AFT
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
Address Family Translation (AFT) translates an IP address of one address family into an IP address of the other address family.
NAT64 prefix
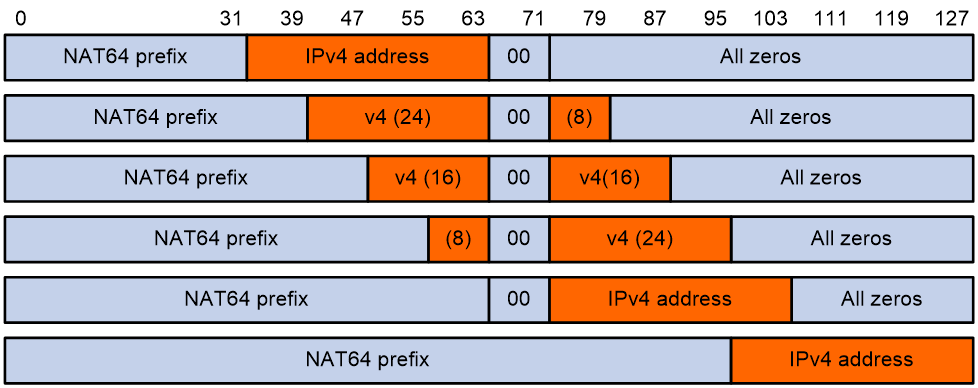
NAT64 prefix is an IPv6 address prefix used to construct an IPv6 address representing an IPv4 node in an IPv6 network. The IPv6 hosts do not use a constructed IPv6 address as their real IP address. The length of a NAT64 prefix can be 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, or 96.
As shown in Figure-1, the construction methods vary depending on the NAT64 prefix length. Bits 64 through 71 in the constructed IPv6 address are reserved bits.
If the prefix length is 32, 64, or 96 bits, the IPv4 address contained in the IPv6 address will be intact.
If the prefix length is 40, 48, or 56 bits, the IPv4 address contained in the IPv6 address will be divided into two parts by bits 64 through 71.
Figure-1 IPv6 address construction with NAT64 prefix and IPv4 address
AFT translation methods
Prefix translation
AFT uses a NAT64 prefix to perform IPv4-to-IPv6 source address translation or IPv6-to-IPv4 destination address translation.
Static translation
Static AFT creates a fixed mapping between an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address. The device supports the following static translation types:
IPv6-to-IPv4 static translation: Translates a source IPv6 address to an IPv4 address, or a destination IPv4 address to an IPv6 address.
IPv4-to-IPv6 static translation: Translates a source IPv4 address to an IPv6 address, or a destination IPv6 address to an IPv4 address.
Port block group-based IPv6-to-IPv4 source address translation: Translates a pair of source IPv6 address and port to a pair of IPv4 address and port.
Dynamic translation
Dynamic AFT creates a dynamic mapping between an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address.
When dynamic AFT performs IPv6-to-IPv4 source address translation, the Not Port Address Translation (NO-PAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) modes are available.
NO-PAT : NO-PAT translates one IPv6 address to one IPv4 address. An IPv4 address assigned to one IPv6 host cannot be used by any other IPv6 host until it is released.NO-PAT supports all IP packets.
PAT : PAT translates multiple IPv6 addresses to a single IPv4 address by mapping each IPv6 address and port to the IPv4 address and a unique port. PAT supports the following packet types:TCP packets.
UDP packets.
ICMPv6 echo request and echo reply messages.
PAT supports port blocks for connection limit and user tracing. Port blocks are generated by dividing the port range (1024 to 65535) by the port block size. Port block based PAT maps multiple IPv6 addresses to one IPv4 address and uses a port block for each IPv6 address.
Port block based PAT functions as follows:
When an IPv6 host first initiates a connection to the IPv4 network, it creates a mapping from the host's IPv6 address to an IPv4 address and a port block.
It translates the IPv6 address to the IPv4 address, and the source ports to ports in the port block for subsequent connections from the IPv6 host until the ports in the port block are exhausted.
