Bandwidth management
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
Bandwidth management provides fine-grained control over traffic that flows through the device by using the following information:
Source and destination security zones.
Source and destination IP addresses.
Users.
Applications.
Services。
DSCP priorities.
Time ranges.
Bandwidth management is used in the following scenarios:
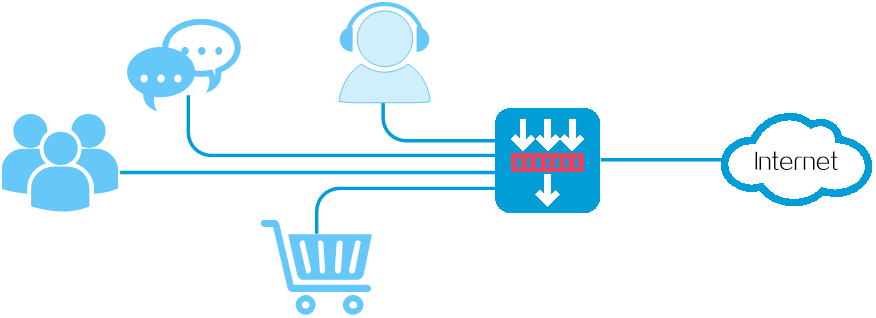
Enterprise intranet users need far more bandwidth than the amount of bandwidth leased from an ISP. This creates a bandwidth bottleneck at the intranet egress.
The P2P traffic on the intranet egress consumes a majority of the bandwidth resources. As a result, bandwidth cannot be guaranteed for key services.
Bandwidth management allows you to deploy different traffic policies on the network egress for different traffic types. Bandwidth management improves bandwidth efficiency and guarantees bandwidth for key services when congestion occurs. The emergence of bandwidth management technology effectively prevents bandwidth waste and network performance degradation. It ensures that key services run smoothly while improving network performance and user experience within the enterprise.
Figure-1 Bandwidth allocation
Bandwidth management process
Bandwidth management is implemented through traffic policies. You can configure traffic profiles and traffic policies in a traffic policy. A traffic profile specifies the guaranteed bandwidth and maximum bandwidth. A traffic policy specifies match criteria to match packets and the traffic profile to apply to matching packets.
Figure-2 Bandwidth management process
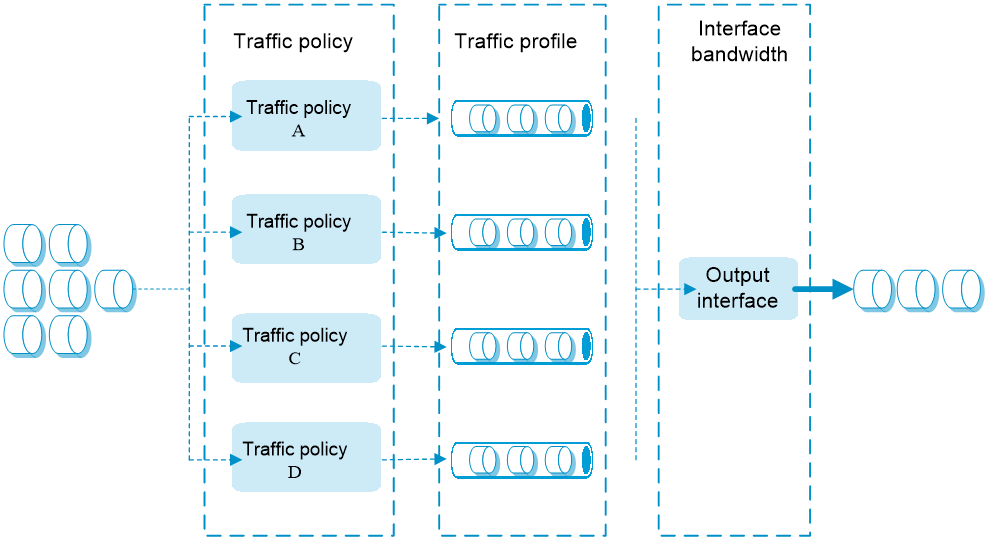
The bandwidth management process is as follows:
If a packet matches a traffic policy, the interface processes the packet according to the traffic profile (if any) specified for the traffic policy.
If no traffic profile is specified for the traffic policy, the packet is forwarded without bandwidth management.
The traffic profile processes the packet according to its settings.
The packet is limited by the interface bandwidth of the output interface.
