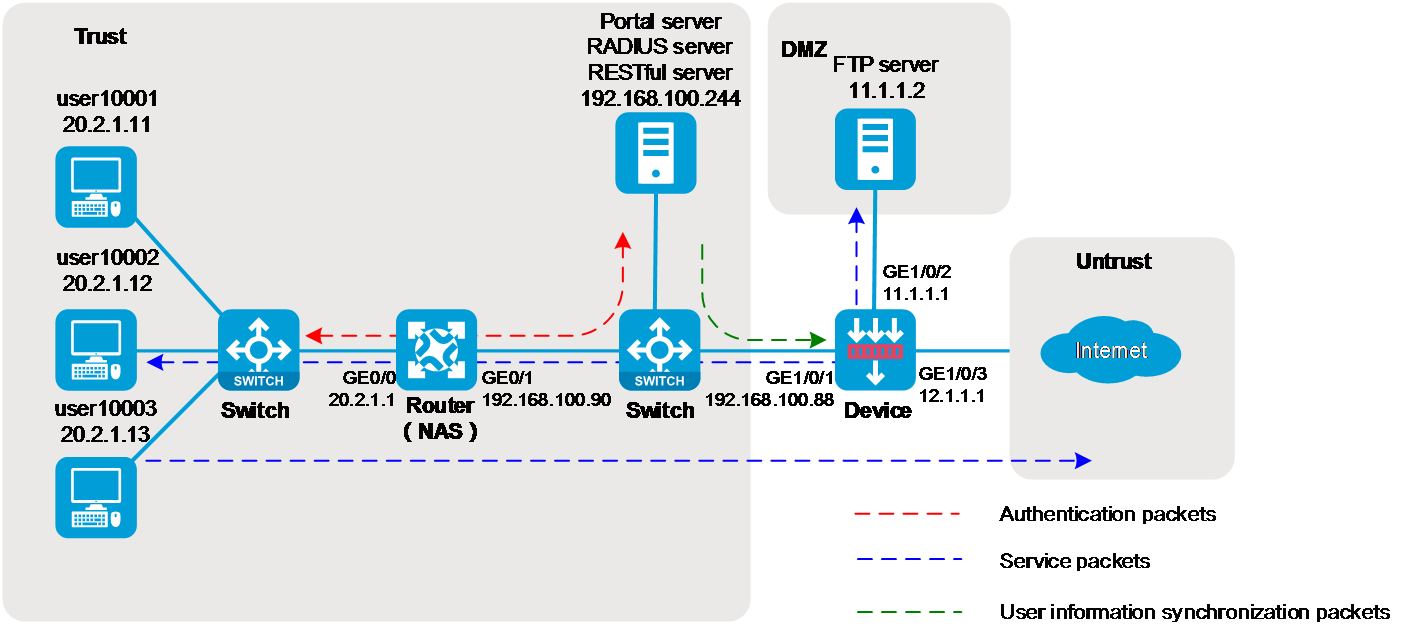
As shown in Figure 1, the enterprise needs to perform identity identification and access control on portal users. The specific requirements are as follows:
An IMC server acts as a portal authentication server, a portal Web server, and a RADIUS server.
The RADIUS server acts as the authentication server.
The RESTful server stores user account information.
The router acts as a NAS to authenticate users. The users use static IP addresses and must pass portal authentication to access the network.
The firewall (Device) performs the following identity-based access control on the users that have passed portal authentication:
User user10001 cannot access the FTP server or the Internet.
User user10002 can access the FTP server but cannot access the Internet.
User user10003 can access the Internet but cannot access the FTP server.
Users from the Internet cannot initiate access to the hosts in security zones trust and dmz.
To implement the purpose of this example, configure the hosts, router, firewall (Device), and IMC server as follows:
Figure 2 Analysis diagram
This configuration example was created and verified on F9900 of the F5000-AI120 device.
This example was created and verified on version 7.1.064, ESS 0701 of the MSR26-30 router.
This example uses IMC PLAT 7.3 (E0506), IMC UAM 7.3 (E0503), IMC CAMS 7.3 (E0501), and IMC SSM 7.3 (E0501) to show the basic configuration of the RADIUS server and portal server.
