Routing table
Introduction
IP routing directs IP packet forwarding on routers. Based on the destination IP address in the packet, a router looks up a route for the packet in a routing table and forwards the packet to the next hop. Routes are path information used to direct IP packets.
A routing information base (RIB) contains global routing information and related information, including route recursion, route redistribution, and route extension information.
Routing protocols, including static and direct routing, each by default have a preference. If they find multiple routes to the same destination, the router selects the route with the highest preference as the optimal route.
The preference of a direct route is always 0 and cannot be changed. You can configure a preference for each static route and each dynamic routing protocol. A smaller preference value indicates a higher priority.
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
View routing table information
Routing tables enables the device to determine the forwarding path of a data packet by its destination IP address. After checking routing tables, the device can determine the next-hop device to which the packet should be sent. Routing table information helps you diagnose and address network connectivity issues. You can optimize forwarding paths by analyzing and adjusting route entries.
Click the
Network tab.In the navigation pane, select
Routing >Routing Table .Click the
IPv4 Routing Table orIPv6 Routing Table tab, and then view routing table information as needed.Figure-1 IPv4 routing table
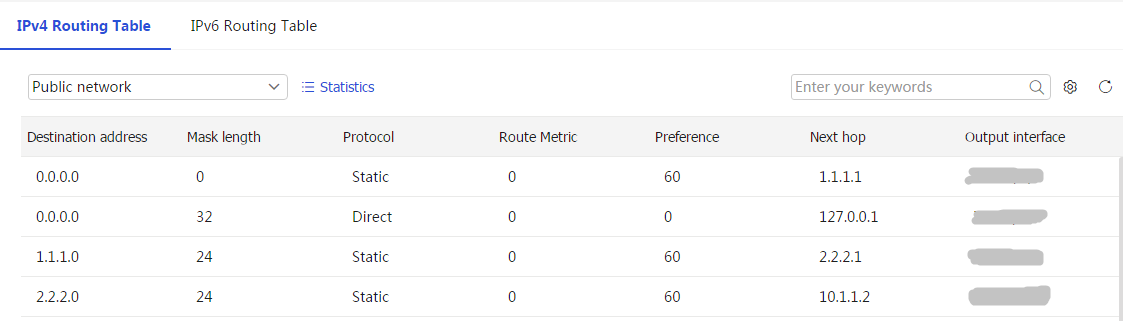
Figure-2 IPv6 routing table
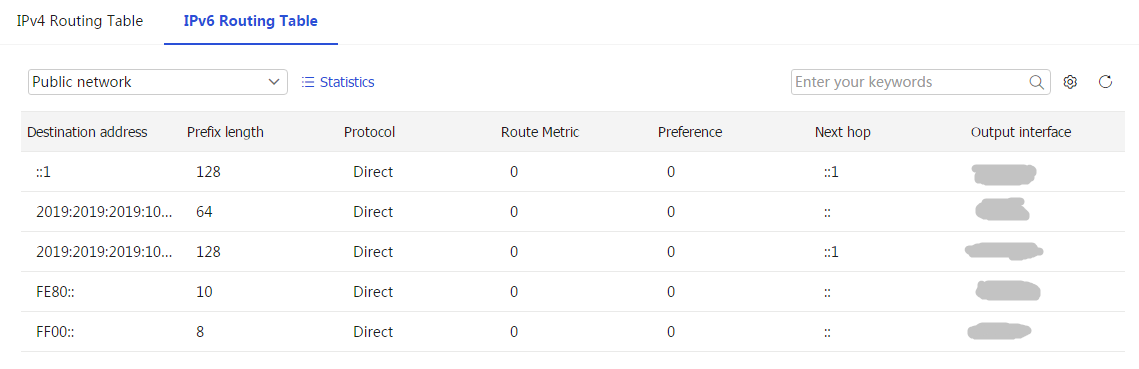
Table-1 Parameters in the IPv4 or IPv6 routing table
Parameter
Description
Destination address
Mask length
Mask length for the IPv4 destination address. This parameter is displayed on only the
IPv4 Routing Table page.Prefix length
Prefix length for the IPv6 destination address. This parameter is displayed on only the
IPv 6 Routing Table page.Protocol
Type of the routing protocol.
Route metric
Metric value of the route.
Precedence
Precedence of the route.
Next hop
Next hop address of the route.
Output interface
Output interface for the destination network segment.
On the
IPv4 Routing Table orIPv6 Routing Table tab, clickStatistics , and then view route statistics as needed.Figure-3 IPv4 route statistics
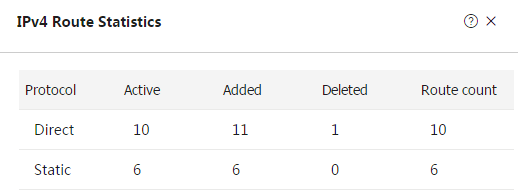
Figure-4 IPv6 route statistics
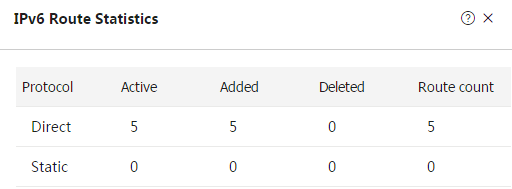
Table-2 Parameters on the IPv4 Route Statistics or IPv6 Route Statistics page