Traffic match criteria
Multiple traffic policies can be configured. In a traffic policy, you can define the match criteria to match packets and specify the traffic profile to apply to matching packets. The device matches traffic policies in their order of appearance on the device. When a traffic policy is matched, the matching process ends and the device applies the traffic profile for the traffic policy to the traffic. If no traffic policy is matched, the device forwards the traffic.
You can configure the following match criteria in a traffic policy:
Source and destination security zones.
Source and destination IP addresses.
Users.
One match criterion can contain multiple match values. For example, you can configure multiple IP addresses for a source IP address match criterion. A match criterion is matched if any of its match values is matched.
Traffic policies support policy nesting, which allows a traffic policy to have a parent traffic policy. A maximum of four nesting levels are supported. The following rules apply when the device matches a traffic policy with a parent traffic policy:
The parent traffic policy is first matched. After the parent traffic policy is matched, the child traffic policy is matched. If the parent traffic policy is not matched, the child traffic policy is ignored and the matching process fails.
If both parent and child traffic policies are matched, the traffic profile for the child traffic policy is executed before the traffic profile for the parent traffic policy is executed. If both parent and child traffic policies are about the same parameter, the smaller value for an upper-limit parameter or the larger value for a lower-limit parameter is applied. If only the parent traffic policy is matched, the traffic profile for the parent traffic policy is applied.
Traffic profile
A traffic profile defines bandwidth resources that can be used by a traffic type. The interface bandwidth can be allocated among multiple traffic profiles. You can configure the following parameters in a traffic profile:
Table-1 Parameters in a traffic profile
Item | Description |
Rate limit mode | You can limit the traffic rate in one of the following ways:
|
Reference mode | A traffic profile can be referenced by multiple traffic policies in one of the following ways:
|
Total guaranteed bandwidth | Guarantees the total minimum bandwidth for key services when congestion occurs. |
Total maximum bandwidth | Controls the total maximum bandwidth for non-key services to prevent them from consuming a large amount of bandwidth. |
Bandwidth allocation among IP addresses | Allocates the total maximum bandwidth dynamically and evenly among online IP addresses. |
Per-IP or per-user guaranteed bandwidth | Guarantees the minimum bandwidth per IP address or per user to provide for bandwidth management at finer granularity. |
Per-IP or per-user maximum bandwidth | Controls the maximum bandwidth allowed per IP address or per user to provide for bandwidth management at finer granularity. |
Connection limits | Limits the total connection count, total connection rate, per-user/per-IP connection count, and per-user/per-IP connection rate. |
Per-IP traffic quota | Limits the monthly traffic quota per IP address. After you configure this function, you can view traffic statistics on the |
Monthly traffic quota | Per-IP monthly traffic quota. |
Forwarding priority | When an interface is congested with packets of multiple traffic profiles, packets with higher priority are sent first. Packets with the same priority have the same chance of being forwarded. |
DSCP marking | Modifies the DSCP value in packets. Network devices can classify traffic by using DSCP values and provide different treatment for packets according to the modified DSCP values. |
TCP MSS | Specifies the TCP maximum segment size. |
Bandwidth check | Enables the device to detect the amount of bandwidth consumed by traffic in real time by source IP address. |
Static thresholds | Specifies the maximum bandwidth threshold and minimum bandwidth threshold. When the device detects that the traffic rate exceeds the maximum bandwidth threshold or falls below the minimum bandwidth threshold, it outputs logs to the log host by using the fast log output feature. |
Dynamic threshold learning | Enables the device to dynamically learn the bandwidth threshold. Enable this option if you do not know the traffic rates in the network. The device will derive the maximum and minimum bandwidth thresholds from multiplying the learned bandwidth threshold by the maximum and minimum tolerance values. The derived maximum and minimum bandwidth thresholds have higher priority than the static thresholds. To view the learning results, access the |
Learning duration | Specifies the learning duration in minutes. After dynamic threshold learning is enabled, the device learns the traffic rates during the specified duration and calculates an average value as the learned bandwidth threshold. As a best practice to ensure the device can learn the traffic of a whole day, set the learning duration to be longer than 1440 minutes (24 hours). If the learning duration is modified while the device is learning, the device will learn the traffic again based on the new learning duration. |
Bandwidth tolerance | Specifies the bandwidth tolerance values. The device derives the maximum and minimum bandwidth thresholds from multiplying the learned bandwidth threshold by the maximum and minimum bandwidth tolerance values. If you do not care about the minimum bandwidth threshold, you can specify only the maximum bandwidth tolerance value. If you do not care about the maximum bandwidth threshold, you can specify only the minimum bandwidth tolerance value. |
Traffic policy matching acceleration
This feature makes the traffic policy configuration changes take effect immediately and accelerates traffic policy matching for packets. When a large number of traffic policies exist, enable traffic policy matching acceleration. If the acceleration fails, the changed match criteria do not take effect. The system still uses the original match criteria to match packets.