AFT translation process
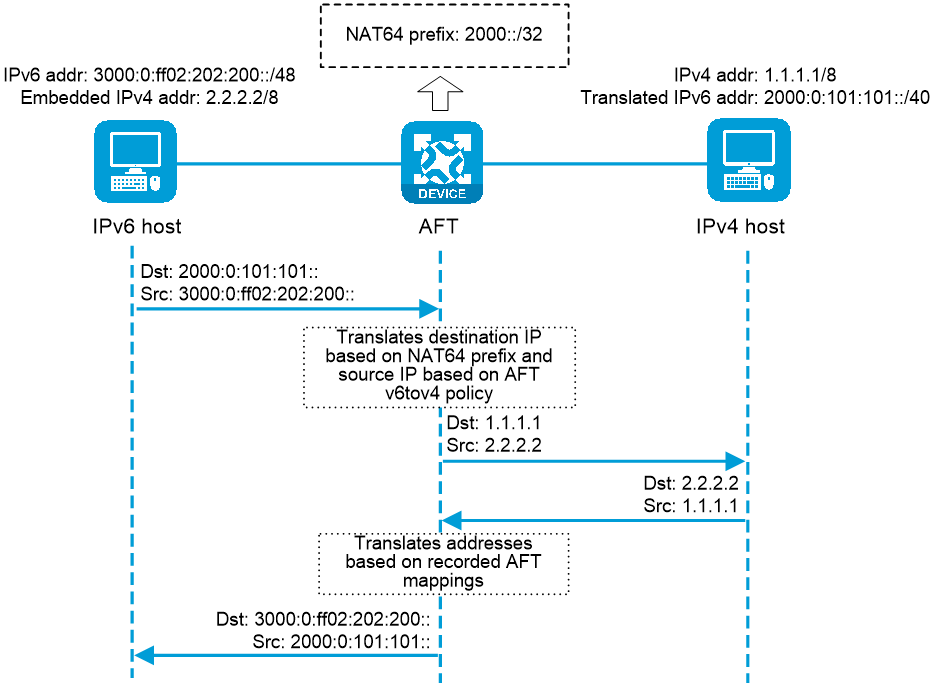
As shown in
Upon receiving a packet from the IPv6 host, AFT compares the packet with IPv6-to-IPv4 destination address translation policies.
If a matching policy is found, AFT translates the destination IPv6 address according to the policy.
If no matching policy is found, AFT does not process the packet.
AFT performs pre-lookup to determine the output interface for the translated packet. PBR is not used for the pre-lookup.
If a matching route is found, the process goes to step 3.
If no matching route is found, AFT discards the packet.
AFT compares the source IPv6 address of the packet with IPv6-to-IPv4 source address translation policies.
If a matching policy is found, AFT translates the source IPv6 address according to the policy.
If no matching policy is found, AFT discards the packet.
AFT forwards the translated packet and records the mappings between IPv6 addresses and IPv4 addresses.
AFT translates the IPv4 addresses in the response packet header to IPv6 addresses based on the address mappings before packet forwarding.
Figure-2 AFT process for IPv6-initiated communication
As shown in Figure-3, when the IPv4 host initiates access to the IPv6 host, AFT operates as follows:
Upon receiving a packet from the IPv4 host, AFT compares the packet with IPv4-to-IPv6 destination address translation policies.
If a matching policy is found, AFT translates the destination IPv4 address according to the policy.
If no matching policy is found, AFT does not process the packet.
AFT performs pre-lookup to determine the output interface for the translated packet. PBR is not used for the pre-lookup.
If a matching route is found, the process goes to step 3.
If no matching route is found, AFT discards the packet.
AFT compares the source IPv4 address of the packet with IPv4-to-IPv6 source address translation policies.
If a matching policy is found, AFT translates the source IPv4 address according to the policy.
If no matching policy is found, AFT discards the packet.
AFT forwards the translated packet and records the mappings between IPv4 addresses and IPv6 addresses.
AFT translates the IPv6 addresses in the response packet header to IPv4 addresses based on the address mappings before packet forwarding.
Figure-3 AFT process for IPv4-initiated communication

vSystem support information
Support of non-default vSystems for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Restrictions and guidelines
AFT compares an IPv6 packet with IPv6-to-IPv4 destination address translation policies in the following order:
IPv4-to-IPv6 source address static mappings.
NAT64 prefixes.
AFT compares an IPv6 packet with IPv6-to-IPv4 source address translation policies in the following order:
IPv6-to-IPv4 source address static mappings.
NAT64 static port translation policies.
IPv6-to-IPv4 source address dynamic translation policies.
AFT compares an IPv4 packet with IPv4-to-IPv6 source address translation policies in the following order:
IPv4-to-IPv6 source address static mappings.
NAT64 prefixes.
Configure AFT
Prerequisites
Complete the following tasks before you configure this feature:
Assign IP addresses to interfaces on the
Network >Interface Configuration >Interfaces page.Configure routes on the
Network >Routing page. Make sure the routes are available.Create security zones on the
Network >Security Zones page.Add interfaces to security zones. You can add interfaces to a security zone on the
Security Zones page or select a security zone for an interface on theInterfaces page.Configure security policies to permit the target traffic on the
Policies >Security Policies page.
