Policy-based routing
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
About PBR
Policy-based routing (PBR) uses user-defined policies to route packets. A policy can specify parameters for packets that match specific criteria such as ACLs, packet lengths, service object groups, or application groups. The parameters include the next hop, output interface, default next hop, and default output interface.
Policy
A policy includes match criteria and actions to be taken on the matching packets. A policy can have one or multiple nodes as follows:
Each node is identified by a node number. A smaller node number has a higher priority.
A node contains
if-match andapply clauses. Anif-match clause specifies a match criterion, and anapply clause specifies an action.A node has a match mode of
permit ordeny .
You can specify a policy for local PBR to guide the forwarding of locally generated packets, or apply a policy to an interface to guide the forwarding of packets received on the interface.
A policy compares packets with nodes in priority order. If a packet matches the criteria on a node, it is processed by the action on the node. Otherwise, it goes to the next node for a match. If the packet does not match the criteria on any node, the device performs a routing table lookup
Node
Match criteria
You can set an ACL, service object group, application group, or packet length match criterion to match packets.
To match a node, a packet must match all types of the match criteria for the node.
Actions
Compare packets with the next node upon failure on the current node. This action is taken when the specified actions (setting the VPN instance, next hop, output interface, default next hop, and default output interface) are not configured or become invalid. For example, the specified next hop is unreachable, the specified output interface is down, or the packets cannot be forwarded in the specified VPN instance.
Set an IP precedence.
Set the DF bit in the IP header.
Specify the forwarding tables that can be used for the matching packets.
Set next hops and default next hops associated with track entries. You can specify that a next hop must be directly connected to take effect.
Set output interfaces and default output interfaces associated with track entries.
PBR and Track
PBR can work with the Track feature to dynamically adapt the availability status of an action to the link status of a tracked object.
The tracked object can be a next hop, output interface, default next hop, or default output interface. The action is valid only when the track entry status changes to
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Configure PBR
Policy-based routing is a mechanism that achieves user-defined traffic forwarding. It allows network administrators to determine the forwarding path of data packets according to specific policies or conditions, which optimizes traffic management and improve resource efficiency in complex networks.
Click the
Network tab.In the navigation pane, select
Routing >Policy-Based Routing >IPv4 PBR (orIPv6 PBR ).Click