To enable traffic policy matching acceleration, choose one of the following methods:
Accelerate manually —For a traffic policy configuration change to take effect immediately, clickAccelerate .Accelerate automatically —The system determines whether to accelerate traffic policy matching at regular intervals. If the traffic policy match criteria change within an interval, the system performs acceleration when the interval expires. If no security policy match criteria change, the system does not perform acceleration when the interval expires. When the number of traffic policies is less than or equal to 100, the interval is 2 seconds. When the number of traffic policies is greater than 100, the interval is 20 seconds.
Bandwidth management for all IPv6 Layer 4 traffic
By default, bandwidth management is performed on traffic flows of TCP, UDP, ICMP, and ICMPv6. This function enables the device to perform bandwidth management on traffic flows of all IPv6 Layer 4 traffic in addition to the IPv4 Layer 4 traffic.
On the
Source NAT and destination NAT bandwidth management
By default, the device uses the IP address, port number, and VPN instance before NAT is performed to match a traffic policy.
To control bandwidth for IP addresses after NAT is performed, click
Real-time traffic trend
The real-time traffic trend display function is used to analyze the use of traffic that matches traffic policies, and presents the traffic use trends to users in the form of a line graph. This helps administrators identify traffic trends, such as which periods see heavier traffic, whether these traffic changes are repetitive, and enables refined management and control based on traffic conditions. This is beneficial for better bandwidth resource allocation and user Internet behavior management.
You can click the Real-time monitoring icon to view real-time traffic trends for a traffic policy.
vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Restrictions and guidelines
Restrictions and guidelines: Configuring parent and child traffic policies
The maximum bandwidth for a child traffic policy must be smaller than or equal to that for its parent traffic policy.
The guaranteed bandwidth for a child traffic policy must be smaller than or equal to that for its parent traffic policy.
The traffic profiles cannot be the same for the child and parent traffic policies.
If a traffic policy has a child traffic policy, the device performs bandwidth check and dynamic threshold learning only for the child traffic policy.
If a traffic policy to be copied has child traffic policies, only the parent traffic policy is copied.
You can specify a parent traffic policy only when creating a traffic policy. You cannot add or modify a parent traffic policy for an existing traffic policy.
The rate limit modes of the child and parent traffic policies must be the same.
A parent traffic policy does not support dynamic and even allocation for maximum bandwidth.
Restrictions and guidelines: Configuring a traffic profile
Bandwidth management is performed on a per-card basis. On a device installed with multiple security service cards, you must consider the number of security service cards when configuring bandwidth parameters in a traffic profile. For example, if the device is installed with three security service cards and you want to limit the uplink maximum bandwidth to 30000 kbps, you must configure the uplink maximum bandwidth to 10000 kbps.
If a TCP MSS is also configured for an interface, the smaller TCP MSS takes effect.
For bandwidth check to take effect, make sure an IP address or address object group is configured as a filtering condition in the traffic policy rule.
If you configure a source IP address or source address object group, the device performs bandwidth check based on source IP addresses.
If you configure a destination IP address or source address object group, the device performs bandwidth check based on destination IP addresses.
If you configure both a source IP address and destination IP address or both a source address object group and a destination address object, the device performs bandwidth check based on source IP addresses.
Restrictions and guidelines: Configuring interface bandwidth
An interface with small default expected bandwidth might experience traffic loss if the following conditions exist:
There is a large amount of traffic on the interface.
The interface uses the default expected bandwidth.
To avoid traffic loss, implicitly set the expected bandwidth to a large value for such an interface. For example, you can set the expected bandwidth of a tunnel interface to a value greater than 64 kbps (the default) if there is a large amount of traffic on the interface.
Restrictions and guidelines: Managing traffic policies
The traffic policy created by copying a traffic policy is placed next to the copied traffic policy.
Configure bandwidth management
Configuration flowchart
Figure-3 shows the configuration flowchart for bandwidth management.
