Manage desktop pools
About desktop pools
A desktop pool is a group of desktop resources that have the same attributes. You can bulk deploy desktops from a desktop pool with ease. Depending on the used desktop virtualization technology, a desktop pool can be one of the following types:
Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) desktop pool—Allows you to bulk create cloud desktops that use the same system configuration and assign the desktops to users. You can configure a VDI desktop pool to provide static, dynamic, manual, shared desktops, or application servers, depending on the desktop persistence requirement.
Intelligent desktop virtualization (IDV) desktop pool—Allows you to bulk deploy a desktop image to IDV desktop clients for users. You can configure an IDV desktop pool to deploy clients that are each accessible to a single user, multiple users, or anonymous users.
Virtual OS infrastructure (VOI)/TCI desktop pool—Allows you to bulk deploy a desktop image to VOI/TCI clients for desktop users. You can configure a VOI/TCI desktop pool to deploy clients that are each accessible to a single user, multiple users, or anonymous users.

When you configure IDV or VOI/TCI desktop pools for anonymous users, follow these restrictions:
Do not select remote roaming for data management policies. Otherwise, data confusion might occur.
After data management policies are configured, if user B deletes a file belonging to user A, user A cannot retrieve the deleted file upon next login.
Physical host desktop pool—Allows you to assign physical hosts to a desktop pool for central management. A user can access a managed physical host remotely from a Workspace client installed on an endpoint. Based on the application scenario, physical host desktop pools are divided into static desktop pools and application server pools. Only local, LDAP, and domain users can access a physical host desktop pool.
