Manage vSwitches
A vSwitch provides software-based switching between VMs, hosts, and the external network.
UIS provides standard and accelerated vSwitches. A standard vSwitch uses a NIC that does not have acceleration functions. Accelerated vSwitches are DPDK-accelerated vSwitches (created on DPDK-enabled hosts).
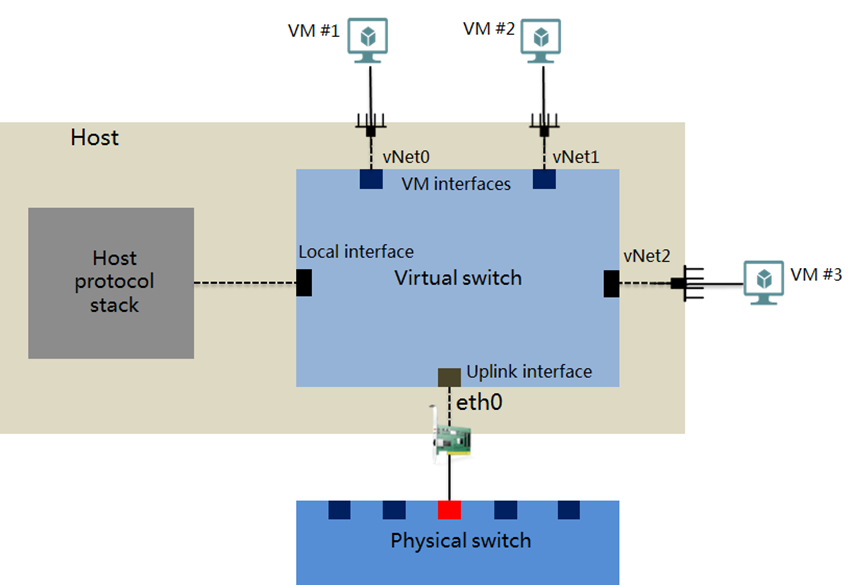
vSwitch logical topology
vSwitch interfaces
A vSwitch provides the following interfaces:
VM interface—An interface that connects to the virtual NIC of a VM for the VM to communicate with other VMs or the external network.
Local interface— An interface that connects to the protocol stack on the host.
Uplink interface— An interface that connects to a physical NIC on the host.
Restrictions and guidelines
If you do not configure an independent migration network switch, the system transmits migration data through management network switch vswitch0.
If you do not configure an independent backup network switch, the system transmits backup data through management network switch vswitch0.
If vswitch0 acts as the management network switch, backup network switch, and migration network switch at the same time, network performance might be degraded and packet loss might occur. To avoid these issues, use vswitch0 only as the management network switch and configure an independent migration network switch and an independent backup network switch.
vSwitches being used by VMs cannot be deleted.
After you add or delete a vSwitch with a network type of service network, the vSwitch will also be added to or removed from the network topology.
Editing vSwitch settings might cause network failures. Please be cautious.
If you cannot select a smart NIC when you create a smart NIC-accelerated vSwitch on a host, enable HugePages on the host and reboot it.
Smart NIC-accelerated vSwitches do not support link aggregation.
Add a vSwitch
On the top navigation bar, click Networks, and then select vSwitches from the navigation pane.
Click Add.
Set the parameters as described in "Parameters."
Click Finish.
Edit a vSwitch
On the top navigation bar, click Networks, and then select vSwitches from the navigation pane.
Click the Edit icon
 for a vSwitch.
for a vSwitch.
Edit the parameters as described in "Parameters."
Click Finish.
Delete vSwitches
On the top navigation bar, click Networks, and then select vSwitches from the navigation pane.
Click the Delete icon
 for a vSwitch.
for a vSwitch.
In the dialog box that opens, click OK.
View the topology for a vSwitch
On the top navigation bar, click Networks, and then select vSwitches from the navigation pane.
Click the View Topology icon
 for a vSwitch to view its topology.
for a vSwitch to view its topology.
Detach a host from a vSwitch
On the top navigation bar, click Networks, and then select vSwitches from the navigation pane.
Click the Delete vSwitch from Host icon
 for a host in the Attached Hosts area.
for a host in the Attached Hosts area.
In the dialog box that opens, click OK.
