SRM
About disaster recovery
Disaster recovery recovers data and resumes service operations for information systems from faults or breakdowns caused by natural disasters and infrastructure failures such as fires, floods, earthquakes, power outages, and network egress failures.
Typically, a disaster recovery system contains two or more identical service systems deployed at geographically dispersed sites. The disaster recovery system monitors the service systems and maintains data consistency among them. When one service system fails, its services fail over to another site to ensure service continuity.
Key metrics for disaster recovery performance measurement
The following metrics are used for measuring the performance of a disaster recovery system:
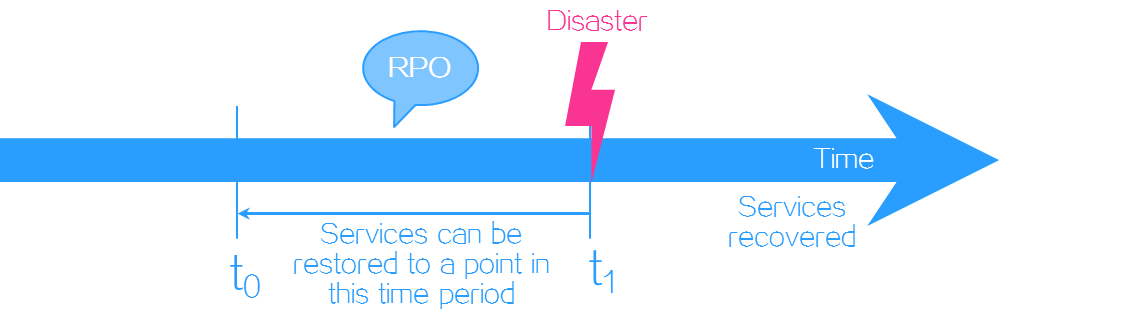
Recovery point objective (RPO)—The maximum acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. It refers to a period of time in which services must be restored and recovered. RPO is used to measure the data loss caused by a disaster and to evaluate the data backup capability of a disaster recovery system. Typically RPO depends on how data is replicated. Synchronous replication can guarantee an RPO of zero, which indicates no data loss. In asynchronous replication, RPO is determined by the replication cycle.
Figure-1 RPO
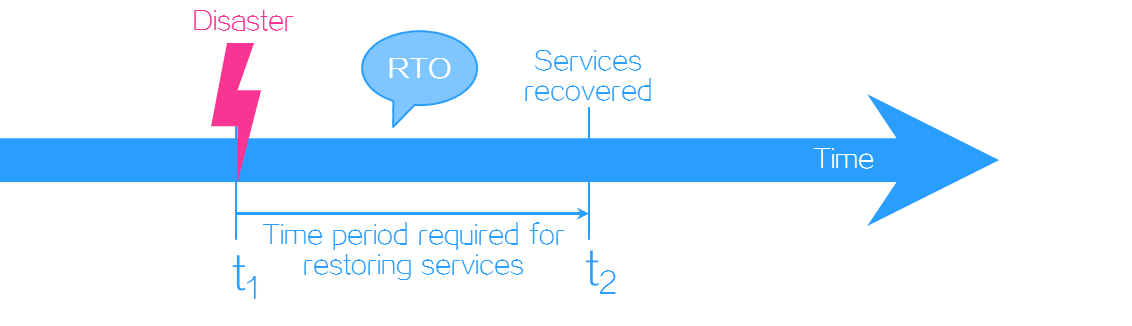
Recovery time objective (RTO)—The maximum tolerable length of time that a service system can be down after a failure or disaster. It defines how long it takes to restore services to running state. RTO is used to measure the data restoration capability of a disaster recovery system. It is determined by the service restoration procedure in disaster recovery. The more automated the restoration steps, the smaller the RTO.
Figure-2 RTO
Types of disaster recovery
Based on the level of protection, the following types of disaster recovery are available:
Data-level disaster recovery—Replicates data among disaster recovery sites at different locations to avoid data loss or damage in the event of a disaster. To one site, the other sites are remote data backup centers.
Application-level disaster recovery—Maintains an identical application system at a backup site for failed important applications to fail over to the backup site after a disaster as soon as possible. It enables application systems to offer complete, reliable, and secure services to users.