Figure-3 Bandwidth management configuration procedure
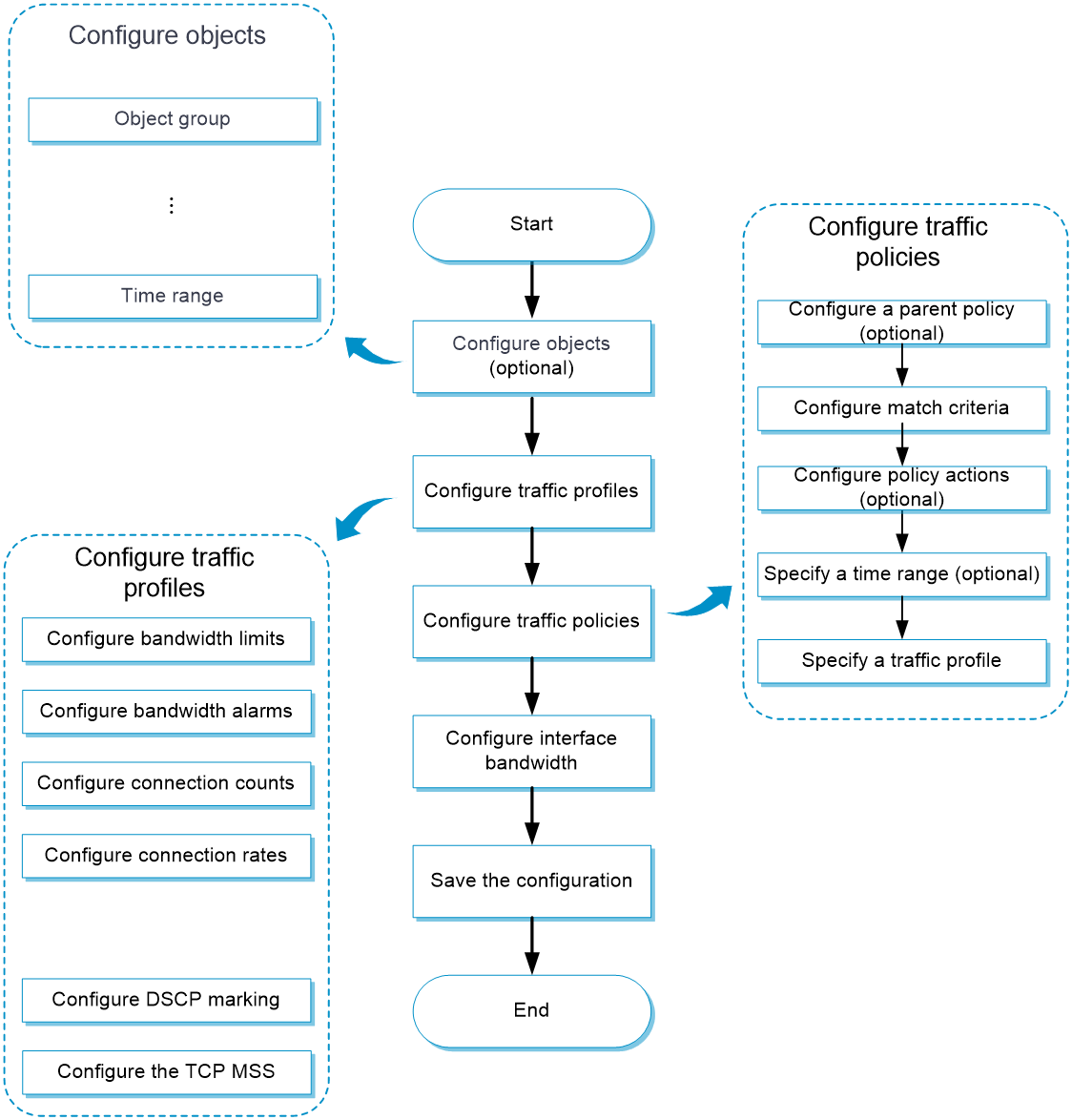
Configuration prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Configure bandwidth management with one traffic profile
In a network with simple traffic classification, you can configure uniform bandwidth limits and priority settings for all traffic through one-profile bandwidth management.
Configure a traffic profile
A traffic profile manages and allocates bandwidth resources in a network. By creating a traffic profile, you can configure the bandwidth limits, bandwidth detection, and reference mode, enabling efficient bandwidth management and allocation.
