NAT
Introduction
Network Address Translation (NAT) translates an IP in the IP packet header to another IP address. It enables private hosts to access external networks and external hosts to access private network resources.
Address translation methods
NAT supports the following address translation methods:
Dynamic NAT—Uses an address pool to translate addresses. It applies to the scenario where a large number of internal users access the external network.
Static NAT—Creates a fixed mapping between a private address and a public address. It supports connections initiated from internal users to external network and from external users to the internal network. Static NAT applies to regular communications.
NAT Server—In actual applications, a server in the internal network might need to provide services such as web or FTP service to the external network. The NAT Server feature maps a public address and port number to the private IP address and port number of an internal server. It allows servers in the internal network to provide services for external users.
NAT ALG
Typically, NAT only translates IP addresses and port numbers in IP headers. However, packets of some application layer protocols contain IP address or port information in the payload, which also requires translation.
Application Level Gateway (ALG) is used to process packets of application layer protocols. It translates the IP address or port information in the payloads of application layer protocol packets, allowing them to transit.
For example, an FTP application includes a data connection and a control connection. The IP address and port number for the data connection depend on the payload information of the control connection. This requires NAT ALG to translate the address and port information for data connection establishment.
If an application layer service (for example, FTP or DNS) exists between the internal and external networks, enable NAT ALG for the application layer protocol. It ensures that the data connection of this protocol can be correctly established after address translation.
NAT session logging
NAT session logging records information about NAT sessions (connections whose source or destination IP addresses are translated by NAT when packets pass through a device) to meet the security audit requirements of the network administrator. NAT session log information includes the IP address and port translation information, user access information, and user network traffic information.
A NAT device generates NAT session logs for the following events:
NAT session establishment.
NAT session removal. This event occurs when you add a configuration with a higher priority, remove a configuration, or change ACLs, when a NAT session ages out, or when you manually delete a NAT session.
Active NAT session logging. Active NAT flows refer to NAT sessions that exist within a period of time. When the specified interval for logging active NAT flows expires, the device records the existing NAT session information and generates a log.
Configuration guide
Analysis
Configure NAT as shown in the following figure:
Configure dynamic NAT (using Easy IP) as shown in the following figure:
Configure dynamic NAT (using a NAT address group) as shown in the following figure:
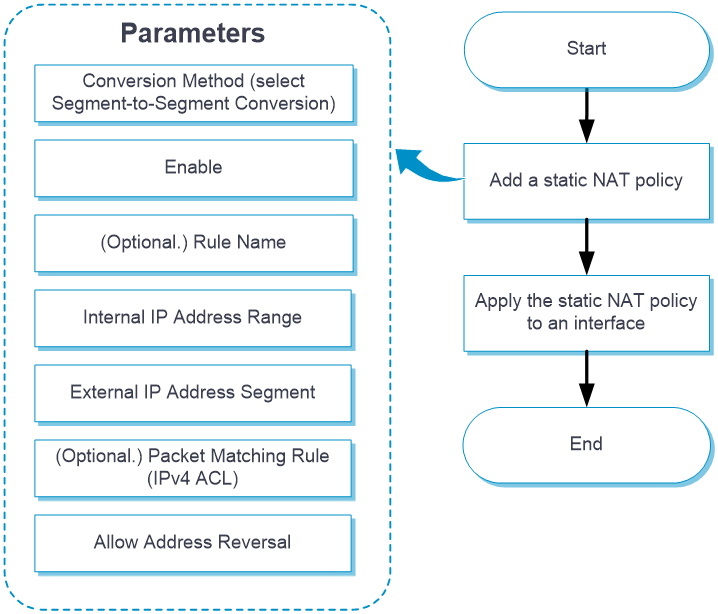
Configure one-to-one static NAT as shown in the following figure:
Configure net-to-net static NAT as shown in the following figure:
Configure NAT Server (a single public address with no or a single public port) as shown in the following figure:
Configure NAT Server (a single public address with consecutive public ports) as shown in the following figure:
Configure NAT Server (consecutive public addresses with no public port) as shown in the following figure:
Configure NAT Server (consecutive public addresses with one single public port) as shown in the following figure:
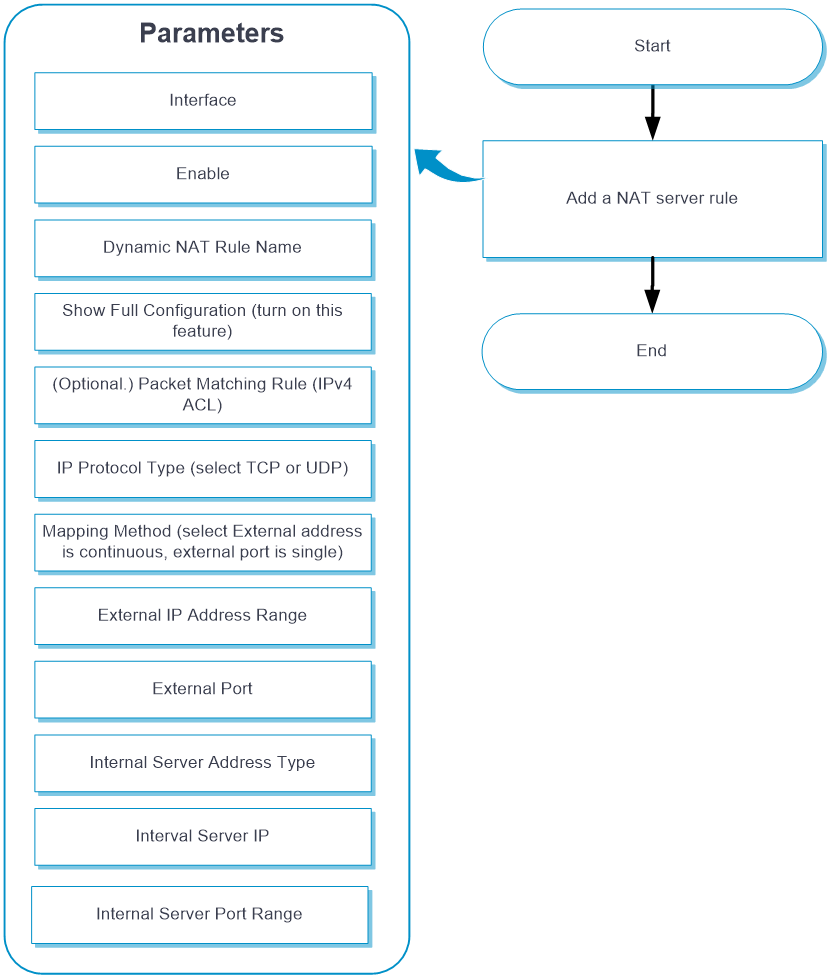
Configure NAT Server (a single public address) as shown in the following figure:
Configure NAT Server (consecutive public addresses) as shown in the following figure:
Configure a NAT address group
Configure a NAT address group
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Address Group Settings tab.
Click Add. Table-1 shows the parameters for configuring an address group.
Table-1 Parameters for configuring an address group
Parameter
Description
Address Group Number
ID of the address group, an integer in the range of 0 to 65535.
Address Group Name
Name of the address group, a string of 1 to 63 characters.
Port Range
Port range of the address group. Both the start port number and end port number are integers in the range of 1 to 65535.
Address Group Members
Add address ranges to the address group.
Click Add.
Enter an IP address in dotted decimal notation in both the Start Address and End Address fields. The end address must be greater than or equal to the start address. To specify a single IP address, enter the same IP address in the Start Address and End Address fields.
Click the OK icon in the Actions column.
You can add multiple address ranges to an address group. Make sure the address ranges do not overlap.
Dynamic NAT (using Easy IP)
Configure dynamic NAT (using Easy IP)
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Address Translation Rules tab.
Click Add. Table-2 shows the parameters for configuring dynamic NAT (using Easy IP).
Table-2 Parameters for configuring dynamic NAT (using Easy IP)
Parameter
Description
Interface
Select an interface on which the rule takes effect.
Enable Dynamic NAT Rule
Select whether to enable the rule.
Dynamic NAT Rule Name
Name of the dynamic NAT rule, a string of 1 to 63 characters.
Show Full Configuration
The default settings are as follows:
The Show Full Configuration feature is turned off.
The value for the Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL) field is empty, which indicates that no ACL is referenced.
Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP) is selected for the External Address Policy field.
Convert both IP address and port number (PAT) is selected for the Conversion Mode field.
The Prioritize keeping the port number unchanged feature is turned off.
To edit the default settings, turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
(Optional.) Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL)
Select an ACL to filter packets. The NAT device performs address translation only on the packets that match an ACL permit rule.
External Address Policy
Source of the NAT addresses used for address translation. Select either of the following options as required:
Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP).
IPv4 Address Group
In this configuration, select Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP).
(Optional.) Conversion Mode
Select an address translation mode. Options include Convert both IP address and port number (PAT) and Only convert IP address (NO-PAT).