VDI desktop pool
Figure-1 shows the supported types of VDI desktop pool. For a comparison of these VDI desktop pools, see Table-1.
Figure-1 Types of VDI desktop pools by authorization type (1)
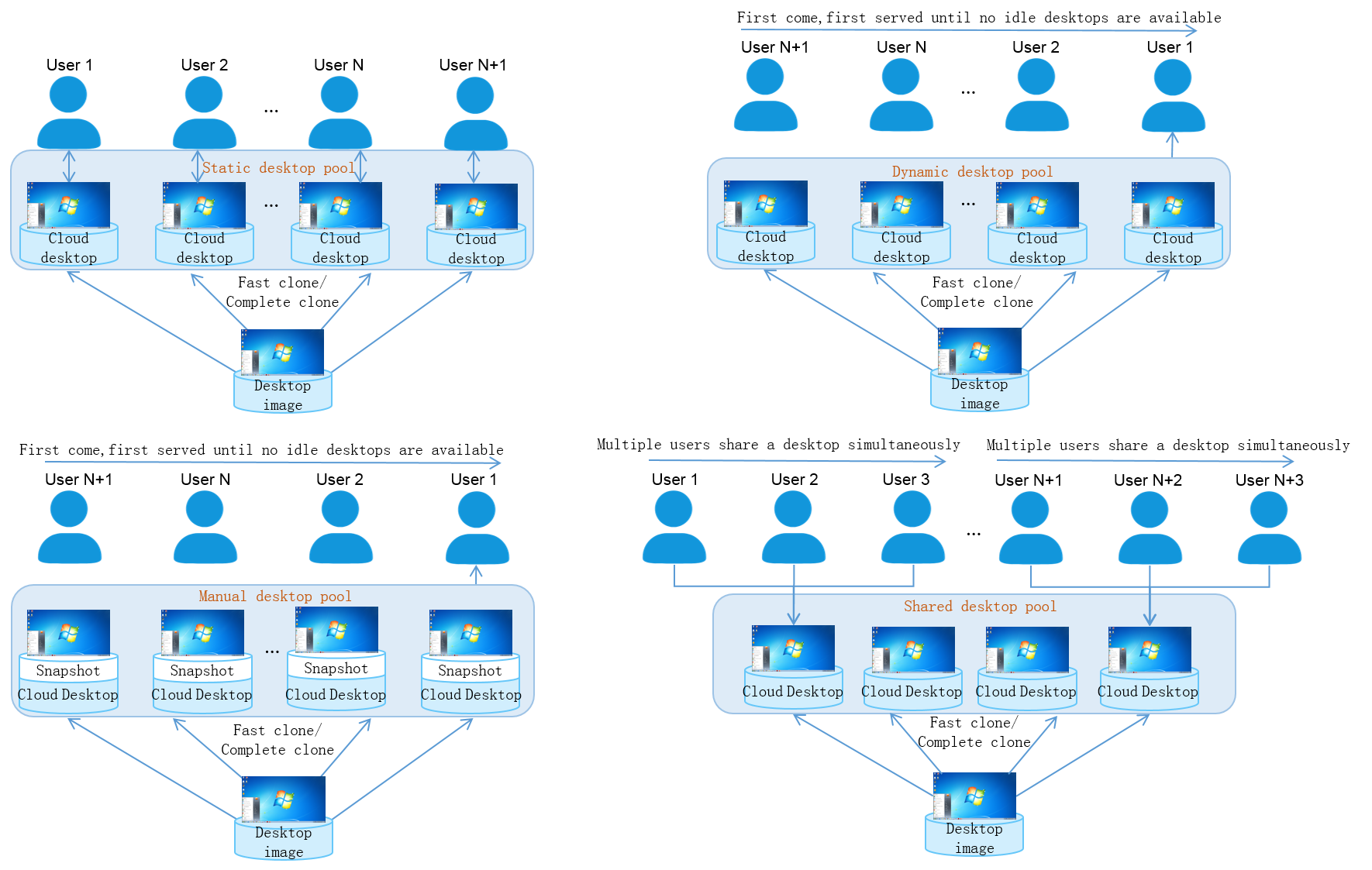
Figure-2 Types of VDI desktop pools by authorization type (2)
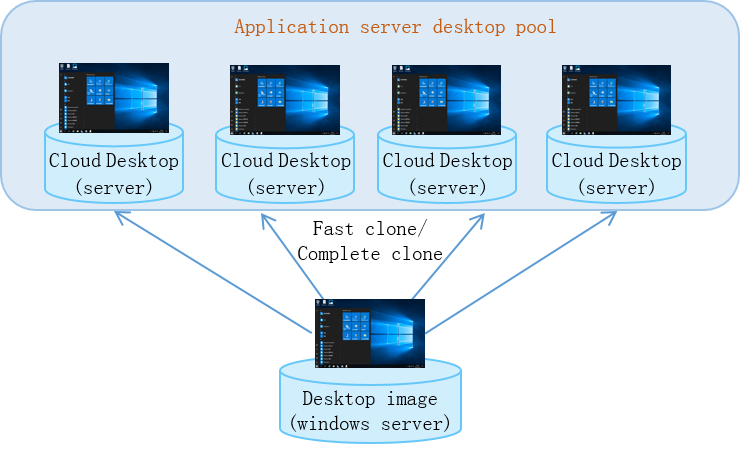
Table-1 Comparison of VDI desktop pools
IDV desktop pool
Figure-3 shows the supported types of IDV desktop pool by authorization type. For a comparison of these IDV desktop pools, see Table-2.
Figure-3 Types of IDV desktop pool by authorization type
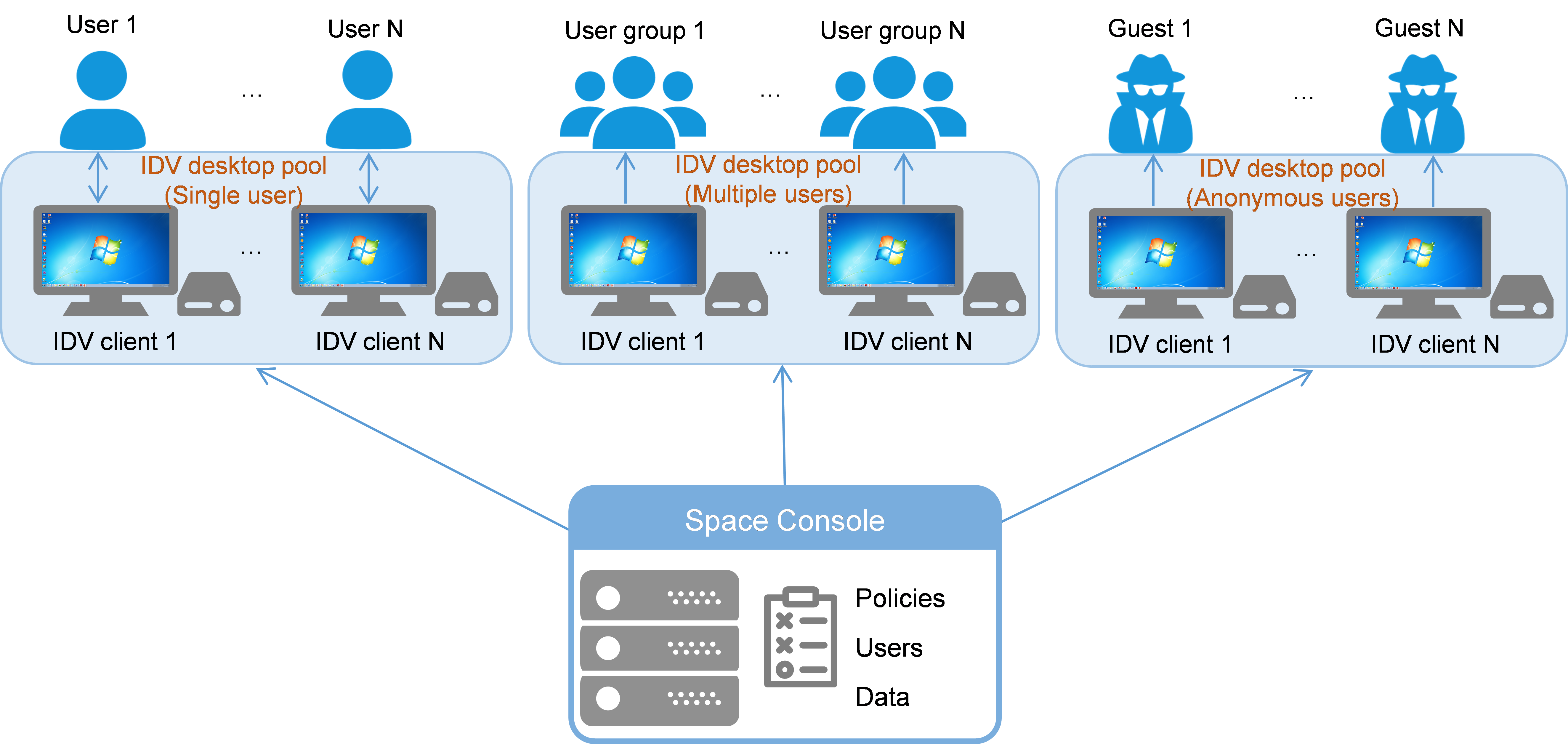
Table-2 Comparison of IDV desktop pools by authorization type
Authorization type | Access control | Data storage | Applicable scenarios |
Single (dedicated) user | Each IDV client is accessible to only one user. | The user has access to all drives available on the physical client and the cloud disk assigned to the user at the server end. | This type of desktop pool is applicable to privacy-sensitive scenarios such as home offices, personal desktops, and financial data processing. |
Multiple users | All IDV clients in the pool are shared by the specified users or user groups. Any one of the specified users can access an IDV client in the pool to obtain desktop services as long as that client is idle. | The users have access only to the system disk (the C drive) on the client endpoint and the cloud disk assigned to each of them. | This type of desktop pool is applicable to client sharing scenarios such as reading rooms or office lobbies. |
