WAN
This help contains the following topics:
Introduction
About WAN interfaces
Typically, an external network refers to a wide area network (WAN). A WAN is a data communication network covering a large physical range. The Internet is an extremely large WAN.
Typically, a device provides multiple WAN interfaces. You can configure the WAN interfaces to enable the device to access the external network.
Internet access modes
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) automatically allocates network configuration information such as IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS server. It reduces the workload of manually configuring network devices. The device requests network configuration information from the server through DHCP, and the server allocates IP addresses and completes automatic network configuration based on the request.
Static IP
A static IP is a fixed IP address configured manually rather than allocated automatically through DHCP. This method is typically used for network devices that need fixed IP addresses. The network administrator manually allocates a fixed IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and more information to a device to ensure that the devices always communicate by using the same IP address.
MTU
The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) specifies the maximum packet size that the data link layer (such as Ethernet) can transmit. When a packet exceeds the MTU size, it must be fragmented into smaller units for transmission, and these units are reassembled into a complete packet at the receiving end. This fragmentation and reassembly mechanism will incur additional overhead and might impact network performance.
In practical applications, understanding and managing MTUs is crucial for ensuring efficient and reliable network communication. Typically, you must consider network devices, connection types, and data transmission requirements to determine the most suitable MTU size.
TCP MSS
The value of TCP Maximum Segment Size (MSS) is an optional parameter of TCP. It defines the maximum length of data transmitted in TCP segments to accommodate the minimum MTU limit in the network.
When a TCP connection is established, each side of the connection advertises the MSS as an option in the TCP packets to the other end. The other end records this MSS value and limits the size of each TCP packet to not exceed this MSS value when transmitting TCP packets. When the length of a TCP packet transmitted by the peer is less than the MSS of the local end, the TCP packet will not be segmented. If not, the peer must segment the TCP packet according to the MSS before transmitting the TCP packet to the local end.
Configuration guide
Analysis
Configure WAN interfaces as shown in the following figure:
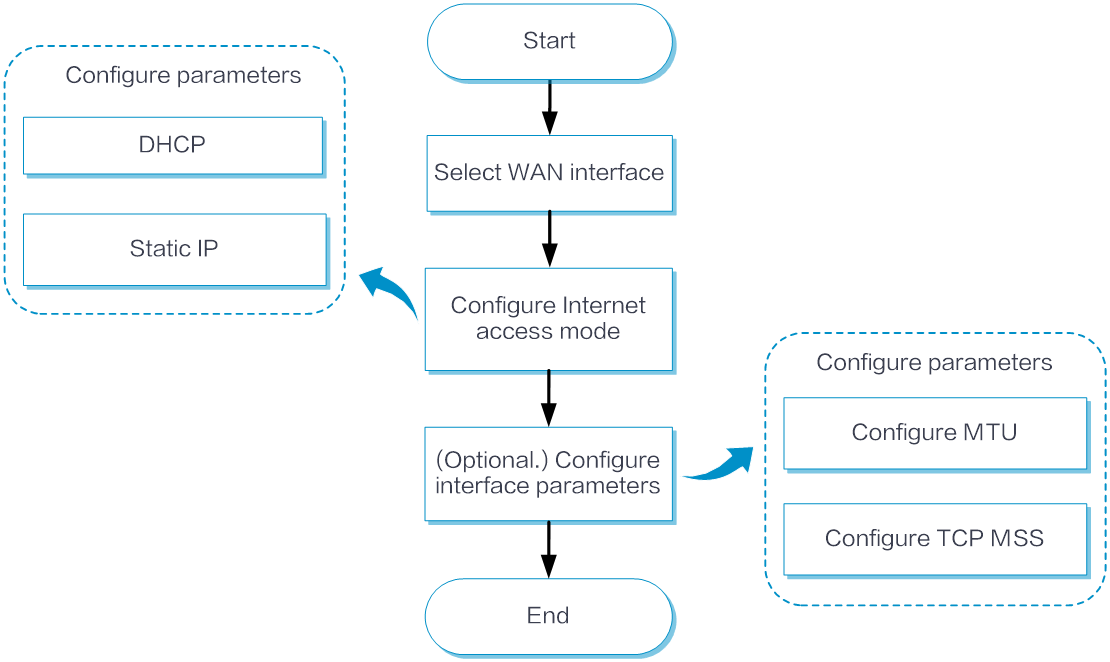
Basic configuration
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > WAN to access the WAN interface configuration page.
Select the interface to be configured and click the Edit icon in the Actions column to configure basic settings. If the interface is a Layer 2 interface, first switch it to a Layer 3 interface before configuring the WAN interface.
(Optional.) Set the interface description in the Interface Description field.
Click the Interface State toggle button to bring up this interface.
Select an Internet access mode from the Internet Access Mode list as needed.
If you select DHCP as the Internet access mode, the DHCP server automatically assigns public IP addresses to the interface for accessing the WAN.
If you select Static IP as the Internet access mode, perform the following tasks:
In the IP Address field, enter the fixed IP address and mask or mask length for accessing the WAN.
In the Default Gateway field, enter the gateway address for accessing the WAN.

If this field displays No configuration, it means that the interface is not configured with any IP address assignment method.
If this field displays Other, it means that the interface already has other configuration, which you can view at the CLI.
Click Submit.
Advanced configuration
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > WAN to access the WAN interface configuration page.
Select the interface to be configured and click the Edit icon in the Actions column for that interface to configure advanced settings. If the interface is a Layer 2 interface, first switch it to a Layer 3 interface before configuring the WAN interface.
(Optional.) In the MTU field, enter the MTU for the interface.
(Optional.) In the TCP MSS field, configure the MSS of TCP segments for the interface.
Click Submit.