the user idle lock state for the account.
Max Entries with Same Username
When users that use the same username with different IP addresses log in and the logins fail, the device records the user information for each IP address. If a user fails to log in with a new IP address after the number of recorded user information entries has reached the maximum number, the device will delete the earliest user information entry related to that username and add a new record.
Lockdown Type Upon Login Failures
Use this drop-down box to change the display style of locked user information. You can view locked user information on the SSL VPN statistics page. Changing the display style of locked user information also clears existing locked user information.
Click
OK .
Configure a local user group
Click the
Objects tab.In the navigation pane, select
User >User Management >Local Users .Click the
User Group tab and then clickCreate . TheCreate User Group page opens.Figure-11 User Group tab
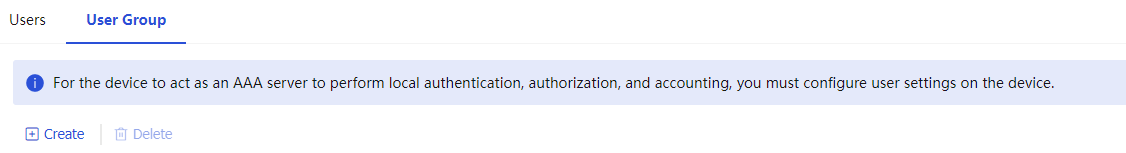
Create a user group.
Figure-12 Creating a user group
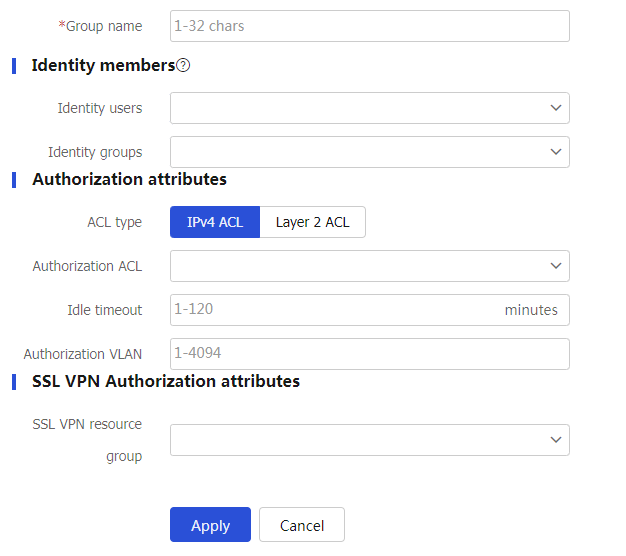
Table-9 User group configuration items
Item
Description
Group name
Name of the local user group.
Identity users
Identity users of the local user group.
Identity groups
User group to which the current user group belongs.
Configure authorization attributes and SSL VPN authorization attributes (see Table-4 ).
Click
Apply .
Configure identity users
To configure identity users, perform the following tasks:
Click the
Objects tab.In the navigation pane, select
User >User Management >Identity Users .You can view the organization structure on the
Identity Users page.Figure-13 Organization structure
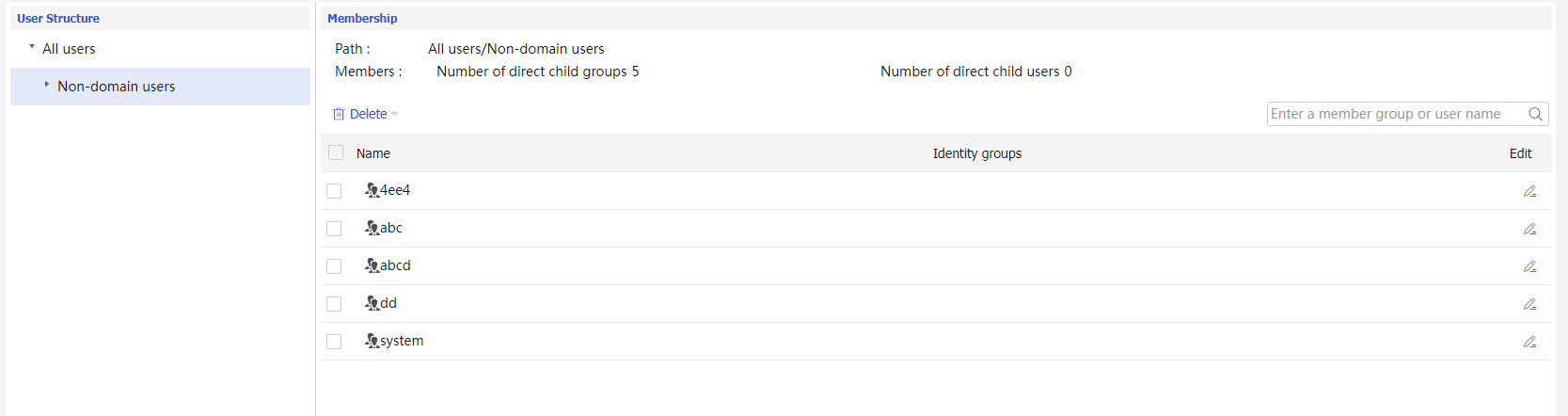
Edit the target identity user or user group.
Figure-14 Editing the target identity user
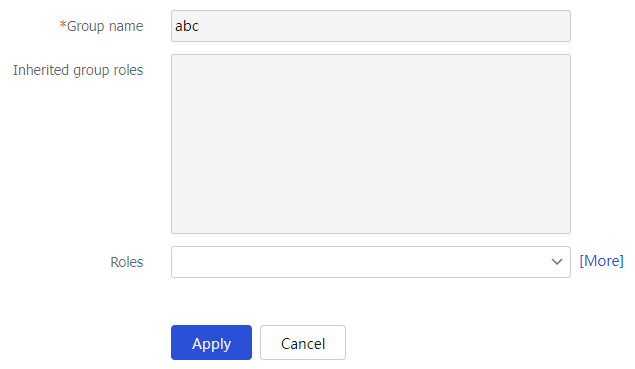
Table-10 Configuration items for configuring identity users
Item
Description
User/User group
Existing identity users or user groups.