If you select Convert both IP address and port number (PAT), the NAT device translates multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address by mapping the private IP address and source port to the public IP address and a unique port.
If you select Only convert IP address (NO-PAT), the NAT device translates a private IP address to a public IP address. The public IP address cannot be used by another internal host until it is released.
(Optional.) Prioritize keeping the port number unchanged
By default, this feature is disabled. Some servers have requirements for the port number range or specific port number in the requests. To ensure service availability, make sure the port numbers are not changed after address translation. In this case, enable this feature. If an address conflict occurs, the ports will be forcibly translated.
Dynamic NAT (using a NAT address group)
Configure dynamic NAT (using a NAT address group)
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Address Translation Rules tab.
Click Add. Table-2 shows the parameters for configuring dynamic NAT (using a NAT address group).
Table-3 Parameters for configuring dynamic NAT (using a NAT address group)
Parameter
Description
Interface
Select an interface on which the rule takes effect.
Enable Dynamic NAT Rule
Select whether to enable the rule.
Dynamic NAT Rule Name
Name of the dynamic NAT rule, a string of 1 to 63 characters.
Show Full Configuration
The default settings are as follows:
The Show Full Configuration feature is turned off.
The value for the Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL) field is empty, which indicates that no ACL is referenced.
Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP) is selected for the External Address Policy field.
Convert both IP address and port number (PAT) is selected for the Conversion Mode field.
The Prioritize keeping the port number unchanged feature is turned off.
To edit the default settings, turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
(Optional.) Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL)
Select an ACL to filter packets. The NAT device performs address translation only on the packets that match an ACL permit rule.
External Address Policy
Source of the NAT addresses used for address translation. Select either of the following options as required:
Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP).
IPv4 Address Group.
In this configuration, select IPv4 Address Group.
Address Group Number
ID of the address group used for address translation.
(Optional.) Conversion Mode
Select an address translation mode. Options include Convert both IP address and port number (PAT) (Default) and Only convert IP address (NO-PAT).
If you select Convert both IP address and port number (PAT), the NAT device translates multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address by mapping the private IP address and source port to the public IP address and a unique port.
If you select Only convert IP address (NO-PAT), the NAT device translates a private IP address to a public IP address. The public IP address cannot be used by another internal host until it is released.
(Optional.) Prioritize keeping the port number unchanged
By default, this feature is disabled. Some servers have requirements for the port number range or specific port number in the requests. To ensure service availability, make sure the port numbers are not changed after address translation. In this case, enable this feature. If an address conflict occurs, the ports will be forcibly translated.
One-to-one static NAT
Configuring one-to-one static NAT
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Static Translation Policies tab.
Click Add. Select One-to-One Conversion (Default) for the Conversion Method field. Table-4 shows the parameters for configuring one-to-one static NAT.
Table-4 Parameters for configuring one-to-one static NAT
Parameter
Description
Enable
Select whether to enable the rule.
(Optional.) Rule Name
Name of the one-to-one static NAT rule, a string of 1 to 63 characters.
Internal IP Address
Specify a private IP address.
External IP Address
Specify a public IP address.
(Optional.) Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL)
Select an ACL to filter packets. The NAT device performs address translation only on the packets that match an ACL permit rule.
Allow Address Reversal
By default, this feature is enabled and cannot be disabled. Reverse address translation uses existing NO-PAT entries to translate destination addresses for packets of connections actively initiated by external hosts to internal hosts. If you specify an ACL, this feature is not supported by default. To enable reverse address translation, turn on the Allow Address Reversal feature.
Click the Address Translation Rules tab.
Click Add.
Select an interface to which the static NAT policy applies. Then, in the Static NAT Policy area, turn on the Apply global static NAT policy to the current interface feature.
Click Submit.
Net-to-net static NAT
Configure net-to-net static NAT
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Static Translation Policies tab.
Click Add. Select Segment-to-Segment Conversion for the Conversion Method field. Table-5 shows the parameters for configuring net-to-net static NAT.
Table-5 Parameters for configuring net-to-net static NAT
Parameter
Description
Enable
Select whether to enable the rule.
(Optional.) Rule Name
Name of the net-to-net static NAT rule, a string of 1 to 63 characters.
Internal IP Address Range
Specify a private IP address range.
External IP Address Segment
Specify a public IP subnet and subnet mask. Configure this field as follows:
Specify a mask in dotted decimal notation. The value range is 255.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.254.
Specify a mask length in the range of 8 to 31.
(Optional.) Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL)
Select an ACL to filter packets. The NAT device performs address translation only on the packets that match an ACL permit rule.
