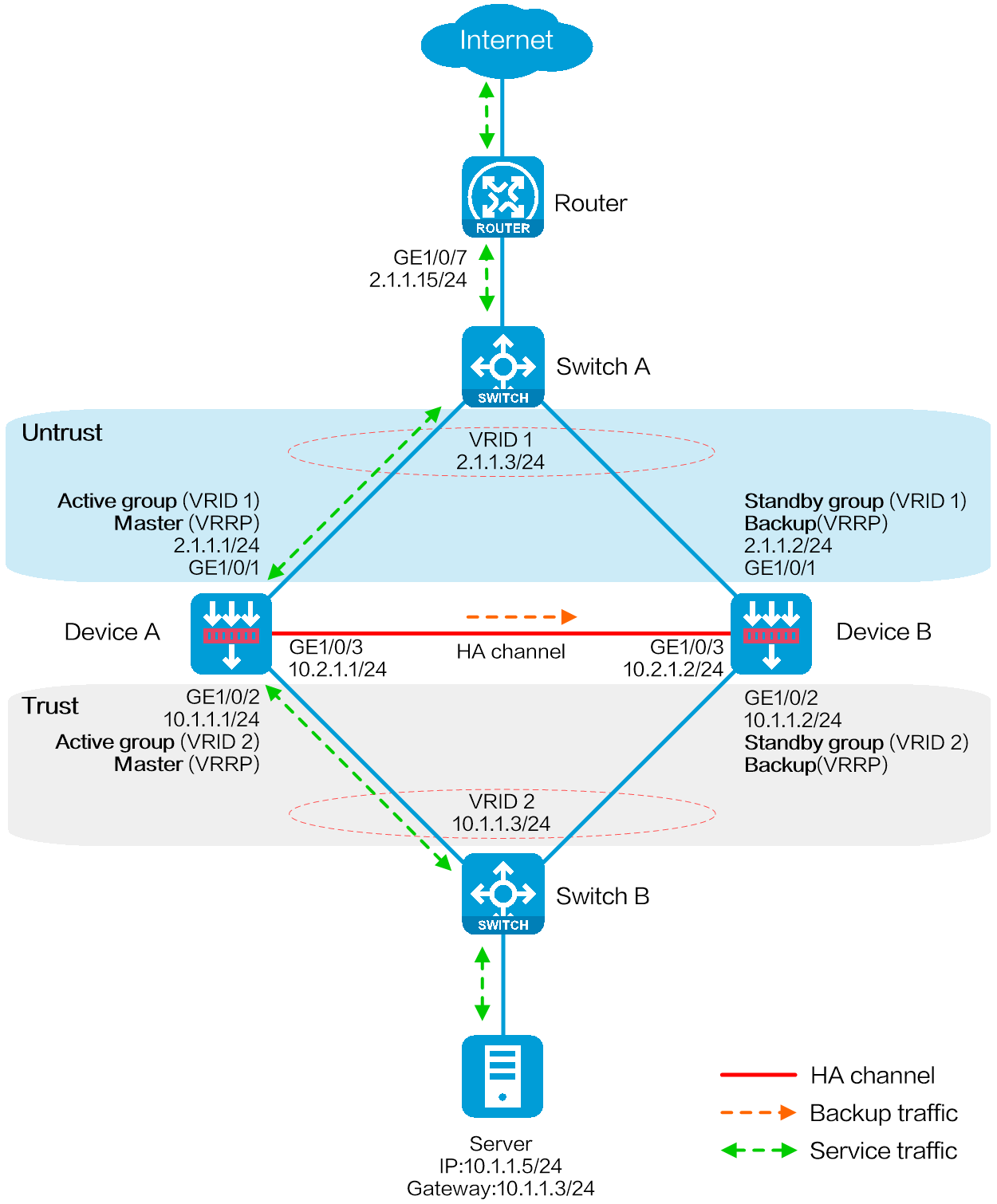
As shown in the following figure, Device A and Device B are border security devices connected to the internal network and the Internet. To improve service stability, use the two devices to form an HA system, with Device A as the primary device, and Device B as the secondary device. When Device A or its attached link fails, Device B takes over to ensure service continuity. In addition, configure the NAT internal server feature on the device for external users to access the internal server via external address 2.1.1.5.