Parameters
Network Type: Select a network type for the vSwitch.
Management—Transmits the control layer data between UIS Manager and the hosts.
Service—Transmits VM service data.
Storage—Transmits data between the hosts and storage servers. This type of vSwitches cannot be used by VMs.
Backup—Transmits the backup data of VMs. A host can have only one vSwitch of this type, and the vSwitch cannot be used by VMs. If you do not configure an independent backup network switch, the system transmits backup data through management network switch vswitch0.
Migration—Transmits the data for migrating VMs. A host can have only one vSwitch of this type, and the vSwitch cannot be used by VMs. If you do not configure an independent migration network switch, the system transmits migration data through management network switch vswitch0.
Others—Transmits other kinds of data.
Forwarding Mode: Select a forwarding mode for the vSwitch. Only VEB is available.
VEB—In Virtual Ethernet Bridge (VEB) mode, the traffic between VMs is forwarded through the software.
VLAN ID: Enter the VLAN ID of the interface connected to the protocol stack of the host.
Acceleration: State of the acceleration feature. This field displays Smart NIC for a smart NIC-accelerated vSwitch and DPDK for a DPDK-accelerated vSwitch. For a standard vSwitch, this field is empty.
MTU: Set the maximum packet length that the vSwitch allows, in bytes.
Multicast: Set the state of multicast forwarding.
DPDK: Configure whether to enable DPDK or not. Enabling DPDK can improve the network performance of the VM.
NIC Type: Select Physical Interfaces for a standard vSwitch, and select Smart NIC for a smart NIC-accelerated vSwitch. A smart NIC offers high forwarding performance without using the compute resources of a host. To create a smart NIC-accelerated virtual switch on a host, install a smart NIC and enable HugePages on the host. NICs include common NICs and security NICs.
Select Interfaces: Select interfaces on NICs.
For a standard vSwitch, select host physical NICs. A physical interface can be used only by one vSwitch. This parameter is unavailable if all physical interfaces on the hosts have been used. If the vSwitch is not assigned a physical interface, VMs attached to the vSwitch can communicate only with each other but cannot communicate with external networks. If you specify multiple physical interfaces for the vSwitch, you must configure the link aggregation mode and LB mode. If you use security NICs, you can select only one physical interface.
For a smart NIC-accelerated vSwitch, select one or two physical interfaces. If you select two interfaces, make sure they are on the same smart NIC.
IP: Enter an IP address for the vSwitch.
Subnet Mask: Enter the subnet mask of the IP address.
Gateway: Enter a gateway address for the vSwitch.
LAGG Mode: Select a link aggregation mode for the physical NICs. Options include Static and Dynamic. As a best practice, use dynamic link aggregation mode. If you select the dynamic link aggregation mode, you must enable LACP on the physical switch. This parameter is available only when you select multiple physical interfaces.
LB Mode: Select the load balancing mode for physical NICs on the vSwitch. This parameter is available only when you select multiple physical interfaces.
Advanced—Performs load balancing based on Ethernet type, IP protocol, source IP address, destination IP address, source port, and destination port of the packets. As a best practice, use advanced load balancing mode in an environment that requires precise load balancing.
Basic—Performs load balancing based on the source MAC address and VLAN tag of the packets.
Primary/Backup—Performs load balancing based on the primary and backup physical NICs. When the primary NIC fails, the system automatically switches the traffic to the backup NIC. This option is available only when the link aggregation mode is Static.
Fallback: Select whether to switch services from the backup NIC back to the primary NIC after the primary NIC recovers. This parameter is required when the load balancing mode is Primary/Backup.
Primary NIC Selection: Select the method used to select the primary NIC. This parameter is required when the load balancing mode is Primary/Backup.
Rate-Based: The system automatically selects the primary NIC based on the rates of the NICs. The NIC with the highest rate becomes the primary NIC. When multiple NICs have the same rate, the system randomly selects a NIC as the primary NIC.
Manual: You specify the primary NIC by arranging the LB priorities of the NICs. The NIC with the highest priority is the primary NIC. You must configure the LB priorities for the NICs in this mode.
LB Priority: Arrange the NICs to define their LB priorities. The NIC on the top has the highest priority and is the primary NIC.
Host Name: Enter the name of the host to which the vSwitch is attached.