An IMC server logs off an online user only if it receives an accounting-stop request for that user. For the NAS to send accounting-stop requests to the IMC server, you must configure accounting settings in the user authentication domain on the NAS. However, you do not need to configure accounting parameters on the IMC server because accounting is not required.
Configure IP addresses for interfaces and a default route to ensure the network connectivity of the router:
# Assign IP address 20.2.1.1 to interface GigabitEthernet 0/0.
<Router> system-view
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 0/0
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0] ip address 20.2.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/0] quit
# Assign IP address 192.168.100.90 to interface GigabitEthernet 0/1.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 0/1
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/1] ip address 192.168.100.90 255.255.255.0
[Router-GigabitEthernet0/1] quit
# Configure a default route to ensure that the router can reach the FTP server and the Internet.
[Router] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.100.88
Configure SNMP to ensure that the IMC server can monitor and manage the router:
# Enable the SNMP agent.
[Router] snmp-agent
# Enable all SNMP versions, and create the read-only community public and the read and write community private.
[Router] snmp-agent sys-info version all
[Router] snmp-agent community read public
[Router] snmp-agent community write private
Configure a RADIUS scheme:
# Create a RADIUS scheme named rs1 and enter its view.
[Router] radius scheme rs1
# Configure the primary authentication server, the primary accounting server, and the keys for secure communication.
[Router-radius-rs1] primary authentication 192.168.100.244
[Router-radius-rs1] primary accounting 192.168.100.244
[Router-radius-rs1] key authentication simple admin
# Exclude the ISP domain name from the usernames sent to the RADIUS server.
[Router-radius-rs1] user-name-format without-domain
[Router-radius-rs1] quit
Configure an authentication domain:
# Create an ISP domain named dm1 and enter its view.
[Router] domain dm1
# Configure users to use RADIUS scheme rs1 for authentication, authorization, and accounting in the ISP domain.
[Router-isp-dm1] authentication portal radius-scheme rs1
[Router-isp-dm1] authorization portal radius-scheme rs1
[Router-isp-dm1] accounting portal radius-scheme rs1
[Router-isp-dm1] quit
Configure portal authentication:
# Configure a portal authentication server named newpt, with IP address 192.168.100.244, plaintext password admin, and portal packet listening port number 50100.
[Router] portal server newpt
[Router-portal-server-newpt] ip 192.168.100.244 key simple admin
[Router-portal-server-newpt] port 50100
[Router-portal-server-newpt] quit
# Create a portal Web server named newpt and specify http://192.168.100.244:8080/portal as the URL of the server.
[Router] portal web-server newpt
[Router-portal-websvr-newpt] url http://192.168.100.244:8080/portal
[Router-portal-websvr-newpt] quit
# Enable direct portal authentication on GigabitEthernet 0/0.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 0/0
[Router–GigabitEthernet0/0] portal enable method direct
# Specify portal Web server newpt on GigabitEthernet 0/0.
[Router–GigabitEthernet0/0] portal apply web-server newpt
# Specify domain dm1 as the portal authentication domain on GigabitEthernet 0/0.
[Router–GigabitEthernet0/0] portal domain dm1
[Router–GigabitEthernet0/0] quit
Configure IP addresses for interfaces and a default route to ensure the network connectivity of the firewall:
# Assign IP address 192.168.100.88 to interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 192.168.100.88 255.255.255.0
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Assign IP address 11.1.1.1 to interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Assign IP address 12.1.1.1 to interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/3.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ip address 12.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Configure a static route to ensure that the firewall can reach the user network.
[Device] ip route-static 20.2.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.100.90
# Configure a default route to ensure that the firewall can reach the Internet. This example uses 12.1.1.2 as the IP address of the next hop for the route. In an actual network, use the IP address provided by the ISP.
[Device] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 12.1.1.2
Add interfaces to security zones:
# Create security zone trust and enter its view. Add interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to the security zone.
[Device] security-zone name trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
# Create security zone dmz and enter its view. Add interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to the security zone.
[Device] security-zone name dmz
[Device-security-zone-DMZ] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-DMZ] quit
# Create security zone untrust and enter its view. Add interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to the security zone.
[Device] security-zone name untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
Configure a security policy to ensure that the firewall and IMC can reach each other.
This step ensures that the firewall can synchronize user identity information from IMC.