Figure 1 Network diagram
This configuration example was created and verified on F9900 of the F5000-AI120 device.
Before you set up an RBM system, verify that the following hardware settings are consistent on the candidate member devices:
Device model.
Number and type of management interfaces of active and standby devices, service interfaces, and interfaces for setting up the RBM channels. Do not use one interface for multiple purposes.
Location, number, and type of disks. A device not with disks installed has small log storage and do not support some types of logs or reports.
Before you set up an RBM system, verify that the following software settings are consistent on the candidate member devices:
Software environment and version, including boot packages, system packages, feature packages, and patches.
Licensed signature libraries and features, such as signature library types, signature library version, validation time, and number of licensed resources.
Interface numbers.
Type, speed, and number of the interfaces for setting up the RBM channels. As a best practice, use aggregate interfaces.
Aggregate interface numbers and aggregation member port numbers.
Security zone configuration on the interfaces at the same location.
Multi-CPU packet distribution policy (configured with the forwarding policy command).
Assign IPv4 addresses to interfaces:
# Assign an IPv4 address to each interface according to the network diagram as follows.
<Router> system-view
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/7
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/7] ip address 2.1.1.15 255.255.255.0
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/7] quit
# Assign IP addresses to other interfaces in the same way according to the network diagram. (Details not shown.)
Configure route settings for network connectivity.
This example takes static route configuration as an example. Configure route settings according to the actual network requirements.
# Configure static route settings according to the network diagram. In this example, specify 2.1.1.3 (virtual IPv4 address of VRRP group 1) as the next hop for traffic to the internal network, and specify 3.1.1.15 as the next hop for traffic to the Internet.
[Router] ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 2.1.1.3
[Router] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 3.1.1.15
# Create VLAN 10 on Switch A, and configure the interfaces that connect Switch A to Device A, Device B, and Router as access ports, and then assign the ports to VLAN 10.
# Add interfaces to VLANs and set the link type according to the network diagram as follows.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] vlan 10
[SwitchA-vlan10] quit
[SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port access vlan 10
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port access vlan 10
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
[SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port access vlan 10
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Create VLAN 10, configure the interfaces connected to Device A, Device B, and Host to operate at Layer 2, and assign the interfaces to VLAN 10 as access interfaces.
# Add interfaces to VLANs and set the link type according to the network diagram as follows.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] vlan 10
[SwitchB-vlan10] quit
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port access vlan 10
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port access vlan 10
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port access vlan 10
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
Assign IPv4 addresses to interfaces:
# Assign an IPv4 address to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 2.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to other interfaces in the same way according to the network diagram. (Details not shown.)
Add interfaces to security zones.
# Add interfaces to security zones according to the network diagram.
[DeviceA] security-zone name untrust
[DeviceA-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-security-zone-Untrust] quit
[DeviceA] security-zone name trust
[DeviceA-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceA-security-zone-Trust] quit
Configure route settings for network connectivity:
This example takes static route configuration as an example. Configure route settings according to the actual network requirements.
# Configure a static route for Layer 3 connectivity between the internal and external networks according to the network diagram. The next hop for the static route to the external network is 2.1.1.15.
[DeviceA] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 2.1.1.15
Configure security policy settings to permit specific service packets:
Perform this task only on the primary device. After the RBM system is set up, the secondary device automatically synchronizes its security policy configuration with the primary device.
# Configure a rule named untrust-trust to allow the external user at 202.38.1.5/24 to actively access the internal server as follows.
[DeviceA] security-policy ip
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip] rule name untrust-trust
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-0-trust-untrust] source-zone untrust
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-0-trust-untrust] destination-zone trust
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-0-trust-untrust] source-ip-host 202.38.1.5
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-0-trust-untrust] action pass
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-0-trust-untrust] quit
# Configure rules to permit VRRP protocol packets. When the HA channel is disconnected, Device A and Device B can exchange VRRP protocol packets to elect a VRRP master.
