IPv6 (NAT66)
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
IPv6-to-IPv6 Network Address Translation (NAT66) translates an IPv6 address in the IPv6 header to another IPv6 address. NAT66 is configured on edge devices of IPv6 networks to allow private users to access external networks and external users to access private network resources such as a Web server.
NAT66 prefix translation
NAT66 prefix translation, also known as IPv6-to-IPv6 Network Prefix Translation (NPTv6), replaces the IPv6 prefix in an IPv6 address of the packet header with another IPv6 prefix. NAT66 prefix translation supports the following translation methods:
Source address translation —Translates prefixes in source IPv6 addresses when users in the internal network access the external network.Destination address translation —Translates prefixes in destination IPv6 addresses when users in the external network access servers in the internal network.
NAT66 prefix translation uses the IPv6 prefix as the packet match criterion.
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Restrictions and guidelines
Restrictions and guidelines: NAT66 prefix translation
Source prefix translation rules on different interfaces do not support mapping different internal prefixes to the same external prefix.
Destination prefix translation rules on different interfaces do not support mapping the same external prefix to different internal prefixes.
Each source or destination prefix translation rule on one interface must be unique.
Configure NAT66
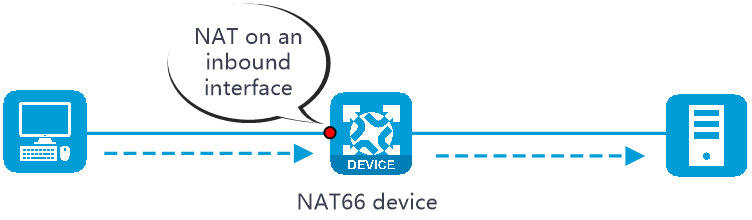
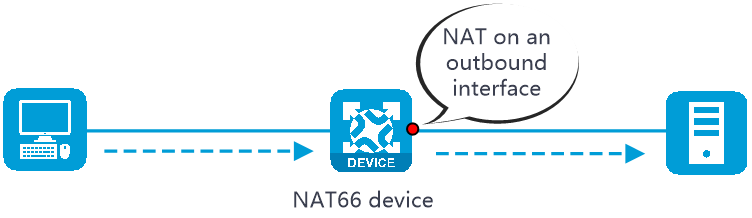
NAT66 can be performed in the inbound or outbound direction.
Inbound NAT —Performs address translation for packets received on an interface, as shown in Figure-1.Outbound NAT —Performs address translation for packets to be sent out of an interface, as shown in Figure-2.
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Configure NAT66 prefix translation
Click the
Network tab.In the navigation pane, select
Interface N AT >IPv 6 .Click
Create to create a NAT66 prefix translation rule.Figure-3 Clicking Create
Figure-4 Creating a NAT66 prefix translation rule
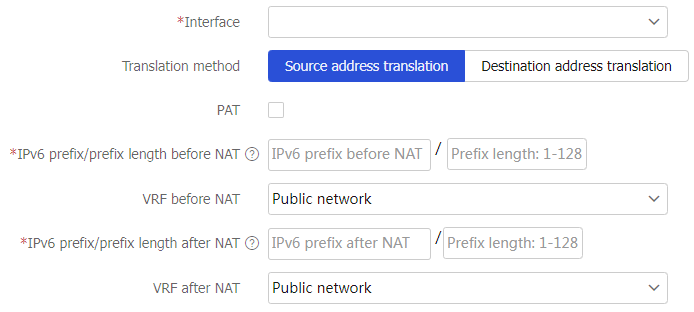
Table-1 Configuration items for NAT66 prefix translation
Item
Description
Interface
Interface to which the NAT66 prefix translation rule is applied.
Translation method
Select one of the following translation methods: Source address translation —Translates the source IP address of packets to be sent out of the interface.Destination address translation —Translates the destination IP address of packets received on the interface.PAT
Enable the source port translation for matching packets. T he option is available only when the translation method is source address translation. Protocol type
Specify a protocol type. I f you do not specify this option, translation is performed on packets of all protocols. T he option is available only when the translation method is destination address translation. IPv6 prefix/prefix length before NAT
IPv6 prefix and prefix length for packet match.
For source address translation, the IPv6 address prefix and prefix length are used to identify the matching source IPv6 address in the packet header.
For destination address translation, the IPv6 address prefix and prefix length are used to identify the matching destination IPv6 address in the packet header.
VRF before NAT
VRF to which the packet belongs before the translation.
Port before NAT
Specify a port number used to match the source port in the packet header.
The option is available only when the protocol type is 6 (TCP) or 17 (UDP).
IPv6 prefix/prefix length after NAT
IPv6 prefix and prefix length used to replace the prefix in the source or destination IPv6 address of the matching packets.
IPv6 prefix length before and after the translation must be the same.
VRF after NAT
VRF to which the packet belongs after the translation.
Port after NAT
Specify a port number used to replace the source port number of matching packets.
The option is only available when the protocol type is 6 (TCP) or 17 (UDP).
Click
OK .