Group role
Group role inherited by the current user or user group.
Role
Role of the user or user group. You can select one or more existing roles or create new roles.
Manage online users
To manage online users, perform the following tasks:
Click the
Objects tab.In the navigation pane, select
User >User Management >Online Users .Manage online users.
Figure-15 Online users
Table-11 Configuration items for managing online users
To create a static identity user:
Click the
Objects tab.In the navigation pane, select
User >User Management >Online Users .Click
Static Identity Users tab.Click
Create to configure a static identity user.Figure-16 Static identity users
Figure-17 Creating a static identity user
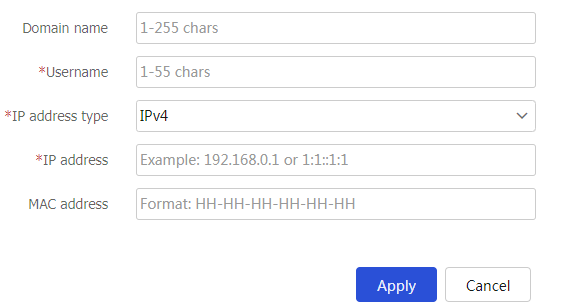
Table-12 Static identity user configuration items
Item
Description
Domain name
Specify the identity domain to which the static identity user belongs.
Username
Specify the username for the static identity user.
IP address type
Specify the type of the IP address bound to the static identity user. Options are
IPv4 andIPv6 .IP address
Specify the IP address bound to the static identity user.
MAC address
Specify the MAC address bound to the static identity user.
Click
Apply .
Configure a user import policy
Create a user import policy
Click the
Objects tab.In the navigation pane, select
User >User Management >User Import Policies .Click
Create . TheCreate User Import Policy page opens.Figure-18 User import policy
Create a user import policy.
Figure-19 Creating a user import policy
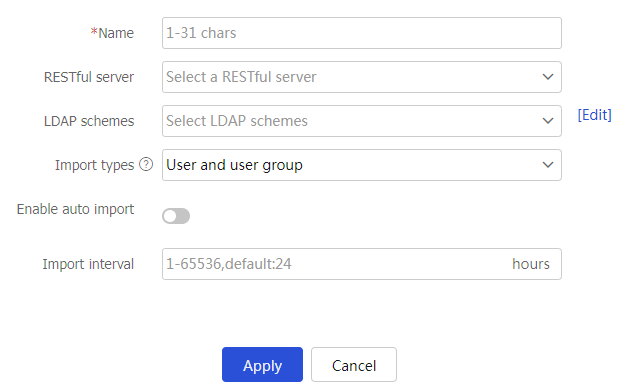
Table-13 User import policy configuration items
Item
Description
Name
Enter the name of a user import policy.
The name uniquely identifies a user import policy.
RESTful server
Select a RESTful server.
The device imports identity users and online users from the RESTful server.
LDAP schemes
Select LDAP schemes.
The device imports identity users from the LDAP servers specified in the LDAP schemes.
Import types
Select the type of information to be imported.
This parameter is applicable only to LDAP schemes.
Enable auto import
Select this item to enable automatic user import.
After this feature is enabled, the device first imports identity users and online users from the servers specified in the user import policy and then periodically imports identity users from the servers.
Import interval
Enter the automatic import interval.
The device automatically imports identity users from the servers specified in the user import policy at the specified interval.
Click
OK . The user import policy is displayed on theUser Import Policy page.
Manually import users
After you configure the user import policy, you can manually import identity users and online users from the servers specified in the user import policy.
Figure-20 User import policy list

To manually import users, perform the following tasks:
Manually import identity users —The device initiates user information requests to the servers, imports user account information from the servers, and then creates corresponding identity users. If the device fails to import an account, the device skips the account and continues to import the next account.Manually import online users —The device initiates a real-time online user information request to the server and then imports all online user information. The device can import online identity users only from an IMC RESTful server.
Configure the email server
The device sends a created random password or generated random verification code in an email notification to a user. Before you configure the email address of the receiver, you must configure the email server.
To configure the email server, perform the following tasks:
Click the
Objects tab.In the navigation pane, select
User >User Management >Email Server .Configure the email server.
Figure-21 Configuring the email server
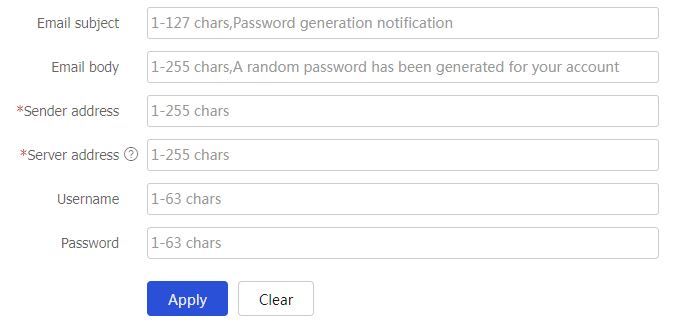
Table-14 Email server configuration items
Item
Description
Sender address
Set the address of the email sender.
Server address
Enter the URL of the email server, which starts with smtp://.
Username
Enter the username used to log in to the email server.
Password
Enter the password used to log in to the email server.