Allow Address Reversal
By default, this feature is enabled and cannot be disabled. Reverse address translation uses existing NO-PAT entries to translate destination addresses for packets of connections actively initiated by external hosts to internal hosts. If you specify an ACL, this feature is not supported by default. To enable reverse address translation, turn on the Allow Address Reversal feature.
Click the Address Translation Rules tab.
Click Add.
Select an interface to which the static NAT policy applies. Then, in the Static NAT Policy area, turn on the Apply global static NAT policy to the current interface feature.
Click Submit.
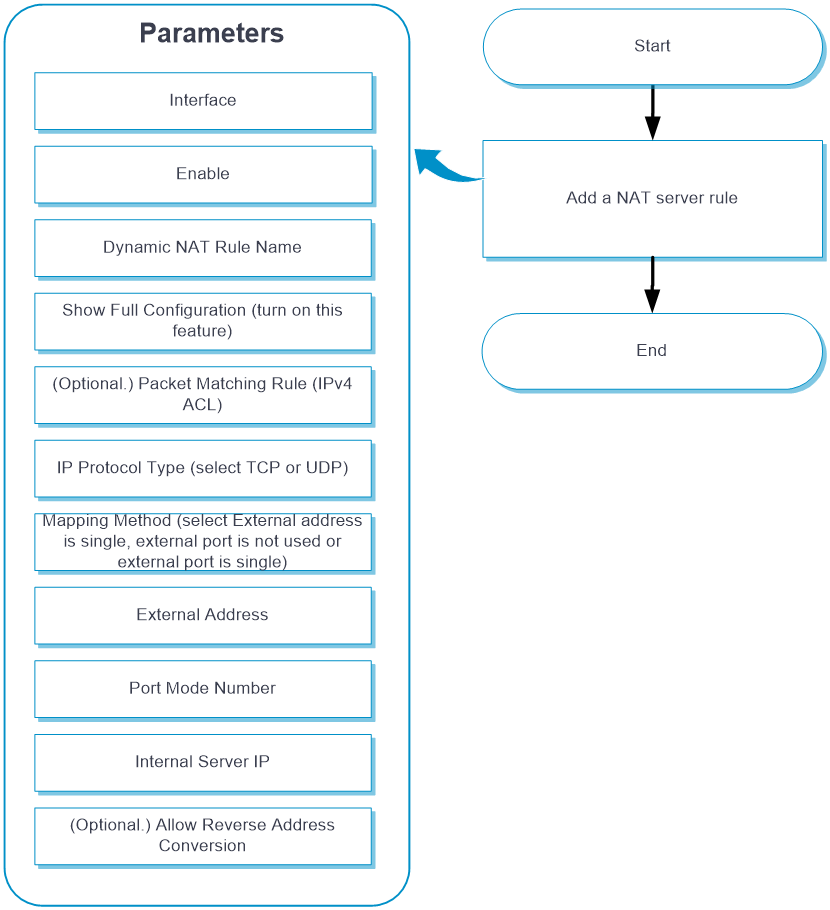
NAT Server (a single public address with no or a single public port)
Configure NAT Server (a single public address with no or a single public port)
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Internal Server tab.
Click Add. Table-6 shows the parameters for configuring NAT Server (a single public address with no or a single public port).
Table-6 Parameters for configuring NAT Server (a single public address with a single or no public port)
Parameter
Description
Interface
Select an interface on which the NAT server rule takes effect.
Enable
Select whether to enable the rule.
Dynamic NAT Rule Name
Name of the NAT server rule, a string of 1 to 63 characters.
Show Full Configuration
The default settings are as follows:
The Show Full Configuration feature is turned off.
The value for the Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL) field is empty, which indicates that no ACL is referenced.
Effective for all protocol types is selected for the IP Protocol Type field.
External address is single, external port is not used is selected for the Mapping Method field.
Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP) is selected for the External Address field.
To edit the default settings, turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL)
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Select an ACL to filter packets. The NAT device performs address translation only on the packets that match an ACL permit rule.
IP Protocol Type
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Specify a protocol type by using either of the following methods:
Select a protocol name. Options include ICMP, TCP, and UDP.
Specify a protocol number, an integer in the range of 1 to 255.
In this configuration, select TCP or UDP.
Mapping Method
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Select External address is single, external port is not used or external port is single.
External Address
Specify the IP address used by the internal server for providing services. Select one of the following options as required:
Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP).
Use the main IP address of the Loopback interface as the external address of the internal server.
Specify an IP address.
Port Mode Number
Select either of the following options as required:
Single Port.
