Manage virtual switches for a host
About virtual switch management
A virtual switch (vSwitch) is a software-simulated network platform that can act as a switch entity. It mainly provides the following functions:
Port connection—Uses virtual ports to connect VMs, hosts, and external networks.
Automatic port extension—Scales up virtual ports automatically to adapt to service requirements.
VLAN-based traffic isolation—Uses VLANs to isolate traffic in different VLANs. For example, you can assign different VLANs to the service network, storage network, and management network to isolate traffic and guarantee network performance.
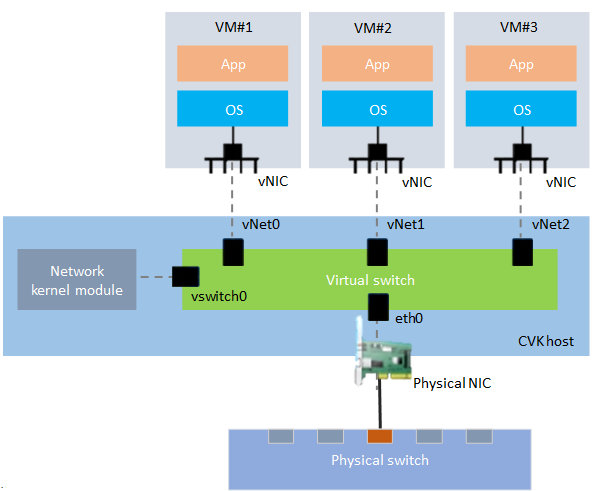
As shown in Figure-1, with a virtual switch configured, the system forwards received data packets to the virtual switch for processing. Then, the virtual switch forwards packets out of the corresponding virtual ports. A virtual switch provides the following virtual ports:
VM port—Connects a virtual switch to its vNICs for communication between vNICs or vNICs and the external network (vNet0, vNet2, and vNet3, for example).
Kernel port—Connects a virtual switch to the network kernel module of the service host OS (vswitch0, for example).
Uplink port—Connects a virtual switch to the physical NIC of the service host (eth0, for example). By default, the uplink port permits packets from all VLANs. If you configure VLANs for VM or kernel ports, make sure the uplink port permit the VLANs to ensure that the service host and VMs can communicate with the external network.
Each uplink port connects to a physical network adapter. You can aggregate the links between uplink ports and physical adapters to achieve link redundancy.
You can create a virtual switch for a cluster or for a host. Virtual switches created in either method function the same. This section describes virtual switch management for a single host.
Creation method | Description |
Cluster-based | Creates virtual switches with the same flavors for all hosts in a cluster. |
Host-based |
|
Configuration workflow
Add a virtual switch—Add virtual switches for the management network, service network, storage network, migration network, or backup network.
Configure advanced settings—Configure port mirroring and DHCP services.
Apply virtual switches—Apply virtual switches to VMs. For more information, see "Edit a VM."
Manage virtual switches—Edit or delete virtual switches on a host and view virtual interface traffic.