To configure a traffic profile:
Select
Load Balancing >B andwidth M anagement >Traffic Profile .Click
Create on theTraffic Profile tab.Figure-4 Traffic Profile page
Figure-5 Create Traffic Profile page
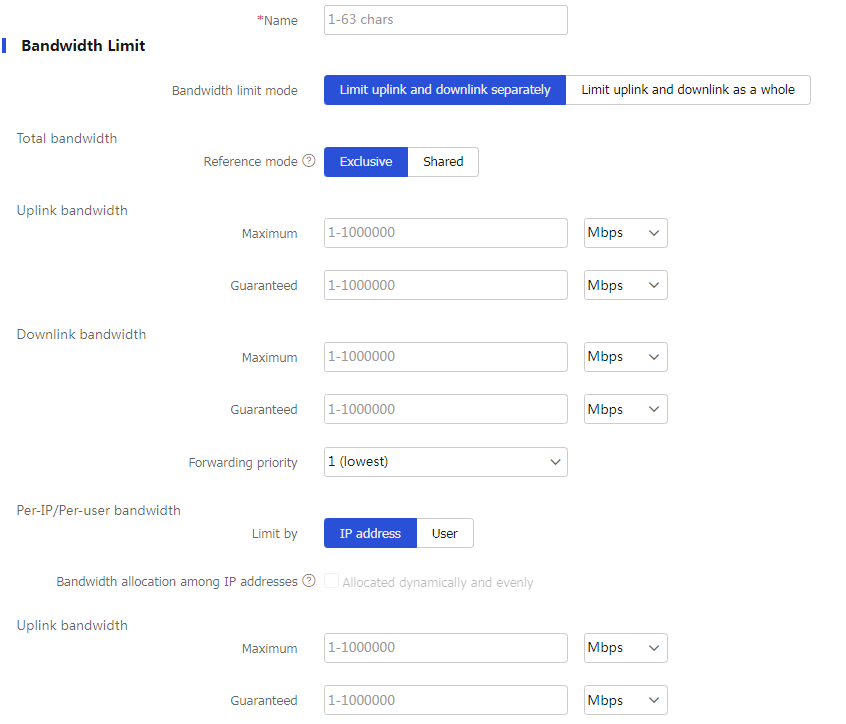
Configure a traffic profile.
Table-2 Traffic profile configuration items
Item
Description
Name
Enter a name for the traffic profile.
Bandwidth limit mode
Select
Limit uplink and downlink separately orLimit uplink and downlink .Reference mode
Select
Exclusive orShared .Total uplink maximum bandwidth
Set the total uplink maximum bandwidth.
Total uplink guaranteed bandwidth
Set the total uplink guaranteed bandwidth.
Total downlink maximum bandwidth
Set the total downlink maximum bandwidth.
Total downlink guaranteed bandwidth
Set the total downlink guaranteed bandwidth.
Forwarding priority
Set the forwarding priority. A greater priority value means a higher priority.
Bandwidth allocation among IP addresses
Select this option to allocate the total maximum bandwidth dynamically and evenly among online IP addresses.
Per-IP uplink maximum bandwidth
Set the per-IP uplink maximum bandwidth.
Per-IP downlink maximum bandwidth
Set the per-IP downlink maximum bandwidth.
Per-user uplink maximum bandwidth
Set the per-user uplink maximum bandwidth.
Per-user downlink maximum bandwidth
Set the per-user downlink maximum bandwidth.
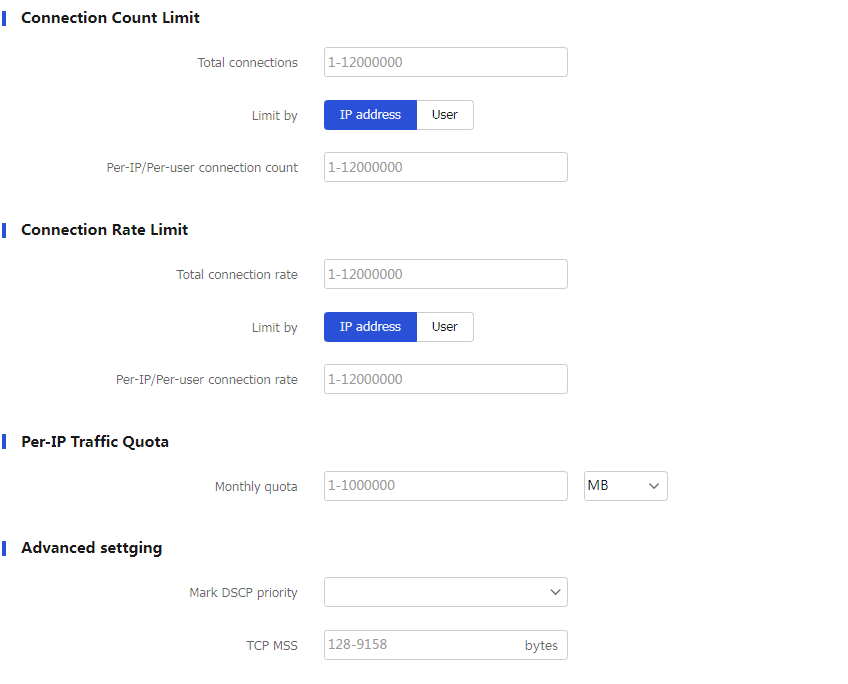
Total connection count
Set the total connection count.