Do not use port.
External Port
Specify the port number used by the internal server for providing services. This field is displayed only when you select Single Port from the Port Mode Number list.
Internal Server IP
Private IP address of the internal server.
Internal Server Port
Private port number of the internal server. This field is available only when you select the TCP or UDP IP protocol type.
(Optional.) Allow Reverse Address Conversion
By default, an internal server in the private network cannot proactively access the external network. Turn on this feature only if necessary and no security risk exists.
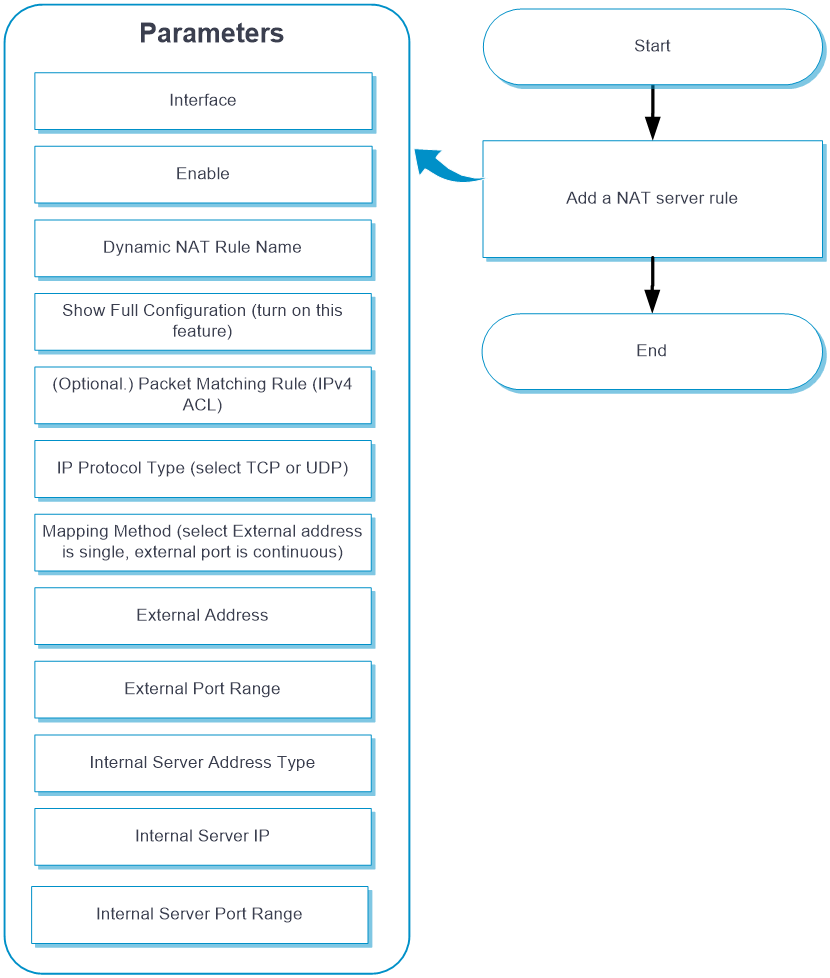
NAT Server (a single public address with consecutive public ports)
Configure NAT Server (a single public address with consecutive public ports)
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Internal Server tab.
Click Add. Table-7 shows the parameters for configuring NAT Server (a single public address with consecutive public ports).
Table-7 Parameters for configuring NAT Server (a single public address with consecutive public ports)
Parameter
Description
Interface
Select an interface on which the NAT server rule takes effect.
Enable
Select whether to enable the rule.
Dynamic NAT Rule Name
Name of the NAT server rule, a string of 1 to 63 characters.
Show Full Configuration
The default settings are as follows:
The Show Full Configuration feature is turned off.
The value for the Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL) field is empty, which indicates that no ACL is referenced.
Effective for all protocol types is selected for the IP Protocol Type field.
External address is single, external port is not used is selected for the Mapping Method field.
Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP) is selected for the External Address field.
To edit the default settings, turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL)
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Select an ACL to filter packets. The NAT device performs address translation only on the packets that match an ACL permit rule.
IP Protocol Type
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Specify a protocol type by using either of the following methods:
Select a protocol name. Options include ICMP, TCP, and UDP.
Specify a protocol number, an integer in the range of 1 to 255.
In this configuration, select TCP or UDP.
Mapping Method
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Select External address is single, external port is continuous.
External Address
Specify the IP address used by the internal server for providing services. Select one of the following options as required:
Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP).
Use the main IP address of the Loopback interface as the external address of the internal server.
