MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
This feature enables the device to learn the MAC address of a terminal (a PC for example) when a Layer 3 device (typically a gateway) exists between the device and the terminal for network traffic control.
Figure-1 MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device workflow
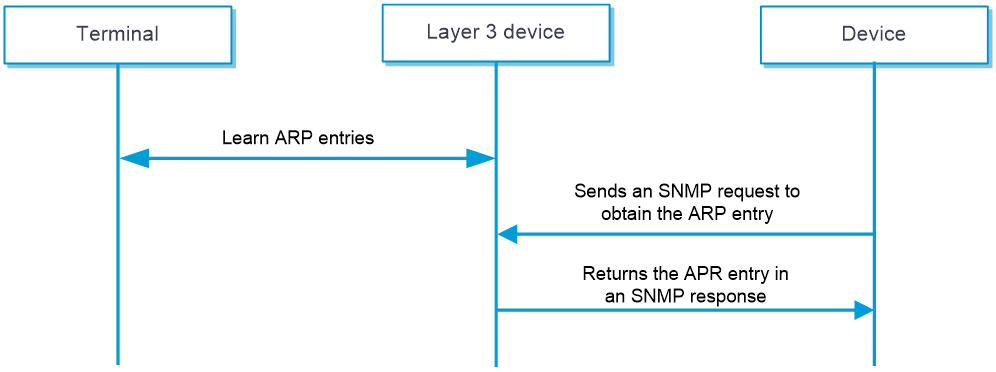
As shown in Figure-1, MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device proceeds as follows:
The Layer 3 device learns the IP-MAC binding of the terminal, and then generates an ARP entry.
The device sends SNMP requests to the Layer 3 device at the specified intervals to request the ARP entry.
The Layer 3 device sends a response that contains the ARP entry.
Upon receiving the response, the device saves the ARP entry in the memory. Then it can learn the MAC address of the terminal.
Restrictions and guidelines
Only MAC addresses mapped from IPv4 addresses can be learned.
Make sure no NAT devices exist between the device and the Layer 3 device.
This feature is not applicable to a VRF network.
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Assign IP addresses to interfaces on the
Network >Interface Configuration >Interfaces page.Configure routes on the
Network >Routing page. Make sure the routes are available.Create security zones on the
Network >Security Zones page.Add interfaces to security zones. You can add interfaces to a security zone on the
Security Zones page or select a security zone for an interface on theInterfaces page.Configure security policies to permit the target traffic on the
Polic ies >Security Policies page.Make sure the Layer 3 device supports SNMPv2c or SNMPv3, has SNMP agent enabled, and has a community name configured.
Configure MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device
When terminals use dynamic IP addresses for network access, IP address-based traffic filtering can no longer provide precise access control. In such cases, MAC addresses must be used as a supplementary criterion to filter traffic. However, in a scenario deployed with multiple Layer 3 devices, a device cannot directly obtain the MAC addresses of terminals connected to other Layer 3 devices. To resolve this issue, enable MAC address learning through Layer 3 devices.
Select
System >Maintenance >MAC Learning Through L3 Device >L3 Device Access Setting .Click
Enable to enable MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device.Figure-2 Enabling MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device
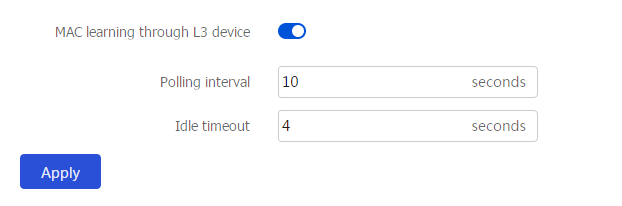
(Optional.) Set the polling interval and idle timeout
Table-1 Configuration items for MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device
Item
Description
Polling interval
Interval for sending SNMP requests, in seconds
Idle timeout
Idle timeout for SNMP responses, in seconds
Click
Apply .Add a Layer 3 device:
Click
Add .Figure-3 Adding a Layer 3 device running SNMPv2c
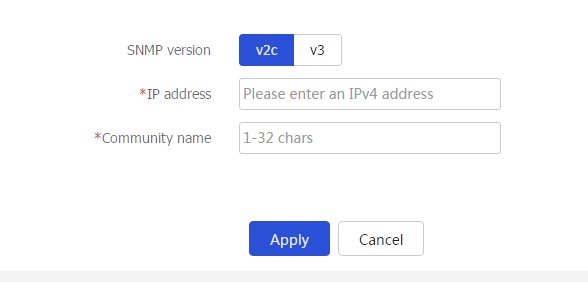
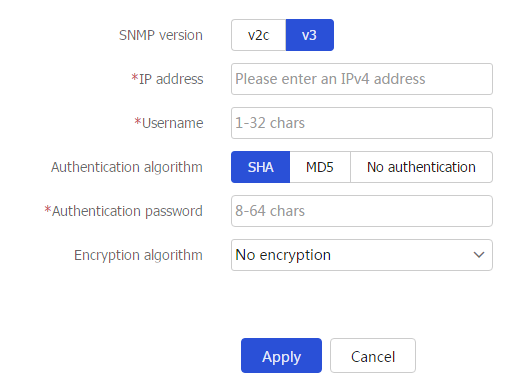
Figure-4 Adding a Layer 3 device running SNMPv3
Configure the following settings:
Table-2 Layer 3 device settings
Item
Description
SNMP version
SNMP version. Options include v2c and v3.
IP address
IP address of the target Layer 3 device, typically the gateway of the terminal network. Only IPv4 addresses are supported.
Community name (SNMPv2c)
Devices in a community use a community name for authentication. The device can communicate with the Layer 3 device only if it has the same community name as the SNMP agent on the Layer 3 device.
Username (SNMPv3)
Authentication can be performed only if the device and the SNMP agent on the Layer 3 device have the same username.
Authentication algorithm
For a successful authentication, make sure these settings are the same as those on the SNMP agent of the Layer 3 device.
Authentication password
Encryption algorithm
Encryption password
Click
OK .After MAC address learning is completed, you can view the learning records the
System >Maintenance >MAC Learning Through L3 Device >Learned ARP Entries page.Figure-5 Learned ARP entries