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip] rule name vrrp1
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-1-vrrp1] source-zone trust
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-1-vrrp1] destination-zone local
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-1-vrrp1] service vrrp
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-1-vrrp1] action pass
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-1-vrrp1] quit
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip] rule name vrrp2
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-2-vrrp2] source-zone local
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-2-vrrp2] destination-zone trust
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-2-vrrp2] service vrrp
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-2-vrrp2] action pass
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-2-vrrp2] quit
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip] rule name vrrp3
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-3-vrrp3] source-zone untrust
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-3-vrrp3] destination-zone local
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-3-vrrp3] service vrrp
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-3-vrrp3] action pass
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-3-vrrp3] quit
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip] rule name vrrp4
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-4-vrrp4] source-zone local
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-4-vrrp4] destination-zone untrust
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-4-vrrp4] service vrrp
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-4-vrrp4] action pass
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip-4-vrrp4] quit
[DeviceA-security-policy-ip] quit
Configure RBM settings
In this example, Ethernet interfaces are used for control and data channel setup. If a device has both RBM and Ethernet interfaces, use the RBM interface for control and data channel setup to protect device security and stability. Do not use an RBM interface as a service interface.
# Specify two devices for the RBM system, with Device A as the primary device, and Device B as the secondary device. When Device A or its attached link fails, Device B takes over to ensure service continuity.
[DeviceA] remote-backup group
[DeviceA-remote-backup-group] remote-ip 10.2.1.2
[DeviceA-remote-backup-group] local-ip 10.2.1.1
[DeviceA-remote-backup-group] data-channel interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceA-remote-backup-group] device-role primary
RBM_P[DeviceA-remote-backup-group] undo backup-mode
RBM_P[DeviceA-remote-backup-group] hot-backup enable
RBM_P[DeviceA-remote-backup-group] configuration auto-sync enable
RBM_P[DeviceA-remote-backup-group] configuration sync-check interval 12
RBM_P[DeviceA-remote-backup-group] quit
# Configure VRRP groups and associate them with RBM. This configuration implements unified management and traffic direction for the VRRP groups.
RBM_P[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
RBM_P[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 2.1.1.3 active
RBM_P[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
RBM_P[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
RBM_P[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 10.1.1.3 active
RBM_P[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
Configure the NAT internal server.
You only need to configure NAT settings on the primary device Device A. The NAT settings will be automatically synchronized to the secondary device Device B.
# Configure the internal server, allowing external hosts to access the internal server via 202.38.1.5, and bind it to VRRP group 1.
RBM_P[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
RBM_P[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] nat server global 2.1.1.5 inside 10.1.1.5 vrrp 1
RBM_P[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
Configure security services on Device A. (Details not shown.)
# After completing hot backup system configuration, configure security services. Configure the modules whose configuration information can be backed up by the hot backup system only on the primary device (Device A).
Assign IPv4 addresses to interfaces:
# Assign an IPv4 address to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 2.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to other interfaces in the same way according to the network diagram. (Details not shown.)
Add interfaces to security zones.
# Add interfaces to security zones according to the network diagram.
[DeviceB] security-zone name untrust
[DeviceB-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-security-zone-Untrust] quit
[DeviceB] security-zone name trust
[DeviceB-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[DeviceB-security-zone-Trust] quit
Configure route settings for network connectivity:
This example takes static route configuration as an example. Configure route settings according to the actual network requirements.
# Configure a static route for Layer 3 connectivity between the internal and external networks according to the network diagram. The next hop for the static route to the external network is 2.1.1.15.
[DeviceB] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 2.1.1.15
Configure RBM settings
In this example, Ethernet interfaces are used for control and data channel setup. If a device has both RBM and Ethernet interfaces, use the RBM interface for control and data channel setup to protect device security and stability. Do not use an RBM interface as a service interface.