Specify an IP address.
External Port Range
Specify the port range used by the internal server for providing services. This field is available only when you select the TCP or UDP IP protocol type.
Internal Server Address Type
Select either of the following options as required:
Single Address.
Address Range.
Internal Server IP
If you select Single Address from the Internal Server Address Type list, specify the private IP address of the internal server.
If you select Address Range from the Internal Server Address Type list, specify the private IP address range of the internal server.
Internal Server Port Range
Private port range of the internal server. This field is available only when you select the TCP or UDP IP protocol type.
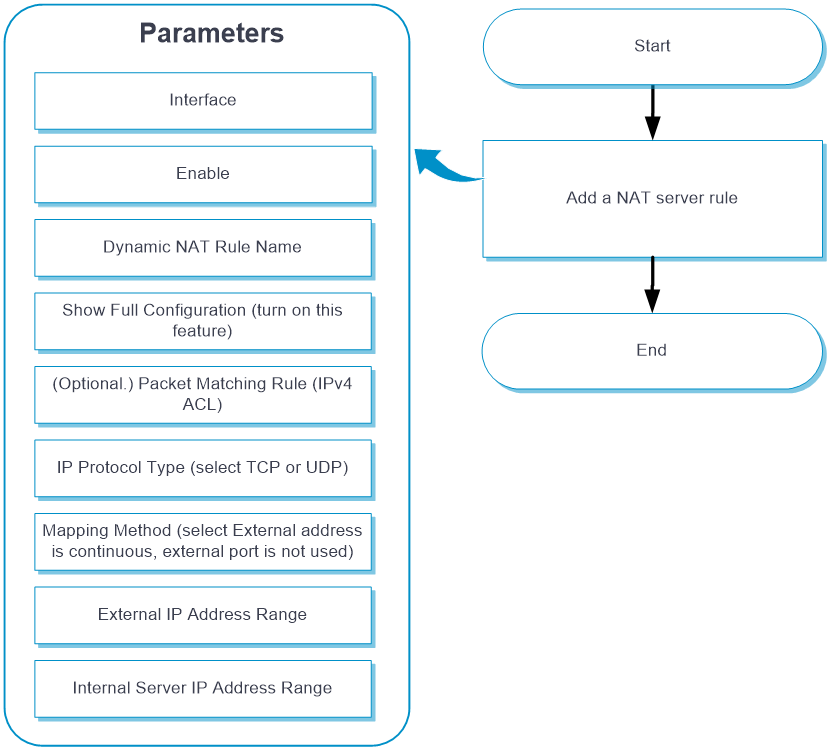
NAT Server (consecutive public addresses with no public port)
Configure NAT Server (consecutive public addresses with no public port)
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Internal Server tab.
Click Add. Table-8 shows the parameters for configuring NAT Server (consecutive public addresses with no public port).
Table-8 Parameters for configuring NAT Server (consecutive public addresses with no public port)
Parameter
Description
Interface
Select an interface on which the NAT server rule takes effect.
Enable
Select whether to enable the rule.
Dynamic NAT Rule Name
Name of the NAT server rule, a string of 1 to 63 characters.
Show Full Configuration
The default settings are as follows:
The Show Full Configuration feature is turned off.
The value for the Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL) field is empty, which indicates that no ACL is referenced.
Effective for all protocol types is selected for the IP Protocol Type field.
External address is single, external port is not used is selected for the Mapping Method field.
Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP) is selected for the External Address field.
To edit the default settings, turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL)
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Select an ACL to filter packets. The NAT device performs address translation only on the packets that match an ACL permit rule.
IP Protocol Type
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Specify a protocol type by using either of the following methods:
Select a protocol name. Options include ICMP, TCP, and UDP.
Specify a protocol number, an integer in the range of 1 to 255.
In this configuration, select TCP or UDP.
Mapping Method
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Select External address is continuous, external port is not used.
External IP Address Range
Specify the IP address range used by the internal server for providing services.
Internal Server IP Address Range
Specify the private IP address range of the internal server.
NAT Server (consecutive public addresses with one single public port)
Configure NAT Server (consecutive public addresses with one single public port)
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Internal Server tab.
Click Add. Table-9 shows the parameters for configuring NAT Server (consecutive public addresses with one single public port).
Table-9 Parameters for configuring NAT Server (consecutive public addresses with one single public port)
Parameter
Description
Interface
Select an interface on which the NAT server rule takes effect.
Enable
Select whether to enable the rule.
Dynamic NAT Rule Name
Name of the NAT server rule, a string of 1 to 63 characters.