Configure NAT64 prefix translation
AFT uses a NAT64 prefix to perform IPv4-to-IPv6 source address translation or IPv6-to-IPv4 destination address translation.
Create a NAT64 prefix
Click the
Policies tab.In the navigation pane, select
Interface NAT >AFT .On the
NAT64 Prefixes tab, clickAdd .Configure a NAT64 prefix and click
Apply .Figure-4 Clicking Add
Figure-5 Adding a NAT64 prefix
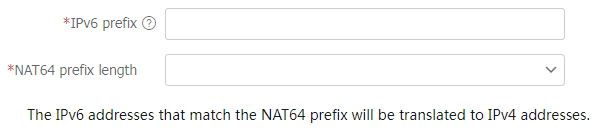
Table-1 NAT64 prefix configuration items
Item
Description
IPv6 prefix
Specify a NAT64 prefix.
NAT64 prefix length
Select a NAT64 prefix length. Options are 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, and 96.
Enabling AFT on interfaces
Click the
Policies tab.In the navigation pane, select
Interface NAT >AFT .On the
AFT On Interfaces tab, select the interfaces to which you want to apply the AFT policy.Click
Enable . Enable AFT on all interfaces involved in communication between IPv4 and IPv6 networks.Figure-6 Enabling AFT on interfaces
Configure static translation
Static AFT creates a fixed mapping between an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address. AFT policies support the following static translation types:
IPv6-to-IPv4 static translation: Translates a source IPv6 address to an IPv4 address, or a destination IPv4 address to an IPv6 address.
IPv4-to-IPv6 static translation: Translates a source IPv4 address to an IPv6 address, or a destination IPv6 address to an IPv4 address.
Create an AFT policy
Click the
Policies tab.In the navigation pane, select
Interface NAT >AFT .On the
AFT Policies tab, clickCreate .Configure an AFT policy and click
Apply .Figure-7 Clicking Create
Figure-8 Creating an AFT policy
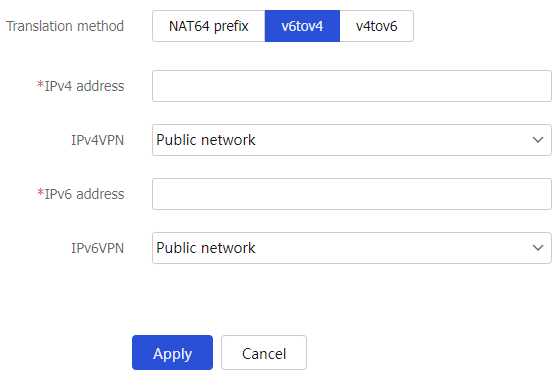
Table-2 AFT policy configuration items
Item
Description
Translation method
Translation method used by the AFT policy. Supported translation methods are:
v6tov4 : Select this option to create an IPv6-to-IPv4 source address static mapping.v4tov6 : Select this option to create an IPv4-to-IPv6 source address static mapping.
IPv4 address
Specify the IPv4 address for the static mapping.
IPv4VPN
Specify the VRF to which the IPv4 address belongs.
IPv6 address
Specify the IPv6 address for the static mapping.
IPv6VPN
Specify the VRF to which the IPv6 address belongs.
Enabling AFT on interfaces
For more information, see "
Configure dynamic translation
Dynamic AFT creates a dynamic mapping between an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address.
Create an AFT policy
Click the
Policies tab.In the navigation pane, select
Interface NAT >AFT .On the
AFT Policies tab, clickCreate .Select the
NAT64 Prefix translation method, configure the other parameters, and clickApply .Figure-9 Clicking Create
Figure-10 Creating an AFT policy
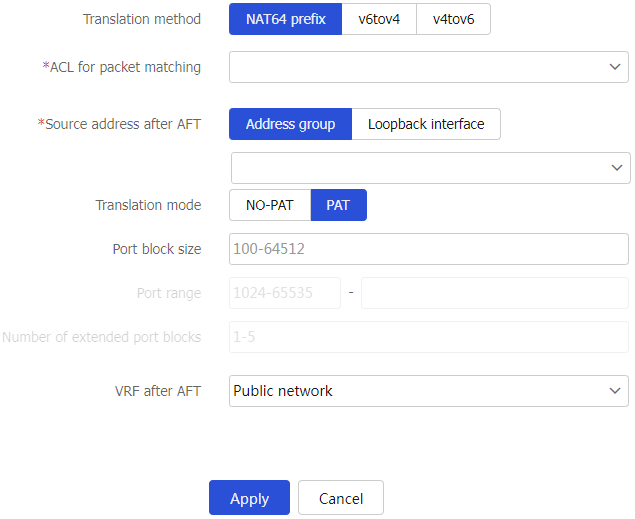
Table-3 AFT policy configuration items
Item
Description
ACL for packet matching
Select the ACL for matching the IPv6 packets for address translation.