Array-based replication
Disaster recovery relies on array-based replication to back up and protect data. Array-based replication copies all or some data sets of an application from a host disk or storage array to another storage medium to prevent misoperations or failures from causing data loss. Array-based replication can be performed synchronously or asynchronously.
Synchronous replication
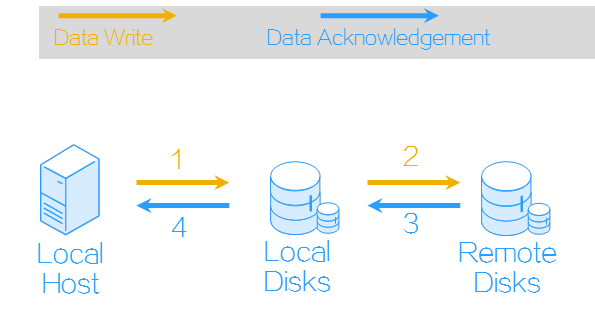
Synchronous replication ensures data consistency between the storage volumes in a replication pair. In synchronous replication, each IO operation releases resources only after both the local and remote volumes in a replication pair return write operation completion. Synchronous replication provides the highest level of data integrity at the cost of decreased performance caused by data transmission latency, and it requires the round trip delay between source and destination arrays to be short. Typically, synchronous replication is used for short-distance replication (10 to 100 km, or 6.21 to 62.13 miles) in scenarios that require strict data consistency and near-zero data loss, such as internal systems of banks.
Figure-3 Synchronous replication
Asynchronous replication
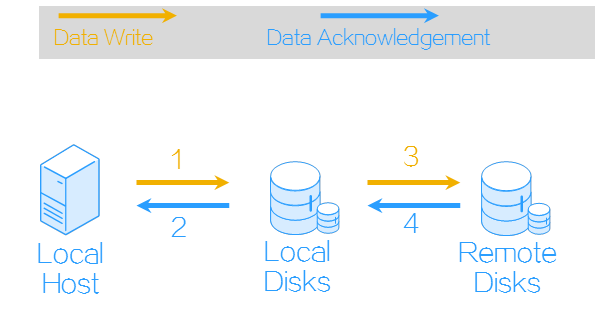
Asynchronous replication is performed periodically and thus cannot ensure data consistency between volumes in a replication pair. In asynchronous replication, a local volume creates a snapshot after it finishes a write operation and copies the snapshot to a remote volume. Asynchronous replication offers high performance but does not guarantee zero data loss because source and destination volumes might have inconsistent data. Asynchronous replication does not require high bandwidth or short transmission distance, which makes it suitable for systems that require high performance, have light write loads, and does not require high array IOPS performance or short delay, such as databases and file systems.
Figure-4 Asynchronous replication
About UIS site recovery management
UIS site recovery management (SRM) provides disaster recovery services for applications based on array-based replication.
Application scenarios
UIS SRM is applicable to data centers in homogeneous clouds (with same H3C UIS version deployed). UIS SRM can decrease RPO and RTO to minutes and replicate data for storage arrays regardless of whether they support storage replication adapters (SRAs).