Show Full Configuration
The default settings are as follows:
The Show Full Configuration feature is turned off.
The value for the Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL) field is empty, which indicates that no ACL is referenced.
Effective for all protocol types is selected for the IP Protocol Type field.
External address is single, external port is not used is selected for the Mapping Method field.
Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP) is selected for the External Address field.
To edit the default settings, turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL)
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Select an ACL to filter packets. The NAT device performs address translation only on the packets that match an ACL permit rule.
IP Protocol Type
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Specify a protocol type by using either of the following methods:
Select a protocol name. Options include ICMP, TCP, and UDP.
Specify a protocol number, an integer in the range of 1 to 255.
In this configuration, select TCP or UDP.
Mapping Method
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Select External address is continuous, external port is single.
External IP Address Range
Specify the IP address range used by the internal server for providing services.
External Port
Specify the port number used by the internal server for providing services. This field is available only when you select the TCP or UDP IP protocol type.
Internal Server IP
Specify the private IP address of the internal server.
Internal Server Port Range
Specify the private port number range of the internal server. This field is available only when you select the TCP or UDP IP protocol type.
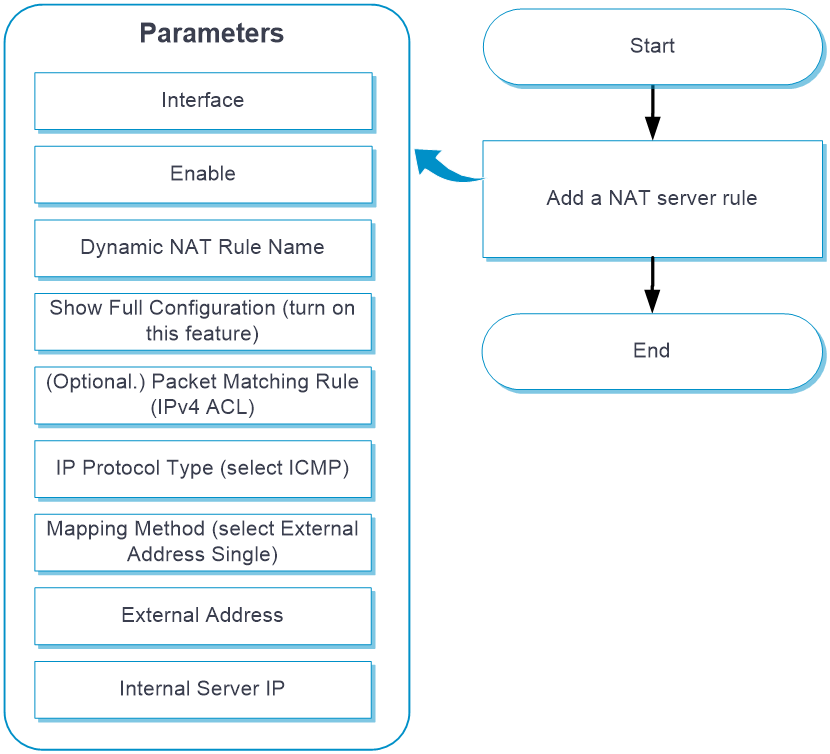
NAT Server (a single public address)
Configure NAT Server (a single public address)
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Internal Server tab.
Click Add. Table-9 shows the parameters for configuring NAT Server (a single public address).
Table-10 Parameters for configuring NAT Server (a single public address)
Parameter
Description
Interface
Select an interface on which the NAT server rule takes effect.
Enable
Select whether to enable the rule.
Dynamic NAT Rule Name
Name of the NAT server rule, a string of 1 to 63 characters.
Show Full Configuration
The default settings are as follows:
The Show Full Configuration feature is turned off.
The value for the Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL) field is empty, which indicates that no ACL is referenced.
Effective for all protocol types is selected for the IP Protocol Type field.
External address is single, external port is not used is selected for the Mapping Method field.
Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP) is selected for the External Address field.
To edit the default settings, turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL)
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Select an ACL to filter packets. The NAT device performs address translation only on the packets that match an ACL permit rule.
IP Protocol Type
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Specify a protocol type by using either of the following methods:
Select a protocol name. Options include ICMP, TCP, and UDP.
Specify a protocol number, an integer in the range of 1 to 255.
In this configuration, select ICMP.
Mapping Method
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Select External Address Single.
Internal Server IP
Specify the private IP address of the internal server.