Anonymous users | Allows anyone to access an IDV desktop as a guest without providing user account information. | Anonymous users do not have cloud disks. They can use only the storage on the client endpoints. | Anonymous access is applicable to public service scenarios such as government service centers, libraries, and nurse stations. |
VOI/TCI desktop pool
Figure-4 shows the supported types of VOI/TCI desktop pool by authorization type. For a comparison of these IDV desktop pools, see Table-3.
Figure-4 Types of VOI desktop pool by desktop authorization type
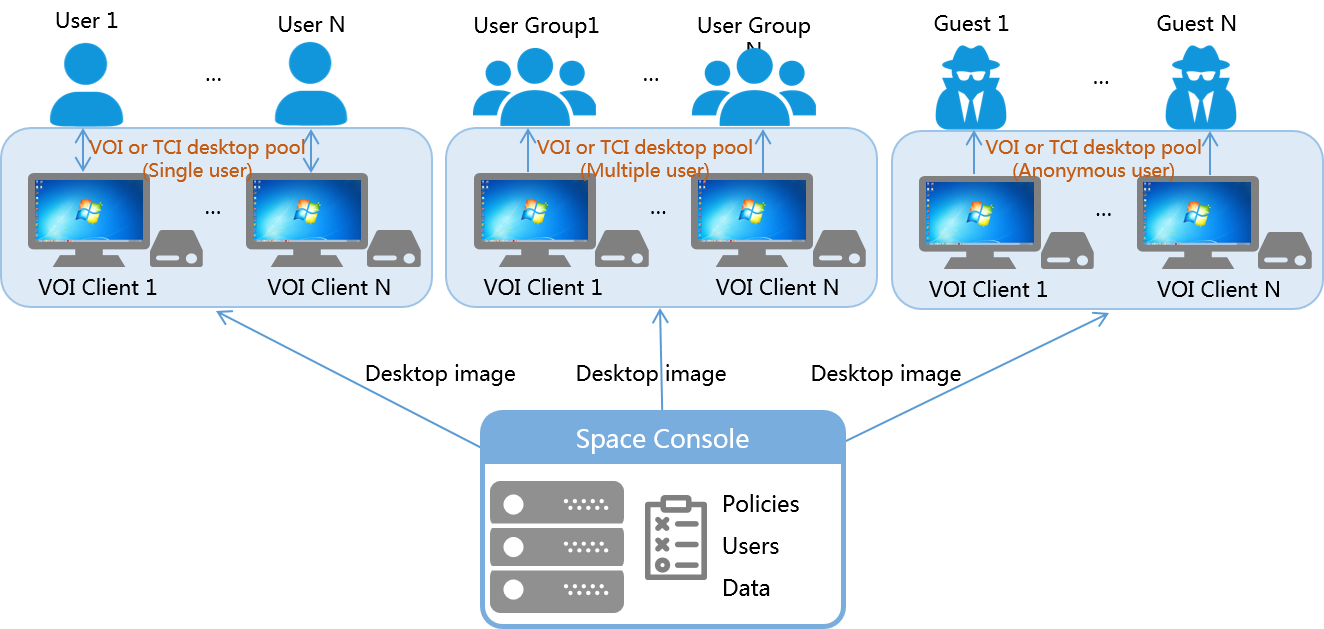
Table-3 Comparison of VOI/TCI desktop pools by authorization type
Authorization type | Access control | Data storage | Applicable scenarios |
Single (dedicated) user | Each VOI/TCI client is accessible to only one user. | The user has access to all drives available on the physical client and the cloud disk assigned to the user at the server end. | This type of desktop pool is applicable to privacy-sensitive scenarios such as home offices, personal desktops, and financial data processing. |
Multiple users | All VOI/TCI clients in the pool are shared by the specified users or user groups. Any one of the specified users can access a VOI/TCI client in the pool to obtain desktop services as long as that client is idle. | The users have access only to the system disk (the C drive) on the client endpoint and the cloud disk assigned to each of them. | This type of desktop pool is applicable to client sharing scenarios such as reading rooms or office lobbies. |