Mechanisms
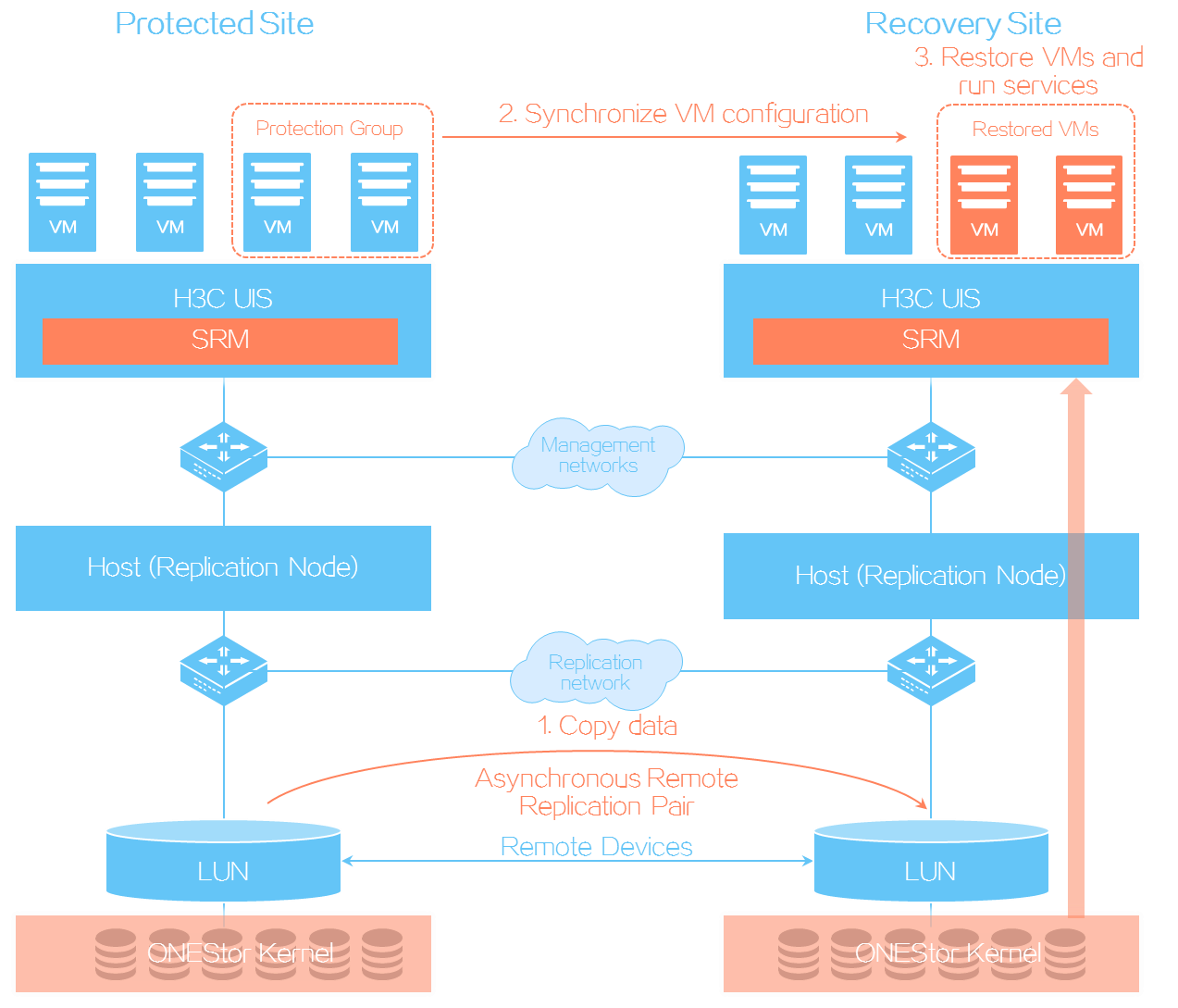
UIS SRM ensures data consistency and service continuity as follows:
At the storage level, SRM backs up data through asynchronous replication between storage arrays.
At the service level, SRM copies configuration of protected VMs from a protected site to a recovery site in each protection group.
When the protected site fails, SRM restores protected VMs at the recovery site by using the data backed up at the storage and service levels based on a recovery plan.
|
For array-based replication to operate correctly, make sure the following conditions are met: · The protected and recovery sites use the same replication technology. · Storage replication and snapshot features have been licensed on storage arrays. |
Figure-5 Storage replication and disaster recovery procedure
Features
Cost-effective disaster recovery plan
SRM relies on distributed storage replication to copy data of protected VMs at the storage level and decreases RPO and RTO to minutes. SRM allows a pair of sites to back up each other to protect user investments.
SRM supports both ONEStor and storage arrays that support storage replication and snapshots. If storage arrays do not support SRAs, you must manually prepare the storage environment before failing over services.
Automated disaster recovery
SRM synchronizes VM configuration changes from a protected site to a recovery site in time and allows you to simulate disaster recovery on schedule to ensure availability of the disaster recovery system.
Replicating protected VM data at the storage level, SRM reduces the impacts of disaster recovery services on server performance.
One-stop disaster recovery solution
SRM offers a disaster recovery solution that includes both storage configuration and disaster recovery task configuration. You can directly configure compute, storage, and network resource mappings for the protected and recovery sites.
SRM allows unified management of the protected and recovery sites. It can synchronize the disaster recovery configuration on the recovery site with the protected site. You do not need to configure SRM on multiple consoles.
Support for various disaster recovery scenarios
SRM allows you to simulate disaster recovery without interrupting running services. This mechanism can help you achieve the expected recovery target and decrease RTO.