About load balancing
What is load balancing
Load balancing is a cluster technology that distributes services among multiple real servers to improve processing capability and service availability.
The system allows you to create IPv4 or IPv6 load balancers that provide services at virtual service IP addresses. On a load balancer, you can configure one or multiple listeners to listen for the connection requests that clients send over a certain protocol on specific ports and to forward the requests to the real servers in a real server group based on a forwarding policy. You can enable health check for the system to monitor the running status of real servers. If a real server has health issues, the load balancer attached to the real server will distribute new requests to healthy real servers in the same real server group.
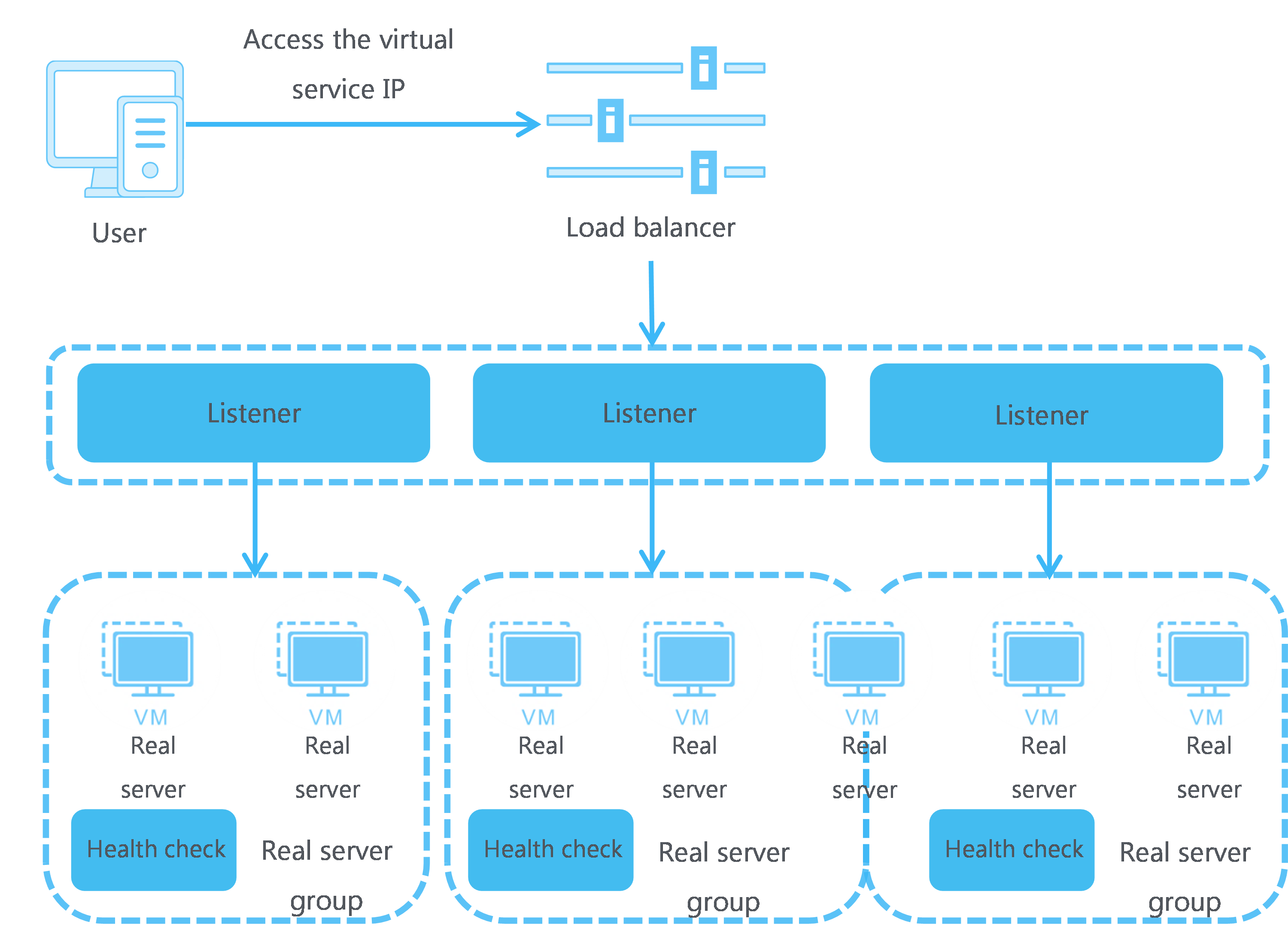
Figure-1 Load balancing working mechanism
Concepts
Listener—A listener listens for the connection requests sent by clients over a specific protocol on a certain port and distributes the requests to back-end servers based on load balancing settings such as the LB algorithm and session persistence. You must create a minimum of one listener on a load balancer.