Per-IP/Per-user connection count
Set the per-IP/per-user connection count.
Total connection rate
Set the total connection rate.
Per-IP/Per-user connection rate
Set the per-IP/per-user connection rate.
Monthly traffic quota
Set the per-IP monthly traffic quota.
Mark DSCP priority
Set the DSCP priority to be marked for packets.
TCP MSS
Set the TCP MSS.
Click
OK . The new traffic profile appears on theTraffic Profile page.
Configure a traffic policy
You can configure traffic profiles and traffic rules in traffic policy view. A traffic profile specifies the guaranteed bandwidth and maximum bandwidth. A traffic rule specifies match criteria to match packets and the traffic profile to apply to matching packets.
To configure a traffic policy:
Select
Load Balancing >B andwidth M anagement >Traffic P olic ies .Click
Create on theTraffic P olicy page.Figure-6 Traffic Policy page
Figure-7 Create Traffic Policy page

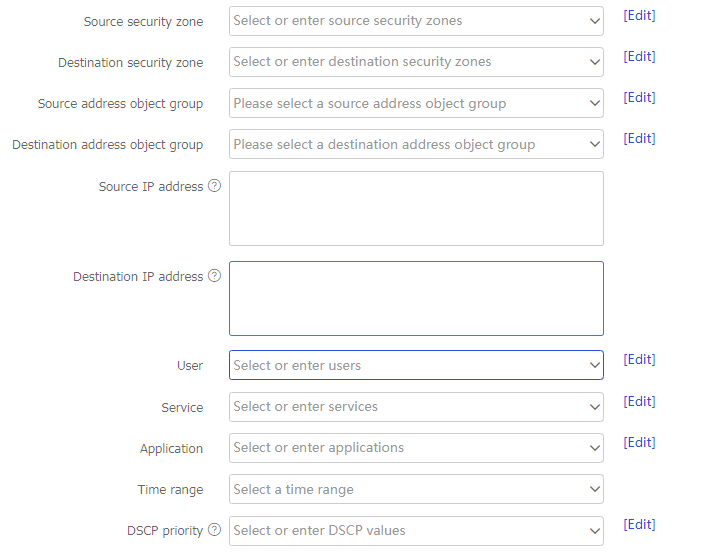
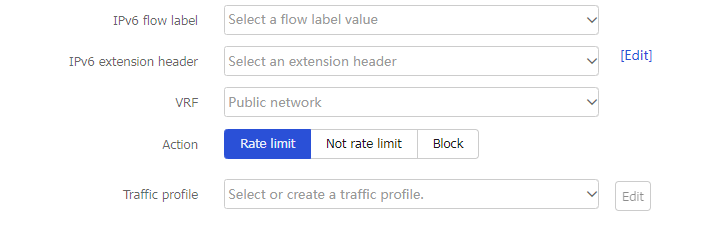
Create a traffic policy.
Table-3 Traffic policy configuration items
Item
Description
Name
Enter a name for the traffic policy.
Source security zone
Specify a source security zone as a match criterion.
Destination security zone
Specify a destination security zone as a match criterion.
Source IP address
Specify a source IP address object group as a match criterion.
Destination IP address
Specify a destination IP address object group as a match criterion.
User
Specify an identity user or user group as a match criterion.
Application
Specify an application or application group as a match criterion.
Service
Specify a service object group as a match criterion.
Time range
Specify a time range during which the policy is in effect.
DSCP priority
Specify a DSCP priority as a match criterion.