# Enter IPv4 security policy view.
[Device] security-policy ip
# Configure a rule named trust-local to permit packets from security zone trust to security zone local.
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule 0 name trust-local
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-trust-local] source-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-trust-local] destination-zone local
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-trust-local] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-trust-local] quit
# Configure a rule named local-trust to permit packets from security zone local to security zone trust.
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule 1 name local-trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-trust-local] source-zone local
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-trust-local] destination-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-trust-local] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-trust-local] quit
Configure SNMP for the IMC server to monitor and manage the firewall.
# Enable the SNMP agent.
[Device] snmp-agent
# Enable all SNMP versions, and create the read-only community public and the read and write community private.
[Device] snmp-agent sys-info version all
[Device] snmp-agent community read public
[Device] snmp-agent community write private
Configure NETCONF over SOAP for the IMC server to issue configuration to the firewall:
# Enable NETCONF over SOAP over HTTP.
[Device] netconf soap http enable
# Enable NETCONF over SOAP over HTTPS.
[Device] netconf soap https enable
Enable RESTful for the firewall for communication with the IMC server:
# Enable RESTful access over HTTP.
[Device] restful http enable
# Enable RESTful access over HTTPS.
[Device] restful https enable
Configure the HTTP service for local device management user admin.
[Device] local-user admin class manage
[Device-luser-manage-admin] service-type http
[Device-luser-manage-admin] quit
Configure the user identification feature:
# Enable the user identification feature.
[Device] user-identity enable
# Create a RESTful server named rest1 and enter its view.
[Device] user-identity restful-server rest1
# Specify the username and password for logging in to the RESTful server as both admin.
[Device-restfulserver-rest1] login-name admin password simple admin
# Specify the URIs for requesting information such as the network access user account information and online network access user information from the RESTful server. (The URIs of the IMC server are fixed as follows. Only the IP address can be replaced.)
[Device-restfulserver-rest1] uri get-user-database http://192.168.100.244:8080/imcrs/ssm/imcuser/accessUser
[Device-restfulserver-rest1] uri get-user-group-database http://192.168.100.244:8080/imcrs/ssm/imcuser/acces
sUserGroup
[Device-restfulserver-rest1] uri get-online-user http://192.168.100.244:8080/imcrs/ssm/imcuser/onlineUser
[Device-restfulserver-rest1] uri put-online-user http://192.168.100.244:8080/imcrs/ssm/imcuser/uploadOnlineU
ser
[Device-restfulserver-rest1] uri put-offline-user http://192.168.100.244:8080/imcrs/ssm/imcuser/uploadOfflin
eUser
[Device-restfulserver-rest1] quit
# Create an identity user import policy named imc and enter its view.
[Device] user-identity user-import-policy imc
# Specify RESTful server rest1 for the identity user import policy.
[Device-identity-user-impt-policy-imc] restful-server rest1
# Set the interval for automatic identity user account import to 1 hour.
[Device-identity-user-impt-policy-imc] account-update-interval 1
[Device-identity-user-impt-policy-imc] quit
# Enable automatic identity user account import.
[Device] user-identity user-account auto-import policy imc
# Import identity user accounts from the servers specified in identity user import policy imc. (Execute this command after the device can communicate normally with the IMC server.)
[Device] user-identity user-account import policy imc
# Import online identity users from the servers specified in identity user import policy imc. (Execute this command after the device can communicate normally with the IMC server and users have come online.)
[Device] user-identity online-user import policy imc
Configure a security policy to permit only user10002 to access the FTP server and permit only user10003 to access the Internet:
# Configure a security policy rule named user10002 to permit only user10002 to communicate with the FTP server and deny others from accessing the FTP server.
[Device] security-policy ip
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule 2 name user10002
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-user10002] source-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-user10002] source-zone dmz
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-user10002] destination-zone dmz
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-user10002] destination-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-user10002] user user10002
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-user10002] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-user10002] logging enable
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-user10002] quit
# Configure a security policy rule named user10003 to permit only user10003 to access the Internet and deny Internet users from accessing the internal network.
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule 3 name user10003
[Device-security-policy-ip-3-user10003] source-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-3-user10003] destination-zone untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-3-user10003] user user10003
[Device-security-policy-ip-3-user10003] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-2-user10003] logging enable
[Device-security-policy-ip-3-user10003] quit
[Device-security-policy-ip] quit
Add the firewall to IMC for device monitoring and management.