Real server group—A group of real servers that process the same service type.
Real server—A cloud host that processes services.
Virtual server and virtual service IP—To distribute traffic in a balanced way, the load balancer uses a virtual server that provides virtual services and real servers (cloud hosts) that process actual services. The virtual service IP address is configured on the LB device for users to request services. The LB device distributes user requests from the public or private network matching the virtual server to the real servers based on the specified policies.
Health check—With health check enabled, the system monitors the running status of real servers. If a real server fails health check, the system stops distributing requests to it. Only healthy real servers can receive traffic from load balancers.
Session persistence—Session persistence recognizes the association between clients and servers when they interact. Through session persistence, a load balancer distributes matching user requests to the same back-end server. As a result, requests from a user in a specific period of time are distributed to the same cloud host, and the user does not need to log in to different servers.
Service chain—When traffic is transmitted in a network, it goes through multiple service instances, such as load balancer, firewall, and third-party security devices. In this way, the network can provide secure, fast, and stable services to users. A service chain can arrange service instances in the specified sequence. You can assign service nodes in a service chain as resources no matter where they are located. You can use SDN to define service chains. A service instance can be a firewall, load balancer, intrusion prevention system, or a pool of these resources. The system allows you to use a load balancer as a service instance and bind it to a service chain. For more information, see the procedure of creating a service chain. A service chain can contain only one service instance.
Benefits
Service continuity—The system provides the ping, TCP, HTTP, and HTTPS listening mechanisms to prevent single points of failure from interrupting services.
Smooth service processing and high fault tolerance—The system distributes traffic evenly to healthy cloud hosts to reduce the response delays caused by unbalanced load distribution.
High scalability—The system allows you to configure scaling on a per-application basis by customizing various monitoring metrics. The system supports automatic back-end server scale-up and scale-down, which enables you to focus on services without considering resource bottlenecks.
Application scenarios
Service distribution
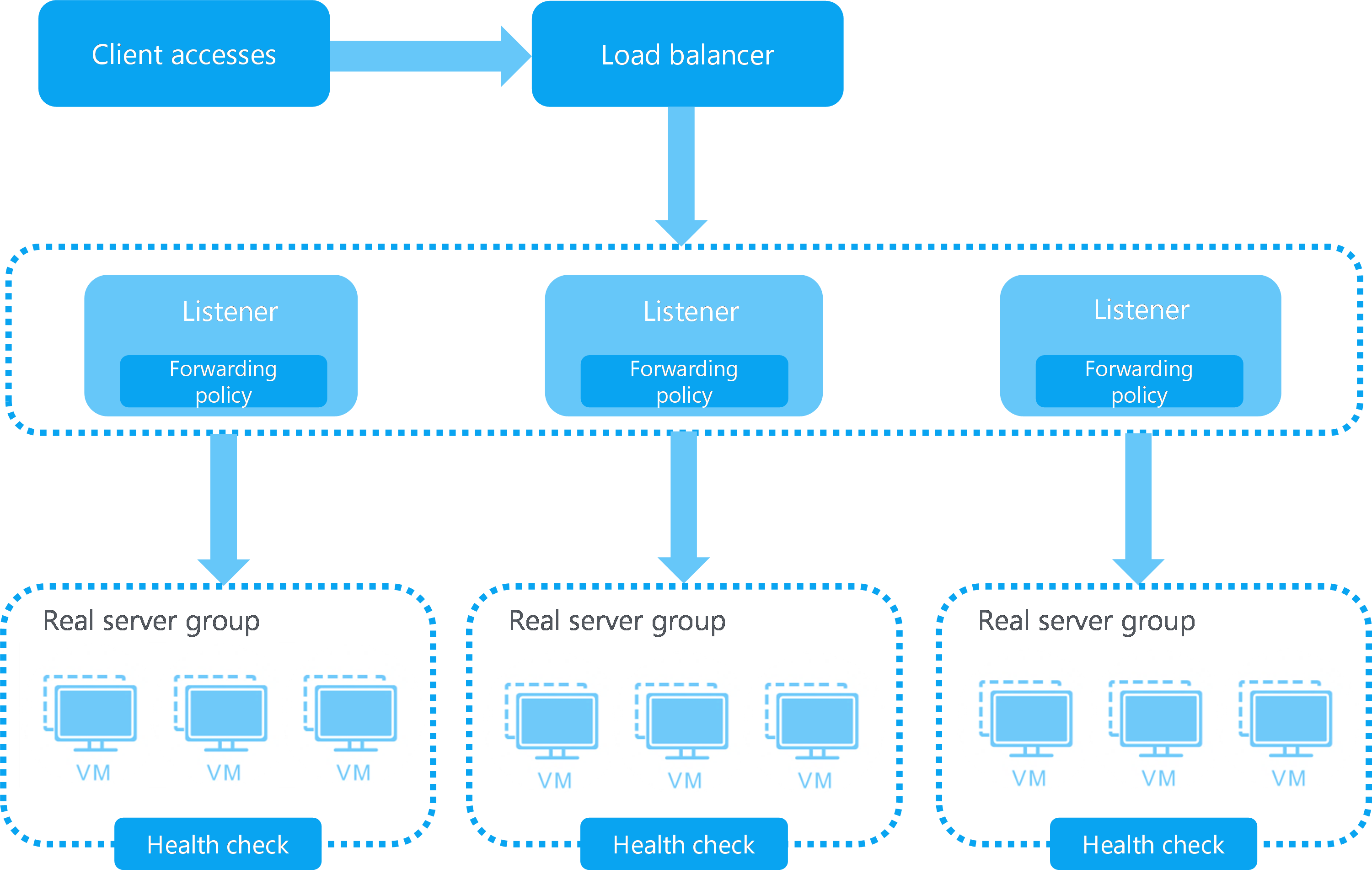
Load balancers can distribute traffic of intensively accessed services to multiple real servers based on an LB algorithm and distribute the traffic of a client to a fixed real server to improve access efficiency. For high availability, the system automatically bypasses failed real servers and distributes traffic only to the real servers that are running correctly.