Create .Configure IPv4 or IPv6 PBR policy parameters.
Figure-1 Creating an PBR policy
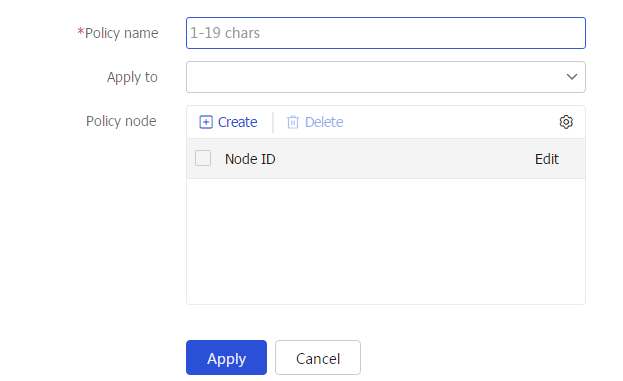
Table-1 IPv4 or IPv6 PBR policy configuration items
Item
Description
Policy name
Enter a PBR policy name.
Apply to
Apply the PBR policy locally (for local PBR) or to specific interfaces (for interface PBR).
Figure-2 Creating an IPv4 policy node
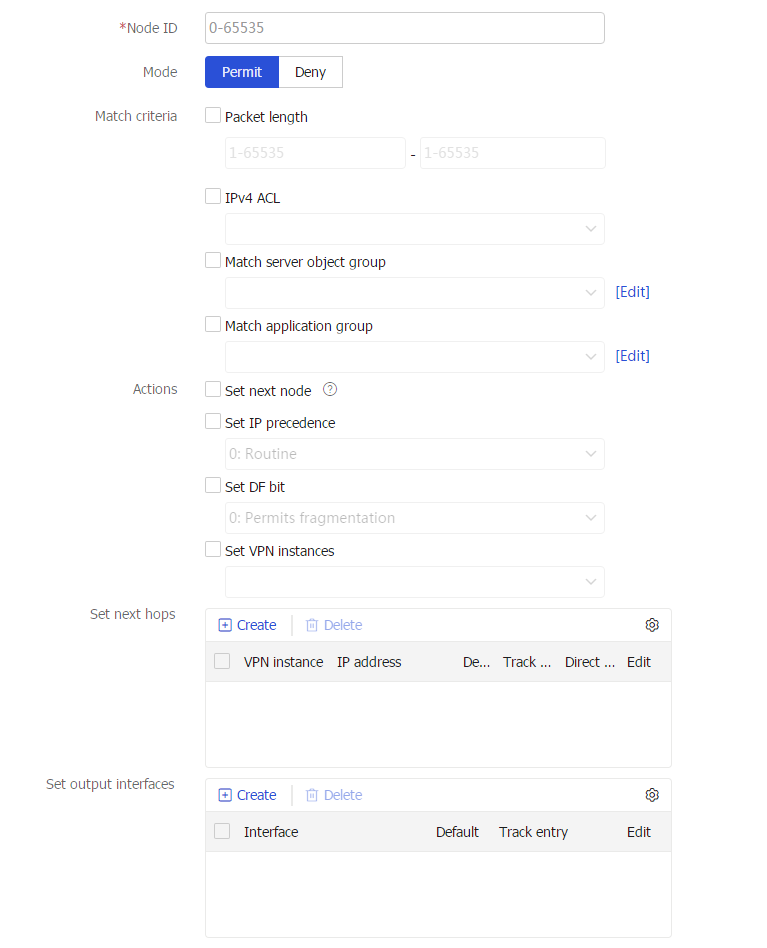
Figure-3 Creating an IPv6 policy node
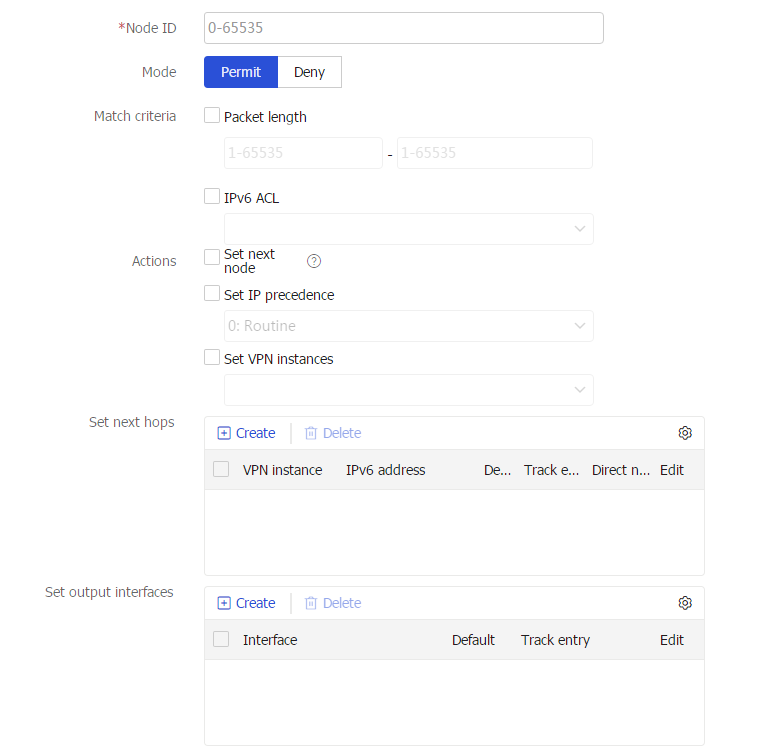
Table-2 Policy node configuration items
Item
Description
Node ID
Enter a policy node ID. A smaller ID has a higher priority. A policy compares packets with nodes in priority order.
Mode
Select a match mode for the policy node. Options include:
Permit
Deny
Match criteria
Specify packet match criteria. Options include:
Packet length : Specify the shortest and longest IP packet lengths.IPv4/IPv6 ACL : Specify an ACL number of name. You can select an existing ACL or create a new ACL.Match server object group : Specify a service object group name. You can select an existing service object group or create a new service object group. This parameter is supported by only IPv4 PBR.Match application group : Specify an application group name. You can select an existing application group or create a new application group. This parameter is supported by only IPv4 PBR.
Actions-Set next node
Compare packets with the next node upon failure on the current node.
Actions-Set IP precedence
Set the precedence for IP packets. Eight precedence values (0 to 7) are available. Each precedence value corresponds to a precedence type
Actions-Set DF bit
Set the Don't Fragment (DF) bit in the IP header of matching packets. Options include:
0 : Allows packet fragmentation.1 : Prohibits packet fragmentation.
This parameter is supported by only IPv4 PBR.
Actions-Set VPN instances
Specify forwarding tables for the public network or VPN instances.
Set next hops
Set next hops for matching packets. You can specify multiple next hops for backup or load sharing.
Click
Create , and configure the following next hop address parameters:VPN instance
IP address/IPv6 address
Default
Track entry
Direct next hop
Click
OK . The created next hop address will be displayed on the next hop address list.
Set output interfaces
Set output interfaces for matching packets. You can specify multiple output interfaces for backup or load sharing.
Click
Create , and configure the following output interface parameters:Interface
Default
Track entry
Click
OK . The created output interface will be displayed on the output interface list.
The output interface must be P2P type. Using a non-P2P output interface can result in forwarding failures when the interface has multiple next hops. Non-P2P interfaces include broadcast and NBMA interfaces such as Ethernet and virtual-template interfaces.
On the
Create Policy Node page, clickOK .The created policy node will be displayed on the policy node list.
On the
Create IPv4 Policy orCreate IPv6 Policy page, clickOK .The created policy will be displayed on the IPv4 or IPv6 PBR policy list.