IPv6 flow label
Specify an IPv6 flow label as a match criterion.
IPv6 extension header
Specify an IPv6 extension header as a match criterion.
VRF
Specify a VPN instance as a match criterion.
Action
Specify an action for the policy:
Rate limit —Limits the rate of matching packets by referencing a traffic profile.Not rate limit —Does not limit the rate of matching packets.Block —Blocks matching packets.
Traffic profile
Specify a traffic profile.
Click
OK . The new traffic policy appears on theTraffic P olicy page.For the traffic policy configuration to take effect immediately, click
Accelerate .Figure-8
Accelerate 
Configure interface bandwidth
Select
Load Balancing >B andwidth M anagement >I nterface B andwidth .Click
Create on theI nterface B andwidth page.Figure-9 Interface Bandwidth page
Figure-10 Create Interface Bandwidth page
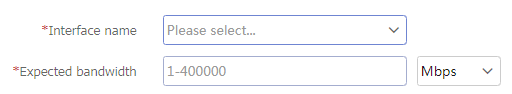
Create an interface bandwidth entry.
Table-4 Interface bandwidth configuration items
Item
Description
Interface name
Select an interface.
Expected bandwidth
Specify the expected bandwidth value.
Click
OK . The new interface bandwidth entry appears on theI nterface B andwidth List page.
Configure bandwidth management with parent/child traffic profiles
For networks with complex traffic classification and requiring specific bandwidth allocation for applications, user groups, or devices, you can use parent/child traffic profiles for precise traffic management, ensuring individual network needs.
Configure a traffic profile
See "
Configure a traffic policy
Configure a traffic policy (see "
Configur e a traffic policy ").On the page for creating a traffic policy, select a parent policy for it.
Figure-11 Selecting a parent policy

Click
OK . The new traffic policy appears in the traffic policy list.
Configure interface bandwidth
Configure bandwidth alarms
This feature enables the device to monitor real-time bandwidth thresholds (maximum and minimum) for traffic entering the traffic profile based on IP addresses. When bandwidth crosses configured thresholds, the device quickly sends logs to alert users.
Configure a traffic profile
Configure a traffic profile (see "
Configur e a traffic profile ").On the page for creating a traffic profile, configure bandwidth alarms.
Figure-12 Bandwidth alarms
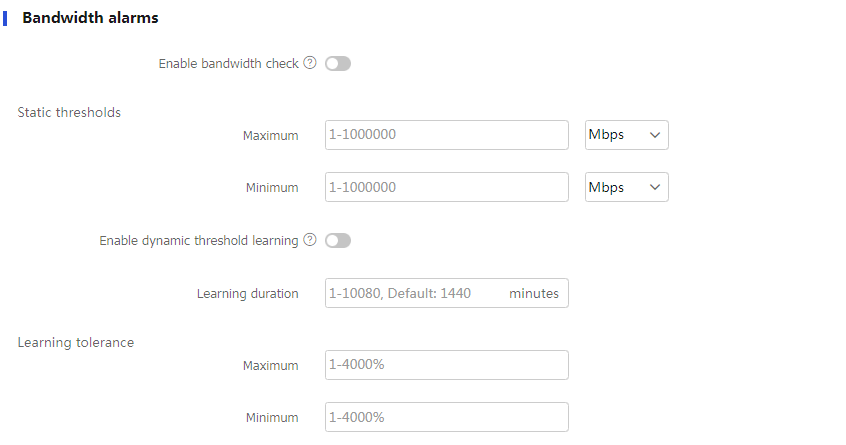
Table-5 Bandwidth alarm configuration items
Item
Description
Enable bandwidth check
Enable the device to detect the amount of bandwidth consumed by traffic in real time by IP address.
Static threshold-Maximum
Set the maximum static threshold.
Static threshold-Minimum
Set the minimum static threshold.
Enable dynamic threshold learning
Enable the device to dynamically learn bandwidth thresholds.
Learning duration
Set the learning duration.
Learning tolerance-Maximum
Set the maximum bandwidth tolerance value.
The device derives the maximum bandwidth threshold from multiplying the learned bandwidth threshold by the maximum bandwidth tolerance value.
Learning tolerance- Minimum
Set the minimum bandwidth tolerance value.
The device derives the minimum bandwidth threshold from multiplying the learned bandwidth threshold by the minimum bandwidth tolerance value.
Configure a traffic policy
See "