Source address after AFT
Specify the IPv4 address used for IPv6-to-IPv4 source address translation. You can select an address group or a loopback interface.
Translation mode
Select a translation mode. Options are
NO-PAT andPAT .Port block size
Set the port block size, which is the number of ports in one port block.
This parameter is available only when the translation mode is PAT.
Port range
Specify the port range within which port blocks are divided.
This parameter is available only when the translation mode is PAT.
Number of extended port blocks
Set the number of port blocks used for port allocation to the IP addresses when all ports in the allocated port blocks are used.
This parameter is available only when the translation mode is PAT.
VRF after AFT
Specify the VRF to which the address belongs after AFT.
Enabling AFT on interfaces
For more information, see "
Configure NAT64 static port translation
NAT64 static port translation translates a pair of source IPv6 address and port to a pair of IPv4 address and port.
Figure-11 NAT64 static port translation configuration flowchart
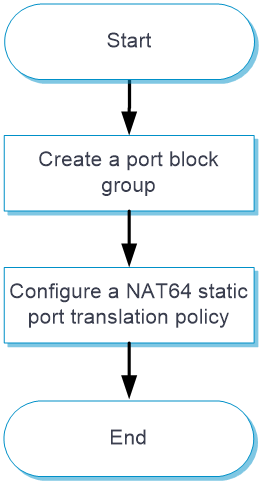
Create a port block group
Click the
Policies tab.In the navigation pane, select
Interface NAT >AFT .On the
NAT64 Static Port Translation tab, clickPort block group .Click
Create .Configure a port block group and click
Apply .Figure-12 Clicking Port block group

Figure-13 Clicking Create

Figure-14 Creating a port block group
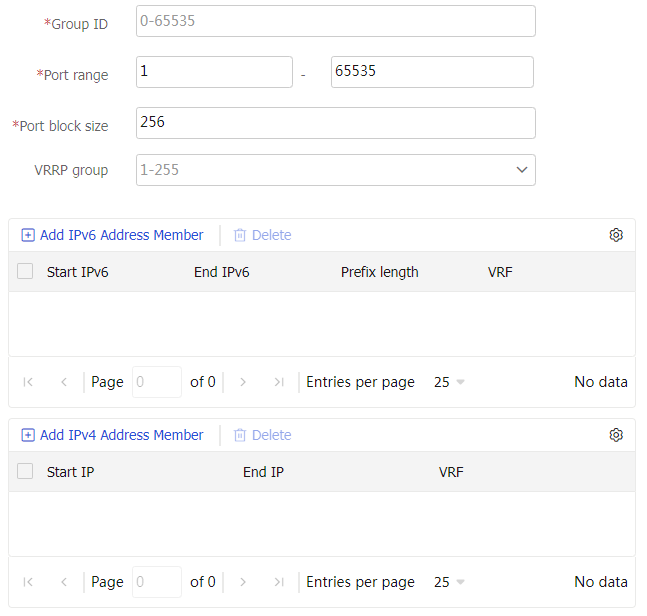
Table-4 Port block group configuration items
Item
Description
Group ID
Specify a port block group ID.
Port range
Specify the port range used for AFT.
Port block size
Specify the port block size. The port range will be equally divided to port blocks of the specified size.
VRRP group
Specify a virtual router ID (VRRP group number). The master device in the specified VRRP group replies to ARP requests with virtual IP and MAC addresses. This feature is required in an HA system. Support for this feature depends on the device model. This feature is available on the Web interface only if it is supported.
Start IPv6
Start IPv6 address of an IPv6 address range to be translated.
End IPv6
End IPv6 address of an IPv6 address range to be translated.
Prefix length
Prefix length of the IPv6 addresses to be translated.
Start IP
Start IPv4 address of an IPv4 address range used for IPv6-to-IPv4 source address translation.
End IP
End IPv4 address of an IPv4 address range used for IPv6-to-IPv4 source address translation.
VRF
VRF to which the IPv4 or IPv6 addresses belong.
Configure a NAT64 static port translation policy
Click the
Policies tab.In the navigation pane, select
Interface NAT >AFT .On the
NAT64 Static Port Translation tab, clickCreate .Configure the policy parameters and click
Apply .Figure-15 Clicking Create

Figure-16 Creating a NAT64 static port translation policy

Table-5 NAT64 static port translation configuration items
Item
Description
Translation method
Translation method used by the NAT64 static port translation policy. Only the
v6tov4 translation method is supported.Port block group
Port block group used by the policy.
Enabling AFT on interfaces
For more information, see "