Enter the URL of IMC in the address bar of a browser to log in to IMC.
In this example, the URL for IMC is http://192.168.100.244:8080/imc/. The username and password are both admin. (Details not shown.)
Adding the firewall:
# Click the Resource tab.
# From the navigation pane, select Resource Management > Add Device.
# On the page that opens, configure the parameters as shown in Figure 103:
In the Telnet Settings area, set both the username and password to admin.
Use the default settings for other parameters.
By default, the read-only SNMP community string is public and the read and write SNMP community string is private.
# Click OK.
# Add the router at 192.168.100.90 to IMC in the same way.
Modify NETCONF settings:
# Click the Resource tab.
# From the navigation pane, select View Management > Device View.
# Click the link in the firewall Label column for the target device.
Figure 4 Device list
# In the right pane, click Configure > Modify NETCONF Settings.
# In the dialog box that opens, click the plus sign (+) to add a protocol as shown in Figure 105.
This example sets both the username and password to admin.
Figure 5 Modifying NETCONF settings
# Click OK.
Synchronize security services from the firewall to the IMC server to ensure that the configuration and user information is consistent on the firewall and IMC server:
# Click the Service tab.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Service Manager > Device Management.
# On the Devices tab, view the firewall displayed in the device list.
Figure 6 Device management page (1)
# Select the firewall, click Synchronize, and then view the synchronization status in the Sync Status column.
The synchronization process might take a long time. Please wait.
Figure 7 Device management page (2)
Figure 8 Device management page (3)
Configure user authentication system parameters and user notification parameters to ensure that the IMC server synchronizes user online and offline information to the firewall in real time:
# Click the Service tab.
# From the navigation pane, select Security Service Manager > Global Parameters.
# Configure the user authentication system parameters, and then click OK.
Select a protocol based on the protocol type of the portal authentication server.
The username and password must be the same as those configured on the router for logging in to the IMC server.
Figure 9 Configuring user authentication system parameters
# Click the User tab.
# From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Service Parameters > System Settings.
# Click the Configure icon for User Notification Parameters.
# Click Add.
# On the page that opens, configure the parameters as needed, and then click OK.
Because no shared key is used in this example, you can enter a shared key randomly.
Figure 10 Configuring user notification parameters
Enter the URL of IMC in the address bar of a browser to log in to IMC.
In this example, the URL for IMC is http://192.168.100.244:8080/imc/. The username and password are both admin. (Details not shown.)
Add the router to IMC as an access device:
# Click the User tab.
# From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Access Device Management > Access Device.
# Click Add.
# Set the shared key to admin, and configure other parameters as needed.
Figure 11 Adding an access device
# Click OK.
|
|
NOTE: · The IP address of the access device specified on IMC must be the source IP address of outgoing RADIUS packets specified on the router. By default, if no source IP address is specified for outgoing RADIUS packets, the IP address of the packet outgoing interface is used. · If you have executed the nas-ip or radius nas-ip command on the router to specify a source IP address for outgoing RADIUS packets, you must configure the specified address as the IP address of the access device. · In this example, the IP address 192.168.100.90 of the packet outgoing interface is used as the IP address of the access device. |
Add an access policy:
# Click the User tab.
# From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Access Policy.
# Click Add.
# Set the access policy name to Portal, and use the default settings for other parameters.
Figure 12 Adding an access policy
# Click OK.
Add an access service:
# Click the User tab.
# From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Access Service.
# Click Add.
# On the page that opens, configure the following parameters:
Specify the service name as Portal.
Select Portal from the Default Access Policy list.
Figure 13 Adding an access service
# Click OK.
Add an access user:
# Click the User tab.
# From the navigation pane, select Access User > All Access Users.
# Click Add.
# On the page that opens, configure the following parameters:
Enter user in the User Name field.
Enter user10001 in the Account Name field.
Enter admin in the Password and Confirm Password fields.
Select Portal in the Access Service area.
Figure 14 Adding an access user
# Click OK.
# Add user accounts user10002 and user10003 in the same way.
Enter the URL of IMC in the address bar of a browser to log in to IMC.
In this example, the URL for IMC is http://192.168.100.244:8080/imc/. The username and password are both admin. (Details not shown.)