Figure-2 Service distribution
DRX
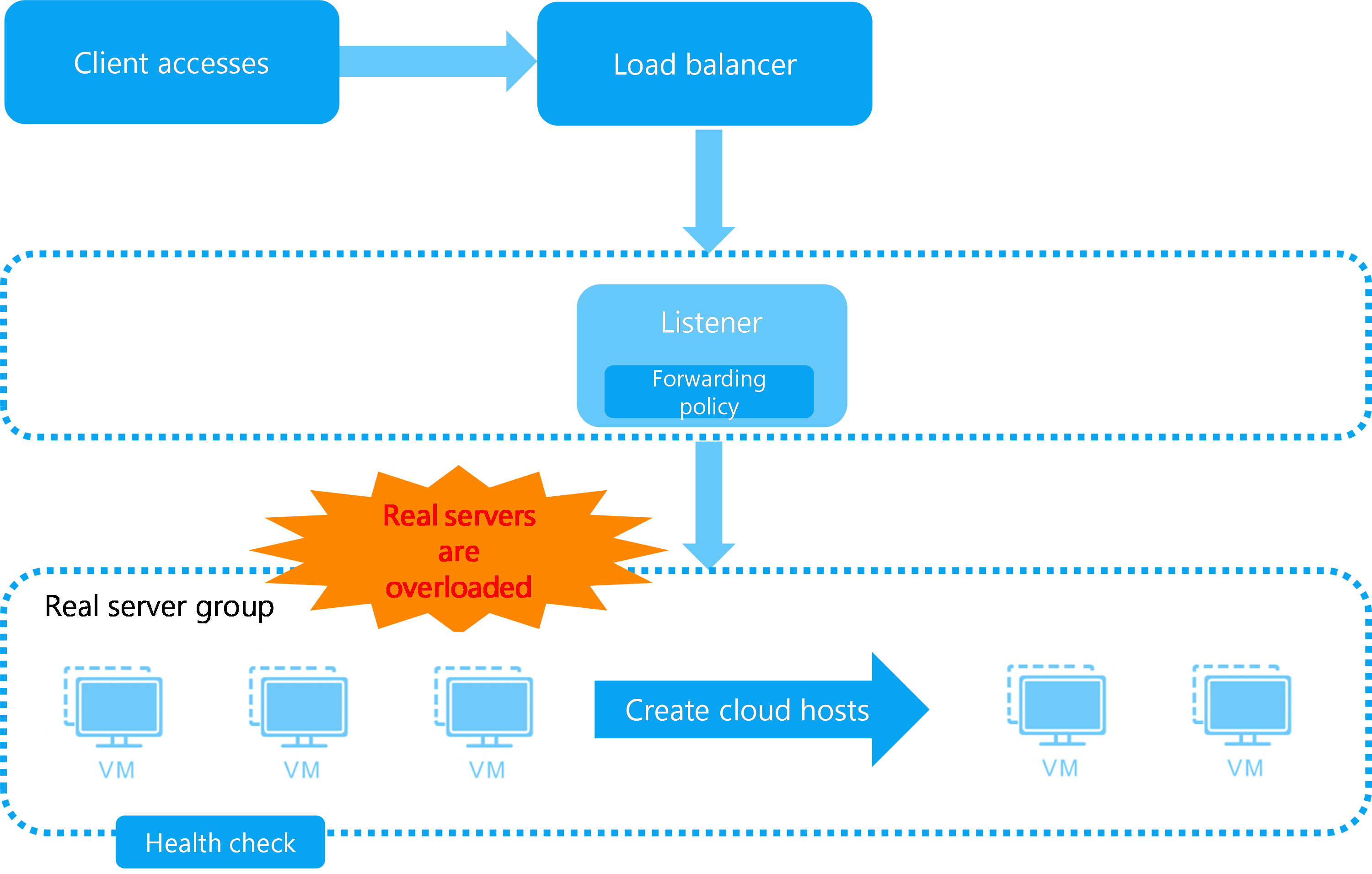
Some services have large fluctuations in the demand for IT resources, and their peak traffic might be several times the normal traffic. You can configure dynamic resource extension (DRX) for load balancing resources of those services. When the traffic of a service surges up, the system fast copies a specified number of cloud hosts and adds them to the real server group for the service. When the traffic of the service drops to the normal level, the system automatically deletes or shuts down excess cloud hosts.
Figure-3 DRX
Relationship with other cloud services
Table-1 Relationship with other cloud services
|
Service |
Relationship |
|
VPC/classic network |
The virtual service IP addresses of load balancers are provided by the private networks of VPCs or subnets of classic networks. |
|
Cloud host |
Cloud hosts act as real servers to process service requests. |
|
Elastic IP |
Load balancers use elastic IP addresses to communicate with the public network. |