Anonymous access | Allows anyone to access a VOI/TCI desktop as a guest without providing user account information. | Anonymous users do not have cloud disks. They can use only the storage on the client endpoints. | Anonymous access is applicable to public service scenarios such as government service centers, libraries, and nurse stations. |
Physical host desktop pool
Figure-5 shows how Space Console manages physical host desktop pools.
Figure-5 Physical host desktop pool management
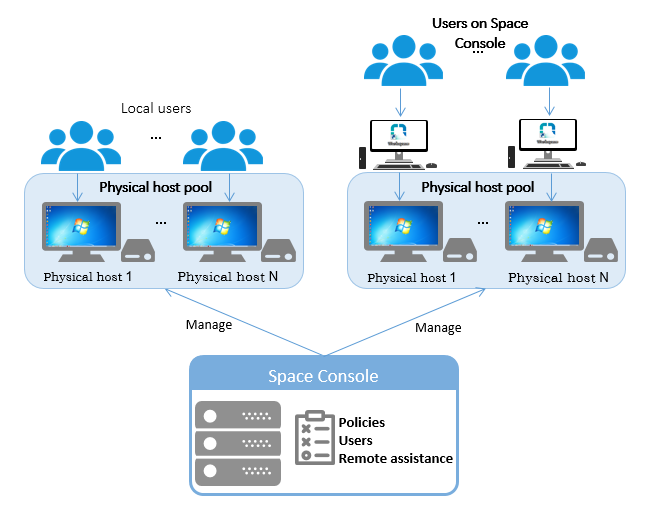
You can assign physical hosts to a desktop pool for central management, including host boot, host shutdown, host reboot, remote assistance, and user authorization. The local users configured on a managed physical host can access it as usual. On Space Console, you also can authorize users to remotely access the physical hosts in a physical host desktop pool by using a client installed on endpoints. You can use physical host desktop pools as application server pools to provide virtual applications. Only local, LDAP, and domain users can access a physical host desktop pool.
The following table shows the support of physical hosts for Workspace features:
Items | Description |
Operating system | Windows 7, Windows 10, and Windows Server. |
Policies |
|
Management actions | Remote shutdown and restart. |
Security gateway |
|
Remote desktop | Remote desktop connection. |
VNC remote O&M | Remote O&M through VNC. |
Users |
|
USB device access control | Management of USB devices connected to a physical host. |
Local network access management | Network access management based on firewalls of Windows, such as the IP addresses, subnet masks, and port denylist. |
Prerequisites
Make sure you have completed the following tasks in Space Console:
Add hosts and cluster resources.
Add users.
Create desktop images.