Configure the portal server:
# Click the User tab.
# From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Portal Service > Server.
# Configure the portal server parameters as needed. This example uses the default settings.
Figure 15 Configuring the portal server
Add an IP group:
# Click the User tab.
# From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Portal Service > IP Group.
# Click Add.
# Configure the parameters as needed.
Figure 16 Adding an IP group
# Click OK.
Add a portal device:
# Click the User tab.
# From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Portal Service > Device.
# Click Add.
# Set the shared key to admin and configure other parameters as shown in Figure 117.
Figure 17 Adding a portal device
# Click OK.
Associate the portal device with the IP group:
# Click the User tab.
# From the navigation pane, select User Access Policy > Portal Service > Device.
# Click the Port Group icon in the Operation column for the router.
Figure 18 Device list
# Click Add.
# Configure the parameters as needed.
Figure 19 Adding a port group
# Click OK.
Configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway settings on each host. Make sure the hosts can communicate with other devices on the network. (Details not shown.)
On the hosts, verify that the users can pass portal authentication:
# Enter the URL of the portal Web server in the address bar of a browser.
In this example, the URL is http://192.168.100.244:8080/portal.
# Enter the username and password.
# Click Log In.
# Verify that the user has passed portal authentication.
Figure 20 Portal authentication success page
On the IMC server, verify that you can view users user10001, user10002, and user10003 on the online user list of the User > Access User > Online Users page.
On the firewall, view identity user information:
# View information about all identity users.
[Device] display user-identity all user
User ID Username
0x2 user10001
0x3 user10002
0x4 user10003
# View information about online identity user user10001.
[Device] display user-identity online-user null-domain name user10001
User name: user10001
IP : 20.2.1.11
MAC : 0011-95e4-4aa9
Type: Dynamic
Total 1 records matched.
# View information about online identity user user10002.
[Device] display user-identity online-user null-domain name user10002
User name: user10002
IP : 20.2.1.12
MAC : 0011-95e4-4aa3
Type: Dynamic
Total 1 records matched.
# View information about online identity user user10003.
[Device] display user-identity online-user null-domain name user10003
User name: user10003
IP : 20.2.1.13
MAC : 0011-95e4-4aa2
Type: Dynamic
Total 1 records matched.
Verify that the firewall can perform identity-based access control on the users:
# Verify that user user10001 cannot ping the FTP server.
C:\>ping 11.1.1.2
Pinging 11.1.1.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Request time out.
Request time out.
Request time out.
Request time out.
Ping statistics for 11.1.1.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),
# Verify that user user10002 can ping the FTP server.
C:\>ping 11.1.1.2
Pinging 11.1.1.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 11.1.1.2: bytes=32 time=36ms TTL=253
Reply from 11.1.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=253
Reply from 11.1.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=253
Reply from 11.1.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=253
Ping statistics for 11.1.1.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 36ms, Average = 9ms
# When user user10002 pings the FTP server, verify that the firewall generates a log as follows.
[Device]%Nov 6 10:19:53:920 2017 H3C FILTER/6/FILTER_ZONE_EXECUTION_ICMP: -Context
=1; SrcZoneName(1025)=Trust;DstZoneName(1035)=DMZ;Type(1067)=ACL;SecurityPolicy(
1072)=user10002;RuleID(1078)=2;Protocol(1001)=ICMP;SrcIPAddr(1003)=20.2.1.12;Src
MacAddr(1021)=7425-8a37-b5f6;DstIPAddr(1007)=11.1.1.2;IcmpType(1062)=ECHO(8);Icm
pCode(1063)=0;MatchCount(1069)=1;Event(1048)=Permit;
# Verify that user user10003 can ping hosts on the Internet.
In this example, the user pings the host at 12.1.1.2.