# Specify two devices for the RBM system, with Device A as the primary device, and Device B as the secondary device. When Device A or its attached link fails, Device B takes over to ensure service continuity.
[DeviceB] remote-backup group
[DeviceB-remote-backup-group] remote-ip 10.2.1.1
[DeviceB-remote-backup-group] local-ip 10.2.1.2
[DeviceB-remote-backup-group] data-channel interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceB-remote-backup-group] device-role secondary
RBM_S[DeviceB-remote-backup-group] undo backup-mode
RBM_S[DeviceB-remote-backup-group] hot-backup enable
RBM_S[DeviceB-remote-backup-group] configuration auto-sync enable
RBM_S[DeviceB-remote-backup-group] configuration sync-check interval 12
RBM_S[DeviceB-remote-backup-group] quit
# Configure VRRP groups and associate them with RBM. This configuration implements unified management and traffic direction for the VRRP groups.
RBM_S[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
RBM_S[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 2.1.1.3 standby
RBM_S[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
RBM_S[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
RBM_S[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 10.1.1.3 standby
RBM_S[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Specify the default gateway as 40.1.1.1 for the server.
# Verify that the external host can access the internal server. On Device A, you can see information about the NAT session generated for traffic from the external host to the internal server.
RBM_P[DeviceA] display nat session verbose
Slot 1:
Initiator:
Source IP/port: 202.38.1.5/52082
Destination IP/port: 2.1.1.5/80
DS-Lite tunnel peer: -
VPN instance/VLAN ID/Inline ID: -/-/-
Protocol: TCP(6)
Inbound interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Source security zone: Untrust
Responder:
Source IP/port: 10.1.1.5/80
Destination IP/port: 202.38.1.5/52082
DS-Lite tunnel peer: -
VPN instance/VLAN ID/Inline ID: -/-/-
Protocol: TCP(6)
Inbound interface: GigabitEthernet1/0/2
Source security zone: Trust
State: TCP_ESTABLISHED
Application: HTTP
Rule ID: 2
Rule name: 3
Start time: 2024-5-29 16:16:59 TTL: 9995s
Initiator->Responder: 551 packets 32547 bytes
Responder->Initiator: 956 packets 1385514 bytes
Total sessions found: 1
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7
port link-mode route
ip address 2.1.1.15 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8
port link-mode route
ip address 3.1.1.14 255.255.255.0
#
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 3.1.1.15
ip route-static 10.1.1.0 24 2.1.1.3
#
vlan 10
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port access vlan 10
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port access vlan 10
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port access vlan 10
#
vlan 10
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port access vlan 10
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port access vlan 10
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port access vlan 10
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 2.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 2.1.1.3 active
nat server global 2.1.1.5 inside 10.1.1.5 vrrp 1
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 10.1.1.3 active
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode route
ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
security-zone name Trust
import interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
#
security-zone name Untrust
import interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
#
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 2.1.1.15
#
security-policy ip
rule 0 name untrust-trust
action pass
source-zone untrust
destination-zone trust
source-ip-host 202.38.1.5
rule 1 name vrrp1
action pass
source-zone trust
destination-zone local
service vrrp
rule 2 name vrrp2
action pass
source-zone local
destination-zone trust
service vrrp
rule 3 name vrrp3
action pass
source-zone untrust
destination-zone local
service vrrp
rule 4 name vrrp4
action pass
source-zone local
destination-zone untrust
service vrrp
#
remote-backup group
data-channel interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
configuration sync-check interval 12
local-ip 10.2.1.1
remote-ip 10.2.1.2
device-role primary
#
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 2.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 2.1.1.3 standby
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 10.1.1.3 standby
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode route
ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
security-zone name Trust
import interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
#
security-zone name Untrust
import interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
#
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 2.1.1.15
#
remote-backup group
data-channel interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
configuration sync-check interval 12
local-ip 10.2.1.2
remote-ip 10.2.1.1