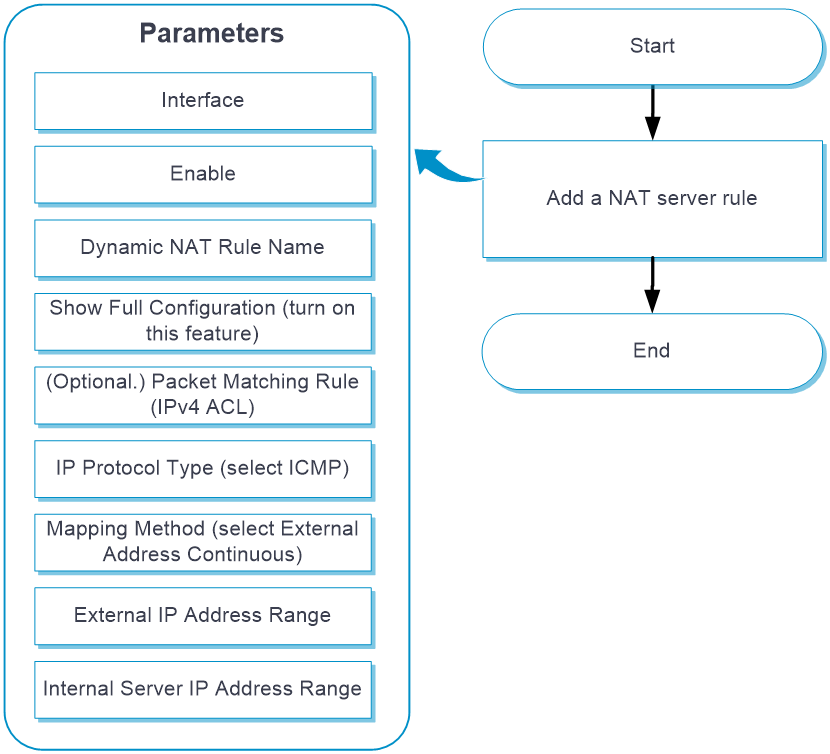
NAT Server (consecutive public addresses)
Configure NAT Server (consecutive public addresses)
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Internal Server tab.
Click Add. Table-9 shows the parameters for configuring NAT Server (consecutive public addresses).
Table-11 Parameters for configuring NAT Server (consecutive public addresses)
Parameter
Description
Interface
Select an interface on which the NAT server rule takes effect.
Enable
Select whether to enable the rule.
Dynamic NAT Rule Name
Name of the NAT server rule, a string of 1 to 63 characters.
Show Full Configuration
The default settings are as follows:
The Show Full Configuration feature is turned off.
The value for the Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL) field is empty, which indicates that no ACL is referenced.
Effective for all protocol types is selected for the IP Protocol Type field.
External address is single, external port is not used is selected for the Mapping Method field.
Use the current interface's main IP as the converted external address (Easy IP) is selected for the External Address field.
To edit the default settings, turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Packet Matching Rule (IPv4 ACL)
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Select an ACL to filter packets. The NAT device performs address translation only on the packets that match an ACL permit rule.
IP Protocol Type
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Specify a protocol type by using either of the following methods:
Select a protocol name. Options include ICMP, TCP, and UDP.
Specify a protocol number, an integer in the range of 1 to 255.
In this configuration, select ICMP.
Mapping Method
This field is displayed only when you turn on the Show Full Configuration feature.
Select External Address Continuous.
External IP Address Range
Specify the IP address range used by the internal server for providing services.
Internal Server IP Address Range
Specify the private IP address range of the internal server.
ALG
Configure NAT ALG
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Application Layer Gateway tab.
To enable NAT ALG for all protocols, select Select All, and then click Submit.
To enable NAT ALG for a single or some protocols, select the protocol or protocols, respectively. Then, click Submit.
Log settings
Configure NAT logging
From the left navigation pane, select Configure > Network Config > More > NAT.
Click the Log Settings tab.
NAT session logging provides the following features:
NAT session logging for active NAT flows. To enable this feature, turn on NAT Active Stream Log. To disable this feature, turn off NAT Active Stream Log.
NAT session logging for NAT session establishment events. To enable this feature, turn on Log NAT new session. To disable this feature, turn off Log NAT new session.
NAT session logging for NAT session removal events. To enable this feature, turn on Log NAT delete session. To disable this feature, turn off Log NAT delete session.
Select an IPv4 ACL number from the Packet Matching Rule ACL(IPv4) list.
If you do not specify any ACL, all NATed data flows might trigger NAT session logging.
If you specify an ACL, only data flows matching an ACL permit rule can trigger NAT session logging.
Click Submit.