C:\>ping 12.1.1.2
Pinging 12.1.1.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 12.1.1.2: bytes=32 time=37ms TTL=253
Reply from 12.1.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=253
Reply from 12.1.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=253
Reply from 12.1.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=253
Ping statistics for 12.1.1.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 36ms, Average = 9ms
# When user user10003 pings the host on the Internet, verify that the firewall generates a log as follows.
[Device]%Nov 6 10:19:53:920 2017 H3C FILTER/6/FILTER_ZONE_EXECUTION_ICMP: -Context
=1; SrcZoneName(1025)=Trust;DstZoneName(1035)=Untrust;Type(1067)=ACL;SecurityPolicy(
1072)=user10003;RuleID(1078)=3;Protocol(1001)=ICMP;SrcIPAddr(1003)=20.2.1.13;Src
MacAddr(1021)=7425-8a37-b5f6;DstIPAddr(1007)=12.1.1.2;IcmpType(1062)=ECHO(8);Icm
pCode(1063)=0;MatchCount(1069)=1;Event(1048)=Permit;
[Router] display current-configuration
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
port link-mode route
ip address 20.2.1.1 255.255.255.0
portal enable method direct
portal domain dm1
portal apply web-server newpt
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 192.168.100.90 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet3/0
port link-mode route
combo enable copper
#
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 192.168.100.88
#
snmp-agent
snmp-agent local-engineid 800063A28074258A37B5F500000001
snmp-agent community write private
snmp-agent community read public
snmp-agent sys-info version all
#
radius scheme rs1
primary authentication 192.168.100.244
primary accounting 192.168.100.244
key authentication cipher $c$3$hhbEbD5Ycvw7VWqljAoMoU7hQRgcUjtg
user-name-format without-domain
#
domain dm1
authentication portal radius-scheme rs1
authorization portal radius-scheme rs1
accounting portal radius-scheme rs1
#
domain system
#
domain default enable system
#
local-user admin class manage
password hash $h$6$UbIhNnPevyKUwfpm$LqR3+yg1IjNct39MkOR0H0iQXLkYB3jMqM4vbAeoXOh
babIIFnjJPEGR00YiYA1Sz4LiY3FmEdru2fOLMb1shQ==
service-type telnet http
authorization-attribute user-role network-admin
#
portal web-server newpt
url http://192.168.100.244:8080/portal
#
portal server newpt
ip 192.168.100.244 key cipher $c$3$+UmaGOco7eHsjOqlrp8lI4eYe0A8NpYU
#
return
[Device] display current-configuration
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 192.168.100.88 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode route
ip address 12.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
security-zone name Trust
import interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
#
security-zone name DMZ
import interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
#
security-zone name Untrust
import interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
#
line vty 0 63
authentication-mode scheme
user-role network-admin
#
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 12.1.1.2
ip route-static 20.2.1.0 24 192.168.100.90
#
snmp-agent
snmp-agent local-engineid 800063A280487ADA9593B700000001
snmp-agent community write private
snmp-agent community read public
snmp-agent sys-info version all
snmp-agent target-host trap address udp-domain 192.168.100.244 params securityn
ame public v2c
#
local-user admin class manage
password hash $h$6$UbIhNnPevyKUwfpm$LqR3+yg1IjNct39MkOR0H0iQXLkYB3jMqM4vbAeoXOh
babIIFnjJPEGR00YiYA1Sz4LiY3FmEdru2fOLMb1shQ==
service-type ssh telnet terminal http https
authorization-attribute user-role level-3
authorization-attribute user-role network-admin
authorization-attribute user-role network-operator
#
netconf soap http enable
netconf soap https enable
restful http enable
restful https enable
#
user-identity enable
user-identity user-account auto-import policy imc
#
user-identity restful-server rest1
login-name admin password cipher $c$3$phGy00HA6OP6pIpGI0KOKZEOPuLVbtt/
uri get-user-database http://192.168.100.244:8080/imcrs/ssm/imcuser/accessUser
uri get-user-group-database http://192.168.100.244:8080/imcrs/ssm/imcuser/acces
sUserGroup
uri get-online-user http://192.168.100.244:8080/imcrs/ssm/imcuser/onlineUser
uri put-online-user http://192.168.100.244:8080/imcrs/ssm/imcuser/uploadOnlineU
ser
uri put-offline-user http://192.168.100.244:8080/imcrs/ssm/imcuser/uploadOfflin
eUser
#
user-identity user-import-policy imc
account-update-interval 1
restful-server rest1
#
security-policy ip
rule 0 name trust-local
action pass
source-zone trust
destination-zone local
rule 1 name local-trust
action pass
source-zone local
destination-zone trust
rule 2 name user10002
action pass
logging enable
source-zone trust
source-zone dmz
destination-zone dmz
destination-zone trust
user user10002
rule 3 name user10003
action pass
logging enable
source-zone trust
destination-zone untrust
user user10003
#